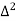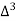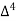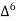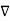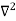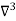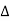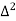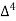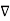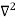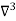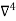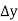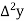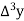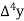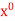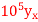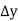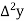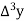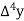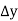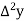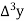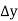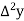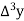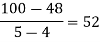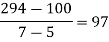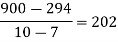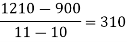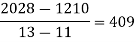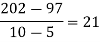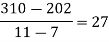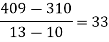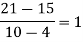Unit-3
Numerical Integration and Differentiation
Q1) Given that
X | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 |
Y | 0.841 | 0.891 | 0.932 | 0.963 |
Find 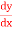 at
at 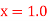 .
.
A1) Here the first derivative is to be calculated at the beginning of the table, therefore forward difference formula will be used
Forward difference table is given below:
X | Y |
|
|
|
1.0
1.1
1.2
1.3 | 0.841
0.891
0.932
0.962 |
0.050
0.041
0.031 |
-0.009
-0.010 |
-0.001 |
By Newton’s forward differentiation formula for differentiation

Here 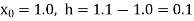
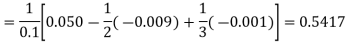
Q2) Find the first and second derivatives of the function given below at the point 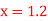 :
:
X | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
Y | 0 | 1 | 5 | 6 | 8 |
A2) Here the point of the calculation 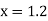 is at the beginning of the table,
is at the beginning of the table,
Forward difference table is given by:
X | Y |
|
|
|
|
1
2
3
4
5 | 0
1
5
6
8 |
1
4
1
2 |
3
-3
1 |
-6
4
|
-10
|
By Newton’s forward differentiation formula for differentiation
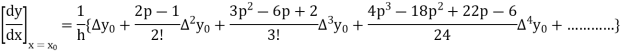
Here 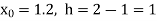 ,
, 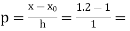 0.
0.
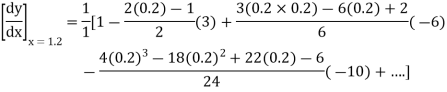
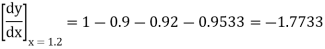
Again
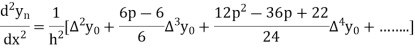
At 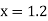
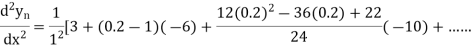
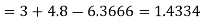
Q3) From the following table of values of x and y find 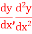 for
for 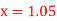
X | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | 1.20 | 1.25 | 1.30 |
Y | 1.0000 | 1.02470 | 1.04881 | 1.07238 | 1.09544 | 1.11803 | 1.14017 |
A3) Here the value of the derivative is to be calculated at the beginning of the table.
Forward difference table is given by
X | Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.00
1.05
1.10
1.15
1.20
1.25
1.30 | 1.0000
1.02470
1.04881
1.07238
1.09544
1.11803
1.14017 |
0.02470
0.02411
0.02357
0.02306
0.02259
0.02214 |
-0.00059
-0.00054
-0.00051
-0.00047
-0.00045 |
0.00005
0.00003
0.00004
0.00002 |
-0.00002
0.00001
-0.00002 |
0.00003
-0.00003 |
-0.00006 |
From Newton’s forward difference formula for differentiation, we get
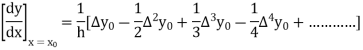
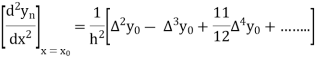
Here 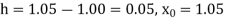
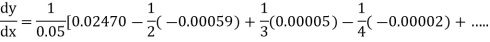
=0.48763
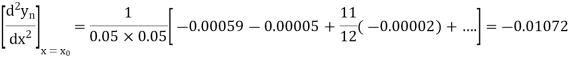
Q4) Define Newton backward difference forward formula.
A4) This method is useful for interpolation near the ending of a set of tabular values.
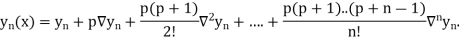
Where 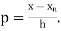
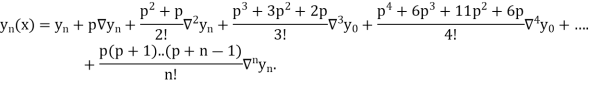
Differentiating both side with respect to p, we get
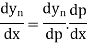
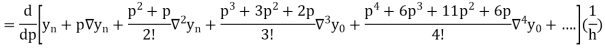
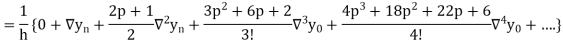
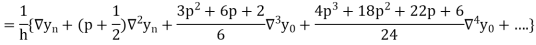
This formula is applicable to compute the value of 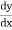 for non tabular values of x.
for non tabular values of x.
Q5) Given that
X | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0..4 |
Y | 1.10517 | 1.22140 | 1.34986 | 1.49182 |
Find 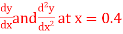 ?
?
A5) Backward difference table:
X | Y |
|
|
|
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4 | 1.10517
1.22140
1.34986
1.49182 |
0.11623
0.12846
0.14196 |
0.01223
0.01350 |
0.00127 |
Newton’s Backward formula for differentiation
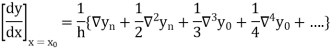
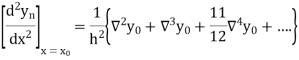
Here 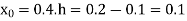
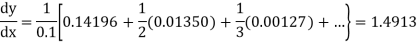
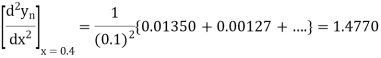
Q6) Given that
X | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.0 |
Y | 0 | 0.128 | 0.544 | 1.296 | 2.432 | 4.0 |
Find the derivative of y at  ?
?
A6) The difference table is given below:
X | Y |
|
|
|
|
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0 | 0
0.128
0.544
1.296
2.432
4.0 |
0.128
0.416
0.752
0.136
1.568
|
0.288
0.336
0.384
0.432 |
0.048
0.048
0.048 |
0
0 |
Since the point 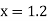 is at the beginning of the table therefore
is at the beginning of the table therefore
From Newton’s forward difference formula for differentiation, we get
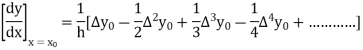
Here 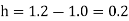
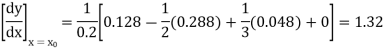
Since the point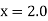 is at the end of the table therefore
is at the end of the table therefore
Backward difference table is:
X | Y |
|
|
|
|
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0 | 0
0.128
0.544
1.296
2.432
4.000 |
0.128
0.416
0.752
0.136
1.568 |
0.288
0.336
0.384
0.432 |
0.048
0.048
0.048 |
0
0 |
Newton’s Backward formula for differentiation

Q7) Write down the formula for Stirling, Bessel’s and Evertte’s.
A7) Stirling’s formula-
Stirling’s formula is defined as-
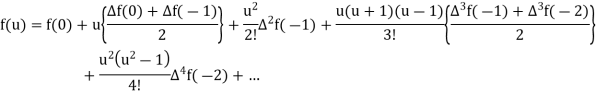
Note-
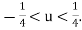
Bessel’s formula-
The formula given below is called Bessel’s formula-
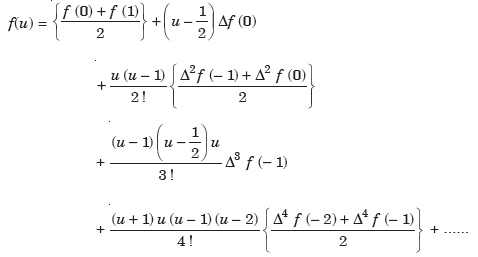
Note- this formula is useful when u =1/2 and gives best estimates when ¼<u<3/4
Everette’s formula-
The Everette’s formula is defined as-
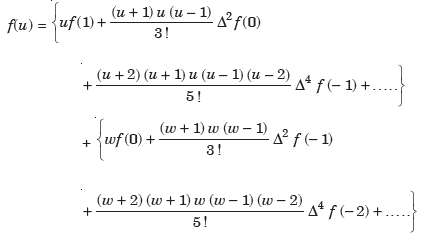
Here w = 1 – u,
When u > ½, it gives best estimate.
Q8) By using Stirling formula to find 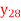 , given-
, given-
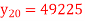
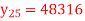
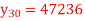
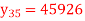
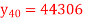
A8) Suppose the origin is at 30 and h = 5
a + hu = 28
Where h = 5 and a = 35 then-
u = -0.4
The difference table will be as follows-
U | X | y |
|
|
|
|
-2
-1
0
1
2 | 20
25
30
35
40 | 49225
48316
47236
45926
44306 |
-909
-1080
-1310
-1620 |
-171
-230
-310 |
-59
-80 |
-21 |
By using Stirling formula, we get-
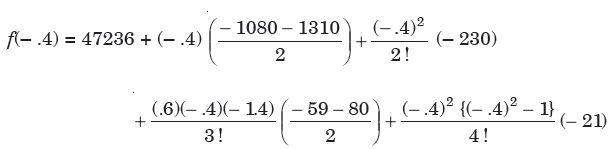
= 47691.8256
So that, we have 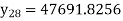
Q9) By using Stirling’s formula, compute 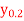 from the table given below
from the table given below
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 23.967 | 28.060 | 31.788 | 35.209 | 38.368 |
A9)
Here let the origin is at 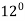 , h = 1,
, h = 1,
u | y |
|
|
|
|
-2
-1
0
1
2 | 0.23967
0.28060
0.31788
0.35209
0.38368
|
0.04093
0.03728
0.034121
0.03159
|
-0.00365
-0.00307
-0.00062
|
0.00058
-0.00045
|
-0.00013
|
Then using Stirling’s formula-
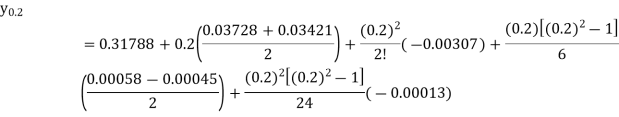
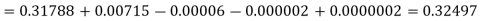
Q10) By using Bessel’s formula to find 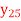 . Given
. Given 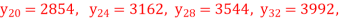
A10)
The central difference table-
U | y |
|
|
|
-1
0
1
2 | 2854
3162
3544
3992 |
308
382
448
|
74
66
|
-8
|
By using Bessel’s formula-
We get-
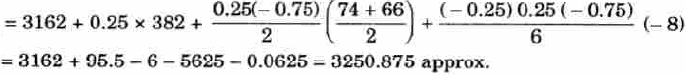
Q11) By using Everette’s formula, Evaluate f (30) if
f (20) = 2854, f (28) = 3162
f (36) = 7088, f (44) = 7984
A11) Let’s origin is 28,
A = 28, h = 8
A +hu = 30
28 + 8u = 30
U = 0.25
And w = 1-u = 1-0.25 = 0.75
The difference table is-
U | y |
|
|
|
-1
0
1
2 | 2854
3992 |
308
382
448
|
3618
-3030
|
-6648
|
By using Everette’s formula-
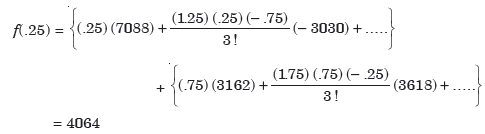
So that the value of f (30) = 4064
Q12) By means of Newton’s divided difference formula, find the values of 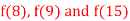 from the following table:
from the following table:
x | 4 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 11 | 13 |
f(x) | 48 | 100 | 294 | 900 | 1210 | 2028 |
A12) We construct the divided difference table is given by:
x | f(x) | First order divide difference | Second order divide difference | Third order divide difference | Fourth order divide difference |
4
5
7
10
11
13 | 48
100
294
900
1210
2028 |
|
|
|
0
0 |
By Newton’s Divided difference formula
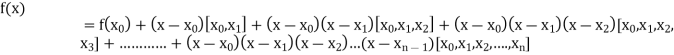 .
.
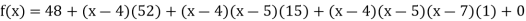
Now, putting 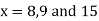 in above we get
in above we get
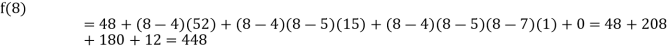 .
.
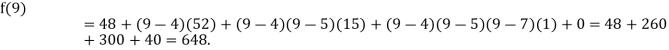
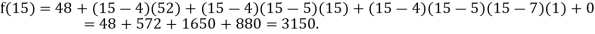
Q13) The following values of the function f(x) for values of x are given:

Find the value of 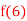 and also the value of x for which f(x) is maximum or minimum.
and also the value of x for which f(x) is maximum or minimum.
A13) We construct the divide difference table:
x | f(x) | First order divide difference | Second order divide difference | Third order divide difference |
1
2
7
8 | 4
5
5
4 |
|
|
0 |
By Newton’s divided difference formula
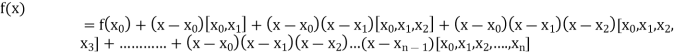 .
.
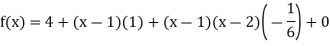
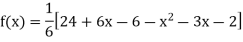
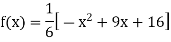
Putting 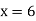 in above we get
in above we get
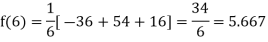
For maximum and minimum of 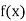 , we have
, we have
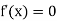
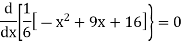
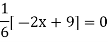
Or 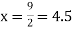
Q14) Write down the Lagrange’s inverse interpolation formula
A14) Lagrange’s inverse interpolation formula is given by
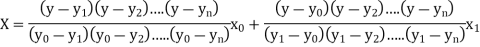
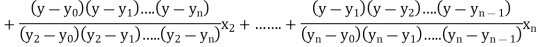
Q15) Use the inverse interpolation to find value of x at 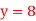 for the following data:
for the following data:
X | 1 | 3 | 4 |
Y | 4 | 12 | 19 |
A15) Here 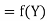 , we have the data
, we have the data
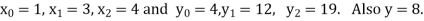
The Lagrange’s inverse interpolation formula is given by
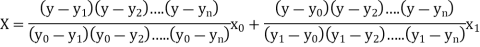
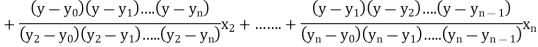
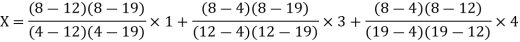
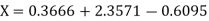
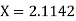 .
.
Q16) Use the inverse Lagrange’s method to find the root of the equation 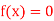 , give data
, give data 
X | 30 | 34 | 38 | 42 |
F(x) | -30 | -13 | 3 | 18 |
A16) Here 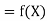 , we have the data
, we have the data

Also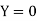 .
.
The Lagrange’s inverse interpolation formula is given by
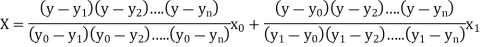
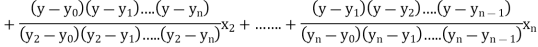
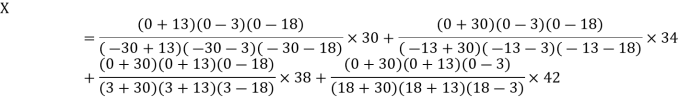
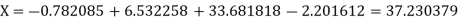
Thus, the approximate root of the given equation is 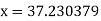 .
.
Q17) Define trapezoidal method.
A17) Let the interval 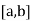 be divided into n equal intervals such that
be divided into n equal intervals such that 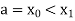 <
<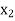 <…. <
<…. <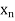 =b.
=b.
Here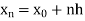 .
.
To find the value of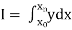 .
.
Setting n=1, we get
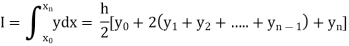
Or I = 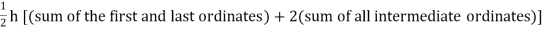
The above is known as Trapezoidal method.
Note: In this method second and higher difference are neglected and so f(x) is a polynomial of degree 1.
Q18) Compute the value of 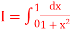 ?
?
Using the trapezoidal rule with h=0.5, 0.25 and 0.125.
A18) Here 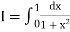
For h=0.5, we construct the data table:
X | 0 | 0.5 | 1 |
Y | 1 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
By Trapezoidal rule
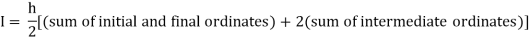
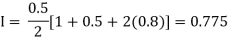
For h=0.25, we construct the data table:
X | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1 |
Y | 1 | 0.94117 | 0.8 | 0.64 | 0.5 |
By Trapezoidal rule
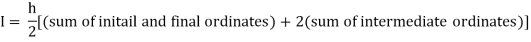
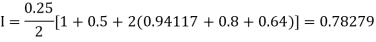
For h = 0.125, we construct the data table:
X | 0 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.5 | 0.625 | 0.75 | 0.875 | 1 |
Y | 1 | 0.98461 | 0.94117 | 0.87671 | 0.8 | 0.71910 | 0.64 | 0.56637 | 0.5 |
By Trapezoidal rule
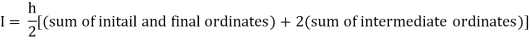
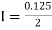 [(1+0.5) +2(0.98461+0.94117+0.87671+0.8+0.71910+0.64+0.56637)]
[(1+0.5) +2(0.98461+0.94117+0.87671+0.8+0.71910+0.64+0.56637)]
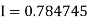
Q19) Using Simpson’s 1/3 rule with h = 1, evaluate
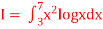
A19) For h = 1, we construct the data table:
X | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 9.88751 | 22.108709 | 40.23594 | 64.503340 | 95.34959 |
By Simpson’s Rule
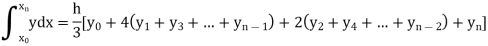
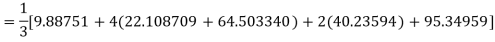
= 177.3853
Q20) Define Simpson’s 3/8 rule.
A20) Let the interval 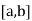 be divided into n equal intervals such that
be divided into n equal intervals such that 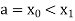 <
<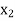 <…. <
<…. <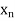 =b.
=b.
Here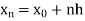 .
.
To find the value of 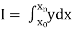 .
.
Setting n=3, we get
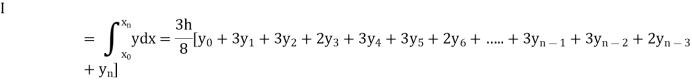
Is known as Simpson’s 3/8 rule which is not as accurate as Simpson’s rule.
Note: In this rule the fourth and higher differences are neglected and so f(x) is a polynomial of degree 3.
Q21) Evaluate 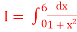
A21) Let us divide the range of the interval [0,6] into six equal parts.
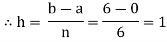
For h=1, we construct the data table:
X | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0588 | 0.0385 | 0.027 |
By Simpson’s 3/8 rule
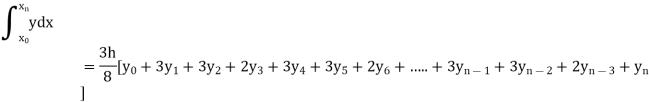
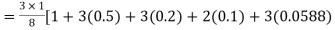 +3(0.0385) +0.027]
+3(0.0385) +0.027]
=1.3571