Unit-5
Geotechnical properties of reinforced soil
Q1) Give the geotechnical properties of reinforced soil.
A1)
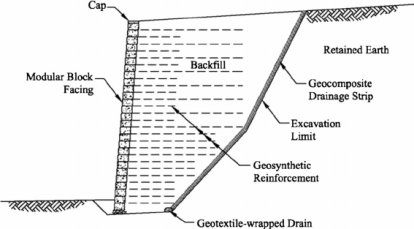
Q2) What is a reinforced earth wall?
A2)
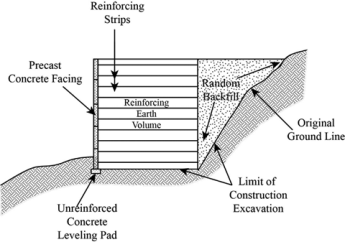
Q3) Give the advantages and disadvantages of a reinforced soil structure.
A3) Advantages of reinforced Soil Structures
Disadvantages
The following general disadvantage is also associated with all soil bolstered structures.
Q4) Give the history and use of soil reinforcement.
A4)
HISTORY OF SOIL REINFORCEMENT
USE OF SOIL REINFORCEMENT
INTRODUCTION
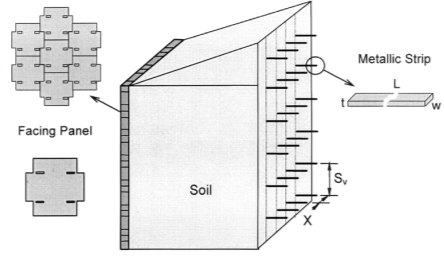
Q5) What are the strip reinforcing elements?
A5)
Q6) Define geotextile sheet.
A6)

Q7) What is geogrid and metallic grid?
A7)
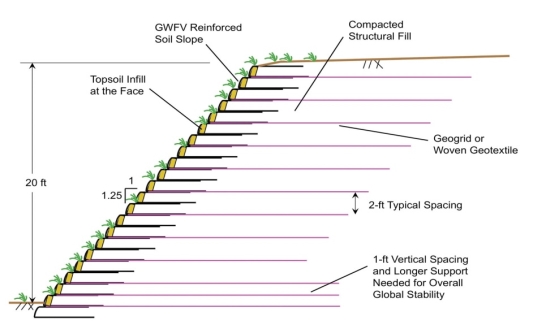
Q8) Explain the shallow foundation of soil with reinforcement.
A8)
Q9) Give the design consideration.
A9)
(a): Pore water Pressures Generated among the bolstered Fill
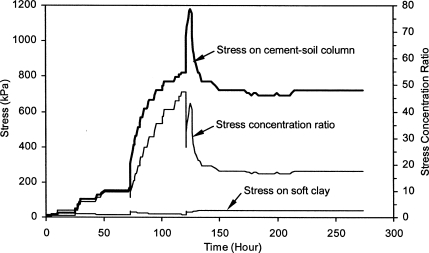
1. Total stress analysis ignoring reinforcement lateral voidance. This analysis neglects the dissipation of pore water pressures through the semipermeable inclusions to supply a conservative estimate of the steadiness of the structure at the top of the construction. Considering the short condition and also the conservative assumptions during this analysis, an element of safety of one.1 is suggested. This analysis determines minimum reinforcement necessities that will preclude collapse throughout the construction of the structure. That is, it provides reinforcement necessities for a short scenario within which stability is provided largely by the tensile forces within the reinforcements with solely a minor contribution by the undrained shear length of the backfill. The undrained soil shear strength of the backfill for this analysis ought to be supported by loose undrained (UU) triaxial tests. The specimens ought to be ready at representative field densities and wetness placement conditions, and tested at these placement conditions below project-specific confining pressures. Though the authors contemplate testing below unsaturated conditions as AN adequate approach, testing below absolutely saturated conditions represents an extra degree of ideology that the designer could contemplate on a project-specific basis.
2. Effective stress analysis accounting for full lateral voidance by the reinforcement. Full voidance of the bolstered fill is assumed for the long conditions. This analysis provides a practical analysis of the long stability of the structure, as a result of the dissipation of pore water pressures generated throughout construction ought to have occurred through the semipermeable inclusions. This analysis determines the minimum reinforcement necessities which will offer adequate stability below long conditions following the dissipation of pore water pressures generated throughout the construction of the structure. it'sstressed that the transmission of the reinforcements ought to be designated so the generation of pore water pressures is prevented at the soil-reinforcement interface. Typically, the soil shear strength ought to be supported by consolidated undrained (CIU) triaxial tests performed on saturated samples with pore pressure measurements or consolidated drained (CD) triaxial tests. The long-run style issue of safety usually needed for reinforcement of granular fills (e.g. 1.3 to 1.5) ought to be employed in this analysis.
Designing for Condition
(b): Wetting Front Advancing into the bolstered Fill
As loss of strength could occur attributable to a wetting front advancing into the bolstered fill geosynthetic transmission necessities ought to be established to avoid the advancement of wetting front for expected conditions. A two-phase analysis is additionally planned during this case. These analyses, summarized in Table one, area unit as follows:
1) Total stress analysis ignoring the result of lateral voidance in preventing the advancement of a wetting front. This analysis is performed exploitation shear strength properties of the bolstered soil mass outlined exploitation saturated specimens. The results of this analysis offer an estimate of the steadiness of the structure below an advancing wetting front. This analysis is conservative as a result of the backfill is assumed saturated, which mustn't occur in actual follow as a result of the wetting front is intercepted by the semipermeable reinforcements. Consequently, an element of safety of one.1 is suggested during this case. Water pressure which will develop as water fills surface cracks (induced by desiccation, freeze/thaw, or slope movements) ought to be accounted for exploitation boundary water pressures within the analysis.
Q10) What is idealized soil?
A10) IDEALIZED SOIL RESPONSE MODELS FOR THE ANALYSIS OF SOIL-FOUNDATION INTERACTION
The analysis of the response of soil media to external hundreds constitutes an element of elementary importance to the analysis of soil-foundation interaction issues.
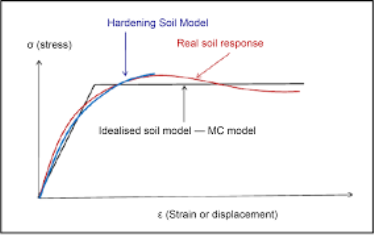
The classical theories of the physical property and physical property square measure 2 such idealizations usually utilized within the analysis of issues inthe soil.