UNIT 1
Introduction
- What is an operating system and explain its features?
Sol:
An Operating system (OS) is software that acts as an interface between the end-user and computer hardware. Every computer must have at least one OS to run other programs. An application like Chrome, MS Word, Games, etc needs some environment in which it will run and perform its task. The OS helps you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer's language. The user can't use any computer or mobile device without having an operating system.
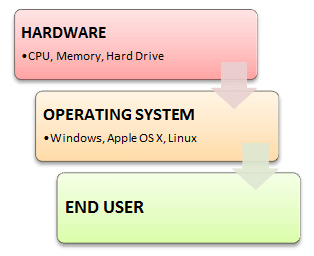
Introduction Operating System
History of OS
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage
- The General Motors Research Lab implemented the first OS in the early 1950s for their IBM 701
- In the mid-1960s, operating systems started to use disks
- In the late 1960s, the first version of the Unix OS was developed
- The first OS built by Microsoft was DOS. It was built in 1981 by purchasing the 86-DOS software from a Seattle company
- The present-day popular OS Windows first came to existence in 1985 when a GUI was created and paired with MS-DOS.
Features of Operating System
Here is a list of commonly found important features of an Operating System:
- Protected and supervisor mode
- Allows disk access and file systems Device drivers Networking Security
- Program Execution
- Memory management Virtual Memory Multitasking
- Handling I/O operations
- Manipulation of the file system
- Error Detection and handling
- Resource allocation
- Information and Resource Protection
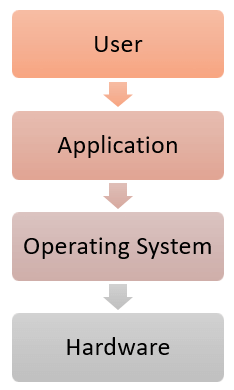
2. What is a Kernel in an operating system explain?
Sol:
The kernel is the central component of a computer operating system. The only job performed by the kernel is to manage the communication between the software and the hardware. A Kernel is at the nucleus of a computer. It makes communication between the hardware and software possible. While the Kernel is the innermost part of an operating system, a shell is the outermost one.
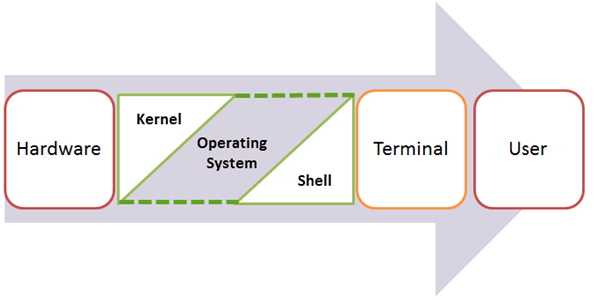
Features of Kennel
- Low-level scheduling of processes
- Inter-process communication
- Process synchronization
- Context switching
Types of Kernels
Many types of kernels exist, but among them, the two most popular kernels are:
1. Monolithic
A monolithic kernel is a single code or block of the program. It provides all the required services offered by the operating system. It is a simplistic design that creates a distinct communication layer between the hardware and software.
2. Microkernels
Microkernel manages all system resources. In this type of kernel, services are implemented in different address spaces. The user services are stored in the user address space, and kernel services are stored under the kernel address space. So, it helps to reduce the size of both the kernel and operating system.
3. What are the Functions of an Operating System?
Sol:
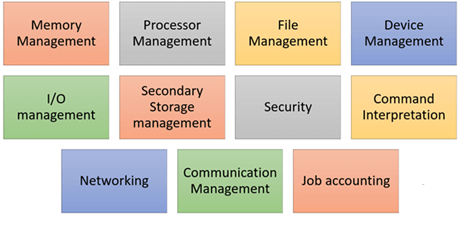
The function of an Operating System
In an operating system software performs each of the function:
- Process management:- Process management helps the OS to create and delete processes. It also provides mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
2. Memory management:- Memory management module performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of memory space to programs in need of these resources.
3. File management:- It manages all the file-related activities such as organization storage, retrieval, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
4. Device Management: Device management keeps track of all devices. This module also responsible for this task is known as the I/O controller. It also performs the task of allocation and de-allocation of the devices.
5. I/O System Management: One of the main objects of any OS is to hide the peculiarities of that hardware device from the user.
6. Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have several levels of storage which include primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be stored in primary storage or cache so that a running program can reference it.
7. Security:- The security module protects the data and information of a computer system against malware threats and authorized access.
8. Command interpretation: This module is interpreting commands given by the and acting system resources to process those commands.
9. Networking: A distributed system is a group of processors that do not share a memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors communicate with one another through the network.
10. Job accounting: Keeping track of time & resources used by various jobs and users.
11. Communication management: Coordination and assignment of compilers, interpreters, and other software resources of the various users of the computer systems.
4. What are the different types of operating systems?
Sol:
Types of Operating system
- Batch Operating System
- Multitasking/Time-Sharing OS
- Multiprocessing OS
- Real-Time OS
- Distributed OS
- Network OS
- Mobile OS
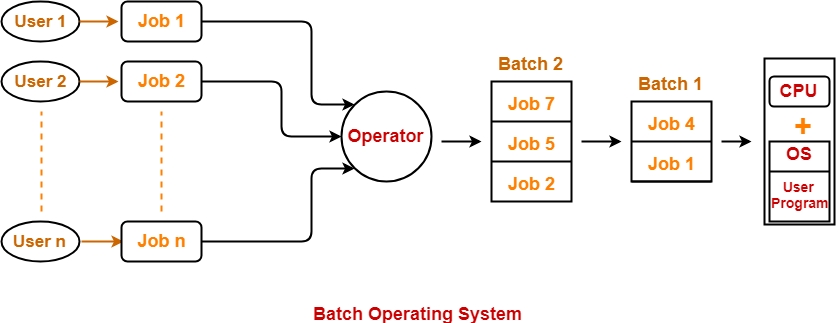
Batch Operating System
Some computer processes are very lengthy and time-consuming. To speed the same process, a job with a similar type of needs are batched together and run as a group.
The user of a batch operating system never directly interacts with the computer. In this type of OS, every user prepares his or her job on an offline device like a punch card and submit it to the computer operator.
Multi-Tasking/Time-sharing Operating systems
The time-sharing operating system enables people located at a different terminal(shell) to use a single computer system at the same time. The processor time (CPU) which is shared among multiple users is termed time-sharing.
Real-time OS
A real-time operating system time interval to process and respond to inputs is very small. Examples: Military Software Systems, Space Software Systems.
Distributed Operating System
Distributed systems use many processors located in different machines to provide very fast computation to their users.
Network Operating System
Network Operating System runs on a server. It provides the capability to serve to manage data, users, groups, security, application, and other networking functions.
Mobile OS
Mobile operating systems are those OS which is especially that are designed to power smartphones, tablets, and wearables devices.
Some most famous mobile operating systems are Android and iOS, but others include BlackBerry, Web, and watchOS.
5. What are the advantages and disadvantages of the operating systems?
Sol:
The advantage of using the Operating System
- Allows you to hide details of hardware by creating an abstraction
- Easy to use with a GUI
- Offers an environment in which a user may execute programs/applications
- The operating system must make sure that the computer system convenient to use
- Operating System acts as an intermediary among applications and the hardware components
- It provides the computer system resources with easy to use the format
- Acts as an intermediator between all hardware's and software's of the system
Disadvantages of using Operating System
- If any issue occurs in OS, you may lose all the contents which have been stored in your system
- The operating system software is quite expensive for small size organizations which adds a burden on them. Example Windows
- It is never entirely secure as a threat can occur at any time
Summary
- An operating system is a software that acts as an interface between the end-user and computer hardware.
- Operating systems were first developed in the late 1950s to manage tape storage.
- The kernel is the central component of a computer operating system. The only job performed by the kernel is to manage the communication between the software and the hardware.
- The two most popular kernels are Monolithic and MicroKernels
- Process, Device, File, I/O, Secondary-Storage, Memory management are various functions of an Operating System.
- Batch, Multitasking/Time-Sharing, Multiprocessing, Real-Time, Distributed, Network, Mobile are various types of Operating Systems.
6. Explain the Simple Batch System of an operating system
Sol:
In a batch operating system,
- Firstly, the user prepares his job using punch cards.
- Then, he submits the job to the computer operator.
- The operator collects the jobs from different users and sorts the jobs into batches with similar needs.
- Then, the operator submits the batches to the processor one by one.
- All the jobs of one batch are executed together.
Advantages-
- It saves the time that was being wasted earlier for each process in context switching from one environment to another environment.
- No manual intervention is needed.
Disadvantages-
Point-01:
Priority can not be set for the jobs. |
In a batch operating system,
- All the jobs of a batch are executed sequentially one after the other.
- The output is obtained only after all the jobs are executed.
- Thus, priority can not be implemented if a certain job has to be executed on an urgent basis.
Point-02:
Batch operating system may lead to starvation. |
In a batch operating system,
- The jobs of a particular batch might take a long time for their execution.
- This might lead to starvation to other jobs in other batches.
Point-03:
CPU may remain idle for a long time. |
In a batch operating system,
- If the jobs of a batch require some I/O operation, then the CPU must wait till the I/O operation gets completed.
- Since I/O devices are very slow, the CPU remains idle for a long time.
- CPU can not take any other job and execute it.
Point-04
There is a lack of interaction between a user and his job. |
In a batch operating system,
- Once a batch is submitted for execution, the user is not able to interact with any of his jobs.
- If a job requires the user to input data during run time, then the user must wait till the other jobs of the batch get executed.
- This also increases the overall execution time.
7. Explain Multi programmed Batch System of an operating system
Sol:
- This sort of OS is utilized to execute more than one job at the same time by a single processor.
- It builds the CPU by sorting out jobs with the goal that the CPU consistently has one job to execute.
- The idea of multiprogramming is depicted as pursues:
- Every one of the jobs that enter the system is kept in the job pool (in a disk). The operating system stacks a lot of jobs from the job pool into the main memory and starts to execute.
- During execution, the job may need to wait for some task, for example, an I/O operation, to finish. In a multiprogramming system, the operating system changes to another activity and executes. At the point when that job needs to wait, the CPU is changed to another job, etc.
- At the point when the first job completes the process of waiting and it recovers the CPU.
- For whatever length of time that in any event, one job needs to execute, the CPU is never idle.
- Multiprogramming operating systems utilize the component of job scheduling and CPU scheduling.
8. Explain the Time-Sharing System of an operating system
Sol:
- Time-sharing systems are not accessible in the 1960s.
- Time-sharing or performing multiple tasks is a legitimate expansion of multiprogramming. That is processor time is shared among numerous users at the same time is called time-sharing.
- The primary contrast between Multi-programmed Batch Systems and Time-Sharing Systems is, in Multi-programmed batch systems its goal is to expand processor use, while in Time-Sharing Systems its goal is to minimize response time.
- Numerous jobs are executed by the CPU by switching between them, however, the switches happen in much less time so that the user can get a prompt response.
- For instance, in transaction processing, the processor executes every user program in a short burst or quantum of calculation.
- That is if n users are available, every user can get time quantum.
- At the point when the user presents the instruction, the response time is seconds all things considered.
- The operating system utilizes CPU scheduling and multiprogramming to give every user a little part of a time.
- Computer systems that were structured essentially as batch systems have been altered to time-sharing systems.
- For instance IBM's OS/360.
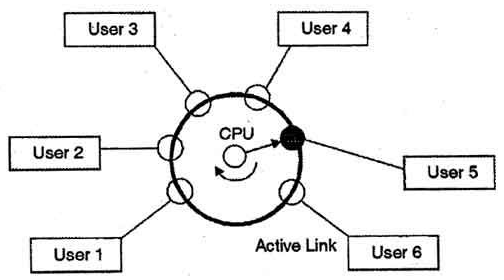
Time-Sharing Operating System
- As the name itself recommends, in a time-sharing system or performing various tasks system, different jobs can be executed on a system simultaneously by sharing the CPU time among them.
- It is viewed as a logical expansion of multiprogramming because the two do synchronous execution yet vary in their prime aims.
- The fundamental goal of time-sharing systems is to limit reaction time yet not boosting the processor use(which is the target of multiprogramming systems).
- The time-sharing systems were created to give an intuitive utilization of the computer system.
- A time-shared system utilizes CPU planning and multiprogramming to give every user a little segment of a period shared computer.
- It enables numerous users to share computer resources all the while. As the system switches quickly from one user to the next, a brief timeframe opening is given to every user for their executions.
- The time-sharing operating system guarantees that every one of the assignments gets the chance to get to the CPU individually and for a fixed little interval of time. This interval is known as the time quantum.
- Eg: Unix Systems
Advantages of Time-Sharing OS:
- Each user gets an equivalent chance
- Fewer chances of duplication of programming
- CPU inert time can be diminished
Disadvantages of Time-Sharing OS:
- Unwavering quality issue
- One must need to deal with the security and respectability of user programs and information.
- Information correspondence issue
Time-Sharing Operating System
9. Explain Personal Computer System of an operating system in detail
Sol:
A personal computer is a general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities and original sale price make it useful for individuals, and is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator. This contrasts with the batch processing or time-sharing models that allowed larger, more expensive minicomputer and mainframe systems to be used by many people, usually at the same time. A related term is “PC” which was initially an acronym for “personal computer,” but later became used primarily to refer to the ubiquitous Wintel platform.
Software applications for most personal computers include, but are not limited to, word processing, spreadsheets, databases, web browsers, and e-mail clients, digital media playback, games, and myriad personal productivity and special-purpose software applications. Modern personal computers often have connections to the Internet, allowing access to the World Wide Web and a wide range of other resources. Personal computers may be connected to a local area network (LAN), either by a cable or a wireless connection. A personal computer may be a desktop computer or a laptop, netbook, tablet, or a handheld PC.
Early computer owners usually had to write their programs to do anything useful with the machines, which even did not include an operating system. The very earliest microcomputers, equipped with a front panel, required hand-loading of a bootstrap program to load programs from external storage (paper tape, cassettes, or eventually diskettes). Before very long, automatic booting from permanent read-only memory became universal. Today’s users have access to a wide range of commercial software, freeware, and free and open-source software, which are provided in ready-to-run or ready-to-compile form. Software for personal computers, such as applications and video games, are typically developed and distributed independently from the hardware or OS manufacturers, whereas software for many mobile phones and other portable systems is approved and distributed through a centralized online store.
Since the early 1990s, Microsoft operating systems and Intel hardware have dominated much of the personal computer market, first with MS-DOS and then with Windows. Popular alternatives to Microsoft’s Windows operating systems include Apple’s OS X and free open-source Unix-like operating systems such as Linux and BSD. AMD provides the major alternative to Intel’s processors.
Computer systems consist of three components as shown in the below image: Central Processing Unit, Input devices, and Output devices. Input devices provide data input to the processor, which processes data and generates useful information that’s displayed to the user through output devices. This is stored in the computer’s memory.
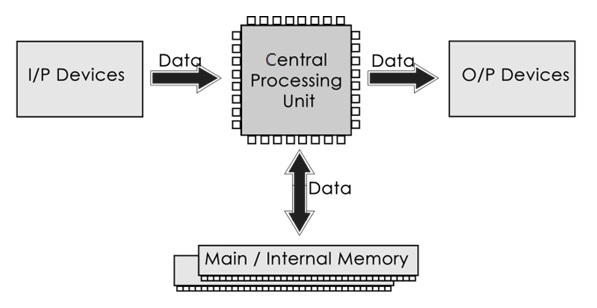
Central Processing Unit
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is called "the brain of the computer" as it controls the operation of all parts of the computer. It consists of two components: The arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), and Control Unit.
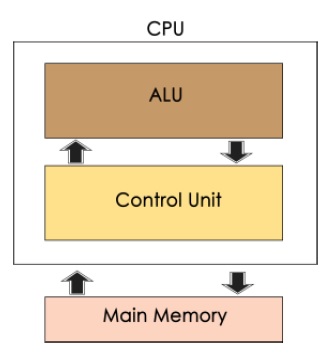
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Data entered into the computer is sent to RAM, from where it is then sent to ALU, where the rest of the data processing takes place. All types of processing, such as comparisons, decision-making, and processing of non-numeric information takes place here, and once again data is moved to RAM.
Control Unit
As the name indicates, this part of the CPU extracts instructions, performs execution, maintains and directs operations of the entire system.
Functions of Control Unit
Control unit performs the following functions −
- It controls all activities of the computer
- Supervises flow of data within CPU
- Directs the flow of data within the CPU
- Transfers data to Arithmetic and Logic Unit
- Transfers results to memory
- Fetches results from memory to output devices
Memory Unit
This is a unit in which data and instructions given to the computer as well as results given by the computer are stored. The unit of memory is "Byte".
1 Byte = 8 Bits
10. What is the Parallel System of an operating system?
Sol:
- Parallel Processing Systems are intended to accelerate the execution of programs by isolating the program into numerous pieces and processing those fragments simultaneously.
- Such systems are multiprocessor systems called tightly coupled systems.
- Parallel systems manage the synchronous utilization of numerous computer resources that can incorporate a single computer with various processors, various computers associated by a network to frame a parallel processing cluster or a blend of both.
- Parallel systems are harder to program than computers with a single processor because the engineering of parallel computers fluctuates appropriately and the procedures of numerous CPUs must be composed and synchronized.
- A few models for interfacing processors and memory modules exist, and every topology requires an alternate programming model.
- The three models that are most regularly utilized in structuring parallel computers incorporate synchronous processors each with its very own memory, asynchronous processors each with its memory, and asynchronous processors with a typical, shared memory.
- Parallel operating systems are essentially worried about dealing with the resources of parallel machines.
- This task faces numerous difficulties: application software engineers request all the performance possible, numerous equipment configurations exist and change all-around quickly, yet the operating system should progressively be good with the standard adaptations utilized in computers.
- Today, new applications emerge and request faster computers. Business applications are the most utilized on parallel computers.
- A computer that runs such an application; ought to have the option to process an enormous amount of data in modern ways. These applications incorporate designs, virtual reality, and decision support, parallel databases, medical diagnosis, etc.
- We can say almost certainly that business applications will characterize future parallel computer design however scientific applications will stay significant users of parallel processing innovation.