Module-1
Atomic and Molecular Structure
Q1- Explain the energy level Homonuclear diatomic molecule & calculate the evolved energy.
A- H2 molecule consist of two H atoms and their two electrons. Two 1s orbitals give two MOs- one bonding that is σ and another one is antibonding that is σ*. The bonding orbital is in lower in energy state, the two electron occupies the bonding MO. The MO electron configuration of H2 molecule is written as (σ1s) 2.
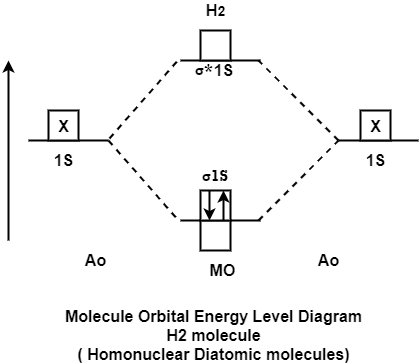
Energy evolved =
[No. of electron in BMO (-) + No. of electron in Anti Bonding Molecular Orbital * (+)]
=2*(- ) + 0*(+ )
= -2
This evolved energy is called as stabilization energy.
The molecule is stable so it is diamagnetic.
Q2-Calculate the stabilization energy of hetronuclear CO molecule.
A- [No. of electron in BMO * (-) + No. of electrons in anti bonding molecular orbital * (+)]
=(8) * (-) + (2) * (+)
= -6
Q3- Define Energy Bands?
A- Energy bands consisting of a large number of closely spaced energy levels exist in crystalline materials. The bands can be thought of as the collection of the individual energy levels of electrons surrounding each atom.
Q4- Define Liquid Crystals?
A- Liquid Crystal is the fourth state that enters under the right conditions and consequences. The matter which shows the property between the conventional Liquid and Solid Crystals.
Q5- Mention the different phases of Liquid Crystal and explain thermotropic liquid crystal.
A- There are several phases in Liquid Crystal.
1-Mesomorphic Phases
1.1-Thermotropic Liquid Crystal
1.2-Lyotropic Liquid Crystal
Thermotropic Liquid Crystal class can be prepared by heating. The known crystals are organic compounds. Ex.- bis-(p-methylbenzal)-p.
While at another end the Lyotropic Liquid Crystal are prepared by the mixture of two or more components.
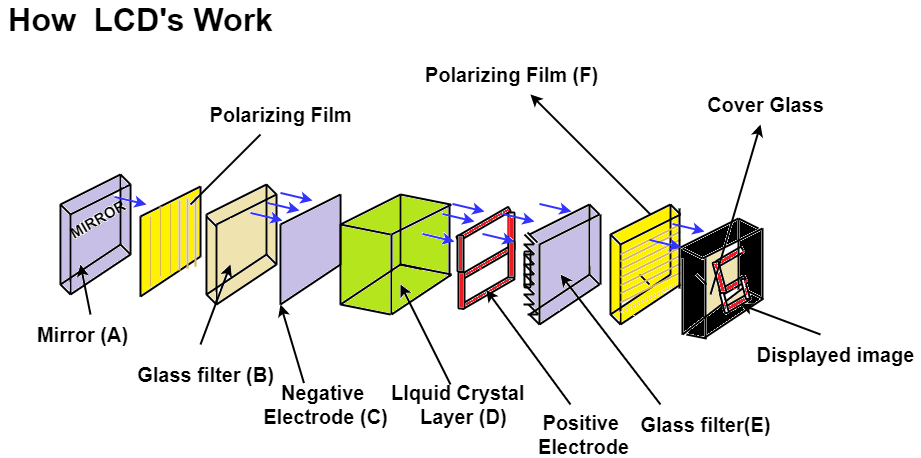
Q6- Explain the working of Liquid Crystal Display.
A- Working of Liquid Crystal Display:
It is based on change in optical properties of LCD which is caused by electric fields. In LCD the thin film of Liquid Crystal usually the Nematic crystal is sandwich in between thin transparent electrodes. The arrangement is provided to apply an electric field across a small area of this thin film usually called as pixel. This is used to apply electric field across a small area of this thin film of liquid crystal. TFT Matrix means thin film transistor matrix. This is the arrangement which provide electric field to the small region of this liquid crystal film on both side of transparent electrode polarized filter is placed. One polarizing filter placed between backlight and the LC films while another one is placed between liquid crystal film and screen. The white light is meant to pass through the filter then after that this light fall on Liquid Crystal film the liquid crystal changes the polarization of light and this change is controlled by applying electric field to various point on the Liquid Crystal film. This electric field is applied at various point which are called as Pixels with help of TFT matrix, change in polarization lead to change in intensity of light at different points. The combine effect of change in intensity at all the point form the image which can be seen at the screen. Eg.Computer Screen, Watches etc.
Q7- What is Perfect Crystals?
A- Perfect Crystal: A perfect crystal is that crystal in which atoms are arranged in that manner that atoms possess equal numbers of positive ions as well as the negative ions hence systematical manner, geometrical manner arrangement of the ions without any defects are called as perfect crystal. This perfectness of a crystal explains many properties of crystal like magnetic property of crystal etc.
Q8- Classify the Point Crystals.
A-
Q9- What is Schottkey Defects?
A- Schottkey: This defect comes in known in the name of scientist Walter H. Schottkey. In his model he explains about the loss of Ions from the original lattice. There would be the equal loss of the positive and negative ions from the lattice to maintain the neutrality of the lattice. Hence this defect is called Schottkey Vacant defect.
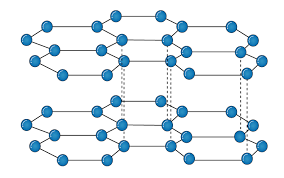
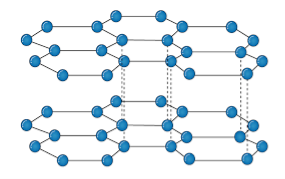
Q10- Explain the structure of Graphite.
A- The carbon atom is sp2 hybridized that means there is 4 valence electron in their outermost shell as in the diamond the all 4 valence electron are covalently bonded while in graphite the 3 electron makes a covalent bond while the remaining 1 electron are free. The interconnection of these carbon atoms forms the hexagonal structure. The C-C bond bond length is 1.42 Angstrom. This hexagonal layer attached toward each other by weak Vander Wall forces at a distance of 3.35 Angstrom. This is the reason why graphite is soft.
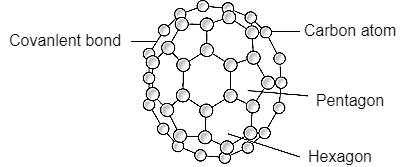
Q11- Describe the structure of Fullerene.
A- Fullerene is a soccer ball like structure which is hollow from inside and is polymorphic in nature (arrange in hexagon and pentagon form) These are arranged in manner that posses 2 hexagon share a common wall while 2 different pentagon never share the common wall. Each carbon atom is sp2 hybridized. Electric spark is produced at graphite ectrode at inert atmosphere and low pressure which gives back black soot that consist of fullerene and impurities. These impurities are removed by the method of sublimation.
Q12- Mention the applications of Nano material.
A-
A- Nanomaterial will be used as the next generation computer chips.
B- Nanomaterial will be responsible for the High Definition TV.
C- Branch deals in reducing the cost of the flat panel displays.
D- Nanotechnology plays a major role in improving the density of the battery.
E- Nanotechnology contributes in the changing trends by playing the major role in improving the sensivity of the sensors.