Unit-2
Spectroscopic techniques and Applications
Q1- What is spectroscopy?
A 1) Spectroscopy is the branch of science which deals with the determination of the structure of compound through the interaction of magnetic radiation with the matter. The term spectroscopy refers to the measurement of radiation intensity as a function of wavelength through spectroscopy.
Q2- What does electromagnetic spectrum consists?
A2)
Q3- What do you understand by microwave spectroscopy?
A 3) Microwave Spectroscopy is also called as the Rotational spectroscopy. It is the measurement of energy of transition between Q4uantized rotational states of molecules in the gas phase. The rotational spectra of non-polar molecules cannot be observed by this method while it can be measured by Raman spectroscopy. Rotational spectroscopy is sometimes referred to as pure rotational spectroscopy to distinguish it from rotational-vibrational spectroscopy where changes in rotational energy occur together with changes in vibrational energy and also from ro-vibronic spectroscopy (or just vibronic spectroscopy) where rotational, vibrational and electronic energy changes occur simultaneously.
Q5- Explain vibrational spectroscopy with its applications.
A 5) The change in the vibrational motion of molecule is absorbed in the Infrared Region this is why it is also called as the Infrared Spectroscopy. If vibration in the molecule persists then it should change its dipole moment that may be the magnitude form or oriented with its direction.
Applications:
1-Infrared techniQ6ue is used in organic and inorganic chemistry.
2-This is used in Q7uality control, dynamic measurement.
3-This is majorly used in the forensic labs.
4-Infrared Spectroscopy is used in measuring the degree of polymerization in manufacturing the polymers.
Q6- Explain Monochromator.
A6-
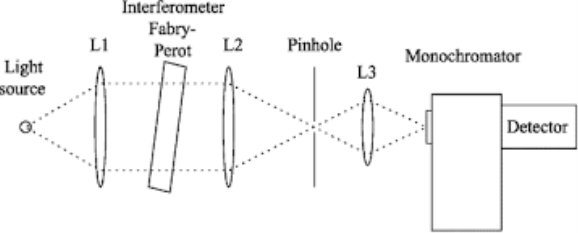
Monochromator used to measure the wavelength of the light. As the figure shows monochromator is placed between the sample and the source of light passing from that the light passes to the detector. Here the monochromatic used to detect the wavelength of the light form the source. While on moving further there is a Double beam Ultraviolet-Visible instrument is used here is a splitter and a series of mirrors to get the beam to a reference sample and the sample to be analyzed, this allows for more accurate readings. In the simultaneous Ultraviolet-Visible instruments monochromator is removed hence it has a diode array detectors that allows the instrument to simultaneously detect the absorbacne at all wavelengths. This instrument is much faster and accurate than double and single Ultraviolet-Visible instrument.
Q7- Mention the uses of ultraviolet & visible spectroscopy.
A 7)
1- This is majorly used in the analytical chemistry.
2- This can be used as a detector for the High performance liQ10uid chromatography.
3- Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy is used as the semiconductor in the industry to measure the thickness and optical properties of wafer.
Q8- What is Raman Spectroscopy?
A 8) Raman Spectroscopy deals with the analysis of the chemical in a non-destructive form. This help in extracting a detailed information about the chemical structure, phase and polymorphy, crystallinity and molecular interactions. This is purely based on the interaction of light with a chemical bonds in the material.