Unit - 2
Cloud Computing
Q1) What is Cloud Computing?
A1) Cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing services -- from applications to storage and processing power -- typically over the internet and on a pay-as-you-go basis.
A fundamental concept at the back of cloud computing is that the region of the carrier, and among the info such as the hardware or operating machine on which it's miles walking, are in large part irrelevant to the user.
It is with this in thoughts that the metaphor of the cloud changed into borrowed from antique telecoms network schematics, wherein the public telephone community later termed as net changed frequently which represented as a cloud to denote.

Q2) Explain the Working of cloud computing
A2) Rather than owning their own computing infrastructure or data centers, companies can rent access to anything from applications to storage from a cloud service provider.
One benefit of using cloud computing services is that firms can avoid the upfront cost and complexity of owning and maintaining their own IT infrastructure, and instead simply pay for what they use, when they use it.
In turn, providers of cloud computing services can benefit from significant economies of scale by delivering the same services to a wide range of customers.
Cloud computing services cover a vast range of options now, from the basics of storage, networking, and processing power through to natural language processing and artificial intelligence as well as standard office applications. Pretty much any service that doesn't require you to be physically close to the computer hardware that you are using can now be delivered via the cloud.
Q3) What are the Examples of cloud computing?
A3) Cloud computing underpins a full-size variety of offerings. That includes purchaser offerings like Gmail or the cloud again-up of the images to your phone, although to the offerings which permit huge businesses to host all their information and run all in their packages within the cloud.
Netflix is based on cloud computing services to run its video streaming service and its other commercial enterprise structures too, and feature some of different companies.
Cloud computing is turning into the default alternative for many apps: software program vendors are increasingly more supplying their applications as offerings over the internet in preference to standalone merchandise as they try to interchange to a subscription model.
However, there is a capacity drawback to cloud computing, in that it may also introduce new fees and new risks for organizations using it.
Benefits:
Reduced IT costs
Moving to cloud computing may reduce the cost of managing and maintaining your IT systems. Rather than purchasing expensive systems and equipment for your business, you can reduce your costs by using the resources of your cloud computing service provider. You may be able to reduce your operating costs because:
Scalability
Your business can scale up or scale down your operation and storage need quickly to suit your situation, allowing flexibility as your needs change. Rather than purchasing and installing expensive upgrades yourself, your cloud computer service provider can handle this for you. Using the cloud frees up your time so you can get on with running your business.
Business continuity
Protecting your data and systems is an important part of business continuity planning. Whether you experience a natural disaster, power failure or other crisis, having your data stored in the cloud ensures it is backed up and protected in a secure and safe location. Being able to access your data again quickly allows you to conduct business as usual, minimising any downtime and loss of productivity.
Collaboration efficiency
Collaboration in a cloud environment gives your business the ability to communicate and share more easily outside of the traditional methods. If you are working on a project across different locations, you could use cloud computing to give employees, contractors and third parties access to the same files. You could also choose a cloud computing model that makes it easy for you to share your records with your advisers (e.g., a quick and secure way to share accounting records with your accountant or financial adviser).
Q4) What is AWS?
A4) AWS (Amazon Web Services) is a comprehensive, evolving cloud computing platform provided by Amazon that includes a mixture of infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (Paas) and packaged software as a service (SaaS) offering. AWS services can offer different organizational tools such as compute power, database storage and content delivery services.
AWS was launched in 2006 from the internal infrastructure that Amazon.com built to handle its online retail operations. AWS was one of the first companies to introduce a pay-as-you-go cloud computing model that scales to provide users with compute, storage or throughput as needed.
AWS offers many different tools and solutions for enterprises and software developers that can be used in data centres in up to 190 countries. Groups such as government agencies, education institutions, non-profits and private organizations can use AWS services.
Q5) How AWS works?
A5) AWS is separated into different services; each can be configured in different ways based on the user's needs. Users should be able to see configuration options and individual server maps for an AWS service. More than 100 services comprise the Amazon Web Services portfolio, including those for compute, databases, infrastructure management, application development and security.
Q6) Explore the Important AWS Services.
A6) Amazon Web Services offers a wide range of different business purpose global cloud-based products. The products include storage, databases, analytics, networking, mobile, development tools, enterprise applications, with a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
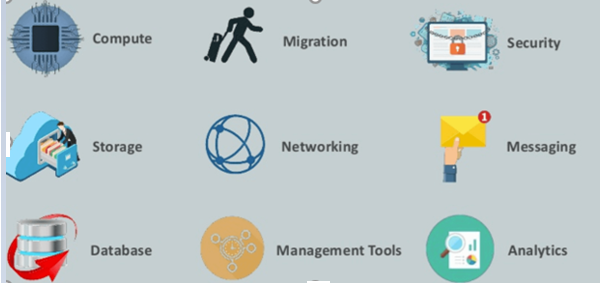
AWS Compute Services
Here, are Cloud Compute Services offered by Amazon:
Migration
Migration services used to transfer data physically between your datacenter and AWS.
Storage
Security Services
Database Services
Analytics
Management Services
Internet of Things
Application Services
Deployment and Management
Developer Tools
Mobile Services
Business Productivity
Desktop & App Streaming
Artificial Intelligence
Q7) State the Advantages of AWS
A7)
AWS lets in groups to use the already familiar programming fashions, working systems, databases, and architectures.
It's miles a price-powerful carrier that allows you to pay simplest for what you use, without any up-front or lengthy-time period commitments.
You'll no longer require putting money into going for walks and keeping records facilities.
Gives rapid deployments
May effortlessly add or remove capacity.
Allow cloud access speedy with infinite capacity.
Total value of ownership is very low in comparison to any personal/devoted servers.
Offers centralized billing and management
Offers hybrid talents
Let’s in you to deploy your software in multiple regions round the arena with just a few clicks
Q8) What are the Disadvantages of AWS?
A8)
In case you want greater immediately or in-depth help, you will ought to choose paid assist applications.
Amazon net services can also have a few common cloud computing troubles whilst you pass to a cloud. For example, downtime, restricted control, and backup safety.
Aws units default limits on sources which differ from area to location. These assets consist of pics, volumes, and snapshots.
Hardware-level modifications occur for your software which might not offer the first-rate overall performance and usage of your programs.
Q9) What is Google?
A9) Google is an internet search engine. It uses a proprietary algorithm that's designed to retrieve and order search results to provide the most relevant and dependable sources of data possible.
Google's stated mission is to "organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful." It is the top search engine in the world, a position that has generated criticism and concern about the power it has to influence the flow of online information.
Google is so dominant that the term "Google" can also be used as a verb, so that when someone searches for something on Google, they may say they "Googled" it.
Google began as a search project by Larry Page and Sergey Brin when they were Ph.D. students at Stanford University.
The search engine algorithm they developed was unique because it ranked pages not only based on their content, but on how many other webpages linked back to them.
Page and Brin determined that links to a page were a sign of its online authority, and Google's algorithm therefore returned more useful results, helping propel Google to become the most-used search engine.
Google's algorithm was patented and named PageRank. The current search technology is based on some of these principles, but has evolved to the point where there are many more variables at play.
Although the Google corporation has since branched out to provide many other products beyond search, the search engine is still Google's most popular service.
A10) What is Microsoft?
A10) Microsoft is a US-based technology company. It was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen in 1975 and quickly grew to become the largest software company in the world. Today, Microsoft is still widely known for its software, but the company also develops hardware and provides several cloud services.
Microsoft's most recognizable software titles include Windows and Office. Microsoft Windows is the world's most popular desktop operating system and Office is the most popular productivity suite. Below is a list of some of the software, hardware, and cloud services provided by Microsoft.
Software
Hardware
Services
A11) What is the concept Vendor Offering – IBM?
A11) IBM gives three hardware systems for cloud computing.
[1] Those structures provide built-in help for virtualization. For virtualization IBM gives IBM WebSphere utility infrastructure that helps programming fashions and open requirements for virtualization.
The management layer of the IBM cloud framework consists of IBM Tivoli middleware
[2] Control equipment offer abilities to alter snap shots with automatic provisioning and de-provisioning, monitor operations and meter usage while tracking expenses and allocating billing. The last layer of the framework provides incorporated workload equipment.
[3] Workloads for cloud computing are offerings or times of code that can be achieved to meet unique business needs.
[4] IBM gives tools for cloud-based collaboration, improvement and test, application improvement, analytics, business-to-enterprise integration, and protection.
[5] IBM cloud computing emerged from the union of its mainframe computing and virtualization technologies. Called the original virtualization employer,
[6] IBM’s first experiments in virtualization occurred in the 1960s with the improvement of the digital gadget (vm) on cp-forty and cp-67 running systems.
Cp-sixty-seven, a hypervisor used for software program trying out and improvement, enabled reminiscence sharing throughout vms at the same time as giving each person their own virtual reminiscence space.
With the device partitioned into separate vms, mainframes ought to run multiple applications and tactics on the identical time, making the hardware greater green and price-effective.
[7] IBM started out selling vm generation for the mainframe in 1972
In February 1990, IBM released the Rs/6000 (which later became known as electricity processor) based totally servers.
The servers, in mixture with the IBM mainframe, were constructed for complex and mission-critical virtualization. Power structures servers consist of powervm hypervisors with stay partition mobility and energetic reminiscence sharing. Stay migration turned into introduced with power6 in can also 2007.
Subsequent, IBM regarded to enforce standardization and automation of their era so that it will maintain up with the proliferation of data produced through an increasing number of efficient hardware and statistics centers.
This mixture of virtualization, standardization and automation led to the development of IBM cloud computing
[8] IBM started out to expand a method for cloud computing in 2007, announcing that it deliberates to construct clouds for company customers and provide offerings to fill what it seemed as gaps in current cloud environments.
[9] In October 2007, IBM announced a partnership with google to sell cloud computing in universities. In addition to donating hardware and machines, the two organizations also supplied a curriculum to train college students about cloud computing.
[10] IBM claimed in April 2011 that 80% of fortune 500 companies have been using IBM cloud, and that their software program and services had been utilized by more than 20 million cease-person clients, with clients such as American airlines, Aviva, Carfax, Frito-Lay, India first existence coverage corporation,
On 4 June 2013 IBM announced its acquisition of SoftLayer, to shape an IBM cloud offerings division.
In 2011, IBM smart cloud incorporated Hadoop-based infosphere big insights for massive statistics,[17] green hat for software testing [18] and nirvanix for cloud storage. In 2012, the then new CEO Virginia Rometty said the corporation deliberate to spend $20 billion on acquisitions by way of 2015. Via 2014, the name smart cloud become replaced with merchandise that have a prefix of IBM cloud.
A product called IBM cloud manager with open stack become IBM’s integration of open stack together with a multitude of fee additions that could serve employer customers. A product called IBM cloud orchestrator could serve the orchestration needs of a corporation. The aforementioned smart cloud merchandise was discontinued.
Via 2016, the aforementioned product called IBM cloud supervisor with open stack turned into discontinued, even though the offerings business enterprise can be the usage of other variations of open stack for massive scale cloud deployments.
Public, private and hybrid cloud fashions
Q12) State the name of cloud provision models given by IBM
A12)
non-public cloud, owned and operated by the client
non-public cloud, owned via the purchaser, but operated by IBM (or every other issuer)
non-public cloud, owned and operated via IBM (or any other company)
virtual personal cloud services (based on multi-tenanted guide for individual businesses)
public cloud offerings (primarily based at the provision of functions to people).