Unit - 1
Quantity Estimation for Buildings
Q1) What are measurement units for various building materials?
A1)
Unit of measurement of various items of work is based upon their size, shape, and the nature.
Principal units for various items of work are as follows:
a) Mass voluminous and thick works shall be taken in cubic unit or volume (cu.m).
b) Thin, shallow and surface work shall be taken in square unit the thickness shall be specified in description of item and measurement of length and breadth or projection shall be taken to calculate area (sq. m).
c) Long and thin work shall be taken in linear or running units and linear measurement shall be taken (running meter).
d) Piece work, job work etc, shall be taken in number.
Q2) Explain centre line method?
A2)
As the name itself implied, the total centre line length of wall of same have similar foundation is worked from plan of structure and is then multiple by respective dimension to obtain required quantity of structures.
Total length of centre line remains same for sub structure and superstructure item except in cases where are cross wall like at junction of wall.
This method is simple and easy in calculate for same structure having no cross wall.
If there are crossed wall, then special care is to taken in taking out dimension at all such junction point.
The simple rule is to deduct half width of respective item for each junction point from total length of centre line.
In case of building have different types of walls each set wall is considered separate i.e., 1st determine total length of centre line of each type and make deduction for each junction as state above and multiple by respective width and depth that item to find out its quantity.
This method has length will remain same for excavation in foundation, for concrete in foundation for all footings and for superstructure.
This method is quick and easy but required special attention and considered at junction meetings point of partition or cross wall, etc.
Procedure: -
- Prepare the foundation plan of given drawing, write centre line length of each wall.
- Find the total length of centre line of long and short wall, having same type of footing.
- Calculate the number of junctions of cross wall with main or external wall. It should be noted that corner of building where two wall meet are not taken in junction and if two wall meet a wall at some point take n= 2 at that point.
- Length for item = total centre line length -n x (½ x width of item).
n = number of junctions of cross wall with main walls.
5. For building have different type of wall each set of walls is separate taken.
Advantage: -
1) It can used for calculate of quantity of rectangle circular and polygons building.
2) This method is simple and quick.
3) Calculate are easy and less.
Q3) Work out the following plans quantity upto plinth level of both long wall short wall method and centre line method.
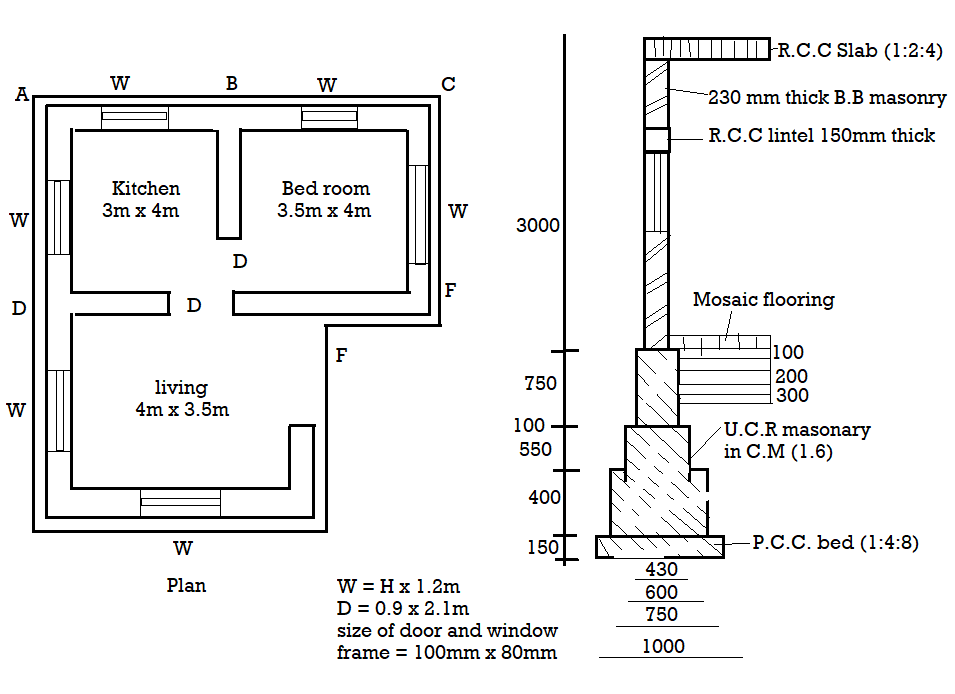
A3) By long wall short wall method,
Long wall:
(ABC, DEF) = 6.96m
(GH) = 4.23 m
Short wall:
(AD, BE, CF) = 4.23 m
(DG, HI) = 3.73 m
Sr.no | Description | No | Length | Width | Height | Quantity | Total quantity |
1 | Earthwork in excavation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Long wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (ABC, DEF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L=6.96 +1 = 7.96 m | 2 | 7.96 | 1 | 1.2 | 19.10m3 | 43.56 m3 |
| (GH) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4.23 + 1 = 5.23m | 1 | 5.23 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.28 m3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Short wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (AD, BE, CF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4.23 - 1 = 3.23 m | 3 | 3.23 | 1 | 1.2 | 11.63m3 |
|
| (DG, HI) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 3.73 - 1 = 2.73 m | 1 | 2.73 | 1 | 1.2 | 6.55m3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 | P.C.C |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Long wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (ABC .DEF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 7.96 m | 2 | 7.96 | 1 | 0.15 | 2.39 m3 |
|
| (GH) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 5.23 | 1 | 5.23 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.78m3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Short wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (AD, BE, CF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 3.23 m | 3 | 3.23 | 1 | 0.15 | 1.45m3 |
|
| (DG, HI) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 2.73 m | 1 | 2.73 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.82m3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 | Plinth quantity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Offset = (0.43 - 0.23)/2=0.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Plinth dimension = clear dimension - 2 x offset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1. Rubble |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| For kitchen |
|
|
|
|
| 10.71 m3 |
| L = 3 - 0.2 = 2.8 m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B = 4 - 0.2 = 3.8 m | 1 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 3.19 |
|
| For bed room |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 3.3 - 0.2 = 2.2 m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B = 4 - 0.2 = 3.8 m | 1 | 2.2 | 3.8 | 0.3 | 3.76 |
|
| For living |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4 = 0.2 = 3.8m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| b = 3.5 - 0.2 = 3.3 m | 1 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 0.3 | 3.76 |
|
| 2.murrum |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| For kitchen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 3 - 0.2 = 2.8 m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B = 4 - 0.2 = 3.8 m | 1 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 2.13 | 7.15 m3 |
| For bed room |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 3.3 - 0.2 = 2.2 m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B = 4 - 0.2 = 3.8 m | 1 | 2.2 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 2.51 |
|
| For living |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4 = 0.2 = 3.8m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| b = 3.5 - 0.2 = 3.3 m | 1 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 0.2 | 2.51 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3.pcc |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| For kitchen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 3 - 0.2 = 2.8 m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B = 4 - 0.2 = 3.8 m | 1 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 0.1 | 1.06 | 3.56 m3 |
| For bed room |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 3.3 - 0.2 = 2.2 m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| B = 4 - 0.2 = 3.8 m | 1 | 2.2 | 3.8 | 0.1 | 1.25 |
|
| For living |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4 = 0.2 = 3.8m |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| b = 3.5 - 0.2 = 3.3 m | 1 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 1.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 | DPC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Long wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (ABC, DEF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L=6.96 +0.43 = 7.33 m | 2 | 7.33 | 0.43 | _ | 6.35 | 14.94 m2 |
| (GH) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4.23 + 0.43 = 4.66m | 1 | 4.66 | 0.43 | _ | 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Short wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (AD, BE, CF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4.23 - 0.43 = 3.8 m | 3 | 3.8 | 0.43 | _ | 4.9 |
|
| (DG, HI) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 3.73 - 0.43 = 3.3 m | 1 | 3.3 | 0.43 | _ | 2.84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Deductions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Door | 3 | 0.9 | 0.43 |
| 1.16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 | Brickwork in superstructure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Long wall |
|
|
|
|
| 36.96 m2 |
| (ABC, DEF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Step 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L= 6.96 + 0.75 = 7.71m | 2 | 7.71 | 0.75 | 0.4 | 4.63 |
|
| Step 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 6.96 +0.6 = 7.56 m | 2 | 7.56 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 4.99 |
|
| Step 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 6.96 +0.43 = 7.39m | 2 | 7.39 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 5.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Long wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (GH) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Step 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4.23 +0.25 =4.98m | 1 | 4.98 | 0.75 | 0.4 | 1.49 |
|
| Step 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 4.23 + 0.6 = 4.89 m | 1 | 4.89 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 1.59 |
|
| Step 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| l= 4.23 +0.43 = 4.66m | 1 | 4.66 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 1.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Short wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (AD, BE, CF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Step 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| l= 4.23 - 0.75 = 3.48m | 3 | 3.48 | 0.75 | 0.4 | 3.13 |
|
| Step 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| l= 4.23 - 0.6 = 3.63m | 3 | 3.63 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 3.59 |
|
| Step 3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| l= 4.23 - 0.43 = 3.88 | 3 | 3.88 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 4.17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Short wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (DG, HI) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Step 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| l= 3.73 - 0.75 = 2.98m | 2 | 2.98 | 0.75 | 0.4 | 1.79 |
|
| Step 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| l= 3.73- 0.6 = 3.13 m | 2 | 3.13 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 2.07 |
|
| Step3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| l = 3.73 - 0.43 = 3.3m | 2 | 3.3 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 2.41 |
|
By centre line method,
Length centre line plan = 2 x 3.23 +2 x 3.73 +3 x 3.73 +4.23 +2 x 3.73
= 38.3m
Total length = length of centre line plan – n x 0.5 x width
= 38.3 – 4 x 0.5 x width
= 38.3 – 2 x width
1 | Earthwork in excavation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 38.3 - 2 x 1 = 36.3 | 1 | 36.3 | 1 | 1.2 | 43.56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 | PCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L= 38.3 - 2 X 1 = 36.3 | 1 | 36.3 | 1 | 0.15 | 5.14 |
|
3 | Brickwork in foundation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Step 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| l = 38.3 - 2 x 0.75= 36.8 | 1 | 36.8 | 0.75 | 0.4 | 11.01 | 36.96 m3 |
| Step 2 |
|
|
|
|
| |
| l= 38.3 - 2 x 0.6 = 37.1 | 1 | 37.1 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 12.24 | |
| Step 3 |
|
|
|
|
| |
| l = 38.3 - 2 x 0.43= 37.45 | 1 | 37.45 | 0.43 | 0.85 | 13.68 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 | DPC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L= 38.3 - 2 x 0.43 = 37.48 | 1 | 37.44 | 0.43 |
| 16.1 | 14.94 m2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door | 3 | 0.9 | 0.43 |
| 1.16 |
Q4) Explain long and short wall method of estimates?
A4)
Long wall and short wall method: In this method measure or find out the external lengths of walls running in the direction generally the long walls out-to-out and the internal length of walls running in the transverse direction in-to-in i.e., of cross or short wall into-in and calculate quantities multiplying the length by the breadth and height of wall
The same nil applicable to the excavation in foundation, to concrete in foundation and to masonry
The simple method is to take the long walls or short walls separately and to find out the centre-to-centre lengths of long wall and short walls from the plan. For symmetrical footing on either side, the centre line remains same for super structure and for foundation and plinth
For long walls add to the center length one breadth of wall, which gives the length of the wall out-to-out, multiplying this length by the breadth and height and get the quantities.
This for finding the quantities of earth work in excavation, for the length of trench out-to-out add to the centre length one breadth of foundation
Adopt the same process for foundation concrete and for each footing. It should be noted that each footing is to be taken separately and the breadth of the particular footing is to be added to the centre length
Long wall length out-to-out centre to centre length + half breadth on one side + half breadth on the other side centre to centre length + one breadth
For short or cross walls sub tract (instead of adding) from the centre length one breadth of wall, which gives the length in-to-in, and repeat the same process as for the long walls, subtracting one breadth instead of adding
Short wall length in-to-in Centre-to-centre length-one breadth
That is, in case of long wall add one breadth and in case of short wall subtract one breadth from the centre length to get the corresponding lengths.
It will be noticed that by taking dimensions in these ways, the long walls are gradually decreasing in length from foundation to superstructure, while the short walls are increasing in length This method is simple and accurate and there is no chance of any mistake. This method may be named as long wall and short wall method, or PWD Method.
The following procedure is adopted.
1. The dimensions of long wall and short wall should be taken separately.
2. Inspective of its lengths, the wall which is taken first is long wall and the wall which is taken next is the short wall.
3. The centre line of the wall of the building is considered for determining the centre to centre line length of long walls and short walls.
4. The centre to centre to centre length of long walls or short walls is obtained by adding half the width of the wall to the internal length of either long wall or short wall.
5. Centre to centre length of long wall internal length of long wall +12 width of the wall.
6. Centre to centre length of short wall internal length of short wall width of the wall.
7. To determine the lengths of different quantities such as earthwork, c.c. Bed in foundation, R.R. Masonry etc, length of long wall centre to centre length of long wall + width, the width is the respective width of the item in consideration.
8. Similarly length of the short wall centre to centre length of the short wall-width, where the width is the respective width of the item such as earthwork, c.c. Bed etc.
Advantages
- This method is simple and accurate
- There are no chances of mistakes in calculation.
- The method gives quantities quickly
Q5) Work out the following plans quantity up to plinth level of both long wall short wall method and centre line method.
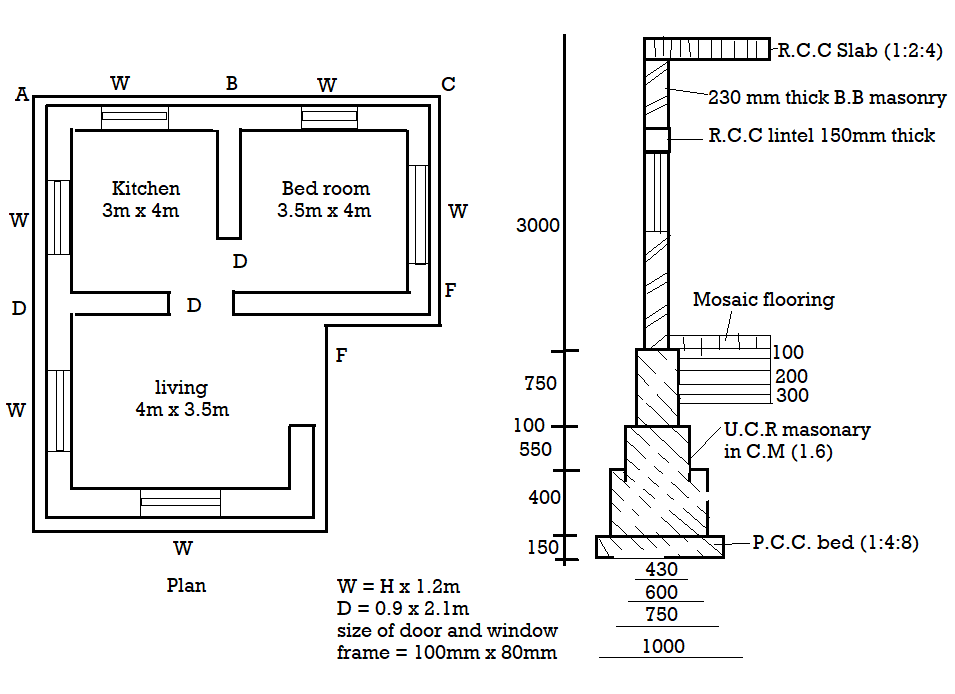
A5) By long wall short wall method,
Long wall:
(ABC, DEF) = 6.96m
(GH) = 4.23 m
Short wall:
(AD, BE, CF) = 4.23 m
(DG, HI) = 3.73 m
1 | Brickwork in superstructure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Long wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (ABC, DEF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L= 6.96 + 0.23 = 7.19 m | 2 | 7.19 | 0.23 | 3 | 9.93 | 22.76 m3 |
| (GH) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| L= 4.23 + 0.23 = 4.46m | 1 | 4.46 | 0.23 | 3 | 8.08 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Short wall |
|
|
|
|
| |
| (AD, BE, CF) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| l= 4.23 - 0.23 = 4 m | 3 | 4 | 0.23 | 3 | 8.28 | |
| (DG, HI) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| l= 3.3.73 - 0.23 = 3.5m | 2 | 3.5 | 0.23 | 3 | 4.83 | |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door | 3 | 0.9 | 0.23 | 2.1 | 1.3 | |
| Window | 6 | 1 | 0.23 | 1.2 | 1.66 | |
| Lintel over door | 3 | 1.2 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| Lintel over window | 6 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.27 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 | Flooring |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kitchen | 1 | 3 | 4 | _ | 12 | 40 m2 |
| Bed room | 1 | 3.5 | 4 | _ | 14 | |
| Living | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | _ | 14 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 | RCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Lintel over door | 3 | 1.2 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 7.83 m3 |
| Lintel over window | 6 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.27 | |
| RCC slab | 1 | Area = 7.4 x 8.4 - 3.4 x 3.5 = 48.7m | 0.15 | 7.31 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 | External plaster with coarse sand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| External perimeter = 2 x 7.19 +2 x 8.19 = 30.76m | 1 | 30.76 | _ | 3.9 | 119.96 | 115.11 m2 |
| H = 0.75 + 3 + 0.15 = 3.9 m |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (external) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Area = 0.9 x 1.2 = 1.08 m2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 0.95 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Window |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Area 1 x 1.2 = 1.2 m2 | 3 | 1 | _ | 1.2 | 3.6 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 | Internal plaster |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Internal perimeter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kitchen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| = 2 x 3 + 2 x 4 = 14m | 1 | 14 | _ | 3 | 42 | 163.67 m2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Bed room |
|
|
|
|
| |
| = 2 x 3.5 + 2 x 4 = 15m | 1 | 15 | _ | 3 | 45 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Living |
|
|
|
|
| |
| = 2 x 4 + 2 x 3.5 = 15 m | 1 | 15 | _ | 3 | 45 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Celling |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Kitchen | 1 | 3 | 4 | _ | 12 | |
| Bed room | 1 | 3.5 | 4 | _ | 14 | |
| Living | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | _ | 14 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (external) | 0.5 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 0.95 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (internal) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduct full face | 2 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 3.78 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Window | 3 | 1 | _ | 1.2 | 3.6 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
By centre line method,
Length centre line plan = 2 x 3.23 +2 x 3.73 +3 x 3.73 +4.23 +2 x 3.73
= 38.3m
Total length = length of centre line plan – n x 0.5 x width
= 38.3 – 4 x 0.5 x width
= 38.3 – 2 x width
1 | Brickwork in superstructure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 38.3 - 2 X 0.23 = 37.84m 1 |
| 37.84 | 0.23 | 3 | 26.11 | 22.76m3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door | 3 | 0.9 | 0.23 | 2.1 | 1.3 | |
| Window | 6 | 1 | 0.23 | 1.2 | 1.66 | |
| Lintel over door | 3 | 1.2 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| Lintel over window | 6 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.27 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 | Flooring |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kitchen | 1 | 3 | 4 | _ | 12 | 40 m2 |
| Bed room | 1 | 3.5 | 4 | _ | 14 | |
| Living | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | _ | 14 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 | RCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Lintel over door | 3 | 1.2 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 7.83 m3 |
| Lintel over window | 6 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.27 | |
| RCC slab | 1 | Area = 7.4 x 8.4 - 3.4 x 3.5 = 48.7m | 0.15 | 7.31 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 | External plaster with coarse sand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| External perimeter = 2 x 7.19 +2 x 8.19 = 30.76m | 1 | 30.76 | _ | 3.9 | 119.96 | 115.11 m2 |
| H = 0.75 + 3 + 0.15 = 3.9 m |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (external) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Area = 0.9 x 1.2 = 1.08 m2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 0.95 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Window |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Area 1 x 1.2 = 1.2 m2 | 3 | 1 | _ | 1.2 | 3.6 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 | Internal plaster |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Internal perimeter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kitchen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| = 2 x 3 + 2 x 4 = 14m | 1 | 14 | _ | 3 | 42 | 163.67 m2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Bed room |
|
|
|
|
| |
| = 2 x 3.5 + 2 x 4 = 15m | 1 | 15 | _ | 3 | 45 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Living |
|
|
|
|
| |
| = 2 x 4 + 2 x 3.5 = 15 m | 1 | 15 | _ | 3 | 45 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Celling |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Kitchen | 1 | 3 | 4 | _ | 12 | |
| Bed room | 1 | 3.5 | 4 | _ | 14 | |
| Living | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | _ | 14 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (external) | 0.5 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 0.95 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (internal) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduct full face | 2 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 3.78 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Window | 3 | 1 | _ | 1.2 | 3.6 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q6) Preparation of an estimate of one room block as shown in fig. For the following item of work
1) Excavation for foundation
2) P.C.C (1:4:8) in foundation
3) U.C.R. Masonry in foundation in C.M. (1:6)
4) O.R. Masonry plinth in C.M. (1:6)
5) D.P.C. At plinth level
- Long wall short wall method
6) Brick work in super structure in C.M(1:6)
7) RCC slab 15 cm thick by
- Long wall short wall method
A6)
Item no | Description | No. | Dimension | Quantity | Explanatory notes | ||||||||||
Length | Breath | Height | |||||||||||||
1 | Excavation for foundation in earth soil of all types removal of the excavates material up to a distance of 50 m beyond the building area |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Long wall | 2 | 8.00 | 1 | 0.90 | 14.40 m3 |
| |||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 4.5 | 1 | 0.90 | 8.10 m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
| Total | 22.50 m3 |
| |||||||||
2 | Providing and laying in situ cement concrete (1:4:8) of trap metal for foundation and bedding including bailing out water, form work compacting and curing etc. complete |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Long wall | 2 | 8.00 | 1 | 0.20 | 3.2m3 |
| |||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 4.50 | 1 | 0.20 | 1.8m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
| Total | 5 m3 |
| |||||||||
3 | Providing un coursed rubble masonry of trap stone in cement mortar (1:6) |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Long wall | 2 | 7.80 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 7.48 m3 |
| |||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 4.70 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 4.52 m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
| Total | 12.00 m3 |
| |||||||||
4 | Providing coursed rubble masonry 11nd sort of trap stones in cement mortar (1:6) in external wall of plinth including bailing out water. |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
| Long wall | 2 | 7.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 3.75m3 |
| ||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 5.00 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 2.50 m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
| Total | 6.25 m3 |
| |||||||||
5 | Providing and lying damp proof course 5 cm thick in cement concrete (1:2:4) layer and bitumen using cement with water proofing compound |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
| Long wall | 2 | 7.50 | 0.50 | - | 7.5 m2 |
| ||||||||
| Short wall | 2 | 5.00 | 0.50 | - | 5.0 m2 |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
|
| Total | 12.5 m2 |
| ||||||||
6 | Providing second class burnt brick masonry with IS type brick or conventional type in cement mortar (1:6) |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Long wall | 2 | 7.30 | 0.30 | 2 | 8.76 m3 |
| |||||||||
Short wall | 2 | 5.20 | 0.30 | 2 | 6.24 m3 |
| |||||||||
Deduction for |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Door D | 1 | 1.20 | 0.30 | 2.00 | 0.72m3 |
| |||||||||
Window W1 | 2 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 1.50 | 0.90m3 |
| |||||||||
Window W2 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 0.30m3 |
| |||||||||
Lintel over door D | 1 | 1.50 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.68m3 |
| |||||||||
Lintel over W1 | 2 | 1.30 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.12m3 |
| |||||||||
Lintel over W2 | 1 | 1.30 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.06m3 |
| |||||||||
|
|
| Total deduction | = | 2.17 m3 |
| |||||||||
| Net quantity of brick masonry (a-b) |
|
|
| = | 2.17 m3 | B | ||||||||
7 | Providing and casting in situ cement concrete M-15 (1:2:4) of trap [ metal for rcc slab 15 cm thick including centering formwork compacting and curing | 1 | 7.40 | 5.90 | 0.15 | 6.55 m3 |
| ||||||||
Q7) What are types of estimates?
A7)
The estimates are broadly classified as:
A) Approximate Estimate: -
1) Preliminary / approximate /Rough estimate.
2) Plinth area estimate.
3) Cubic content method.
4) Approximate quantity method.
B) Detailed estimate: -
1) Detailed estimate/ item rate estimate.
2) Revised estimate.
3) Supplementary estimate.
4) Supplementary and revised estimate.
5) Annual repairs/ annual maintenance estimate.
A) Approximate Estimate:
- It gives the approximate cost of the work and is prepared on the basis of cost of similar works carried out in past.
- This estimate is preliminary study of various aspect of work or project for short time.
- This estimate is prepared for administrative approval.
- E.g., Approximate cost 100 bed hospital at 50.000 per bed comes to be 50,00,000.
B) Detailed estimate:
- It is prepared after its complete set of drawings are required for our work.
- To find out the detailed cost with the help of specification.
- Detailed estimate is prepared for technical sanction from competent authority for arranging contacts, inviting the tenders and for execution of work.
A) Approximate Estimate: -
1) Preliminary / approximate / Rough estimate:
- It is an approximate estimate to find out an approximate cost in short time of proposed project.
- Preliminary estimate is often based on practical experience and information from past projects and their rates.
- If in case of commercial projects works like irrigation, residential building, power project work that earn revenue the probable income also mentioned and investment in project work is also justify.
- If project is non – commercial have the no direct return, it’s utility, prospectus in future and availability of final are considered before final decision is taken, this is done in approximate estimate.
- This estimate is prepared for administration approval.
- It is quick and hence approximate estimate is useful for checking.
- Approximate estimate help to decide planning of proposed project.
2) Plinth area estimate: -
- Plinth area estimate is calculated by finding plinth area of building and multiplying plinth area rate in that particular area.
- Plinth area of proposed building is calculated for covered i.e., roofed portion by measuring outer dimensions at plinth level.
- Plinth area must not include the area of courtyard, open passage.
- This is method is simple and usually adopted in practice.
- This is less accurate method.
- Approximate cost = plinth area of proposed building x rate of plinth area in similar location.
- Even if plan of proposed building is not ready the floor areas of different rooms are calculated from users’ requirements and about 35℅ of it is added for thickness of wall circulation and waste to obtain approximate total plinth area.
3) Cubic content method:
- In this method the volume or cubic content of proposed building is worked out and multiply by the rate per cubic volume.
- To calculate cubic content of building the length, breadth, are measured as external dimensions at floor level and height of building is measured from floor level to top of flat slab.
- As per IS 3861 the foundation and plinth and parapet above roof are not taken into consideration in calculate cubic content.
- This method is more accurate as compare to plinth area method.
4) Approximate quantity method:
- In this method structure is divided into:
Foundation including plinth.
The superstructure.
- The cost per running meter of foundation including plinth is worked out and is multiple by total length of foundation to find total cost of foundation including plinth.
- Also, cost per running meter of superstructure is found out and is multiple by total length of wall of superstructure to get total cost of superstructure.
- Addition of total cost of foundation inclusive plinth and the superstructure gives total cost of structure.
B) Detailed estimation:
1) Detailed estimate / item rate estimate:
- This is the accurate method of estimating.
- It is subdivided into individual item of work and quantities of each item of work are calculate from complete set of drawings.
- And abstract of the estimate cost is prepared by multiplying the quantities of each of the above items by rate of completion of that item.
- The rates of various items of work can be gained from the ‘schedule of rate' prepared by government organization.
- To make provision for unforeseen expenditure for miscellaneous petty items and contingencies 3 to 5℅ of estimated cost is added to it.
- An additional 1 to 2℅ is also provide for work charged establishment.
- The grand total of all above cost is called as total estimated cast of proposed work.
- Detailed estimate is generally prepared in two steps:
1) Taking out dimensions and squaring them i.e., dimensions of various items of work are taken from related drawing and are multiplication to obtain its quantities and is entered in measurement sheet form.
2) Abstracting i.e., Quantities of various items of work calculated as above are multiplied by rates of these items obtained either from schedule of rate or worked out by rate analysis are entered in abstract sheet form. If rate and amount column in abstract sheet form are left blank then it is termed as ‘Bill of quantity’.
- Following documents are required to complete detailed estimate:
- A) A comprehensive report of proposed work.
- B) General specifications of work.
- C) Detailed specifications of work i.e., Various items used in the work.
- D) Detailed working drawings.
- E) Calculations and design components parts of work.
- F) Analysis of rates for item of work not included in schedule of rate
2) Revised estimate: -
It is required to prepared under following conditions: -
- When original sanctioned estimate is exceeded by more than 5℅.
- When expenditure on a work exceeds or likely to exceed the amount of administration sanction by more than 10℅.
- When there is material deviation from original proposal.
- When the market rates of materials change.
3) Supplementary estimate: -
- It is also detailed estimate which is prepared when additional work is required to supplement the original proposed work.
- The abstract must indicate original amount of estimate and total amount including supplementary amount for which fresh sanction is to be obtained.
- Maintenance estimate can also be covered in supplementary estimate.
4) Supplementary and revised estimate:
- This estimate is prepared when particular work is abandoned and cost of the work remaining is less than 95℅ of original sanctioned amount of the work.
5) Annual repair / annual maintenance estimate:
- Its detailed estimate prepared to keep the building or roads in proper working and safe conditions.
- In case of building this includes items such as white washing painting of doors, windows, inside and outside plastering and minor repairs, etc.
- The amount of such estimate should be within 1.5 to 2℅ of original cost of building.
Q8) A bungalow was constructed at a cost of Rs. 25,00, 000.The plinth area of that bungalow of 1600sQft.If a new bungalow with the area is 2500 sq. Ft. Is to be constructed. Calculate the cost of project.
A8)
For completed project,
Cost of project = plinth area x plinth area rates
25,00,000 = 1600 x plinth area rate
Plinth area rate = 25,00,000 / 1600
= Rs. 1562.5/-
For proposed project,
Cost of project = 2500 x 1562.5
Cost of proposed project = Rs. 39,06,620/-
Q9) A hospital building of 170 beds is construction in pune in the cost of construction of Rs. 30 lacs. Find the approximate estimate of a small hospital of 40 beds in some localities by using service unit method.
A9)
Rate per service unit = cost of building / no. Of bed
= 30,00,000 / 170
= Rs. 17647.05 per bed.
Approximate cost of newly proposed hospital of 40 beds,
= no. Of beds x rate per bed
= 40 x 17647.05
Total cost of hospital = Rs. 705882/-
Q10) A bungalow was constructed at a plinth area rate of Rs. 1100/ sq. m. Calculate the total cost of project based on followed data,
a. Cost for water supply – 5℅
b. Cost for electrification – 5℅
c. Cost for sanitation – 6℅
d. Contingencies – 5℅
e. Area of plot – 120 sq. m
f. FSI -0. 8
A10)
Floor space Index = plinth area / area of plot
0.8 = plinth area / 120
Plinth area = 96 sq, m
Cost of construction = plinth area x plinth area rates
= 96 x 1100
= Rs. 1,05,600/-
Cost for water supply = 5℅ of cost of construction
= (5/100) x 1,05,600
= Rs. 5,280/-
Cost for electrification = 5℅ of cost of construction
= (5/100) x 1,05,600
= Rs. 5,280/-
Cost for sanitation = 6℅ of cost of construction
= (6/100) x 1,05,600
= Rs. 6336/-
Final cost = 1,05,600 + 5,280 + 5,280 + 6336
= Rs. 1,22,496/-
Contingencies = 5℅ of final cost
= (5/100) x 1,22,496
= Rs. 6124.8/-
Total cost of project = 1,22,496 + 6,124.8
= Rs. 1,28,620.8/-
Q11) A proposed construction with a carpet area of 1500 sq. Ft is to be constructed in a certain location with plinth area rate Rs. 300 per sq. Ft. Calculate cost of construction.
A11)
Plinth area = carpet area + circulation area + area occupied by wall and column
Carpet area = 1500 sq. m
Assume: -
1) Plinth area = Z
2) Circulation area = 30℅
3) Area of wall and column = 10℅
Z = 1500 + 0.3 Z + 0.1 Z
Z = 1500 + 0.4Z
0.6 Z = 1500
Z = 2500/-
Cost of construction = plinth area x plinth area rate
= 2500 x 300
= Rs. 750,000/-
Q12) Explain PWD schedule of rate?
A12)
To facilitate the preparation of estimates and also to serve as guides in setting rates in connection with contract agreement a schedule of rate for each kind of work is commonly executed.
This is prepared on the basis of rates prevailing in each locality including cost of transport and profit.
All rates should be inclusive of labor, materials and unless specifically mentioned otherwise should include all charges like octopi, toll, ferry charges, local charges, income tax, sales tax, as may have to be incurred by contractor for getting respective items of works executed to proper order and complete and finish.
In schedule of rates necessary analysis of rates for varying condition should be provide.