Unit-1
Introduction to soil exploration
Q1) What is soil exploration and investigation? Explain the purpose of sam.
A1)
Q2) Factor affecting the cost of soil investigation?
A2)
Erratic deposits would like a lot of exploration price than homogenous deposits.
2. Undisturbed sampling:
Need serious expenditure
3. Depth of explorations:
The cost will increase with increases in comprehensive exploration.
4. Nature of project:
For stuff dam, the development cost is low however has a high total cost of exploration, and holding walls have a high cost of construction and low exploration cost. vary is around zero. 1 to 2% of calculable cost betting on importance of project and rate of subsoil.
Q3) Explain the steps in soil exploration?
A3)
The bottom investigation, regardless of the magnitude of the project, consists of 4 phases
Four phases of ground Investigation
1. Available information
2. Reconnaissance
3. Preliminary inventory
4. Detailed investigation
1. Available information
This is the first innovative collection of published Tropical and topographical information of the world hydrological data, details of existing or luster development, local regulations for construction activity S, are made.
2. This within the phone during which the first examination of the world is made by the engineer together with other specialized, such the geologist, land surveyor, geotechnical engineer, etc.
At this stage, a radical study of the present structures for the sort of construction and defects such a hi and settlement, soil profiles in highway or railroad cuts and quarries, version in existing cuts, high watermarks on bridge abutments, outcrop, history cal food and scour levels from the local people are collected.
3. Preliminary investigation
This is a vital phase of the complete program during this stage the engineering plant the investigation program. The primary step towards a ground investigation could be a thorough understanding of the geology of the location, which cables an efficient understanding of the investigation program.
The second step is to get additional details of the under soil strata (e. g. thickness of individual strata) from one or 2 explorative drill holes. All alternative more steps rely upon the magnitude of the work and therefore the character of the soil profile.
During this stage, the attainable location of the bottom water is additionally found. For tiny jobs, the skinny preliminary investigation itself is also sufficient. It is typical to apply to limit the number of quality samples recovered except the one obtained from penetration tests.
The strength and settlement are calculable from standard correlations mistreatment index properties and supplemented by the results from samples obtained from penetration tests. Further, will be} the stage that much decide the flexibleness of the project.
4. Detailed investigation
Additional borings and deep borings are planned from the information obtained from the preliminary borings and deep borings. If the under soil is uniform in stratification, an orderly spacing is also planned.
Many times extra borings are created to find weak soil or rock zones, outcrops and so on which can influence the planning and construction of the project. Drilling is needed to bore a hole into exhausting strata boulders. It can be done by percussion or rotary methodology of drilling.
Necessary unchanged tests ought to also be having sufficient samples ought to be procured to get relevant parameters for design and construction. Such extra samples should be recorded to redefine the planning or construction procedure.
Q4) Explain the Methods of obtaining a soil sample.
A4)
1 trial pits
2 Auger boring
3 wash boring
4. Rotary drilling, core drilling
5. Percussion drilling
1. Trial pits and trenches
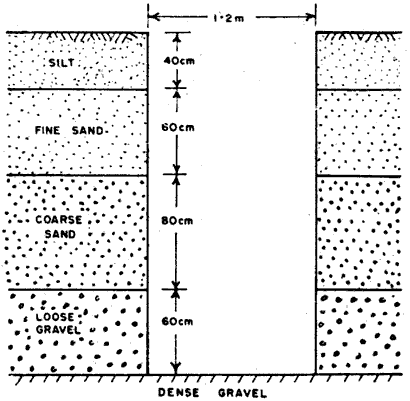
Fig no 1
TRENCHES
This square measure the same as check pits. They supply a protracted continuous exposure of the surface of the bottom on a desired line or section. They are best suited to exploration on slopes. Necessary safety precautions need to be taken as in deep check pits.
2. Auger boring
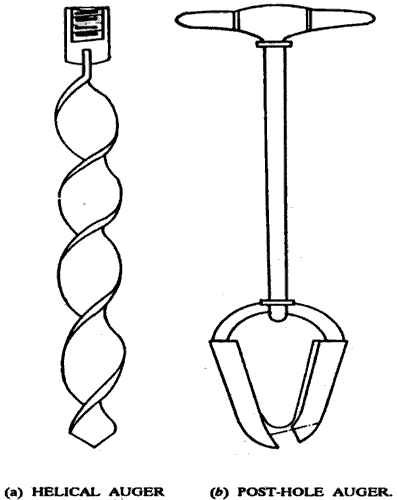
Fig no 2
3. Wash boring
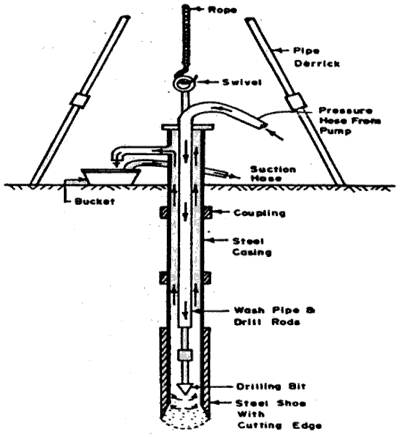
Fig no 3
Advantages
1. Instrument used is relatively light-weight in weight.
2. Cheap technique
3. Quick and easy technique.
Disadvantages
1. it's slow in stiff and coarse-grained soils.
2. Can't be employed in rocky strata.
3. Sensible quality undisturbed samples can't be obtained
4. Not appropriate in areas wherever the H2O table is incredibly near to the ground
4. Rotary drilling:
Q5) Explain open drive sampler and soil piston sample.
A5)
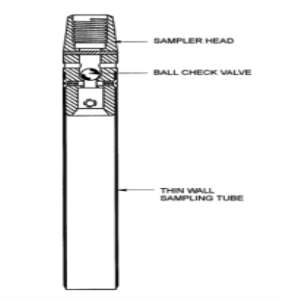
Fig no 6
2. Stationary piston sampler :
Here we have a thin-walled tube fitted with a piston the piston is connected to a rod passing through the sampler head and run inside a hollow boring rod.
Q6) Explain split spoon sampler and rotary sampler.
A6)
Split spoon sampler:
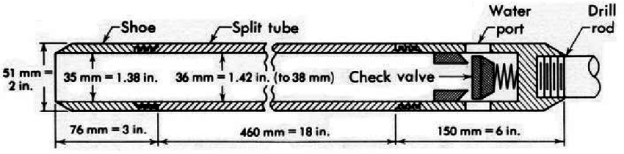
Fig no 8
Rotary sampler:
![Quiz] Rotary Drilling - OILMAN Magazine](https://glossaread-contain.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/epub/1642793418_4455802.png)
Fig no 9
Q7) Explain disturb and undisturbed and block sampler.
A7)
Disturbed and undisturbed sampling
This disturbance could also be within the sort of amendment in water content, soil structure, stress condition, density, or grain size distribution such sample is known as disturbed samples which may be used for determination of properties like grain size water content, relative density, density index, consistency limits.
Block or Chunk Sample
Q8) Explain the depth of exploration and extend of exploration?
A8)
Depth of Exploration
Extend of exploration
Q9) Information Explain the factor affecting disturbance of soil sample. Give on in-situ test and spt test.
A9)
FACTOR AFFECTING DISTURBANCE TO SOIL SAMPLE
1. Area ratio
2. Inside and outside clearance
3. Cutting edge angle
4. The effect of area ratio on sampling tube
5. Sampling speed
6. The material used for sampling tube
7. Roundness
8. Recovery ratio (Fr)
9. ROD, Rock Quality Designation
IN SITU TESTS
In situ tests area unit tests conducted on or within the soil at the positioning. the foremostcommonlyutilized in situ checks area unit the quality penetration test (S P T) the sphere vane tests, the cone penetration check (CPT), the pressure meter check, and also the dilatometer check (DMT).
The vane shear check (V S T) is employed in saturated fine-grained soils to get the un drain shear strength. The borehole shear check (BST) consists of drilling a borehole, removing the drilling tool, and inserting the borehole shear tester right down to the testing depth.
The plate load check (PLT) is one in all the only and oldest in-place tests. The American state bearing magnitude relation check (CBR) may be a style of plate check performed within the field or the laboratory. The in-place checks most ordinarily used offshore area unit the cone penetrates meter test and also the V S T
STANDARD PENETRATION TESTS (SPT)
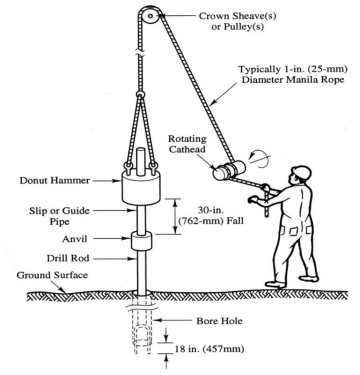
Fig no 10
The take a look at is halted If
(a) 50 blows area unit needed for any a hundred and fifty metric linear unit penetration
(b) one hundred blows area unit needed for three hundred penetration.
(c) 10 sequent blows turn out no advance and are termed as a refusal.
The following precautions ought to be taken whereas closing the take a look at
(a) The split spoon sampler should be in condition and the cutting shoe should be free from wear tear.
(b) The drop press should be of the correct weight and the fall ought to be free resistance.
(c)Very cheap of the borehole should be properly clean before the take a look at is administrated. Otherwise, the take a look at gets administrated within the loose, disturbed soil and not within the undisturbed soil.
(d) Once a casing is employed in the borehole, it ought to be ensured that the casing is driven simply by wanting level at that the S P T is to be administrated. Otherwise, the take a look at gets administrated in a very soil of very cheap of the casing
Q10) Explain cone penetration and dynamic cone penetration test.
A10)
CONE PENETRATION TEST
1. At the start the cone and therefore the friction jacket assembly is during a stationary position
2. The cone is then pushed into the soil at the speed of a pair of20 mm /s by the inner sounding rod at a gradual rate until a collar engages the cone. The forceQc offered by soil for penetration measured on the gauge, and tip resistance purpose resistance. Qt is calculated by q c =Q c /Ac
Where Ac is the base area
3. The sounding rod is pushed more pushing the friction jacket and therefore the cone assembly along. The entire force alphabetic character, needed for this is often once more pressure gauge.
Qt = Qc + Q f, where Q f = force needed to push friction jacket
From this skin friction, fs is calculated
Fs =Q f/A f
Where A f is that the extent of friction jacket.
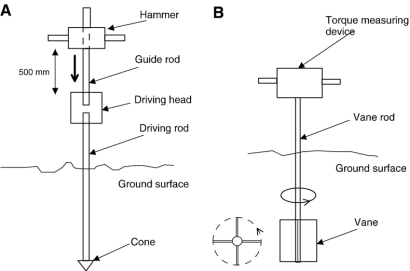
Fig no 11
DYNAMIC CONE PENETRATION TEST (DCPT)
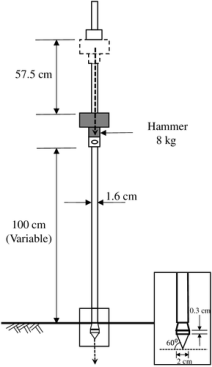
Fig no 12
1. 5 N for 3m depth
1. 75N for 3 to 6m depth
2. 0N for greater than 6 m depth