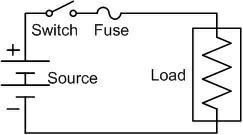
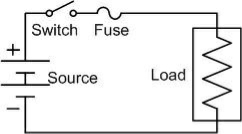
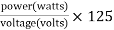The working principle of the fuse is “ heating consequence of the current”. It is fabricated with a lean strip for thread of metallic wire. The connection of the fuse in an electrical circuit is always in series. When the too much current is produced due to the heavy flow of current in the electrical circuit the fuse get soft and it opens the circuit. The extreme flow of current main direct to the collapse of the wires and prevents the supply. Diffuse can be changed by the new fuse with an appropriate rating. It can be designed with elements like copper, zinc, aluminium and silver. They also perform like a circuit breaker for breaking the circuit while the abrupt fault happens in the circuit. This works like a safety measure for protector for humans from risk. Like this, the fuse works Fuse rating = The selection of a fuse can be done by calculating the fuse rating by using the above formula
|
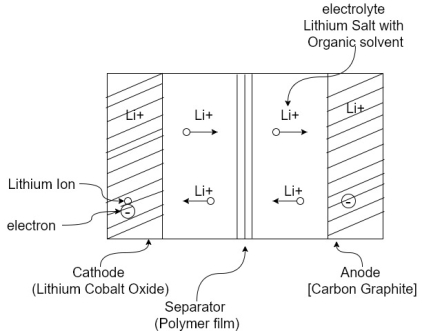
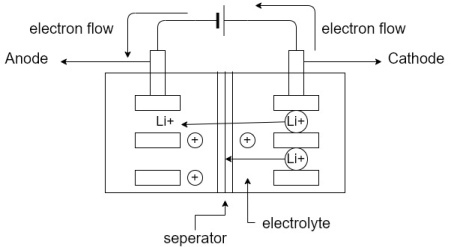
 A2)
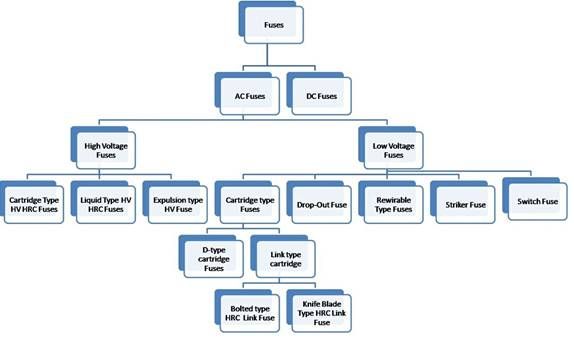
A2) The fuses are classified into to several types based on the application namely AC type fuse and DC type fuse. Again these fuses are classified into several types. The following diagram illustrates the electrical fuse types chart based on the AC fuse and DC fuse.
DC fuse: DC fuses are available superior in size and DC supply has a stable value over 0 volts. So it is tough to remove and deactivate the circuit. There will be a chance of generation of electrical Arc between dissolved wires. To conquer this electrodes located at battery distances. For this reason the size of the DC fuse gets amplified.
AC fuses: The AC fuse is lighter in size and oscillated 50 to 60 times in each and every second from least to highest. As a result, there is no scope for Arc generation between the dissolved wires. For this reason, they can be crammed into a small size. Further, AC fuses are classified into two parts namely HV fuses and LV fuses. Here LV and HV indicates the low voltage and high voltage LV fuses. The low voltage fuses are divided into five types such as rewirable, cartridge, dropout, striker and switch fuses.
Rewirable fuses:
Rewirable fuses are LV fuses, which are almost used in small applications like wiring in in the house, small scale industries, and other tiny current applications. these types of fuses include two essential parts such as a fuse base which has two terminals like in and out. In general, this element is fabricated with porcelain. Another part of this fuse is a fuse carrier, which grip the fuse element. This element is fabricated with aluminium, tinned copper and lead. The main advantage of a fuse carrier is, we can simply plug and remove from the base of the fuse without the risk of shock. As the fuse is damaged due to heavy current, then we can simply eliminate the fuse carrier as well as put back the fuse wire.
Cartridge type fuses:
The cartridge type of fuses has entirely closed containers and the metal contact as well. The applications of this fuses mainly include low voltage (LV), high voltage (HV) and small fuses. again this types of fuses are classified into two types, they are D type and link type fuses.
D type Cartridge Fuse
This type of fuse is composed with the cartridge, base of the fuse, adapt or ring, and cap. The base of the fuse includes a fuse cap, which is packed with the fuse ingredient by cartridge using an adapter ring. It is composed of the cartridge, fuse base, cap and adaptor ring. The fuse base has the fuse cap, which is fitted with the fuse element with a cartridge through the adaptor ring. The connection of the circuit is finished when the tilt of the cartridge builts contact through the conductor.
High Rupturing capacity or Link Type Fuse:
The link type fuse is also known as high rupturing capacity (HRC) or BS type fuse. In this sort of fuse, the current flow with fuse element is specified under standard condition in this BS type fuse, the flow of current by fuse element is given under normal condition. The arc which is generated by the fuse blown is controlled is fabricated with porcelain, ceramic and silver. the container of the fuse element is packed with silica sand. This type of use is again characterized into two parts includes a blade type and bolted type.
Blade and bolted type fuses
The knife type fuse for plugin type of fuses are designed with plastic. this type of use can be simply changeable in the electric current exclusive of any load in bolted type fuse, plates of this fuse are conducting are set to the base of the fuse.
Striker type fuse
Describe the type of fuse is employed for tripping and closing the electrical circuit. This fuses are having plenty of force as well as displacement.
Switch type fuse
Basically the switch type fuse is enclosed with a metal switch and also a fuse. These fuses are mainly used in low and intermediate voltage levels.
HV (High voltage) Fuses
Generally, HV fuses are used to protect the transformers like instrument transformers, small Power transformer and also used in power systems. These fuses are normally charged for voltages over 1500 volt to 138000 volte. The fuse part in HV fuses are fabricated with either copper, silver or in some cases tin is used, in order to offer consistent and steady performance. These fuses are classified into three types which include the following.
Cartridge type HRC fuse
The fuse component of the HRC is cut in The helix form which evades the effect of the corona at the upper voltages. It includes to fuse elements namely low resistance and high resistance, and that are located parallel by each other. The low resistance wires take the usual current which is is blown out as well as decreases the short circuit current throughout the fault state.
Liquid type HRC fuse This type of fuse is packed with carbon tetrachloride also preserved at both the tops of the caps. Once the error occurs when the following current surpasses away from the allowable limit and the element of the fuse is blown out. the flute of the fuse performs as an Arc extinguishing standard for the HRC fuse types. they may be used to protect the transformer as well as the support protection to the breaker circuit.
Expulsion type HV fuse
These types of fuses are extensively used to protect the feeders as well as transformer due to they're low priced. It is designed for 11kV, also their cracking capability is up to 250 MVA. This type of use includes and unfilled open finished cylinder designed with synthetic resin bonded paper. The elements of the fuse are positioned in the cylinder, and the tops of the tubes are linked to appropriate equipment at every finish. The ark generating is blown off in the inside covering of the cylinder, and gases thus shaved destroys the arc. |
|
There are three standard characteristics are available for domestic as well as commercial MCB are given by B,C and D. Each type has its own function Type B
MCB are mainly used where switching surges are small or non exist and are generally suitable for domestic applications and light commercial applications. There are no devices with long high starting current in domestic applications and has the best suited MCB is type B. these are designed to trip at fault currents in the range of 3 to 5 times the rated current. Suppose if the rated current is 10 ampere then the MCB trips at 30-50 A. Type C
MCB are designed for high inductive circuits where surge currents are expected. These are generally used for commercial and industrial applications where a number of fluorescent lamps been turned ON or starting of small motors may give high search currents. These are more sensitive than type B MCB and causes reduced nuisance trips. Type C MCB are designed to operate for trip at the fault currents of 5 to 10 times that of rated current. For 10 A type C MCB, the operating current range is 50 – 100 A. Type D
MCBs are designed for heavy industrial applications where normal surge currents are very high. These are ideal for electrical welders and site Transformers where frequent high surge currents are expected. The most common applications of type D MCBs include motors, UPS systems comma x-ray machines, Transformers and battery charging systems. These are designed to trip at 10 – 20 times The rated current. For 10 A type D MCBs, the operating current range is 100 – 200 A. The setting or characteristics of an MCP are fixed in the factory itself by the manufacturer and they are not adjustable at the user end or at the site. Tripping currents for operation at 0.1 second or less different MCBs are given below.
|
|
|
Types of MCCB | Operating current | Operating time | Application | Suitability | Surge current | Installation location |
Type B | Trips between 3 and 5 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 13 seconds | Domestic applications (lighting and resistive elements) | Resistive load application | Low | Sub feeder of distribution board |
Type C | Trips between 5 and 10 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 5 seconds | Commercial or industrial applications | Inductive load applications | Moderate | At incoming/outgoing of distribution board |
Type D | Trips between 10 to 20 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 3 seconds | Commercial or industrial applications | Inductive capacitive load applications (pumps, motor, large winding motors e.t.c.) | High | At incoming of distribution board/panels |
Type K | Trips between 8 to 12 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 5 seconds | Industrial applications | Inductive and motor loads with high in rush currents | High | At incoming of distribution board/panels |
Type Z | Trips between 2 to 3 times rated current (In) | 0.04 – 5 seconds | Highly sensitive to short circuit and are used for protection of highly sensitive devices such as semiconductor or devices | Medical instruments | Very low | At sub feeder of of distribution board for IT equipment |
|
|
Primary | Secondary |
Electrical energy indirectly obtained from chemical energy. | Electrical energy is already present in the cell in form of chemical energy and then converted to electrical energy. |
Chemical reactions are irreversible (cannot be recharged) | Chemical reactions are reversible. |
Cell is replaced when it goes down. | Cell is recharged back. |
Polarisation is present. | Polarization is absent. |
Low efficiency. | High efficiency. |
Capacity is low. | Capacity is high |
Less cost | High initial cost. |
No maintenance is required. | Frequent charging and other maintenance is required. |
|
|