Unit-5
GSM system for mobile Telecommunication
Q1) What is GPRS?
Sol:
- General Packet Radio System (GPRS) is a packet-based data services for wireless communication.
- A packet radio principle is used to transfer subscriber data packet within GSM mobile station and external packet data network.
- Data is split and transmitted at sender node and reassembled at receiving end. GPRS support IP and X.25, these operate over cellular connection of a GSM.
- According to peter Rysavy, Rysavy Research 1998 GPRS network is as follows:
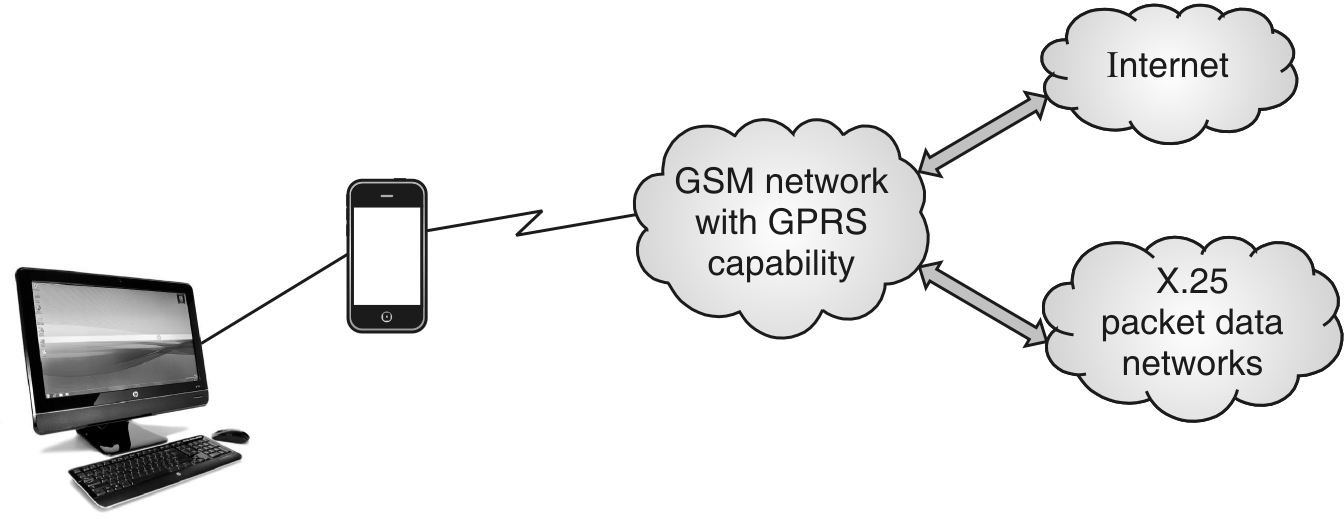
Fig.: GPRS network (1)
- GPRS system has a base of GSM communication and somewhat of circuit switched phone connection, Short Message Service (SMS).
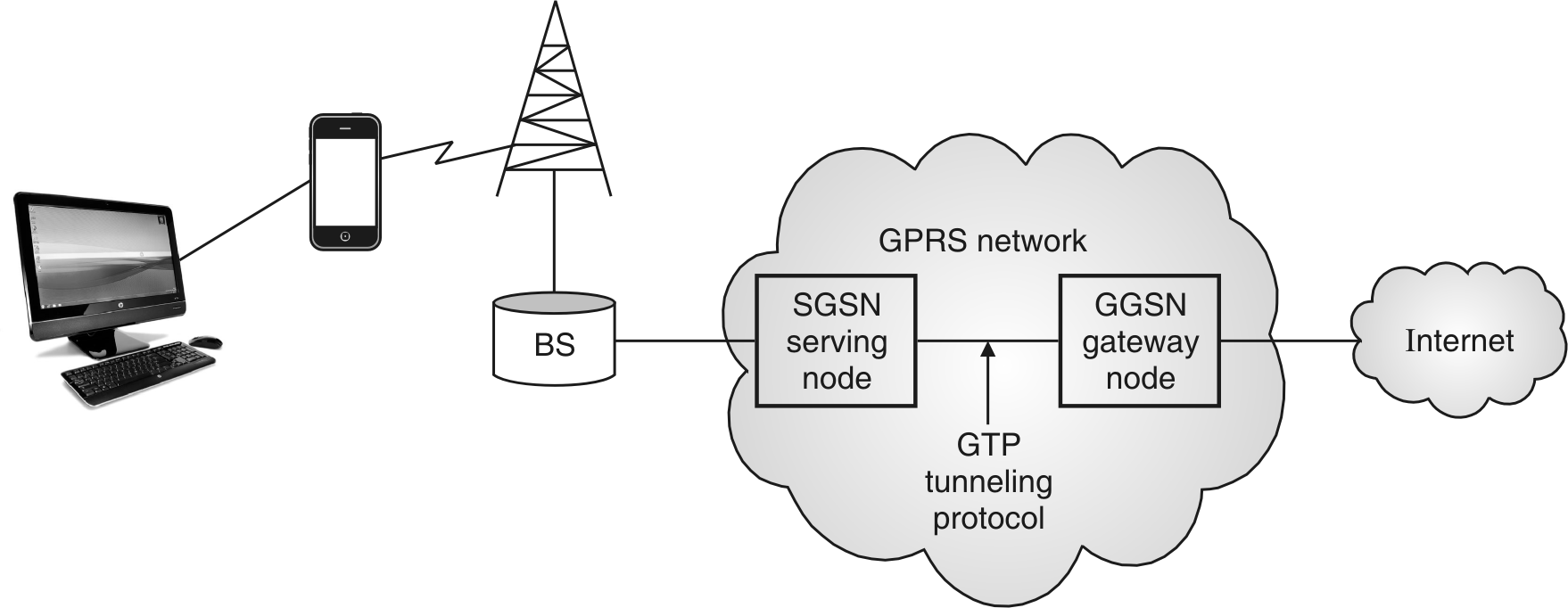
Fig.: GPRS Network (2) (by Peter Rysavy)
Working of GPRS
- SGSN:
It manages to send and receive of packet data to and from MS. It is useful for keeping track of mobile devices within scope of service area. It works in mobility management subscribed user verification and provides data required for billing.
- GGSN:
It has vital role of routing information whichever is necessary for tunneling Protocol Data Unit (PDUs). To SGSN to Serve Distinct MS. It is on interface for external PDNs. i.e. public data units like internet and X.25.
Charging gateway
- It maintains log entries for activities like data being transfer, change in charging terms in peak/off to peak and vice-versa, end of session for GPRS etc.
- It has collection records related to GPRS, usage in buffering of data, storage, transfer of data.
GTP
GPRS tunneling protocol uses to encapsulate IP or X.25 packet which are transferred among SGSN and GGSN.
Q2) Explain about the developments and edge technology?
Sol: Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution (EDGE) introduces a new modulation technique, as well as protocol enhancements for transmitting packets over the radio.
The use of the new modulation and the protocol enhancements, result in dramatically increased throughput and capacity gains enabling 3G services in the existing GSM/GPRS networks. No changes are needed to the existing core network infrastructure to support EDGE. This emphasizes the fact that EDGE is only an “add-on” for BSS.
For EDGE, nine Modulation and Coding Schemes (MCS) are introduced (MCS1 to MCS9) and optimized for different radio environment. Four EDGE coding schemes are using GMSK and five are using 8 PSK Modulation.
Up gradation to EDGE
- Mobile Station (MS) − MS should be EDGE enabled.
- BTS − HW supplied is Edge enabled.
- BSC − Definitions for EDGE timeslots need to be done in BSC.
- GPRS Support Nodes (GSNs) − Definitions for Edge need to be defined in GSNs.
- Databases (HLR, VLR, etc.) − No definition is required.
Benefits of EDGE
- Short-term benefits − Capacity and performance,
- Easy implementation on a GSM/GPRS network,
- Cost effective,
- Increases the capacity and triples the data rate of GPRS,
- Enables new multimedia services,
- Long-term benefit − Harmonization with WCDMA.
What EDGE Would Mean to Subscribers
- Streaming applications
- Very high-speed downloads
- Corporate intranet connections
- Quicker MMS
- Video phone
- Vertical corporate applications - Video conference, Remote presentations.
Q3) With the help of block diagram explain WLL?
Sol: It is the circuit line from subscriber phone to the local central office. As this scheme is cost expensive if the users are less as we may have in rural and remote areas. The expenditure to this line system is more hence the wireless local loop system came into existence. The wireless system uses wireless links to connect the wireless local loop to the local central office.
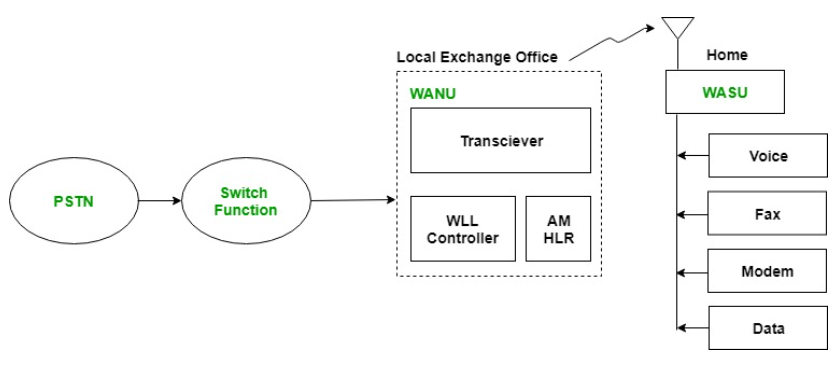
Fig WLL Architecture
Components of WLL are
i) PSTN: It is Public Switched Telephone Network. It has all the circuit switched telephone network.
Ii) Switch Function: It switches PSTN among various WANU.
Iii) WANU: It is called as wireless access network unit present at local exchange office connecting all local WASU. It consists of WLL controller, HLR and access manager.
Iv) WASU: It is called as wireless access subscriber units. The subscriber is provided with this at his place.
Q4) How mobile satellite communication is established?
Sol: The communication between the satellite and the earth is established using radio station on earth. The other way to make this possible through artificial satellites. The mobile satellite communication can be classified
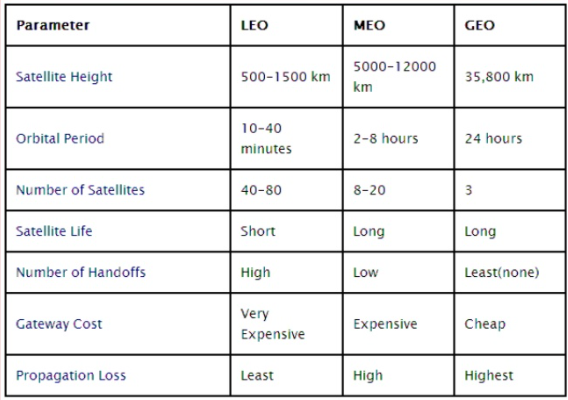
- Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO): As the GEO has high range so only three GEO satellites can cover the complete earth. There is no need for antenna adjustments and they have high life time.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): They require highest number of satellites.
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO): There is low transmission power of the antennas and are used for smaller foot prints.
- Highly Elliptical Orbit (HEO): It has the lowest altitude.
Q5) What are mobile ad hock networks?
Sol: These are wireless ad hoc networks having many mobile devices which form a network. They form the network independently. There is wireless connection between all the mobile nodes. These nodes can move as there are changes in the network topology.
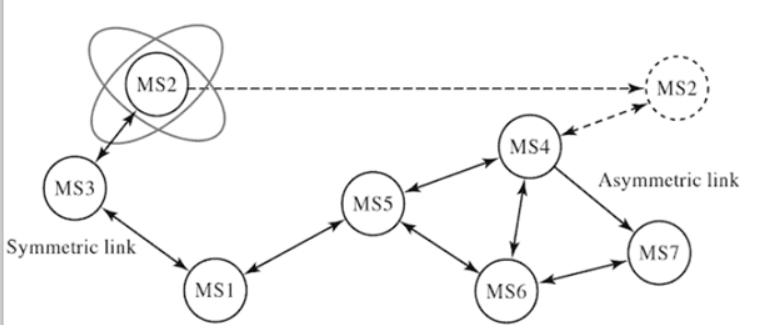
Fig Mobile ad hoc network
The node MS2 changes its connectivity from MS3 to MS4. In this case the other networks have to change the path /topology for transferring data to MS2. IN these types of architecture, the nodes are free to move. The MS connected in the network uses batteries as the source of energy.
Q6) Compare GEO, LEO and MEO?
Sol:
Q7) How Li-Fi networks are more advanced than Wi-Fi explain?
Sol: It is a high-speed wireless communication which uses LEDs. It is similar to the Wi-Fi but Li-Fi allows bidirectional transmission of light. These systems make use of visible light spectrum. The system requires photodiodes and light source as it uses light as a medium for data transmission. They emit light according to the amount of current flowing through them. The LED bulbs having data passes it to the photodiodes at very high speed. The light is received by photodiode and then it is demodulated.
Q8) What are the types of mobile data networks?
Sol: These networks are classified in three categories such as
i) Independent Mobile Data: As the name suggests they are independent networks having their own infrastructure and spectrum services. On the basis of operating frequency band, they can be categorised as independent spectrum and second group of independent mobile data networks.
Ii) Shared Mobile Data: The network here shares the part of its infrastructure with the network which is already existing. This service can use the unused voice channel. This scheme shares the infrastructure which already exists. There is no independent air interface present.
Iii) Overlay Mobile Data: The data service will not only make use of the spectrum allotted for another service but also the MAC frames and air interface of an existing voice oriented digital cellular system GPRS and GSM’s
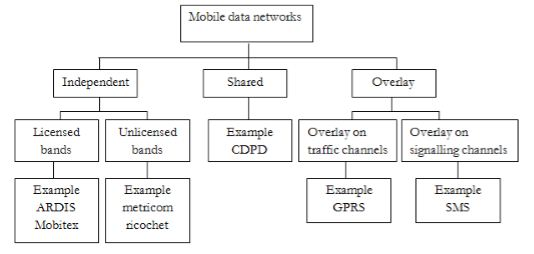
Fig 4 Mobile data network structure
Q9) What is 4G evolution explain?
Sol:
- 4G takes on a number of equally true definitions, depending on whom you are talking to. In simplest terms, 4G is the next generation of wireless networks that will replace 3G networks sometimes in future.
- In another context, 4G is simply an initiative by academic R&D labs to move beyond the limitations and problems of 3G which is having trouble getting deployed
And meeting its promised performance and throughput.
- In reality, as of first half of 2002, 4G is a conceptual framework for or a discussion point to address future needs of a universal high speed wireless network that will interface with wire line backbone network seamlessly.
- 4G is also represents the hope and ideas of a group of researchers in Motorola, Qualcomm, Nokia, Ericsson, Sun, HP, DoCoMo and other infrastructure vendors who must respond to the needs of MMS, multimedia and video applications if 3G never materializes in its full glory.
Need of 4G:
- Firstly, 3G’s maximum data transfer rate of 384 kbps to 2 mbps is much slower than 20mbps to 100mbps of 4G.
- With its use of existing technologies & communication standards, 4G present a comparably inexpensive standard.
- 4G will utilize most of the existing wireless communication infrastructure
Specification:
- 4G can provide 10 times increase in data transfer over 3G.
- This speed can be achieved through OFDM.
- OFDM can not only transfer data at speed of more than 100mbps, but it can also eliminate interference that impairs high speed signals.
Applications:
- 4G will provide for a vast no. Of presently nonexistent application for mobile devices.
- 4G device will differ from present day mobile device in that there will be navigation menus.
- 4G will provide a seamless network for users who travel & required uninterrupted voice/data communication.
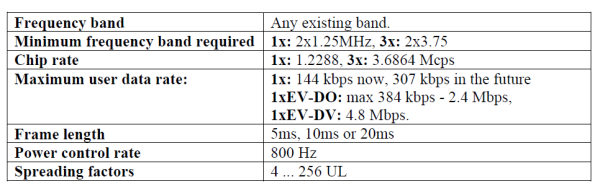
Q10) what is CDMA 2000?
Sol: Cdma2000 specification was developed by the Third Generation Partnership Project 2
(3GPP2), a partnership consisting of five telecommunications standards bodies: ARIB
And TTC in Japan, CWTS in China, TTA in Korea and TIA in North America.
The evolution of cdma2000 1x is labeled cdma2000 1xEV. 1xEV will be implemented in
Steps: 1xEV-DO and 1xEV-DV. 1xEV-DO stands for "1x Evolution Data Only". 1xEVDV
Stands for "1x Evolution Data and Voice". Both 1xEV cdma2000 evolution steps will
Use a standard 1.25 MHz carrier.
Technical Summary for CDMA2000