Unit 1
Introduction
Q1) Define Non- Destructive Testing.
Answer: Non-destructive testing refers to a method of detecting internal flaws in engineering materials without breaking them.
It can be also be defined as the use of non-invasive technique to determine the integrity of a material component or structure or quantitatively measuring some characteristics of an object.
NDT is aimed at extracting information on the physical, chemical, mechanical or metallurgical state of material or structures without damaging its intended utility value.
It is aimed at extracting information on the physical, chemical, mechanical or metallurgical state of materials or structures without damaging its utility value.
Q2) Explain Scope and Advantages of Non-destructive testing.
Answer: Scope of NDT:
2. Advantages of NDT:
Q3) Difference between NDT and Destructive testing.
Answer:
S.No | NDT | Destructive testing |
1. | The use of non-invasive technique is to determine the integrity of a material or component. | Destructive testing includes measuring various mechanical or chemical properties such as tensile strength or chemical composition. |
2. | NDT mostly deals in modern technologies to identify the specimen. | Destructive testing deals in physical testing. |
3. | After testing, NDT will allow the parts to be used for its intended purpose. | Destructive testing will render the part unusable for its intended purpose. |
4. | NDT can be performed on the component which is in service. | Generally performed when component or material sample can no longer be used in service or is readily replaceable. |
5. | Result interpretation is difficult. | Easy in result interpretation. |
6. | Skilled personnel required | Can be performed by without very skilled personnel. |
7. | Some methods involve environmental hazard and expensive equipments | Non-environmental hazards associated and equipments are less costly. |
Q4) Explain Magnetic Particle Testing and Penetrate testing.
Answer:
This method employs the role of magnetic field which may be produced by any of the magnetizing technique. Then a powdered magnet or liquid magnet called as magnetic ink is spread over the surface to be inspected.
Surface or near surface defects cuts the magnetic flux line, which generates a new magnetic pole, at the defect point. This concentrates the iron particles near imperfection or defect giving a clear visualization of defect.
2. Penetrate testing:
In this method, test specimen is coated with liquid of fluorescent dye solution. Then excess penetrant is removed very carefully and developers are applied.
These developers acts as blotter and draws out the trapped penetrant from defect to open surface. These penetrants are now easily visible because of colour contrast between penetrant and developer with fluorescent dyes. Ultraviolet lights are used which make the bleed out penetrant readily seen.
Q5) What is flaw and defect? Explain along with its classification.
Answer: 1. Flaws:
Any discontinuity in the normal physical composition of part which does not have any major effect on the performance of that part is said to be flaw.
Example: Poles, scratches, cracks etc.
2. Defects:
Any interruptions in the normal physical composition of parts, that is, reject able known as defect.
These interruptions may occur in the base metal, weld materials or HAZ discontinuities, which do not meet the requirements of the codes or specifications used to invoke and control an inspection, are referred to as defects.
Classifications of defects:
A crack is a fissure produced in a metal by tearing action.
2. Surface defects:
These defects are intergranular. These defects are due to improper temperature, friction, corrosion, rust, dirt etc.
3. Blow holes, porosity, slag, flakes, solid inclusion.
4. Pock marks and rough surfaces:
Spatter occurs in arc or gas welding as metal particles which are expelled during welding. These particles do not form part of the actual weld.
5. Buldge formation, wavy edges, zipper cracks etc.
6. Distortions, sub-surfaces cracks
Q6) Define Visual inspection in terms of Non destructive Testing.
Answer: Visual inspection is commonly defined as the examination of material, component or product for conditions of non-conformance using light and eyes, alone or in conjunction with various aids.
Visual inspection often also involves, shaking, listening, feeling, and sometimes even smelling the component being inspected.
It consists of major two processes:
It can be performed by direct or indirect methods during various stages of manufacturing or after the component has been placed in service.
It can be done manually or by the help of digital detectors and computer technology which is known vision inspection.
Q7) What are the major classifications of Visual Inspection?
Answer: Visual inspection is commonly defined as the examination of material, component or product for conditions of non-conformance using light eyes.
There are basically two major classifications of Visual Inspection. They are mentioned below:
b. Automated vision inspection:
It is the technology and method which uses an imaging system and a computer to analyze an image and provide imaging based automatic inspection and analysis for automatic inspection, process control and other industries.
Machine can eliminate the human effort. It also allows process equipment to be utilized twenty four hours in a day. Here given the block diagram of automated vision inspection.
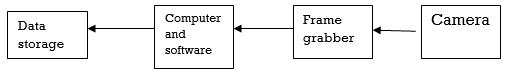
Q8) What is Boroscope? Mention the important equipments used in visual inspection.
Answer: Borescope:
The equipments required for visual inspection are:
Q9) What is ringing or hammer test?
Answer:
The procedure for ringing test is conducted in following manner:
Uses of this test:
Limitations:
In this test method the object is ringed so as to get the sound from the object, with the interpretation of which the soundness of object is judged.
Q10) Explain chalk test or oil whitening testing:
Answer: