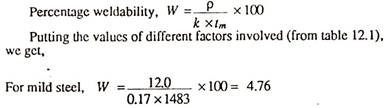Unit IV
Metal Joining (Welding)
Question 1: Determine the relative weldability of mild steel, aluminium, copper, and tungsten for spot welding.
Solution: Referring to equation 12.2, we have,
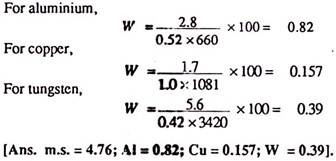
Question 2: Determine the minimum overlap and the size of the electrode tip for spot welding two sheets of mild steel 1.5 mm thick.
Solution: Acceptable spot weld dia, ds = 2.5 +2 mm

Question 3: Determine spot spacing for normal and distortion-free weldments for spot welding two mild steel sheets of 3 mm thickness each.
Solution:
(i) Normal spot spacing =161 = 16 x 3.0 = 48 mm
(ii) Spot spacing for distortion-free welds = 48 t = 48 x 3 = 144 mm
Question 4: Two sheets of low carbon steel 15 mm thick each are to be spot welded by passing a current of 10.000A for 5 hertz in 50 hertz mains supply. The maximum indentation allowed is 10% of the sheet thickness and the density of the spot weld nugget is8gl cm3. If 1380 joule are required to melt one gm of steel, find,
(a) The percent of heat actually utilised in making the spot weld. Take an effective resistance of 200 microhm and use the relationship dn = 6√t to determine the nugget diameter.
(b) The diameter of the cylindrical electrode if the truncated cone angle is 15CP and the tapered length is 30 mm.
Solution:
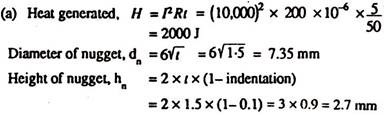
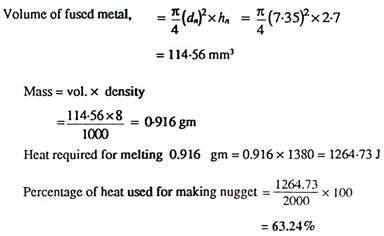
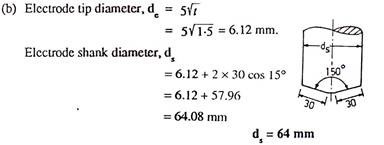
Question 5) what are the Advantages of Adhesive Bonding?
Answer 5) one of the main advantages of adhesive bonding is that it allows for the even distribution of stress loads, thereby reducing the stress on the joint. Since they are applied inside the join, adhesives are also invisible within the assembly. The properties of glues mean that they can form both an adhesive and sealant at the same time, while also resisting vibration and flexing stresses. The ability to act as a seal allows adhesives to help protect a join from corrosion.
While adhesive bonding can be applied to metal-to-metal, plastic, glass, rubber, ceramic and many other material combinations, the process can be used to join irregularly shaped surfaces while offering virtually no change in the dimensions or geometry of the parts. Adhesives also add very little by way of weight to the materials being joined and can be used to quickly bond dissimilar substrates and heat- sensitive materials.
One of the greatest advantages of adhesive bonding is the versatility it affords, allowing for joining of a wide range of items as well as being easy to automate.
Question 6) what are the Disadvantages of Adhesive Bonding?
Answer 6) there are, however, a number of limitations to using adhesives. Firstly, they are prone to failure when exposed to high heat or weathering. Adhesives can also take time to fully fix and acquire full strength. They also often require surface preparation treatments including cleaning the surface of the materials to be joined. Other surface treatments associated with adhesives include abrasion to create a stronger bond. Adhesives can also cause problems related to disassembly when compared to other, less permanent joining techniques.
Question 7) where is Adhesive Bonding Used?
Answer 7) Adhesive bonding is used across many industries including automotive, aerospace, medical and even textiles. Due to the versatility of this process for a range of material types the only real limitations arise with use, such as for outdoor applications that need to withstand weathering.
Question 8) Difference between soldering and brazing
Answer 8)
SR. No. | Brazing | Soldering |
1 | Filler metal has the melting point above 400°c | Filler metal has the melting point below 400°c |
2 | More stable joints can be made | Less stable joints can be made |
3 | High pressure and temperature do not affect the joint | Joints are affected by high temperature and pressure |
4 | Equipment cost is more | Equipment cost is very low. |
Question 9) Advantages of Atomic Hydrogen Welding:
Answer 9)
1) Welding is faster in this welding process.
2) Since hydrogen itself act as shielding gas, separate shielding gas is not required.
3) There is very little distortion of the flame as the intense flame is obtained which can be concentrated at the joints.
4) The electrodes remain cool as the hydrogen gas flow by the electrodes in the holder which also increases the electrodes life.
5) The flow of hydrogen gas and the arc can be easily controlled by the operator and hence the heat produced can also be controlled. So, heat can be adjusted for welding different materials using this welding process.
6) Alloys can be melted without fluxes and without surface oxidation due to the powerful reducing action of the atomic hydrogen.
Question 10) Disadvantages and applications of Atomic Hydrogen Welding?
Answer 10)
1) This process is more costly as compared to other welding processes.
2) A skilled operator is required to operate this welding process.
3) Large quantities of metal cannot be deposited using this welding process.
4) This welding can be done on flat positions only.
5) This welding process is riskier as hydrogen is a highly inflammable gas.
Applications of Atomic Hydrogen Welding:
1) It is mainly used where rapid welding is required like in the case of stainless steel and other special alloys.
2) It can be used for welding most of the ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
3) It is also used for welding thin sheets of metal and small diameter alloys.
4) This process is also used in repairing dies and tools, hard surfacing, and joining parts.
5) It can also be used for very precision welding like correcting machining errors.