Unit-1
Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits
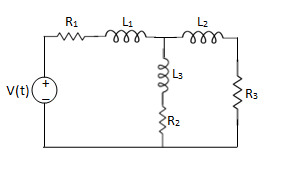
Q1) For the circuits given below write the voltage equations:
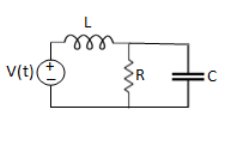
Solution: Let current i1be in loop 1 current and i2 for loop 2
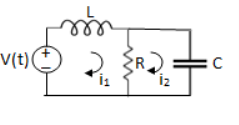
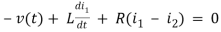
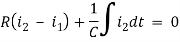
Q2) For the circuits given below write the voltage equations
Solution:
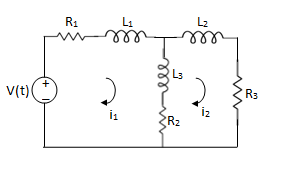
For loop 1
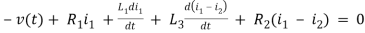
For loop 2

Q3) Use nodal analysis to find current in the circuit?
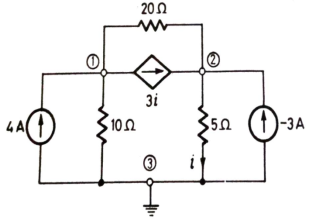
Sol: 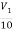 +
+ 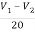 +3i=4
+3i=4
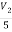 +
+  -3i= -3
-3i= -3
But i= 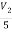
Substituting and solving above equation we get
V2 = 10V
i= 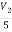 = 2A
= 2A
Q4) Find equivalent resistance R?
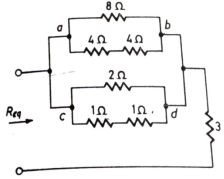
Sol: Equivalent resistance across ab = 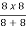 = 4Ω
= 4Ω
Equivalent resistance across cd = 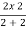 =1Ω
=1Ω
Req = Rab||Rcd +3 =  + 3 = 19/5 Ω
+ 3 = 19/5 Ω
Q5) What is the effect of temperature on the resistance?
- Sol: Resistor: -

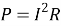
Resistance is affected by temperature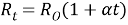
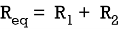


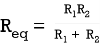
Behavior of Resistance:-


RRR R

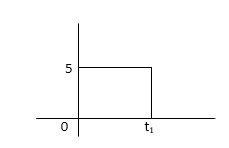
Q6) Derive the time constant for RC circuit?
Sol: The series RC circuit is shown below.

Fig: Series RC circuit
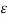 =V
=V
For t>0 applying KVL
Ri(t)+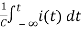 +V=0
+V=0
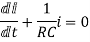
Hence general solution of above equation is calculated same as for RL circuit
i=k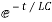
i(0)=- 
Hence, particular solution for network is given as
i=-  for tfor t≥0
for tfor t≥0
=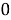 for t<0
for t<0
The time constant is given as 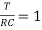
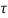 =RC
=RC
Q7) Explain lead-acid battery and Nickle-cadmium battery?
Sol: These are rechargeable batteries. These are also called as storage batteries. They are rechargeable because the electric current reverses the chemical reaction inside the batteries that occurred during use. EX used in mobile phones, MP3 players.
Types of Secondary Cells:
(a) Lead-acid cell: It is most commonly used cell. It has porous lead anode and lead-oxide cathode. Used in automobile inverters. The output is of 2.1V.
(b) Nickel cadmium (NiCd) cell: It has Nickel hydroxide anode and cadmium hydroxide cathode. It delivers high current. It is used in cadmium hydroxide electrolyte. Used in alarm systems, TV equipment.
Q8) With circuit diagram show the source conversion of current to voltage source and vice versa?
- Sol: From VI:
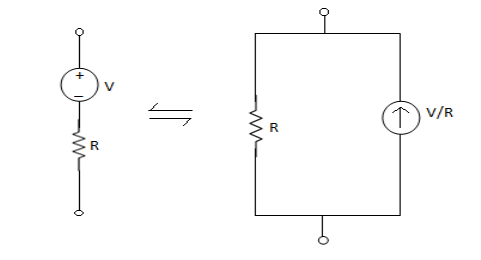
2. From IV:
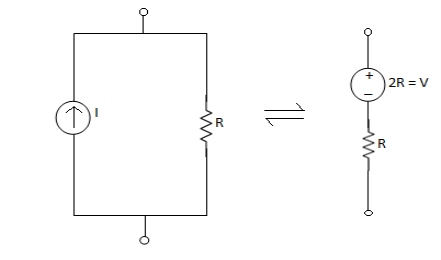
Q9) Take any circuit and write current and voltage division formula?
Sol: VDF - Voltage Division Formula
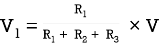
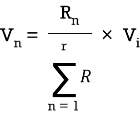
CDF - Current Division Formula
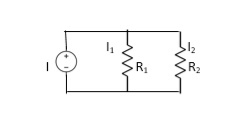
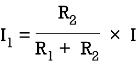
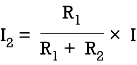
Q10) what are primary batteries. Explain its types?
Sol: These are basically disposable batteries. They can be used only once. They are not rechargeable. EX. AA, AAA.
Types of Primary Batteries:
(a) Carbon- zinc dry cell: These are AA, AAA. They have zinc electrode as negative electrode and carbon as positive electrode. The output voltage of a single cell is about 1.5 V.
(b) Alkaline cell: It is AA type. It lasts long than carbon-zinc cell. It consists of a zinc anode and manganese dioxide cathode in an alkaline electrolyte
(c) Zinc chloride cell: These are heavy duty cells. It is modified zinc-carbon cell.
(d) Mercury cell: It is not used these days. It consists of zinc anode, mercury compound cathode and potassium or sodium hydroxide electrolyte.
(e) Silver oxide cell: This cell consists of a zinc anode, silver oxide cathode, and potassium of sodium hydroxide electrolyte. Normally used in cameras and watches.
(f) Lithium cell: It is light weight. It offers high output voltage. Two forms of 3V output in widespread use: (a) Lithium-sulfurdioxide(LiSO2 ). (b) Lithium- thionyl chloride.