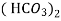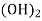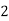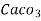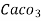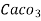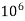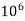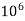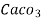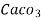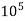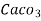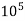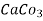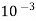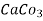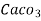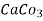Hardness can be defined as the soap consuming capacity of the water sample. soaps are sodium salts of fatty acids like oleic acid, palmitic acid, and stearic acid. they dissolve readily .in water to form lather due to which it has cleansing property.
(calcium stearate)
|
Temporary hardness ( carbonate):-
Mg (Bicarbonates) |
Thus, 1 mg/l = 1 mg of But 1 L OF Water weighs. = 1 kg = 1000 g = 1000*1000 mg = Therefore, 1mg/l = 1 mg of = 1 part of = 1 part of =1 ppm
3. Clarke’s degree is the number of grains (1/7000lb) of Thus,
4. Degree French (°fr) is the part of Thus, 1°fr = 1 part of
5. Milli equivalent per liter (meq / L )is the number of milliequivalents of hardness present per liter. Thus, 1meq/L = 1 meq of = = 50 mg of = 50 mg / l of |
|
Sludge | Scale |
Sludge is a loose, soft, and slimy precipitate | Scale forms hard deposits |
Sludge from non-adherent deposits and can be easily removed | Scale sticks firmly to the inner surface of the boiler and is very difficult to remove. |
Sludge is formed by a substance like CaCl2, MgCl2, MgSO4, etc. | The scale is formed by a substance like CaSO4, Mg(OH)2, etc. |
Sludge is formed at comparatively colder portions of the boiler. | The scale is formed at heated portions of the boiler |
They decrease the efficiency of the boiler but are less dangerous | They decrease the efficiency of the boiler and chances of the explosion are also there. |
They can be removed by blowdown operation | They can’t be removed by blowdown operation. |
|
Figure 01: Cylinder Containing the Zeolite BedProcessIn the water softening process, hard water is passed through a bed of zeolite (inside a cylinder) at a specified rate. Then the cations that cause the water-hardening will remain on the zeolite bed because these cations exchange with the sodium cations of zeolite. Therefore, the water coming out of this cylinder contains sodium cations rather than calcium and magnesium cations.After some time, the zeolite bed gets exhausted, the water flow is stopped, and treat the bed is treated with concentrated brine solution (10%) to regenerate the zeolite. The bed is treated with a brine solution, as it washes away all the calcium and magnesium ions, by exchanging them with sodium ions in a brine solution. hence, this treatment regenerates the zeolite. Q11) Enlist the application of pH meter.A11)