 = 400/
= 400/ = 231VRph= 231/4= 57.75ohm For Delta Connection:IL=4AIph= IL/
= 231VRph= 231/4= 57.75ohm For Delta Connection:IL=4AIph= IL/ =4/
=4/ ==2.30AZph=400/2.30=173.9ohmRph= 173.9/3 = 57.97ohm Q2) Three identical impedances are connected in delta 3-phase supply of 400V. The line current is 30A and total power taken from the supply is 10kW. Calculate the resistance and reactance value of each impedance?A2) VL=Vph=400VIL=30AIph=IL/
==2.30AZph=400/2.30=173.9ohmRph= 173.9/3 = 57.97ohm Q2) Three identical impedances are connected in delta 3-phase supply of 400V. The line current is 30A and total power taken from the supply is 10kW. Calculate the resistance and reactance value of each impedance?A2) VL=Vph=400VIL=30AIph=IL/ = 30/
= 30/ =17.32AZph=Vph/Iph= 400/17.32=23.09ohmP=
=17.32AZph=Vph/Iph= 400/17.32=23.09ohmP= VLIL Cos ØCos Ø = 10000/
VLIL Cos ØCos Ø = 10000/ 400x30 = 0.48Sin Ø =0.88Rph=Zph Cos Ø= 23.09x0.48=11.08ohmXph=Zph Sin Ø = 23.09x0.88=20.32ohm Q3) A star connected alternator supplies a delta connected load. The impedance of the load branch is 6+j5 ohm/phase. The line voltage is 230V. Determine the current in the load branch and power consumed by the load.A3) Zph=
400x30 = 0.48Sin Ø =0.88Rph=Zph Cos Ø= 23.09x0.48=11.08ohmXph=Zph Sin Ø = 23.09x0.88=20.32ohm Q3) A star connected alternator supplies a delta connected load. The impedance of the load branch is 6+j5 ohm/phase. The line voltage is 230V. Determine the current in the load branch and power consumed by the load.A3) Zph= = 7.8ohmVL=Vph=230VIph=Vph/Zph=230/7.8=29.49AIph=IL/
= 7.8ohmVL=Vph=230VIph=Vph/Zph=230/7.8=29.49AIph=IL/ IL=
IL=  Iph=
Iph= x29.49=51.07AP=
x29.49=51.07AP= VLIL Cos Ø =
VLIL Cos Ø =  x 230x51.07x0.768=15.62kW Q4) The load connected to a 3-phase supply comprise three similar coils connected in star. The line currents are 25A and the kVA and kW inputs are 18 and 10 respectively. Find the line and phase voltage, the kVAR input resistance and reactance of each coil?A 4) IL= 25AP= 10000WCos Ø = 10/18 = 0.56P=
x 230x51.07x0.768=15.62kW Q4) The load connected to a 3-phase supply comprise three similar coils connected in star. The line currents are 25A and the kVA and kW inputs are 18 and 10 respectively. Find the line and phase voltage, the kVAR input resistance and reactance of each coil?A 4) IL= 25AP= 10000WCos Ø = 10/18 = 0.56P= VLIL Cos Ø 10000=
VLIL Cos Ø 10000= x VLx25x0.56VL =412.39VVph= VL/
x VLx25x0.56VL =412.39VVph= VL/ = 412.39/
= 412.39/ =238.09VkVFR=
=238.09VkVFR= = 14.96Zph=238.09/25=9.52ohmRph=Zph Cos Ø= 9.52x0.56=5.33ohmXph=Zph Sin Ø = 9.52x0.83=7.88ohm Q5) A balanced delta connected load consisting of three coils draws 8
= 14.96Zph=238.09/25=9.52ohmRph=Zph Cos Ø= 9.52x0.56=5.33ohmXph=Zph Sin Ø = 9.52x0.83=7.88ohm Q5) A balanced delta connected load consisting of three coils draws 8 A at 0.5 p.f from 100V 3-phase ac supply. If the coils are reconnected in star across the same supply. Find the line current and total power consumed?A5) For Delta connection:IL=8
A at 0.5 p.f from 100V 3-phase ac supply. If the coils are reconnected in star across the same supply. Find the line current and total power consumed?A5) For Delta connection:IL=8 AIph= IL/
AIph= IL/ = 8AVph=100VZph=100/8=12.5ohmRph=Zph Cos Ø=12.5x0.5 = 6.25ohmXph=Zph Sin Ø = 12.5x0.866=10.825ohmP=
= 8AVph=100VZph=100/8=12.5ohmRph=Zph Cos Ø=12.5x0.5 = 6.25ohmXph=Zph Sin Ø = 12.5x0.866=10.825ohmP= VLIL Cos Ø =
VLIL Cos Ø =  x 100x 8
x 100x 8 x0.5=1200WFor Star Connection:Vph= VL/
x0.5=1200WFor Star Connection:Vph= VL/ = 100/
= 100/ V=57.73VZph=100/8=12.5ohmIph=57.73/12.5=4.62AP=
V=57.73VZph=100/8=12.5ohmIph=57.73/12.5=4.62AP= VLIL Cos Ø =
VLIL Cos Ø = x 100x 4.62x0.5P= 400W Q6) What are MCB’s?A6) MCB is a switch which automatically turns off when the current flowing through it passes the maximum allowable limit. Generally, MCB is designed to protect against over current and over temperature faults. In MCB there are two contacts one movable and other non-movable. When the current exceeds the predefined limit, a solenoid forces the moveable contact to open and the MCB turns off, thereby stopping the current from flowing in the circuits. It mainly consists of one bi- metallic strip, one trip coil and one hand operated on-off lever. The current in MCB flows from left side of circuit to bimetallic strip further going into the current coil, moving contact and at last through right side of circuit. When circuit is overloaded the bimetallic strip is overheated.
x 100x 4.62x0.5P= 400W Q6) What are MCB’s?A6) MCB is a switch which automatically turns off when the current flowing through it passes the maximum allowable limit. Generally, MCB is designed to protect against over current and over temperature faults. In MCB there are two contacts one movable and other non-movable. When the current exceeds the predefined limit, a solenoid forces the moveable contact to open and the MCB turns off, thereby stopping the current from flowing in the circuits. It mainly consists of one bi- metallic strip, one trip coil and one hand operated on-off lever. The current in MCB flows from left side of circuit to bimetallic strip further going into the current coil, moving contact and at last through right side of circuit. When circuit is overloaded the bimetallic strip is overheated.
|
|
|
|
UNIT - 4
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS ELECTRICAL SAFETY AND INTRODUCTION TO POWER SYSTEM
Q1) Three similar resistors are connected in star across 400V 3-phase lines. Line current is 4A. Calculate the value of each resistor.
A1) For star connection:
IL=Iph=4A
Vph=VL/ = 400/
= 400/ = 231V
= 231V
Rph= 231/4= 57.75ohm
For Delta Connection:
IL=4A
Iph= IL/
=4/ ==2.30A
==2.30A
Zph=400/2.30=173.9ohm
Rph= 173.9/3 = 57.97ohm
Q2) Three identical impedances are connected in delta 3-phase supply of 400V. The line current is 30A and total power taken from the supply is 10kW. Calculate the resistance and reactance value of each impedance?
A2) VL=Vph=400V
IL=30A
Iph=IL/ = 30/
= 30/ =17.32A
=17.32A
Zph=Vph/Iph= 400/17.32=23.09ohm
P= VLIL Cos Ø
VLIL Cos Ø
Cos Ø = 10000/ 400x30 = 0.48
400x30 = 0.48
Sin Ø =0.88
Rph=Zph Cos Ø= 23.09x0.48=11.08ohm
Xph=Zph Sin Ø = 23.09x0.88=20.32ohm
Q3) A star connected alternator supplies a delta connected load. The impedance of the load branch is 6+j5 ohm/phase. The line voltage is 230V. Determine the current in the load branch and power consumed by the load.
A3)
Zph= = 7.8ohm
= 7.8ohm
VL=Vph=230V
Iph=Vph/Zph=230/7.8=29.49A
Iph=IL/
IL=  Iph=
Iph= x29.49=51.07A
x29.49=51.07A
P= VLIL Cos Ø =
VLIL Cos Ø =  x 230x51.07x0.768=15.62kW
x 230x51.07x0.768=15.62kW
Q4) The load connected to a 3-phase supply comprise three similar coils connected in star. The line currents are 25A and the kVA and kW inputs are 18 and 10 respectively. Find the line and phase voltage, the kVAR input resistance and reactance of each coil?
A 4)
IL= 25A
P= 10000W
Cos Ø = 10/18 = 0.56
P= VLIL Cos Ø
VLIL Cos Ø
10000= x VLx25x0.56
x VLx25x0.56
VL =412.39V
Vph= VL/ = 412.39/
= 412.39/ =238.09V
=238.09V
KVFR= = 14.96
= 14.96
Zph=238.09/25=9.52ohm
Rph=Zph Cos Ø= 9.52x0.56=5.33ohm
Xph=Zph Sin Ø = 9.52x0.83=7.88ohm
Q5) A balanced delta connected load consisting of three coils draws 8 A at 0.5 p.f from 100V 3-phase ac supply. If the coils are reconnected in star across the same supply. Find the line current and total power consumed?
A at 0.5 p.f from 100V 3-phase ac supply. If the coils are reconnected in star across the same supply. Find the line current and total power consumed?
A5)
For Delta connection:
IL=8 A
A
Iph= IL/ = 8A
= 8A
Vph=100V
Zph=100/8=12.5ohm
Rph=Zph Cos Ø=12.5x0.5 = 6.25ohm
Xph=Zph Sin Ø = 12.5x0.866=10.825ohm
P= VLIL Cos Ø
VLIL Cos Ø
= 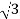 x 100x 8
x 100x 8 x0.5=1200W
x0.5=1200W
For Star Connection:
Vph= VL/ = 100/
= 100/ V=57.73V
V=57.73V
Zph=100/8=12.5ohm
Iph=57.73/12.5=4.62A
P= VLIL Cos Ø
VLIL Cos Ø
= x 100x 4.62x0.5
x 100x 4.62x0.5
P= 400W
Q6) What are MCB’s?
A6)
MCB is a switch which automatically turns off when the current flowing through it passes the maximum allowable limit. Generally, MCB is designed to protect against over current and over temperature faults. In MCB there are two contacts one movable and other non-movable. When the current exceeds the predefined limit, a solenoid forces the moveable contact to open and the MCB turns off, thereby stopping the current from flowing in the circuits.
It mainly consists of one bi- metallic strip, one trip coil and one hand operated on-off lever. The current in MCB flows from left side of circuit to bimetallic strip further going into the current coil, moving contact and at last through right side of circuit. When circuit is overloaded the bimetallic strip is overheated.

|
This deformation of bimetallic strip causes displacement in the latch. This displacement releases the spring through which the MCB is connected to the moving contact. This spring makes moving contact to open MCB.
The current coil or trip coil placed in such a manner that during SC faults, the MMF of that coil causes its plunger to hit the same latch point and force the latch to be displaced. Hence, the MCB will open in the same manner.
Q7) List Advantages of MCB?
A7)
- MCBs are replacing the re-wireable switch i.e., fuse units for low power domestic and industrial applications.
- The disadvantages of fuses, like low SC interrupting capacity (say 3kA), Etc. Are overcome with high SC breaking capacity of 10kA
- MCB is combination of all three functions in a wiring system like switching, overload and short circuits protection. Overload protection can be obtained by using bi-metallic strips whereas shorts circuits protection can be obtained by using solenoid
Q8) Explain Voltage-ELCB?
A8)
It consists of a relay coil; one end of that coil is connected to the metal body and other to the ground. When voltage on the equipment body rises to 50V (danger level) the current in the relay loop moves the relay contact by disconnecting the supply current and saves from electric shock.

|
Q9) Explain Current ELCB?
A9)
It is mostly commonly used ELCB. It consists of transformer having two primary (neutral and line wire) windings and one secondary winding. In balanced condition there is no current in secondary because the neutral wire balances the current through the phase wire.
 |
During fault a small current flow to ground causing imbalance between line and neutral currents. As a result of which current is induced in secondary winding. The sensing circuit connected to the secondary sends signal to the tripping system and the contact is tripped.
Q10) Explain plate earthing?
A10)
A copper plate of dimension 60cm x 60cm x 3.18 is used for earthing. The plate is buried in ground and layered with coal and salt. Then water is poured to maintain the earth’s electrode resistance below maximum value. The earth wire is bolted to the earth plate.
 |



