Unit 02
Water Technology
Q-1 Explain the methods of water softening by lime soda method.
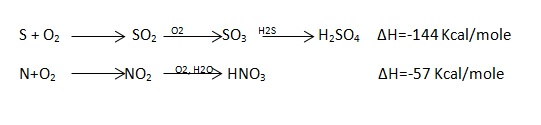
A- Hardness Lime Precipitate
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 -- > CaCO3 + H2O Ca(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 -- > 2CaCO3 + 2H2O Mg(HCO3)2 + Ca(OH)2 -- > CaCO3 + MgCO3 + 2H2O MgCO3 + Ca(OH)2 -- > CaCO3 + Mg(OH)2 CO2 the insoluble products do not contribute to the hardness, but It reacts with the lime, and thereby uses up some lime before the lime can start removing the hardness in water. Lime - Soda softening method is commonly practiced in most of the Public water supply. (Belan1984) The method is universal as water of almost any composition is treated with lime and soda. In this treatment, two reagents are used namely lime and soda ash. Lime as earlier discussed , decreases the carbonate hardness, (Mg2+) and removes C02 from the water.
Soda therefore reduces the non - carbonate hardness, mainly due to Ca2+, that shows after reaction with lime and the reaction occurs after the addition of soda ash is as follows.
Lime and Soda ash Addition:-
Lime Precipitate MgSO4 + Ca(OH)2 -- > Mg(OH)2 + CaSO4 Soda ash Precipitate CaSO4 + Na2CO3 -- > CaCO3 + Na2SO4 2.
Q-2Explain the zeolite process of water softening.
A- In the water softening process, hard water is passed through a bed of zeolite (inside a cylinder) at a specified rate. Then the cations that cause the water-hardening will remain on the zeolite bed because these cations exchange with the sodium cations of zeolite. Therefore, the water coming out of this cylinder contains sodium cations rather than calcium and magnesium cations.
After some time, the zeolite bed gets exhausted, the water flow is stopped and treat the bed is treated with concentrated brine solution (10%) in order to regenerate the zeolite. The bed is treated with a brine solution, as it washes away all the calcium and magnesium ions, by exchanging them with sodium ions in a brine solution. Hence, this treatment regenerates the zeolite.

Q-3 Classify the fuels.
A-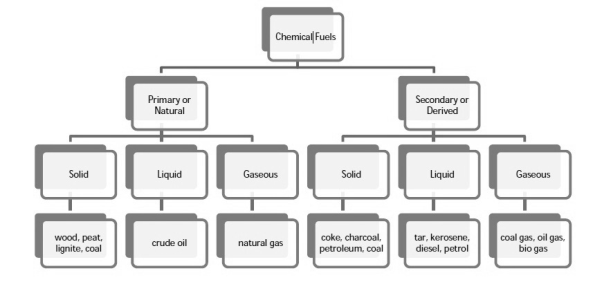
Q-4What is the main purpose of coal analysis?
A- The purpose for coal analysis is
- To decide price of coal
- To determine quality
- To specify use of coal for a particular purpose
- To calculate theoretical calorific values of coal
- To calculate air requirement for complete combustion of coal and design the furnace fire box suitably.
Q-5Compute the proximate analysis results 1.9 gms of a coal sample loses 0.285gm weight at 110°c. 1.5 gm of the same coal sample loses 0.36gm weight at 925°c. 2.15 gms of the coal sample leaves 0.26 gm ash.
Solutions:
M=1.9 gm
( m – m1 )= 0.285 gm ( moisture loss )
Loss in weight due to moisture and VM = 0.36gm
Weight of coal = 2.15 gm
Weight of ash = 0.26gm
- Moisture ( percent ) =
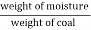 *100
*100
= 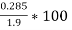 = 15 percent
= 15 percent
2. V.M ( percent ) :-
v.m = 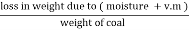 *10
*10
= 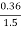 *100-15 = 24 – 15
*100-15 = 24 – 15
= 9 percent
3. Ash ( percent ) :-
Therefore ,
Ash = 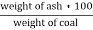
= 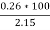
= 12 ( percent )
Q-6 Calculate C , N , H , S from the following observation for a sample of coal.2.05 gms of the coal is burnt in combustion tube. The increase in weight of any hydrous Cacl2 is 0.55 gm and increase in weight of KoH tube is 5.75gm. 0.75 of the coal is kjaldahl experiment released NH3 which is passed in 50ml 0.12 N NaoH to neutralize in back titration. Washings of the bomb pot when 1.8 gm.
Solutions-
Increase in weight of any hydrous calcl2 = 0.55
Mass of coal = 0.75gms
Volume of 0.12 NHCL consumed by NH3 = 50 – 41
= 9 ml
Mass of coal = 1.8gms
Weight of Baso4 = 0.31 gm
- Weight of CO 2 formed = increase in wt. OfKoH
Therefore ,
C percent ) = 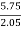 *
*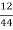 *100 = 76.5 percent .
*100 = 76.5 percent .
Increase in weight of any hydrous Cacl2
= weight of H2O formed
Mass of coal = 2.05gm
H ( percent ) = 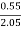 *
*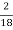 *100
*100
= 2.98 ( percent )
2. N ( percent ) = 
= 
= 2.02 ( percent )
3. S ( percent ) = 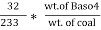 *100
*100
= 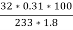
= 2.36 ( percent )
Q-7 Explain the working of Bomb Calorimetre.
A-
- Weigh the pellet of solid fuel or liquid capsule and keep it in the crucible .keep the crucible in the ring of the electrode . Keep the resistance wire touching to the fuel.
- Add about 10 ml of distilled water at the bottom of bomb pot and fix the lid tightly to bomb by screwing.
- Fill the bomb with oxygen at the pressure about 25 kg / cm².
- Place the bomb in calorimeter add known volume of water in the calorimeter so that the bomb gets immersed in the water.
- Place the calorimeter in the water jacket over the plastic studs .keep the thermometer and stirrer in the water of calorimeter.
- Put the plastic cover on the and make electrical connections from battery to electrodes.
- Operate the stirrer for s minutes and note the initial temperature of water ( t1° c ).
- Pass the current for about 5 – 10 seconds to heat the wire so that the fuel catches fire. If the fuel contains S and N elements, they get converted to SO3 and N2O5 .these gases get dissolved in the distilled water in bomb to form H2SO4 and HNO3 ( along with liberation little heat ).
- Note the maximum temperature reached .after that note the rate of fall of temperature per minute and the time taken for reaching to initial temp. Are noted.
- Open the bomb pot and wash the contents at its bottom into a beaker to find out the amount of H2SO4 and HNO3 formed.
Q-8Explain the working of Boy’s Gas Calorimeter.
A-
- Start burning the gas at suitable pressure and adjust the rate of water flow such that the temperature of outgoing water remains constant.
- Burn the gas for 5 – 10 minutes to have the steady temperatures in and around the combustion chamber.
- After the steady ( temperature in and around the combustion chamber ) conditions of outgoing.
A) Volume of gas burnt at given temperature and pressure in certain time period.
B) Quantity of water passed through coil during this period.
C) Mass of water condensed from product gas during the period.
D) The steady rise in temperature of water ( t2 – t1 )
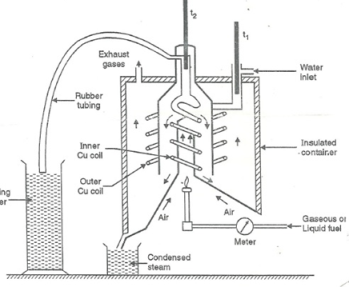
Fig: Boy’s gas calorimeter
Q-9Discuss about Volatilemeter.
A-
- Moisture free coal left in the crucible in first experiment ( m1 ) is covered with a lid loosely . Then it is heated at 925° c in a muffle furnace for 7 minutes .
- The crucible is taken out and cooled in a desiccator.
- Then it is weighed ( m2gms ) the loss in weight ( m1 –m2 ) is due to loss of volatile matter in m gms of the coal sample. ( volatile matter is the lower molecular weight organic compound in a coal and decomposed coal during burning of coal , that escapes without combustion , in the forms of smoke )
Volatile matter (percent ) :- 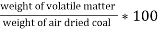
= 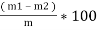
The volatile matter percent can be also determined by taking the fresh weight of the air dried coal but the loss in weight .at 925°c will be due to loss of moisture and volatile matter if W is the mass of coal left at 925° c heating,
Then ,
Volatile matter percent = 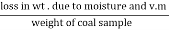 *100
*100
= 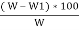 – moisture percent
– moisture percent
Q-10Explain Bomb Pot.
A- It is a cylindrical strong stainless-steel pot having a lid . The lid can be fitted air. Tight to bomb pot by screwing.
- There are two type of electrodes fitted through lid and there is an oxygen inlet valve as its center.
- One of these electrodes is provided with a ring to hold the crucible containing fuel .there is thin resistance wire tied to the electrodes in loop form and the loop touches the fuel.
- The weighed fuel is burnt in the bomb pot in the presence of high-pressure oxygen.
Calorimeter :-
- There is a stainless steel or copper calorimeter in which the bomb pot is kept .it contains a known volume of water and the water is kept circulating around the bomb pot with the help of a stirrer.
- A Beckman thermometer or digital thermometer is kept in the water of calorimeter , which can record the rise in temperature of welter due to absorb in a heat generated .
- There are insulator stands between calorimeter and water jacket.
Accessories :-
- There is a pellet press to convert the powder of solid fuel to pellet form .for a liquid fuel a capsule of negligible weight can be used.
- There is an oxygen cylinder with pressure gauge to fill oxygen in the bomb pot at the pressure of nearly 25 kg / cm².
- There is also a D.C battery of a about 6 volts to start combustion of fuel.
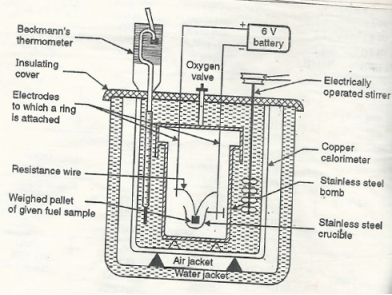
Fig: Bomb Caloriemeter
Q- 11What is Fuse Wire Correction in Bomb Pot?
A- Out of the total obtained little heat is given out by fuse wire when the current is passed for s – 10 sec .to start the combustion. Hence it must be subtracted. Are exothermic and the heat measured includes a small share by these acid formation.