UNIT 3
Q.1 What is one dimensional array?
A one-dimensional array is a group of elements having the same datatype and same name. Individual elements are referred to using common name and unique index of the elements.
The simplest form of an array is one-dimensional-array. The array itself is given name and its elements are referred to by their subscripts. In , an array is denoted as follows:
Array_name[array_size]
Where size specifies the number of elements in the array and the subscript (also called index) value ranges from 0 through size-1.
Declare One Dimensional Array
Here is the general form to declare one dimensional array in
Data_type array_name[array_size];
Here, data_type is any valid data type, array_name is the name of the array, and array_size is the size of array. Here is an example, declaring an array named arr of int type, having maximum element size of 10 elements
Intarr[10];
Initialize One Dimensional Array
Here is the general form to initialize values to one dimensional array
Data_type array_name[array_size] = {comma_separated_element_list};
Here is an example, declaring and initializing values to the array name arr of type int, containing 10 elements
Intarr[10] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
Q.2 Give some of the examples of one dimensional array
Here are some example program, demonstrating one dimensional array
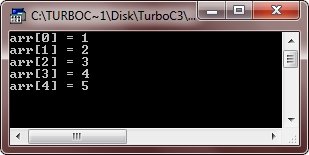
/*One Dimensional Array */
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
Clrscr();
Intarr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Inti;
For(i=0; i<5; i++)
{
Cout<<"arr["<<i<<"] = "<<arr[i]<<"\n";
}
Getch();
}
Here is the sample output of this program:
Here is another example, also demonstrating one dimension array in
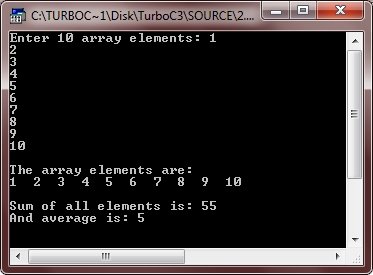
/* One Dimensional Array */
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
Void main()
{
Clrscr();
Intarr[10];
Inti;
Int sum=0, avg=0;
Cout<<"Enter 10 array elements: ";
For(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
Cin>>arr[i];
Sum = sum + arr[i];
}
Cout<<"\nThe array elements are: \n";
For(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
Cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
Cout<<"\n\nSum of all elements is: "<<sum;
Avg = sum/10;
Cout<<"\nAnd average is: "<<avg;
Getch();
}
Here is the sample run of the above program:
Q.3 What is multi-dimensional array?
Two Dimensional Array in C
The two-dimensional array can be defined as an array of arrays. The 2D array is organized as matrices which can be represented as the collection of rows and columns. However, 2D arrays are created to implement a relational database lookalike data structure. It provides ease of holding the bulk of data at once which can be passed to any number of functions wherever required.
Declaration of two dimensional Array in C
The syntax to declare the 2D array is given below.
- Data_type array_name[rows][columns];
Consider the following example.
- Int twodimen[4][3];
Here, 4 is the number of rows, and 3 is the number of columns.
Initialization of 2D Array in C
In the 1D array, we don't need to specify the size of the array if the declaration and initialization are being done simultaneously. However, this will not work with 2D arrays. We will have to define at least the second dimension of the array. The two-dimensional array can be declared and defined in the following way.
- Int arr[4][3]={{1,2,3},{2,3,4},{3,4,5},{4,5,6}};
Q.4 Give some of the example of two dimensional array
Two-dimensional array example in C
- #include<stdio.h>
- Int main(){
- Int i=0,j=0;
- Int arr[4][3]={{1,2,3},{2,3,4},{3,4,5},{4,5,6}};
- //traversing 2D array
- For(i=0;i<4;i++){
- For(j=0;j<3;j++){
- Printf("arr[%d] [%d] = %d \n",i,j,arr[i][j]);
- }//end of j
- }//end of i
- Return 0;
- }
Output
Arr[0][0] = 1
Arr[0][1] = 2
Arr[0][2] = 3
Arr[1][0] = 2
Arr[1][1] = 3
Arr[1][2] = 4
Arr[2][0] = 3
Arr[2][1] = 4
Arr[2][2] = 5
Arr[3][0] = 4
Arr[3][1] = 5
Arr[3][2] = 6
C 2D array example: Storing elements in a matrix and printing it.
- #include <stdio.h>
- Void main ()
- {
- Int arr[3][3],i,j;
- For (i=0;i<3;i++)
- {
- For (j=0;j<3;j++)
- {
- Printf("Enter a[%d][%d]: ",i,j);
- Scanf("%d",&arr[i][j]);
- }
- }
- Printf("\n printing the elements ....\n");
- For(i=0;i<3;i++)
- {
- Printf("\n");
- For (j=0;j<3;j++)
- {
- Printf("%d\t",arr[i][j]);
- }
- }
- }
Output
Enter a[0][0]: 56
Enter a[0][1]: 10
Enter a[0][2]: 30
Enter a[1][0]: 34
Enter a[1][1]: 21
Enter a[1][2]: 34
Enter a[2][0]: 45
Enter a[2][1]: 56
Enter a[2][2]: 78
Printing the elements ....
56 10 30
34 21 34
45 56 78
Q.5 Explain built in user define function
User defined functions are the functions defined by the programmer or user.
C++ provides the facility to user to define their own functions.
When the function gets call anywhere from program the function body gets execute.
Structure
#include<iostream>
Void function_name(){
}
Intmain(){
Function_name();
}
Example
#include<iostream>
Using namespace std;
Int add(int, int);
Int main(){
int a, b, sum;
Cout<<"Enters two numbers ";
Cin>> a >> b;
Sum= add(a, b);
Cout<<"Sum = "<< sum;
Return0;
}
Int add(int a,int b)
{
Int add;
Add= a + b;
Return add; }
}
Q.6 What is function definition and declaration?
Function is declared globally to inform the compiler about function name, function parameters and return type.
Return_typefunction_name([arguments type)];
Example
Void create_function(){
}
Function call
Function call has parameter list with function name. Using function call function can be called anywhere in program.
Function_name([actual arguments]);
Example
Voidcreatefunction() {
cout<<"Function created";
}
int main() {
createfunction();
return0;
}
Function definition.
Function definition consists of block of statements which contains actual execution code. When function gets called in program control comes to the function definition.
Return_typefunction_name([arguments])
{
Statements;
}
Example
Int main() {
createfunction();
return0;
}
voidcreatefunction() {
cout<<”Functoin created.”;
}
Voidmycreateunction();
int main() {
createfunction();
return0;
}
voidcreatefunction() {
cout<<“Function created”;
}
Q.7 What is pass by value and pass by reference in function explain with examples?
Function arguments in c programming
Basically, there are two types of arguments:
- Actual arguments
- Formal arguments
The variables declared in the function prototype or definition are known as Formal arguments and the values that are passed to the called function from the main function are known as Actual arguments.
The actual arguments and formal arguments must match in number, type, and order.
Following are the two ways to pass arguments to the function:
- Pass by value
- Pass by reference
Pass by Value
Pass by value is a method in which a copy of the value of the variables is passed to the function for the specific operation.
In this method, the arguments in the function call are not modified by the change in parameters of the called function. So the original variables remain unchanged.
Example of passing arguments by value to function in C
// arguments pass by value
# include <stdio.h>
Int add (int a, int b)
{
Return( a + b );
}
Int main()
{
Int x, y, z;
x = 5;
y = 5;
z = add(x,y); // call by value
Return 0;
}
//end of program
In this program, function add() is called by passing the arguments x and y.
The copy of the values of x and y are passed to a andb respectively and then are used in the function.
So by changing the values of a andb, there will be no change in the actual arguments x and y in the function call.
Pass by reference
Pass by reference is a method in which rather than passing direct value the address of the variable is passed as an argument to the called function.
When we pass arguments by reference, the formal arguments in the called function becomes the assumed name or aliases of the actual arguments in the calling function. So the function works on the actual data.
Example of passing arguments by reference to function in C
// arguments pass by reference
#include <stdio.h>
Void swap (int *a, int *b) // a and b are reference variables
{
Int temp;
Temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
Int main()
{
Int x = 2, y = 4;
Printf("before swapping x = %d and y = %d\n", x, y);
Swap(&x, &y); // call by reference
Return 0;
} //end of program
In the above program, the formal arguments a andb becomes the alias of actual arguments x and y when the function was called.
So when the variables a andb are interchanged x and y are also interchanged. So the output becomes like this.
Output
Before swapping x = 2 and y = 4
After swapping x = 4 and y = 2
Now, if the function was defined as:
Void swap(int a, int b)
{
Int temp;
Temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
This is the pass by value method so here even if the values are swapped in the function the actual value won’t interchange and output would become like this:
Before swapping x = 2 and y = 4
After swapping x = 4 and y = 2
Q.8 What is calling by value explain with examples?
Call by value in C
- In call by value method, the value of the actual parameters is copied into the formal parameters. In other words, we can say that the value of the variable is used in the function call in the call by value method.
- In call by value method, we can not modify the value of the actual parameter by the formal parameter.
- In call by value, different memory is allocated for actual and formal parameters since the value of the actual parameter is copied into the formal parameter.
- The actual parameter is the argument which is used in the function call whereas formal parameter is the argument which is used in the function definition.
Let's try to understand the concept of call by value in c language by the example given below:
- #include<stdio.h>
- Void change(int num) {
- Printf("Before adding value inside function num=%d \n",num);
- Num=num+100;
- Printf("After adding value inside function num=%d \n", num);
- }
- Int main() {
- Int x=100;
- Printf("Before function call x=%d \n", x);
- Change(x);//passing value in function
- Printf("After function call x=%d \n", x);
- Return 0;
- }
Output
Before function call x=100
Before adding value inside function num=100
After adding value inside function num=200
After function call x=100
Call by Value Example: Swapping the values of the two variables
- #include <stdio.h>
- Void swap(int , int); //prototype of the function
- Int main()
- {
- Int a = 10;
- Int b = 20;
- Printf("Before swapping the values in main a = %d, b = %d\n",a,b); // printing the value of a and b in main
- Swap(a,b);
- Printf("After swapping values in main a = %d, b = %d\n",a,b); // The value of actual parameters do not change by changing the formal parameters in call by value, a = 10, b = 20
- }
- Void swap (int a, int b)
- {
- Int temp;
- Temp = a;
- a=b;
- b=temp;
- Printf("After swapping values in function a = %d, b = %d\n",a,b); // Formal parameters, a = 20, b = 10
- }
Output
Before swapping the values in main a = 10, b = 20
After swapping values in function a = 20, b = 10
After swapping values in main a = 10, b = 20
Q.9 What is call by reference explain with examples?
Call by reference in C
- In call by reference, the address of the variable is passed into the function call as the actual parameter.
- The value of the actual parameters can be modified by changing the formal parameters since the address of the actual parameters is passed.
- In call by reference, the memory allocation is similar for both formal parameters and actual parameters. All the operations in the function are performed on the value stored at the address of the actual parameters, and the modified value gets stored at the same address.
Consider the following example for the call by reference.
- #include<stdio.h>
- Void change(int *num) {
- Printf("Before adding value inside function num=%d \n",*num);
- (*num) += 100;
- Printf("After adding value inside function num=%d \n", *num);
- }
- Int main() {
- Int x=100;
- Printf("Before function call x=%d \n", x);
- Change(&x);//passing reference in function
- Printf("After function call x=%d \n", x);
- Return 0;
- }
Output
Before function call x=100
Before adding value inside function num=100
After adding value inside function num=200
After function call x=200
Call by reference Example: Swapping the values of the two variables
- #include <stdio.h>
- Void swap(int *, int *); //prototype of the function
- Int main()
- {
- Int a = 10;
- Int b = 20;
- Printf("Before swapping the values in main a = %d, b = %d\n",a,b); // printing the value of a and b in main
- Swap(&a,&b);
- Printf("After swapping values in main a = %d, b = %d\n",a,b); // The values of actual parameters do change in call by reference, a = 10, b = 20
- }
- Void swap (int *a, int *b)
- {
- Int temp;
- Temp = *a;
- *a=*b;
- *b=temp;
- Printf("After swapping values in function a = %d, b = %d\n",*a,*b); // Formal parameters, a = 20, b = 10
- }
Output
Before swapping the values in main a = 10, b = 20
After swapping values in function a = 20, b = 10
After swapping values in main a = 20, b = 10
Q.10 What is recursion?
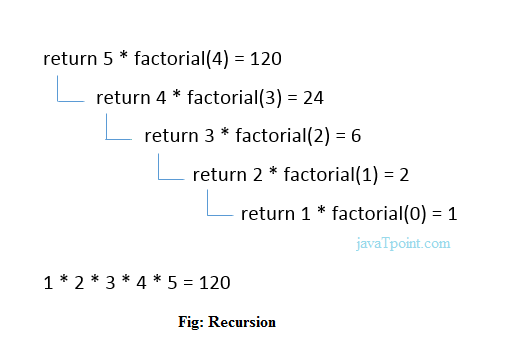
Recursion is the process which comes into existence when a function calls a copy of itself to work on a smaller problem. Any function which calls itself is called recursive function, and such function calls are called recursive calls. Recursion involves several numbers of recursive calls. However, it is important to impose a termination condition of recursion. Recursion code is shorter than iterative code however it is difficult to understand.
Recursion cannot be applied to all the problem, but it is more useful for the tasks that can be defined in terms of similar subtasks. For Example, recursion may be applied to sorting, searching, and traversal problems.
Generally, iterative solutions are more efficient than recursion since function call is always overhead. Any problem that can be solved recursively, can also be solved iteratively. However, some problems are best suited to be solved by the recursion, for example, tower of Hanoi, Fibonacci series, factorial finding, etc.
In the following example, recursion is used to calculate the factorial of a number.
- #include <stdio.h>
- Int fact (int);
- Int main()
- {
- Int n,f;
- Printf("Enter the number whose factorial you want to calculate?");
- Scanf("%d",&n);
- f = fact(n);
- Printf("factorial = %d",f);
- }
- Int fact(int n)
- {
- If (n==0)
- {
- Return 0;
- }
- Else if ( n == 1)
- {
- Return 1;
- }
- Else
- {
- Return n*fact(n-1);
- }
- }
Output
Enter the number whose factorial you want to calculate?5
Factorial = 120
We can understand the above program of the recursive method call by the figure given below: