UNIT 5
- Draw and explain Construction details of D.C. Machine.
Whether machine is D.C. Generator or motor the construction basically remains the same.
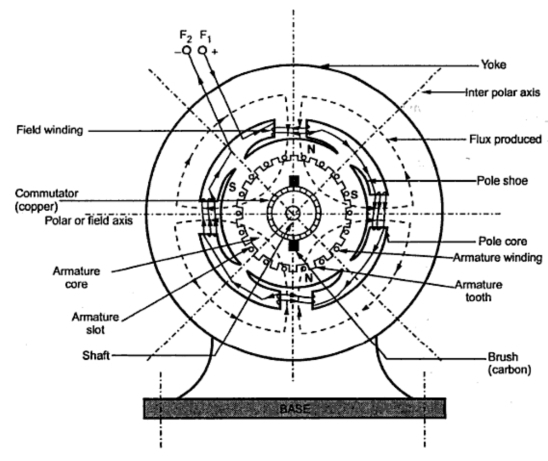
A cross section of typical D.C. Machine
1)Yoke
a) Functions
1. It serve the purpose of outermost cover of the D.C. Machine. So that the insulating materials get protected from harmful atmospheric elements like moisture. Dust and various gases like  , acidic fumes etc.
, acidic fumes etc.
2. It provides mechanical support to the poles.
3. It forms a part of the magnetic circuit.
It provides a path of low reluctance for magnetic flux. The low reluctance path is important to avoid wastage of power to provide same flux large current and hence the power is necessary if the path has high reluctance to produce the same flux.
4.Choice of material: - It is prepared by using cast iron, silicon steel is used which provides high permeability i.e. low reluctance and gives good mechanical strength.
2) Poles
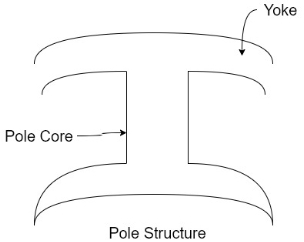
Pole structure
Each Pole is divided into two parts namely
- Pol core
- Pole shoe
Functions of pole core and pole shoe: -
- Pole core basically carries a field winding which is necessary to produce the flux.
- It directs the flux produced through air gap to armature core to the next pole.
- Pole shoe enlarge the area of armature core to come across the flux, which is necessary to produce larger induced e.m.f. To achieve this, sports shoe has been given a particular shape.
Choice of material: -
It is made up of magnetic material like cast iron or cast steel.
As it requires a definite shape and size, laminated construction is used. The laminations of required size and shape are stamped together to get a pole which is then bolted to the yoke.
3) Field Winding (
The field winding is wound on the pole core with a definite direction.
a)Functions:-
To carry current due to which pole core on which the field winding is placed behaves as an electromagnet, producing necessary flux.
As it helps in producing the magnetic field i.e. exciting the poles as an electromagnet it is called Field winding or Exciting winding.
b) Choice of material:-
It has to carry current hence obviously made up of some conducting material.
So aluminium or copper is the choice. But field coils are required to take four types of shape and bent about pole core and copper has good pliability i.e. it can be bend easily. So copper is the proper choice field winding is divided into various coils called field coils. These are connected in series with each other and wound in such direction around pole cores, such that alternate 'N' and 'S' poles are formed.
The total number of poles is denoted as P.
4) Armature
The armature is further divided into two parts namely
- Armature core
- Armature winding
1.Armature core:- Armature core is cylindrical in in shape mounted on the shaft. It consists of slots on its periphery and air ducts to permit the air flow through armature which serves cooling purpose.
a) Functions-
1) Armature core provides house for armature winding i.e. armature conductors.
2)To provide the path of low reluctance to the magnetic flux produced by the field winding.

b) Choice of material: -
As it has to provide a low reluctance path to the flux, it is made up of magnetic material like cast iron or cast steel.
It is made up of laminated construction to keep Eddy current loss as low as possible. A single circular lamination used for the construction of armature core is shown in figure.
3. Armature winding
Armature winding is nothing but the interconnection of the armature conductors placed in the slots provided on the armature core periphery.
When the armature is rotated in case of generator magnetic flux gets cut by armature conductors and e.m.f gets induced in them.
a) Functions
1) curvatures of e.m.f takes place in the armature winding in case of generators.
2) To carry the current supplied in case of D.C. Motors.
3) To do the useful work in the external circuit.
b) Choice of Material: -
As armature winding carries entire current which depends on external load, it has to be made up of conducting material which is copper.
5.Commutator
The basic nature of e.m.f in the armature conductors is alternating. This needs verification in case of D.C. Generator, which is possible by a device called commutator.
a)Functions:
1)To facilitate the collection of current from the armature conductors.
2) To convert internally developed alternating e.m.f to unidirectional (D.C.) e.m.f.
3) To produce unidirectional torque in case of motors
b) Choice of Material:-
As it collects current from armature, it is also made up of copper segments.

It is cylindrical in shape and is made up of wedge-shaped segments of hand drawn high conductivity copper the segments are insulated from each other by thin layer of Mica.
Each commutator segment is connected to the armature conductor by means of copper lug or strip. This construction is shown in figure above.
6. Brushes and Brush Gear
Brushes are stationary and resting on the surface of the commutator.
a) Function-
To collect current from computer and make it available to stationary external circuit.
b) Choice of Material: -
Brushes are normally made up of soft material like carbon.
To avoid wear and tear of commentator the brushes are made up of soft material like carbon.
7) Bearings
Ball bearings are usually used as they are more reliable. For heavy duty machines roller bearing are preferred.
2. A 220 volt DC motor has an armature resistance of 0.75 ohm. It is drawing and armature current of 30 A, driving a certain load. Calculate the induced EMF in the motor under this condition.
V=200V 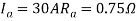
Are the given values
For a motor ,
V=
220=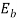 +30*0.75
+30*0.75
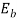 =197.5 V
=197.5 V
This is the induced EMF called a back EMF in a motor
3. Find the useful flux per pole on no load of a 250V 6 pole shunt motor having two circuit connected armature winding with 225 conductors.at normal working temperature the overall armature resistance including brushes is 0.2 ohm. The armature current is 13.3A at the no load speed of 908 RPM.
Solution
V=250 P=6 Z=220 A=2
As two circuit armature
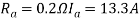
N=908 r.p.m
For a DC shunt motor
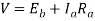
250=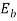 +13.3*0.2 i.e.
+13.3*0.2 i.e. 
Back emf is given by
is given by
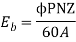
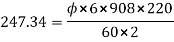

4. Explain Principle of operation of induction motor:

- When the 3Ф A.C supply is connected across the stator of induction motor, the current starts flowing through the stator wdg. i.ethe stator condition.
- Due to this current of flux (Ф) is established in the stator wdg. This flux (Ф) is alternating (changing) in nature. Thus this flux links with the rotor also, and a a Rotating Magnetic Field(RMF) is produced.
- This flux (Ф) induces in the rotor also. The RMF is produced in the air gap between stator and rotor.
- The rotor is rotating part which is till stationary, show the rotating magnetic field is cut by stationary rotor and an EMF is induced in the rotor winding. According to faraday's law of EMI the rotor EMF gives the rise to rotor current which opposes the main cause producing it according Lenz's law.
5. Draw and explain Slip – torque Characteristics.
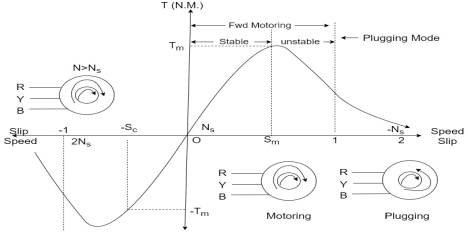
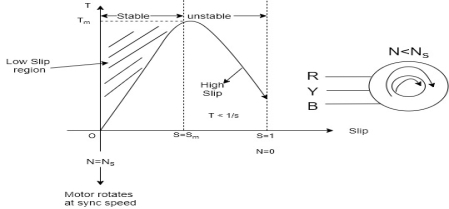
Torque slip region for stable regimen
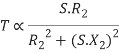
S= small 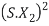 -> Negligible
-> Negligible
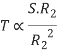

Unstable:-

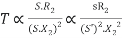 , neglect
, neglect 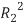
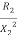 = Constant value
= Constant value
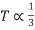 =high slip region
=high slip region
 and vice versa
and vice versa
Various Torques ;
 at starting s=1 and 4N =0
at starting s=1 and 4N =0
 ----------slip is
----------slip is  i.e..
i.e..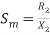
Total Torque
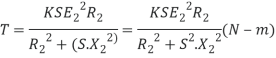
6. Explain 3 phase synchronous machine in detail.
The rotating and stationary parts of an electrical machine can be called as rotor and stator respectively. The rotor or stator of electrical machines acts as a power-producing component and is called as an armature. The electromagnets or permanent magnets mounted on the stator or rotor are used to provide magnetic field of an electrical machine. The generator in which permanent magnet is used instead of coil to provide excitation field is termed as permanent magnet synchronous generator or also simply called as synchronous generator.
Construction of Synchronous Generator
In general, synchronous generator consists of two parts rotor and stator. The rotor part consists of field poles and stator part consists of armature conductors. The rotation of field poles in the presence of armature conductors induces an alternating voltage which results in electrical power generation.
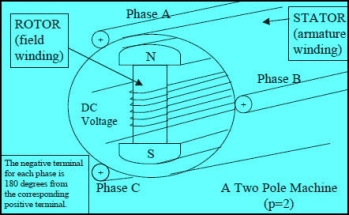
Construction of Synchronous Generator
The speed of field poles is synchronous speed and is given by
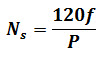
Where, ‘f’ indicates alternating current frequency and ‘P’ indicates number of poles.
Synchronous Generator Working Principle
The principle of operation of synchronous generator is electromagnetic induction. If there exists a relative motion between the flux and conductors, then an emf is induced in the conductors. To understand the synchronous generator working principle, let us consider two opposite magnetic poles in between them a rectangular coil or turn is placed as shown in the below figure.
Now, if we consider a practical synchronous generator, then field magnets rotate between the stationary armature conductors. The synchronous generator rotor and shaft or turbine blades are mechanically coupled to each other and rotate at synchronous speed. Thus, the magnetic flux cutting produces an induced emf which causes the current flow in armature conductors. Thus, for each winding the current flows in one direction for the first half cycle and current flows in the other direction for the second half cycle with a time lag of 120 degrees (as they displaced by 120 degrees). Hence, the output power of synchronous generator can be shown as below figure.