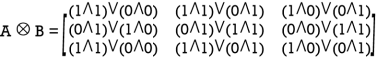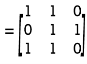Question Bank
UNIT-4
Question Bank
UNIT-4
Q:1 Find the unit vector in the direction of vector
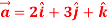
 =
= 
Magnitude of 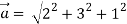
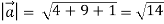
Unit vector in the direction of 
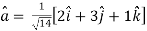
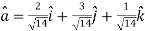
Thus,unit vector in the direction of 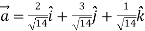
Q:2 Find the unit vector in the direction of the sum of the vectors,
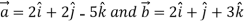
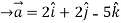
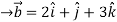
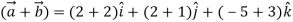
= 4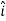 +3
+3
Let 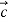 =(
=(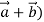
 4
4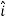 +3
+3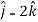
Magnitude of 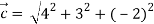
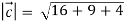 =
= 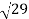
Q:3 ,then show that the vectors
,then show that the vectors 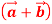 and
and 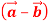 are
are
Perpendicular.
Solution:
Two vectors  are said to be perpendicular if their scalar product is zero
are said to be perpendicular if their scalar product is zero
Ie.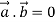
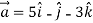
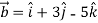
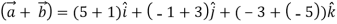
= 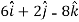
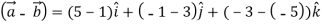
= 
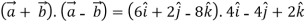
=
= 0
Thus  are perpendicular.
are perpendicular.
Q:4 Test whether the vectors (1,-1,1),(2,1,1) and (3,0,2) are linearly dependent. If so write the relationship for the vectors.
Solution:
Let the given vectors be,
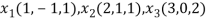
Now we have to write the given vectors in the form 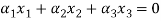
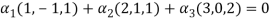
1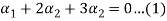
-1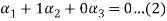
1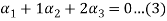
From the second equation 
Now we substitute this value in equation (1)
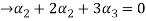
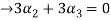
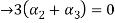
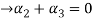
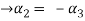
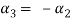
Now substituting 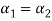 and
and 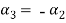 in the third equation
in the third equation
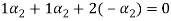
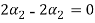
 ....(4)
....(4)
Equation (4) is true for any value of 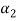 . So that let us assume
. So that let us assume 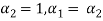 and
and
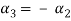
Values of 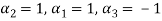
Therefore we can say that given vectors are linearly dependent.
Now the relationship is given by
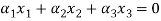
Applying the values in the equation we will get 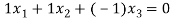
Q:5 Let u = 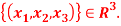 Find the basis of u
Find the basis of u
Solution:
If u= 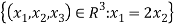 then u=
then u= and so one of such
and so one of such
Basis of u is 
To verify this set of vectors is a basis of U we must show that U=span((2,1,0),(0,0,1)) and that {(2,1,0),(0,0,1)} is a linearly independent vectors in V.let x=(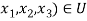 .Then we havethat,
.Then we havethat,
X=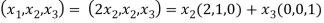
So U = span((2,1,0),(0,0,1)).now consider the following vector equation for 
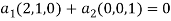
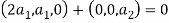
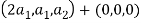 =0
=0
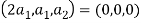
 is a linearly independent set of vectors in R3
is a linearly independent set of vectors in R3
Thus,
{(2,1,0),(0,0,1)} is a basis of U.
Q:6
Let U= {(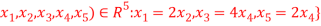 be a subspace of R5.Findd basis of U.
be a subspace of R5.Findd basis of U.
Solution :
U=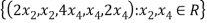
Therefore we have that 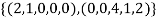 is a basis of U.To verify this,
is a basis of U.To verify this,
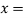 (
( then we have that:
then we have that:
 (
(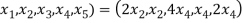 =
= 
So U = span((2,1,0,0,0),(0,0,4,1,2)) .Now consider the following vector equation for 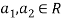
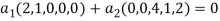
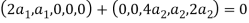
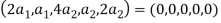
The equation above implies that
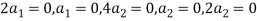
Thus  and so
and so  is a linearly independent set of vectors in U.
is a linearly independent set of vectors in U.
Thus 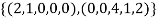 is a basis of U.
is a basis of U.
Q:7 Let  be the vector space over R consisting of all polynomials wit real co-efficient of degree 2 or less.
be the vector space over R consisting of all polynomials wit real co-efficient of degree 2 or less.
Let B = 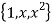 be a basis of the vector space
be a basis of the vector space 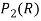 .
.
For each linear transformation T: defined below,find the matrix representation of T w.r.to the basis B.For f(x)
defined below,find the matrix representation of T w.r.to the basis B.For f(x) , define T as follows
, define T as follows
(1) T(f(x)) = 
(2) T(f(x)) = 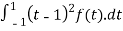
(3) T(f(x))=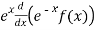
Solution (1):
Given, T(f(x)) = 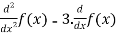
Since the derivative constant function x is zero,we have
T(1)=0
Since the second derivative of the function x is zero, we have
T(x)=-3
Finally we calculate T(x2) = 2-6x
There with respect to the basis { , the matrix for T is
, the matrix for T is

(2) given,
T(f(x)) = 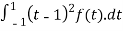
We compute,
T(f(x)) = 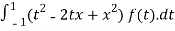
= 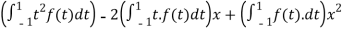
Then we have,
T(1) = 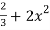
T(x) = -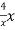
T(x2) = 
Here we calculated the integrals
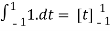 =2,
=2,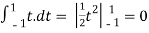
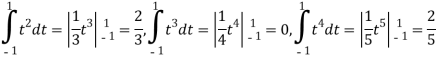
Therefore the matrix for the linear transformation with respect to the basis B=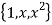
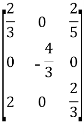
(iii) .given,
T(f(x))=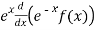
By product rule for derivatives we have
T(f(x))=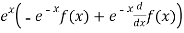
= -f(x)+
Thus we have,
T(1) = 1
T(x) = -x+1
T(x2) =-x2 + 2x
Hence the matrix for the linear transformation T w.r.to., the basis B is,
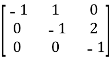
Q:8 Define two functions 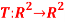 and
and  by
by
T 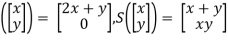
Determine whether T,S and the composite S o T are linear transformation.
Solution:
We will prove that T and S o Tare linear transformation.
X =  , Y =
, Y = 
Then we have
T(x+y) = T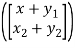 =
= 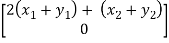
= 
Note ,for any scalar ,we hace
T(rx) = T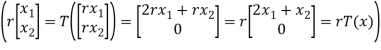
Hence T is a linear transformation.
Q:9
Perform the following column transformations on A in given order 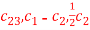
A = 
Solution:
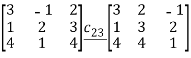
 =
= 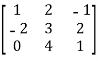
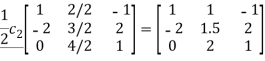
Q:10
Perform row operations for the following matrix
A = 
Applying row operations

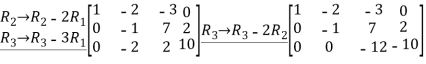
The equivalent matrix is a row echelon matrix having three non-zero rows
 Rank of A is
Rank of A is 
Q:11 Reduce the given matrix into a row-echelon form

Solution:
Given matrix is,
 ,now we perform row operation to reduce into echelon form,
,now we perform row operation to reduce into echelon form,
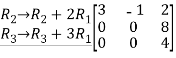
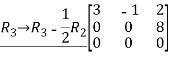
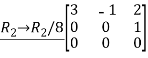
This is also a row-echelon form of the given matrix
Q:12 Reduce the given matrix in a row-echelon form

Solution:
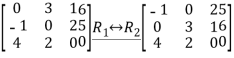
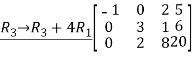
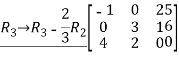
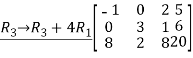
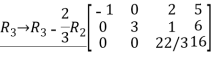
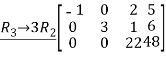
Q:13 Determine bases for  when
when
A =  and then determine rank and nullities of the matrices A and ATA
and then determine rank and nullities of the matrices A and ATA
Solution :
We will first compute AT
AT =  and ATA=
and ATA= =
= 
Next,we will find 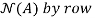 reducing [
reducing [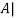 0]:
0]:


Thus the solution to Ax = 0 is given by
X=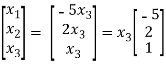
Thus N(A) = 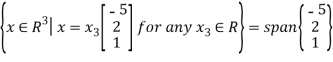
Therefore,
 is a basis for N(A)
is a basis for N(A)
Similarly,we will compute N(ATA) by row reducing 
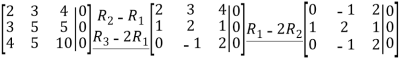
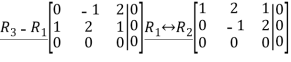
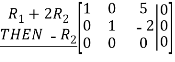
Since the row reduced matrices for  are identical, we can immediately conclude that
are identical, we can immediately conclude that
N(ATA) = span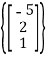 is a basis for N(ATA)
is a basis for N(ATA)
It follows that the nullities of A and ATA are both 1
The rank-nullity theorem tells
Rank of A +nullity of A =3
Hence the rank of A is 2. Similarly,the rank of ATA is 2.
Q:14 Let T: R2 3 be a linear transformation such that,
3 be a linear transformation such that,
T
(a). Find the matrix representation of T(w.r.to standard basis of R3)
(b).Determine the rank and nullity of T.
Solution:
The matrix representation A of the linear transformation is given by
A=[T(e1),T(e2)]
Where
T(e1)= T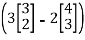
= 3T
= 3
Similarly, we compute T(e2) as follows
Let e2 = 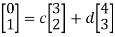
This can be written as 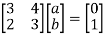
Hence,we obtain
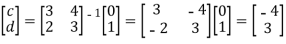
And c=-4,d=-3
Hence 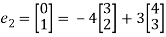
And we have,
T(e2) = T
=-4T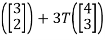
= -4
(b).Determine the rank and nullity of T
Note that the rank and nullity of T are the same as those of the matrix representation A of T in part (a), we obtained
A=
Let us first determine the rank of A.
We have
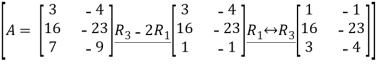
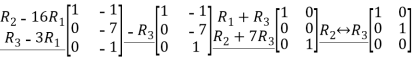
Hence the reduced echelon form matrix of A has two non-zero rows.
So the rank of A is 2
By the rank-nullity theorem,we know that ,
(rank of A)+(nullity of A)=2
Q:15 Solve the following system of equations
2x-y+3z=9
X+y+z=6
x-y+z=2
Solution:
Here 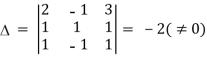
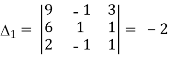
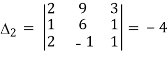
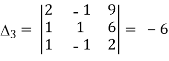
By Cramer’s rule
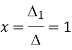
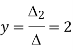
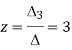
Q:16 For what values of p and q the system of equations 2x+py+6z=8, x+2y+qz=5,x+y+3z=4 has (i) no solution (ii) a unique solution (iii) infinitely many solutions.
Solution:
Here 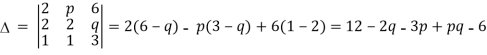
= pq-2q-3p+6=(p-2)(q-3),also
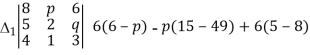
= 48-8q-15p+4pq-18=4pq-18=4pq-8q-15p+30=4q(p-2)-15(p-2)=(4q-15)(p-2),
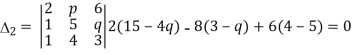
And,
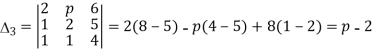
Case 1: when  ie. p
ie. p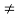 2,q
2,q 3,given system of equation has a unique solution
3,given system of equation has a unique solution
Case 2 when  =0,ie. P=2 or q=3
=0,ie. P=2 or q=3
When p=2,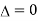 ,
,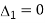 ,
, ,
,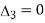
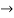 given system of equations has infinitely many solutions.
given system of equations has infinitely many solutions.
When q=3,p 2,D=0,
2,D=0,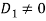 ,Then the system of equations has no solution.
,Then the system of equations has no solution.
Q:17 Find the characteristic equation of the following matrix
Where A =
Solution:
The required equation to get the characteristic equation is,
(A-I ) =0 Where I is the identity matrix and must be 2
) =0 Where I is the identity matrix and must be 2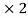 because A is a 2
because A is a 2 2 matrix.
2 matrix.
Det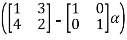 =0
=0
Det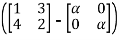 =0
=0
Det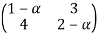 =0
=0
(1-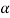 )(2-
)(2-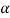 )-(3)(4)=0
)-(3)(4)=0
=
Q:18 Verify the Cayley-Hamilton theorem for A=
Solution:
The characteristic equation of A is
P(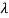 ) =
) = =
= 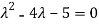
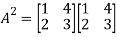 =
= 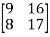
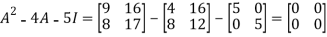
Therefore,Cayley Hamilton theorem is verified.
Q:19 Verify Cayley Hamilton theorem for the following matrix:
A =  for
for 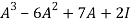
Solution:
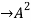 =
= 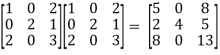
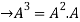 =
= 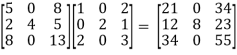
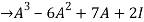 =
= -6
-6 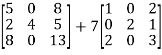 + 2
+ 2
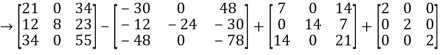
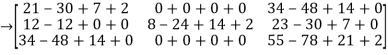
=
Hence theorem verified.
Q:20 Find the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the matrix A=
Solution: We have
A −λ I=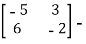 λ
λ
So | A −λ I |=0
⇔ (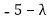 )(
)(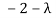 )-18=0
)-18=0
⇔
⇔ (λ-1) (λ+8) =0
⇔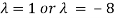
Hence the eigenvalues of A are 1 and -8. To find the eigenvectors we consider each eigenvalue in turn.
If (x, y) is an eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue 1
⇔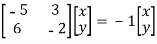
⇔
⇔y=2x
Hence any nonzero vector of the form (x,2x) or equivalently any nonzero multiple of (1,2) is an eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue 1
If (x, y) is an eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue 8
⇔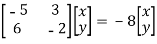
⇔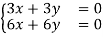
⇔y=-x
Hence any nonzero vector of the form (x, -x) or equivalently any nonzero multiple of (1, -1) is an eigenvector corresponding to the eigenvalue -8.
Q:21 Consider the function 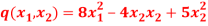 .Determine whether q(0,0) is the global minimum.
.Determine whether q(0,0) is the global minimum.
Solution: Based on matrix technique
Rewrite the above equation
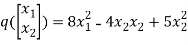
=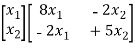
Note that we split the contribution -4 equally among the two components.
equally among the two components.
More succinctly, we can write
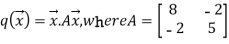
Or
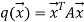
The matrix A is symmetric by construction. By the spectral theorem, there is an orthonormal eigen basis 
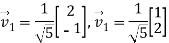
With associated eigenvalues 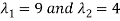 .
.
Let 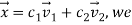 can express the value of the function as follows:
can express the value of the function as follows:
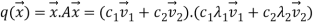
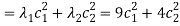
Therefore,  is the global minimum if the function.
is the global minimum if the function.
Q:22 The matrix A=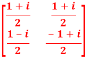 has row vectors.
has row vectors.
Solution:  ,
, 
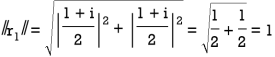
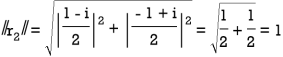
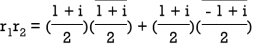
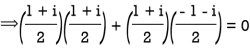
Orthogonal matrix: An orthogonal matrix is the real specialization of a unitarymatrix, and thus always a normal matrix. Although we consider only real matrices here, the definition can be used for matrices with entries from any field.
Suppose A is a square matrix with real elements and of n x n order and AT is the transpose of A. Then according to the definition, if, AT = A-1 is satisfied, then,
A AT = I
Where ‘I’ is the identity matrix, A-1 is the inverse of matrix A, and ‘n’ denotes the number of rows and columns.
Q:23 prove Q=  is an orthogonal matrix
is an orthogonal matrix
Solution: Given Q = 
So, QT =  …..(1)
…..(1)
Now, we have to prove QT = Q-1
Now we find Q-1
Q-1 = 
Q-1 = 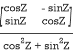
Q-1 = 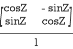
Q-1 = 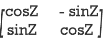 … (2)
… (2)
Now, compare (1) and (2) we get QT = Q-1
Therefore, Q is an orthogonal matrix.
Q:24 Let the encoding matrix be A=
Let the message to be sent by the sender be “WELCOME”.
Since the key is taken as the operation of post-multiplication by a square matrix of order 3, the message is cut into pieces (WEL),(COM),(E), each of length 3, and converted into a sequence of row matrices of numbers:
[23 5 12], [3 15 13], [5 0 0]
Note that, we have included two zeros in the last row matrix. The reason is to get a row matrix with 5 as the first entry.
Next, we encode the message by post-multiplying each row matrix as given below:
Uncoded row matrix Encoding matrix Coded row matrix
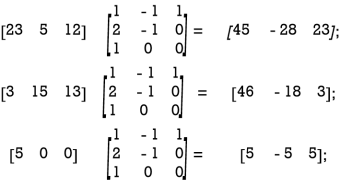
So the encoded message is [45 -28 -23] [46 -18 3] [5 -5 5]
The receiver will decode the message by the reverse key, post-multiplying by the inverse of A.
So the decoding matrix is
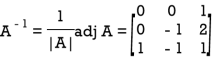
The receiver decodes the coded message as follows:
Coded row matrix Decoding matrix Decoded row matrix
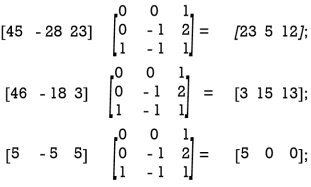
So, the sequence of decoded row matrices is [23 5 12], [3 15 13], [5 0 0]
Thus, the receiver reads the message as “WELCOME”
Q:25 A =  B=
B= 
Solution: We use two Boolean operations Join (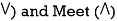

A =
=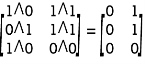
Q:27 Find the Boolean product of A and B, where
A =  , B =
, B = 
Solution: