UNIT- 3
Basic Introduction to Computer Networks
- What are personal area network and what are its types?
PAN(Personal Area Network)
- Personal Area Network is a network arranged within an individual person, typically within a range of 10 meters.
- Personal Area Network is used for connecting the computer devices of personal use is known as Personal Area Network.
- Thomas Zimmerman was the first research scientist to bring the idea of the Personal Area Network.
- Personal Area Network covers an area of 30 feet.
- Personal computer devices that are used to develop the personal area network are the laptop, mobile phones, media player and play stations.
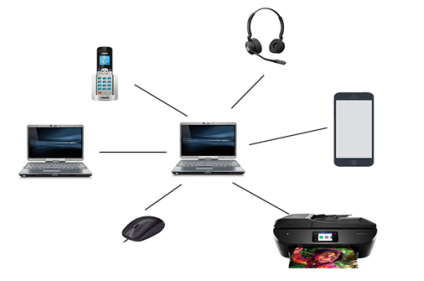
There are two types of Personal Area Network:
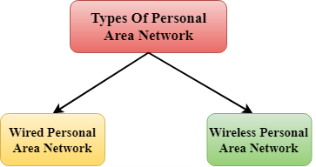
- Wired Personal Area Network
- Wireless Personal Area Network
Wireless Personal Area Network: Wireless Personal Area Network is developed by simply using wireless technologies such as WiFi, Bluetooth. It is a low range network.
Wired Personal Area Network: Wired Personal Area Network is created by using the USB.
Examples of Personal Area Network:
- Body Area Network: Body Area Network is a network that moves with a person. For example, a mobile network moves with a person. Suppose a person establishes a network connection and then creates a connection with another device to share the information.
- Offline Network: An offline network can be created inside the home, so it is also known as a home network. A home network is designed to integrate the devices such as printers, computer, television but they are not connected to the internet.
- Small Home Office: It is used to connect a variety of devices to the internet and to a corporate network using a VPN
2. What is metropolitan area network and what are its uses?
MAN(Metropolitan Area Network)
- A metropolitan area network is a network that covers a larger geographic area by interconnecting a different LAN to form a larger network.
- Government agencies use MAN to connect to the citizens and private industries.
- In MAN, various LANs are connected to each other through a telephone exchange line.
- The most widely used protocols in MAN are RS-232, Frame Relay, ATM, ISDN, OC-3, ADSL, etc.
- It has a higher range than Local Area Network(LAN).
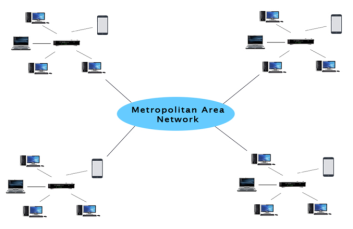
Uses of Metropolitan Area Network:
- MAN is used in communication between the banks in a city.
- It can be used in an Airline Reservation.
- It can be used in a college within a city.
- It can also be used for communication in the military.
3. What is wide area network and what are its advantages and disadvantages?
WAN(Wide Area Network)
- A Wide Area Network is a network that extends over a large geographical area such as states or countries.
- A Wide Area Network is quite bigger network than the LAN.
- A Wide Area Network is not limited to a single location, but it spans over a large geographical area through a telephone line, fibre optic cable or satellite links.
- The internet is one of the biggest WAN in the world.
- A Wide Area Network is widely used in the field of Business, government, and education.
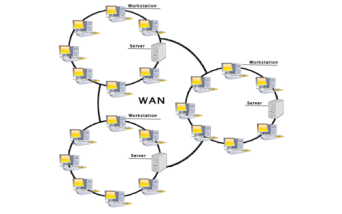
Examples of Wide Area Network:
- Mobile Broadband: A 4G network is widely used across a region or country.
- Last mile: A telecom company is used to provide the internet services to the customers in hundreds of cities by connecting their home with fiber.
- Private network: A bank provides a private network that connects the 44 offices. This network is made by using the telephone leased line provided by the telecom company.
Advantages Of Wide Area Network:
Following are the advantages of the Wide Area Network:
- Geographical area: A Wide Area Network provides a large geographical area. Suppose if the branch of our office is in a different city then we can connect with them through WAN. The internet provides a leased line through which we can connect with another branch.
- Centralized data: In case of WAN network, data is centralized. Therefore, we do not need to buy the emails, files or back up servers.
- Get updated files: Software companies work on the live server. Therefore, the programmers get the updated files within seconds.
- Exchange messages: In a WAN network, messages are transmitted fast. The web application like Facebook, Whatsapp, Skype allows you to communicate with friends.
- Sharing of software and resources: In WAN network, we can share the software and other resources like a hard drive, RAM.
- Global business: We can do the business over the internet globally.
- High bandwidth: If we use the leased lines for our company then this gives the high bandwidth. The high bandwidth increases the data transfer rate which in turn increases the productivity of our company.
Disadvantages of Wide Area Network:
The following are the disadvantages of the Wide Area Network:
- Security issue: A WAN network has more security issues as compared to LAN and MAN network as all the technologies are combined together that creates the security problem.
- Needs Firewall & antivirus software: The data is transferred on the internet which can be changed or hacked by the hackers, so the firewall needs to be used. Some people can inject the virus in our system so antivirus is needed to protect from such a virus.
- High Setup cost: An installation cost of the WAN network is high as it involves the purchasing of routers, switches.
- Troubleshooting problems: It covers a large area so fixing the problem is difficult.
4. What is internetwork and what are its types?
Internetwork
- An internetwork is defined as two or more computer network LANs or WAN or computer network segments are connected using devices, and they are configured by a local addressing scheme. This process is known as internetworking.
- An interconnection between public, private, commercial, industrial, or government computer networks can also be defined as internetworking.
- An internetworking uses the internet protocol.
- The reference model used for internetworking is Open System Interconnection(OSI).
Types Of Internetwork:
1. Extranet: An extranet is a communication network based on the internet protocol such as Transmission Control protocol and internet protocol. It is used for information sharing. The access to the extranet is restricted to only those users who have login credentials. An extranet is the lowest level of internetworking. It can be categorized as MAN, WAN or other computer networks. An extranet cannot have a single LAN, atleast it must have one connection to the external network.
2. Intranet: An intranet is a private network based on the internet protocol such as Transmission Control protocol and internet protocol. An intranet belongs to an organization which is only accessible by the organization's employee or members. The main aim of the intranet is to share the information and resources among the organization employees. An intranet provides the facility to work in groups and for teleconferences.
5. Explain OSI reference model what are its functions and characteristics?
- OSI stands for Open System Interconnection is a reference model that describes how information from a software application in one computer moves through a physical medium to the software application in another computer.
- OSI consists of seven layers, and each layer performs a particular network function.
- OSI model was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984, and it is now considered as an architectural model for the inter-computer communications.
- OSI model divides the whole task into seven smaller and manageable tasks. Each layer is assigned a particular task.
- Each layer is self-contained, so that task assigned to each layer can be performed independently.
Characteristics of OSI Model:
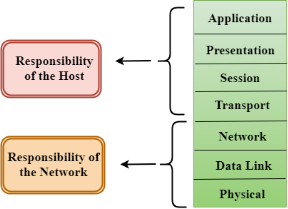
- The OSI model is divided into two layers: upper layers and lower layers.
- The upper layer of the OSI model mainly deals with the application related issues, and they are implemented only in the software. The application layer is closest to the end user. Both the end user and the application layer interact with the software applications. An upper layer refers to the layer just above another layer.
- The lower layer of the OSI model deals with the data transport issues. The data link layer and the physical layer are implemented in hardware and software. The physical layer is the lowest layer of the OSI model and is closest to the physical medium. The physical layer is mainly responsible for placing the information on the physical medium.
Functions of the OSI Layers
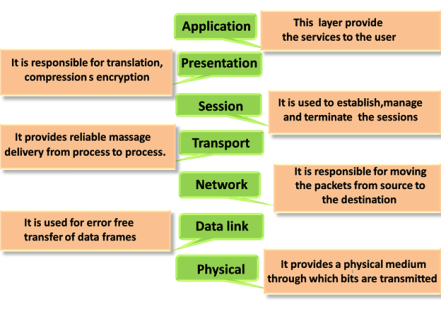
There are the seven OSI layers. Each layer has different functions. A list of seven layers are given below:
- Physical Layer
- Data-Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
6. Explain data link layer and what are its functions?
Data-Link Layer
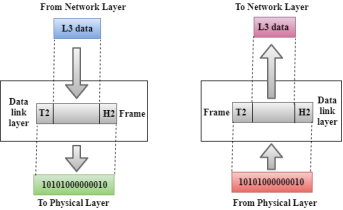
- This layer is responsible for the error-free transfer of data frames.
- It defines the format of the data on the network.
- It provides a reliable and efficient communication between two or more devices.
- It is mainly responsible for the unique identification of each device that resides on a local network.
- It contains two sub-layers:
- Logical Link Control Layer
- It is responsible for transferring the packets to the Network layer of the receiver that is receiving.
- It identifies the address of the network layer protocol from the header.
- It also provides flow control.
- Media Access Control Layer
- A Media access control layer is a link between the Logical Link Control layer and the network's physical layer.
- It is used for transferring the packets over the network.
- Logical Link Control Layer
Functions of the Data-link layer
- Framing: The data link layer translates the physical's raw bit stream into packets known as Frames. The Data link layer adds the header and trailer to the frame. The header which is added to the frame contains the hardware destination and source address.

- Physical Addressing: The Data link layer adds a header to the frame that contains a destination address. The frame is transmitted to the destination address mentioned in the header.
- Flow Control: Flow control is the main functionality of the Data-link layer. It is the technique through which the constant data rate is maintained on both the sides so that no data get corrupted. It ensures that the transmitting station such as a server with higher processing speed does not exceed the receiving station, with lower processing speed.
- Error Control: Error control is achieved by adding a calculated value CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) that is placed to the Data link layer's trailer which is added to the message frame before it is sent to the physical layer. If any error seems to occurr, then the receiver sends the acknowledgment for the retransmission of the corrupted frames.
- Access Control: When two or more devices are connected to the same communication channel, then the data link layer protocols are used to determine which device has control over the link at a given time.
7. Define application layer and what are the main protocols used in the application layer?
Application Layer
- An application layer is the topmost layer in the TCP/IP model.
- It is responsible for handling high-level protocols, issues of representation.
- This layer allows the user to interact with the application.
- When one application layer protocol wants to communicate with another application layer, it forwards its data to the transport layer.
- There is an ambiguity occurs in the application layer. Every application cannot be placed inside the application layer except those who interact with the communication system. For example: text editor cannot be considered in application layer while web browser using HTTP protocol to interact with the network where HTTP protocol is an application layer protocol.
Following are the main protocols used in the application layer:
- HTTP: HTTP stands for Hypertext transfer protocol. This protocol allows us to access the data over the world wide web. It transfers the data in the form of plain text, audio, video. It is known as a Hypertext transfer protocol as it has the efficiency to use in a hypertext environment where there are rapid jumps from one document to another.
- SNMP: SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol. It is a framework used for managing the devices on the internet by using the TCP/IP protocol suite.
- SMTP: SMTP stands for Simple mail transfer protocol. The TCP/IP protocol that supports the e-mail is known as a Simple mail transfer protocol. This protocol is used to send the data to another e-mail address.
- DNS: DNS stands for Domain Name System. An IP address is used to identify the connection of a host to the internet uniquely. But, people prefer to use the names instead of addresses. Therefore, the system that maps the name to the address is known as Domain Name System.
- TELNET: It is an abbreviation for Terminal Network. It establishes the connection between the local computer and remote computer in such a way that the local terminal appears to be a terminal at the remote system.
- FTP: FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. FTP is a standard internet protocol used for transmitting the files from one computer to another computer.
8. Which are the two protocols used in transport layer?
The two protocols used in the transport layer are User Datagram protocol and Transmission control protocol.
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- It provides connectionless service and end-to-end delivery of transmission.
- It is an unreliable protocol as it discovers the errors but not specify the error.
- User Datagram Protocol discovers the error, and ICMP protocol reports the error to the sender that user datagram has been damaged.
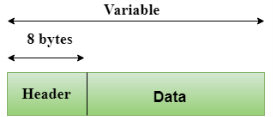
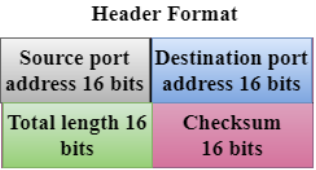
- UDP consists of the following fields:
Source port address: The source port address is the address of the application program that has created the message.
Destination port address: The destination port address is the address of the application program that receives the message.
Total length: It defines the total number of bytes of the user datagram in bytes.
Checksum: The checksum is a 16-bit field used in error detection. - UDP does not specify which packet is lost. UDP contains only checksum; it does not contain any ID of a data segment.
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- It provides a full transport layer services to applications.
- It creates a virtual circuit between the sender and receiver, and it is active for the duration of the transmission.
- TCP is a reliable protocol as it detects the error and retransmits the damaged frames. Therefore, it ensures all the segments must be received and acknowledged before the transmission is considered to be completed and a virtual circuit is discarded.
- At the sending end, TCP divides the whole message into smaller units known as segment, and each segment contains a sequence number which is required for reordering the frames to form an original message.
- At the receiving end, TCP collects all the segments and reorders them based on sequence numbers.
9. Explain some of the Network connecting devices used in computer networks
Hardware devices that are used to connect computers, printers, fax machines and other electronic devices to a network are called network devices. These devices transfer data in a fast, secure and correct way over same or different networks. Network devices may be inter-network or intra-network. Some devices are installed on the device, like NIC card or RJ45 connector, whereas some are part of the network, like router, switch, etc. Let us explore some of these devices in greater detail.
Modem
Modem is a device that enables a computer to send or receive data over telephone or cable lines. The data stored on the computer is digital whereas a telephone line or cable wire can transmit only analog data.
The main function of the modem is to convert digital signal into analog and vice versa. Modem is a combination of two devices −modulator and demodulator. The modulator converts digital data into analog data when the data is being sent by the computer. The demodulator converts analog data signals into digital data when it is being received by the computer.
Types of Modem
Modem can be categorized in several ways like direction in which it can transmit data, type of connection to the transmission line, transmission mode, etc.
Depending on direction of data transmission, modem can be of these types −
- Simplex− A simplex modem can transfer data in only one direction, from digital device to network (modulator) or network to digital device (demodulator).
- Half duplex− A half-duplex modem has the capacity to transfer data in both the directions but only one at a time.
- Full duplex− A full duplex modem can transmit data in both the directions simultaneously.
RJ45 Connector
RJ45 is the acronym for Registered Jack 45. RJ45 connector is an 8-pin jack used by devices to physically connect to Ethernet based local area networks (LANs). Ethernet is a technology that defines protocols for establishing a LAN. The cable used for Ethernet LANs are twisted pair ones and have RJ45 connector pins at both ends. These pins go into the corresponding socket on devices and connect the device to the network.

Ethernet Card
Ethernet card, also known as network interface card (NIC), is a hardware component used by computers to connect to Ethernet LAN and communicate with other devices on the LAN. The earliest Ethernet cards were external to the system and needed to be installed manually. In modern computer systems, it is an internal hardware component. The NIC has RJ45 socket where network cable is physically plugged in.

Ethernet card speeds may vary depending upon the protocols it supports. Old Ethernet cards had maximum speed of 10 Mbps. However, modern cards support fast Ethernets up to a speed of 100 Mbps. Some cards even have capacity of 1 Gbps.
Router
A router is a network layer hardware device that transmits data from one LAN to another if both networks support the same set of protocols. So a router is typically connected to at least two LANs and the internet service provider (ISP). It receives its data in the form of packets, which are data frames with their destination address added. Router also strengthens the signals before transmitting them. That is why it is also called repeater.

Routing Table
A router reads its routing table to decide the best available route the packet can take to reach its destination quickly and accurately. The routing table may be of these two types −
- Static−In a static routing table the routes are fed manually. So it is suitable only for very small networks that have maximum two to three routers.
- Dynamic−In a dynamic routing table, the router communicates with other routers through protocols to determine which routes are free. This is suited for larger networks where manual feeding may not be feasible due to large number of routers.
Switch
Switch is a network device that connects other devices to Ethernet networks through twisted pair cables. It uses packet switching technique to receive, store and forward data packets on the network. The switch maintains a list of network addresses of all the devices connected to it.
On receiving a packet, it checks the destination address and transmits the packet to the correct port. Before forwarding, the packets are checked for collision and other network errors. The data is transmitted in full duplex mode

Data transmission speed in switches can be double that of other network devices like hubs used for networking. This is because switch shares its maximum speed with all the devices connected to it. This helps in maintaining network speed even during high traffic. In fact, higher data speeds are achieved on networks through use of multiple switches.
Gateway
Gateway is a network device used to connect two or more dissimilar networks. In networking parlance, networks that use different protocols are dissimilar networks. A gateway usually is a computer with multiple NICs connected to different networks. A gateway can also be configured completely using software. As networks connect to a different network through gateways, these gateways are usually hosts or end points of the network.

Gateway uses packet switching technique to transmit data from one network to another. In this way it is similar to a router, the only difference being router can transmit data only over networks that use same protocols.
Wi-Fi Card
Wi-Fi is the acronym for wireless fidelity. Wi-Fi technology is used to achieve wireless connection to any network. Wi-Fi card is a card used to connect any device to the local network wirelessly. The physical area of the network which provides internet access through Wi-Fi is called Wi-Fi hotspot. Hotspots can be set up at home, office or any public space. Hotspots themselves are connected to the network through wires.

A Wi-Fi card is used to add capabilities like teleconferencing, downloading digital camera images, video chat, etc. to old devices. Modern devices come with their in-built wireless network adapter.
10. Explain in detail HTTP and its features
- HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol.
- It is a protocol used to access the data on the World Wide Web (www).
- The HTTP protocol can be used to transfer the data in the form of plain text, hypertext, audio, video, and so on.
- This protocol is known as HyperText Transfer Protocol because of its efficiency that allows us to use in a hypertext environment where there are rapid jumps from one document to another document.
- HTTP is similar to the FTP as it also transfers the files from one host to another host. But, HTTP is simpler than FTP as HTTP uses only one connection, i.e., no control connection to transfer the files.
- HTTP is used to carry the data in the form of MIME-like format.
- HTTP is similar to SMTP as the data is transferred between client and server. The HTTP differs from the SMTP in the way the messages are sent from the client to the server and from server to the client. SMTP messages are stored and forwarded while HTTP messages are delivered immediately.
Features of HTTP:
- Connectionless protocol: HTTP is a connectionless protocol. HTTP client initiates a request and waits for a response from the server. When the server receives the request, the server processes the request and sends back the response to the HTTP client after which the client disconnects the connection. The connection between client and server exist only during the current request and response time only.
- Media independent: HTTP protocol is a media independent as data can be sent as long as both the client and server know how to handle the data content. It is required for both the client and server to specify the content type in MIME-type header.
- Stateless: HTTP is a stateless protocol as both the client and server know each other only during the current request. Due to this nature of the protocol, both the client and server do not retain the information between various requests of the web pages.
HTTP Transactions
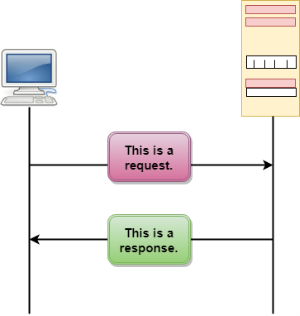
The above figure shows the HTTP transaction between client and server. The client initiates a transaction by sending a request message to the server. The server replies to the request message by sending a response message.
Messages
HTTP messages are of two types: request and response. Both the message types follow the same message format.
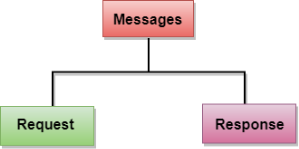
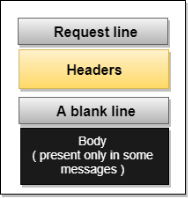
Request Message: The request message is sent by the client that consists of a request line, headers, and sometimes a body.
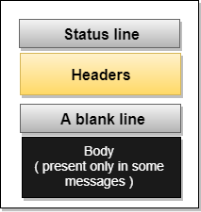
Response Message: The response message is sent by the server to the client that consists of a status line, headers, and sometimes a body.
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
- A client that wants to access the document in an internet needs an address and to facilitate the access of documents, the HTTP uses the concept of Uniform Resource Locator (URL).
- The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is a standard way of specifying any kind of information on the internet.
- The URL defines four parts: method, host computer, port, and path.


- Method: The method is the protocol used to retrieve the document from a server. For example, HTTP.
- Host: The host is the computer where the information is stored, and the computer is given an alias name. Web pages are mainly stored in the computers and the computers are given an alias name that begins with the characters "www". This field is not mandatory.
- Port: The URL can also contain the port number of the server, but it's an optional field. If the port number is included, then it must come between the host and path and it should be separated from the host by a colon.
- Path: Path is the pathname of the file where the information is stored. The path itself contain slashes that separate the directories from the subdirectories and files.