UNIT 1
D.C. Circuits
Q1) Find the current through 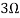 resistance. Using superposition theorem?
resistance. Using superposition theorem?
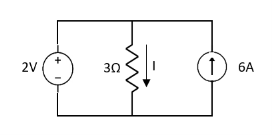
Solution:
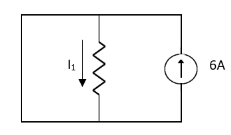
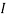 1= 0
1= 0
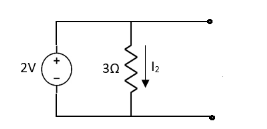
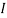 2=
2=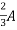
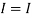 1 +
1 + 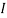 2
2 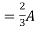
Q2) Find Current I using superposition theorem?
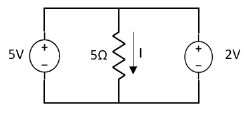
Sol: Since two voltage sources with different magnitude in parallel which cannot be connected as in single branch two different current is not possible (if 5V than I = zero).
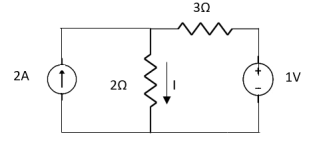
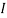 1 =
1 = 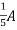
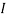 2 =
2 = 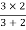
=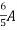
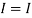 1 +
1 + 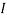 2
2
= 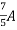
Q3) Find Vth and Rth?
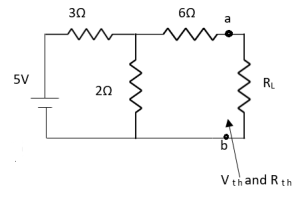
Sol:
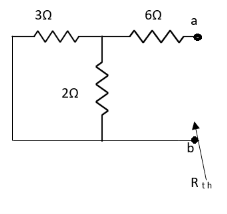
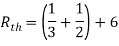
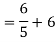
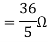
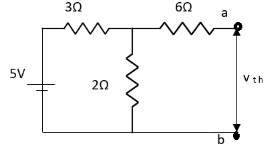
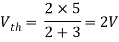
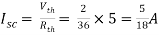
Finding Isc from circuit directly:
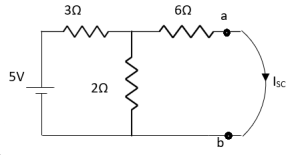
By KCL,
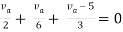
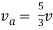
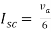
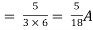
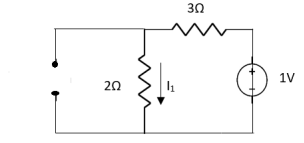
Q4) Find Rth and Vth?
Sol: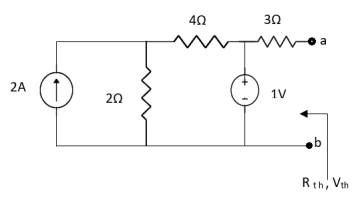
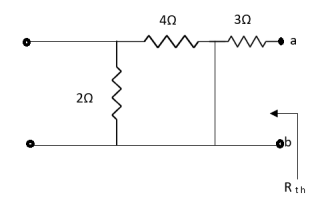
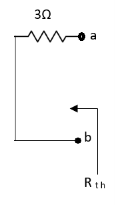
Also, clear from circuit that Vth = 1V.
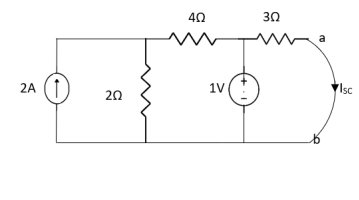
By applying KVL we get,
1-3Isc=0
Isc= A
A
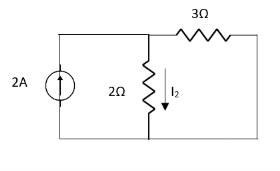
Q5) Find Rth and Isc?
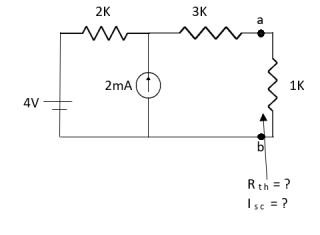
Sol:
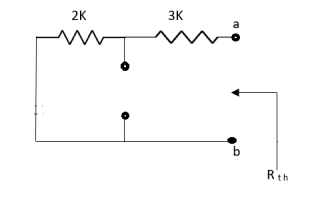
Rth=3k+2k=5k
By applying KVL we get
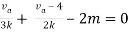
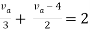
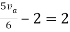
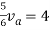
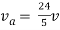
Therefore, 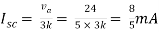
Q6) Find Vx?
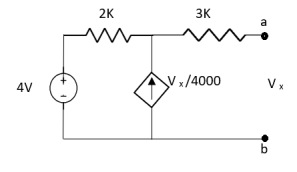
Solution: For Rth
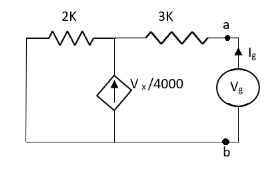
By KCL,
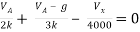
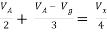
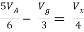
But, 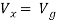
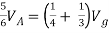
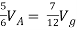
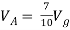
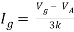
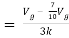
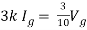
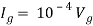
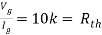
By KVL,
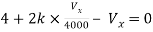
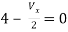
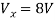
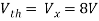
Q7) Find i?
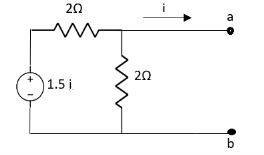
Solution: Since, no independent source is present so,
Isc = 0
And we know that,
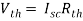
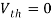
Since Rth cannot be zero
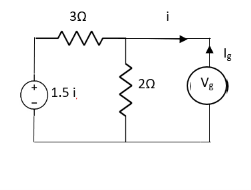
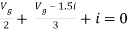
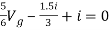
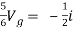
But 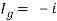
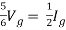
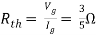
Q8) Find out the Norton’s equivalent
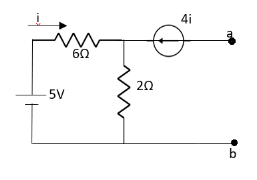
Solution:
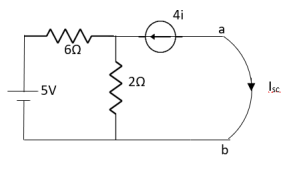
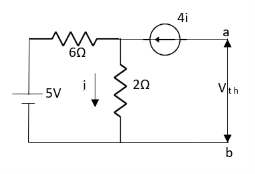
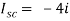
Since, there is no significance of current source
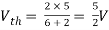
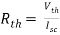
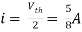
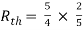
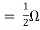
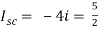 A
A
Q9) For the circuits given below write the voltage equations:
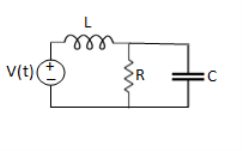
Solution: Let current i1be in loop 1 current and i2 for loop 2
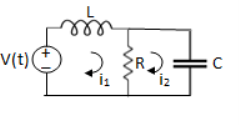
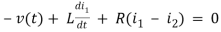
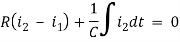
Q10) For the circuits given below write the voltage equations
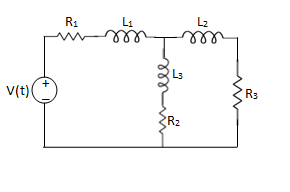
Solution:
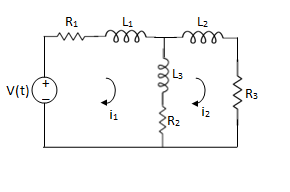
For loop 1
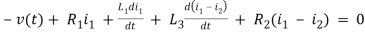
For loop 2
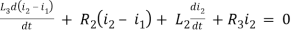
Q11) Using nodal analysis find voltage across 5resistor.
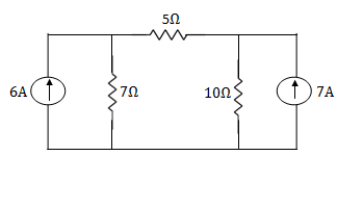
Solution:
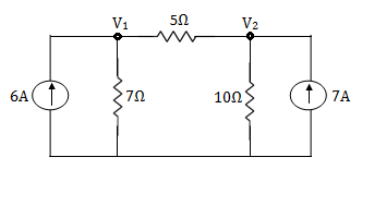
For V1
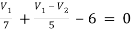
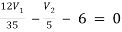
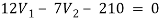 1
1
For V2
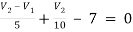
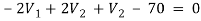
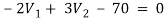 2
2
Solving 1 and 2:
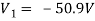
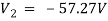
For 5 voltage = 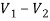
= -50.9 + 57.27
= 6.37V
Q12) Find 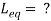
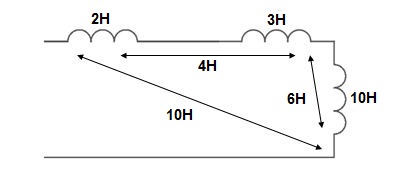
Sol: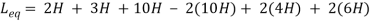
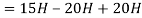
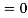
Q12) Find 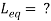
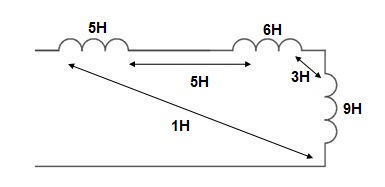
Sol: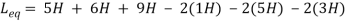
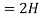
Q13) Use nodal analysis to find current in the circuit?
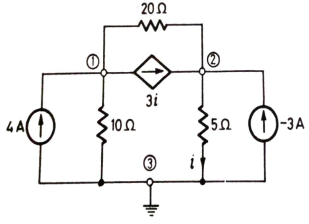
Sol: 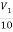 +
+ 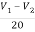 +3i=4
+3i=4
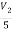 +
+ 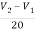 -3i= -3
-3i= -3
But i= 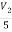
Substituting and solving above equation we get
V2 = 10V
i= 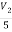 = 2A
= 2A
Q14) Find equivalent resistance R?
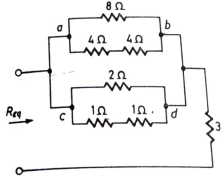
Sol: Equivalent resistance across ab = 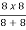 = 4Ω
= 4Ω
Equivalent resistance across cd = 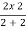 =1 Ω
=1 Ω
Req = Rab||Rcd +3 =  + 3 = 19/5 Ω
+ 3 = 19/5 Ω
UNIT 1
D.C. Circuits
Q1) Find the current through 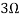 resistance. Using superposition theorem?
resistance. Using superposition theorem?
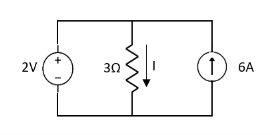
Solution:
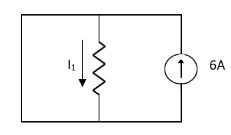
 1= 0
1= 0
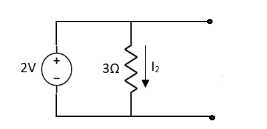
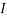 2=
2=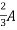
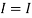 1 +
1 + 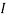 2
2 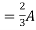
Q2) Find Current I using superposition theorem?
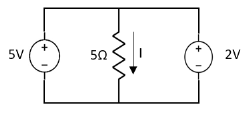
Sol: Since two voltage sources with different magnitude in parallel which cannot be connected as in single branch two different current is not possible (if 5V than I = zero).
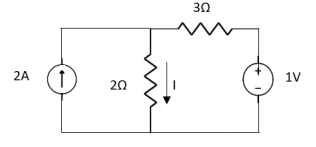
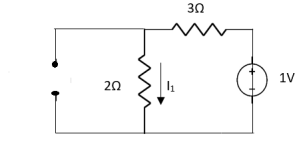
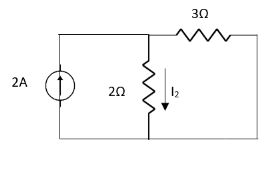
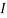 1 =
1 = 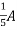
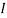 2 =
2 = 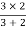
=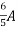
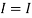 1 +
1 + 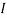 2
2
= 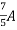
Q3) Find Vth and Rth?
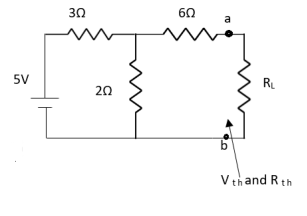
Sol:
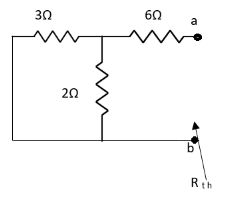
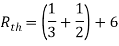
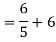
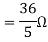
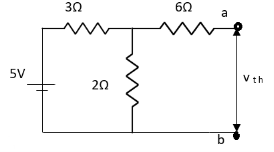
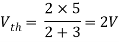
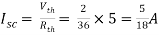
Finding Isc from circuit directly:
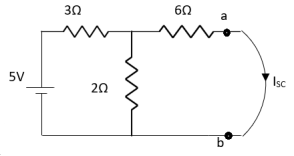
By KCL,
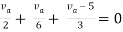
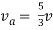
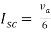
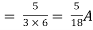
Q4) Find Rth and Vth?
Sol: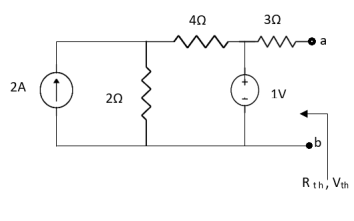
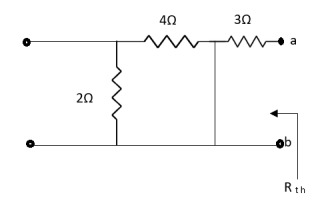
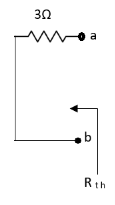
Also, clear from circuit that Vth = 1V.
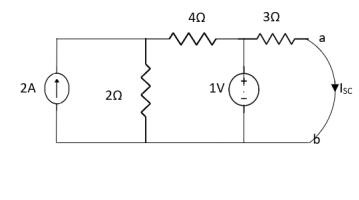
By applying KVL we get,
1-3Isc=0
Isc= A
A
Q5) Find Rth and Isc?
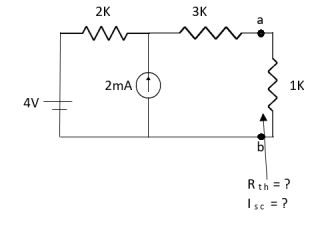
Sol:
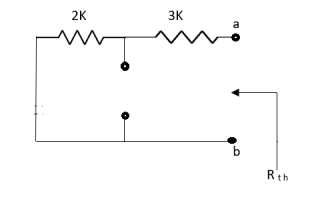
Rth=3k+2k=5k
By applying KVL we get
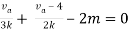
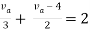
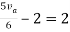
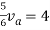
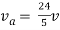
Therefore, 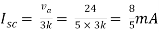
Q6) Find Vx?
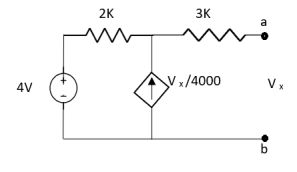
Solution: For Rth
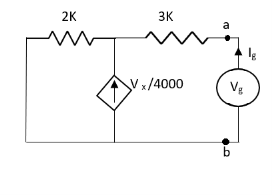
By KCL,
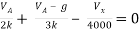
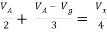
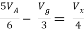
But, 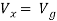
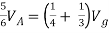
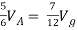
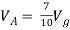
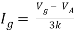
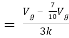
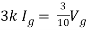
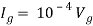
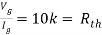
By KVL,
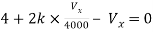
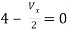
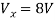
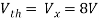
Q7) Find i?
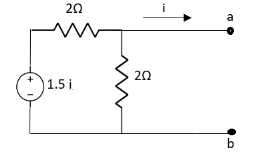
Solution: Since, no independent source is present so,
Isc = 0
And we know that,
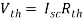
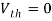
Since Rth cannot be zero
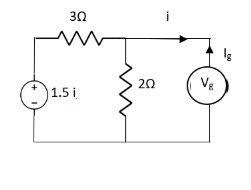
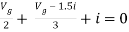
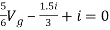
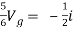
But 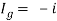
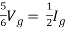
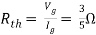
Q8) Find out the Norton’s equivalent
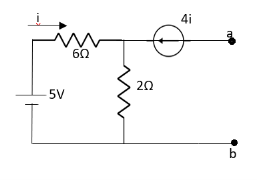
Solution:
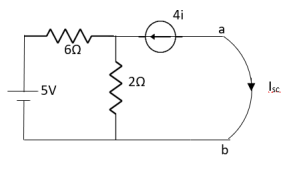
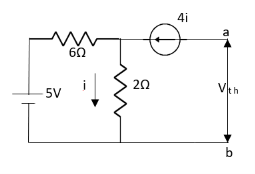
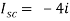
Since, there is no significance of current source
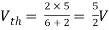
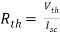
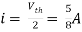
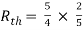
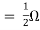
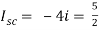 A
A
Q9) For the circuits given below write the voltage equations:
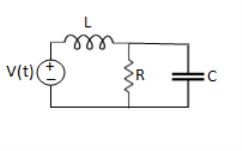
Solution: Let current i1be in loop 1 current and i2 for loop 2
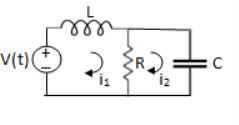
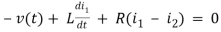
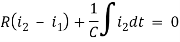
Q10) For the circuits given below write the voltage equations
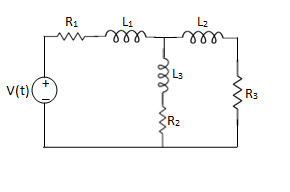
Solution:
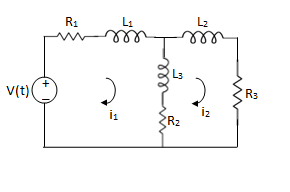
For loop 1
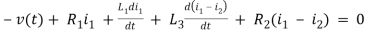
For loop 2
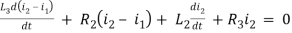
Q11) Using nodal analysis find voltage across 5resistor.
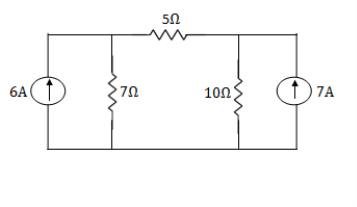
Solution:
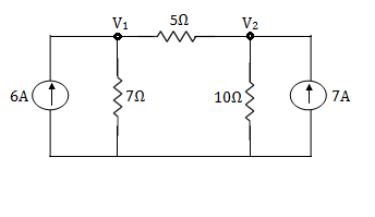
For V1
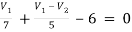
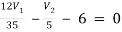
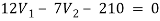 1
1
For V2
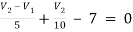
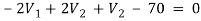
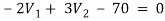 2
2
Solving 1 and 2:
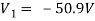
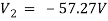
For 5 voltage = 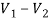
= -50.9 + 57.27
= 6.37V
Q12) Find 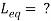
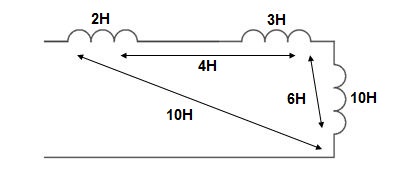
Sol: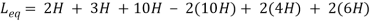
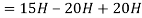
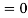
Q12) Find 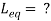
Sol:
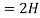
Q13) Use nodal analysis to find current in the circuit?
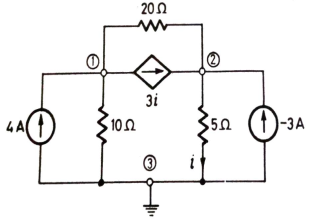
Sol: 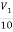 +
+ 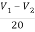 +3i=4
+3i=4
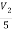 +
+ 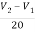 -3i= -3
-3i= -3
But i= 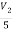
Substituting and solving above equation we get
V2 = 10V
i= 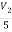 = 2A
= 2A
Q14) Find equivalent resistance R?
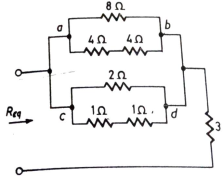
Sol: Equivalent resistance across ab = 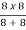 = 4Ω
= 4Ω
Equivalent resistance across cd = 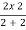 =1 Ω
=1 Ω
Req = Rab||Rcd +3 =  + 3 = 19/5 Ω
+ 3 = 19/5 Ω