Unit - 6
Spillway and Energy Dissipation Device
Q1) What is spillway?
A1)
- It is an arrangement provided at the crest of dam to expel the excess water rises above the full reservoir level.
- This is necessary otherwise water will go on rising even above HFL and will start flowing from top of dam which may affect stability of dam.
- Therefore it is very essential to provides spillway to dispose surplus water on downstream side.
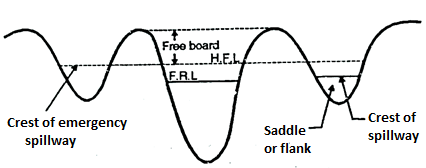
Fig 1: Location of spillway
Definition: The passage provided for disposal of surplus flood water on the downstream side without affecting stability of dam are called as spillways.
Q2) Give the location of spillway.
A2)
Spillway are located at
1. In the body of damn.
2. At one end of the dam.
3. Away from the body of dam independently.
Generally in gravity dam spillways are provided in the body of dam.
Separate spillway is provided in case of earthen dam.
Q3) Which factors affecting spillway capacity?
A3)
The various factors which affect spillway capacity are as follows:
1. Inflow.
2. Capacity of outlet.
3. Possible damage.
4.Available storage capacity.
5. Gates of spillway.
6. Site condition.
7. Type of dam and its purpose.
8. Height of the crest of spillway.
9. Solid material brought by river its nature and amount.
10. Geological condition.
Q4) Explain types of spillway in detail.
A4)
- Emergency Spillway:
- It is provided with an earthen dam. In such spillway part of the length of earthen dam is kept weak above FTL/FRL (Full tank/Reservoir level).
- When abnormal high intensity flood occurs the weaker portion gets washed and flood water flows through that portion which acts as additional spillway and thus avoids possibility of failure of the dam.
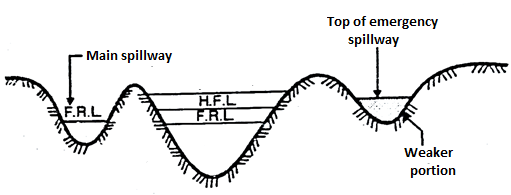
Fig 2: Emergency spillway
The various conditions which may lead to emergency are:
a) When there is mal functioning of spillway gate.
b) When actual flood exceeds the design flood etc.
2. Service Spillways or main spillway
- The service spillways are masonry or concrete structure provided with necessary component. It is necessary for all dams and in most dam it is the only spillway designed to pass design flood.
3. Auxiliary spillway
- This type of spillway is provided so as to supplement the main spillway. It operates only when the design floods in the main spillway is more or exceed.
Q5) Explain gated and un-gated spillway in detail.
A5)
- Gated spillway
Gate are provided over the crest of spillway. It store more water and efficiently and effectively control the outflow from upstream and downstream side.
2. Un-gated spillway or uncontrolled spillway
In such type, no gates are provided over the crest to control the flow and hence it does not need any operation of gate. Surplus flow of water cannot be controlled by un-gated spillway.
Q6) Give classification of spillway based on features.
A6)
1. Oges Spillway
2. Bar Spillway
3. Straight drop spillway or free overfall spillway
4. Side channel spillway.
5. Chute or open channel or trough spillway
6. Shaft spillway or moving glory spillway
7. Siphon spillway
(i) Saddle siphon spillway
(ii) Volute siphon spillway
8. Tunnel spillway
9. Stepped spillway
10. Saddle spillway
Q7) What is ogee spillway?
A7)
Ogee Spillway
The shape of spillway is ogee or S shaped. The main difference between free overfall spillway and ogee spillway is that case of free overfall spillway water flowing over the crest of spillway drops vertically as freeset where in ogee shaped spillway water is guided smoothly over the crest and is made to guide over the downstream face of the spillway.
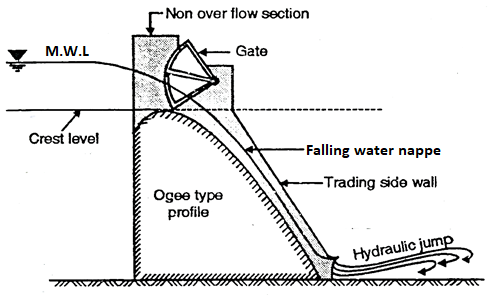
Fig 3: Ogee-spillway
Q8) What is bar spillway?
A8)
Bar Spillway
- It consists of rectangular masonry concrete bar with crest width1 to 1.5 m.It is low height spillway, founded on concrete block, rest on hard rock foundation sometime precast concrete blocks are used for coping of the crest.
- The top of crest is at FRL.
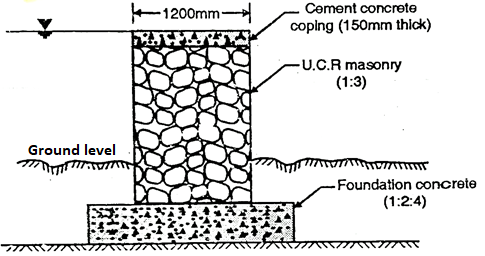
Fig 4: Bar channel Spillway
Q9) Explain vertical drop spillway.
A9)
Straight drop spillway or free overfall spillway or Vertical drop Spillway
Definition: The spillway in which the flow drops freely from the crest is called as straight drop spillway or free overfall spillway. Such type of spillway is not suitable for high drops.
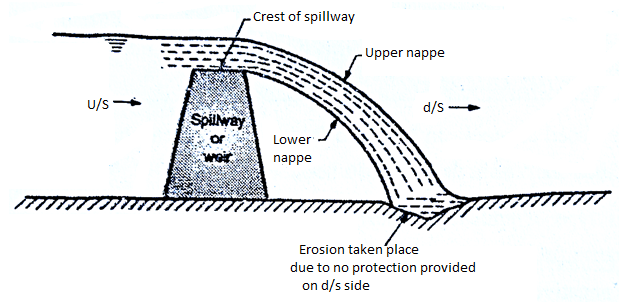
Fig 5: Straight drop spillway without protection on downstream side

Fig 6: Straight drop spillway provided protection on downstream side
Three provisions or Methods to avoid erosion on the d/s side
1. An artificial pool can be created by constructing a low auxiliary dam downstream of the main structure.
2. By excavating a basin which is then provided with a concrete apron.
3. Floor blocks and an end sill can be provided as shown in Fig., to help in the establishment of the jump and thus reduces the d/s scour.
If tailwater depths are sufficient, then a hydraulic jump forms when jet falls freely from the crest, in such case, a long flat concrete apron may be provided.
Q10) What is side channel spillway?
A10)
Side channel spillway
When it is not possible to use overfall spillway especially in embankment dams, then side channel spillway is more suitable. In such type of spillway, water flow after passing over the crest is further conveyed in the side channel which running parallel to the crest as shown in Fig.
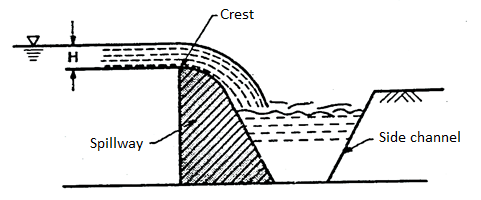
Fig 7: Side channel spillway
This type of channel is preferred under following situations:
(i) It is adopted in case of a long overflow crest provided to limit the surcharge head.
(ii) It is adopted or preferred when the control structure is to be joined to a narrow discharge channel.
(iii) It is preferred when the abutments are very steep.
Q11) Explain chute and shaft spillway.
A11)
Chute Spillway or Trough Spillway
- In case of concrete gravity dams, when the spillway is located within the dam body in the same valley, then an ogee spillway is more suitable.
- However in case of earthen dam or rock fill dams, a separate spillway and but away from main valley is generally constructed in a saddle or in a flank.
- Even in case of gravity dam, if the main valley is narrow, then a separate spillway is required to be provided.
- In such situation, a separate spillway like chute spillway or trough spillway is the best option because this type of spillway is a simplest type, lighter and suitable for any type of foundation. In addition to this, it can be easily constructed and provided independently with low cost. Chute spillway or trough spillway can easily be provided on earth fill dam and rock fill dam. Chute spillway is sometimes termed as a waste weir.
Shaft spillway or morning glory spillway
This type of spillway consists of a vertical flaring funnel act as the crest of the spillway and its bottom end connected to the shaft either vertical or inclined which is further connected at its lower and to a horizontal tunnel extending through or around the dam as shown in Fig. The water flow passes though tunnel is taken to the downstream river channel.
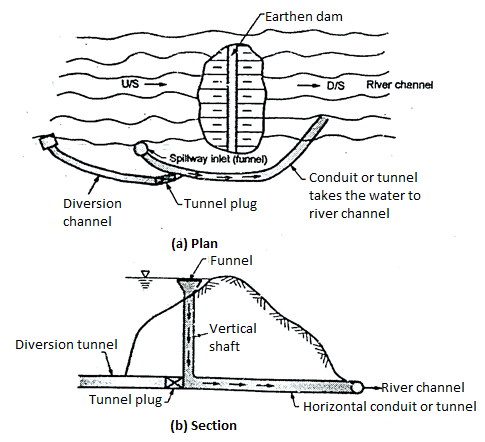
Fig 8: Shaft spillway
Q12) Explain siphon and tunnel spillway.
A12)
Siphon spillway
- This type of a spillway is more suitable when the discharge to be carried is not large and available space is small or limited.
- The siphon spillway automatically maintain the water surface elevation in the dam within the limited range by siphonic action.
- It consist of a closed U-shaped inverted conduit provided with the inlet, short upper leg and throat portion. Siphon spillway taken the water from upstream side of dam to the downstream side of the dam by the principle of siphonic action. Fig. Shows siphon discharging freely.
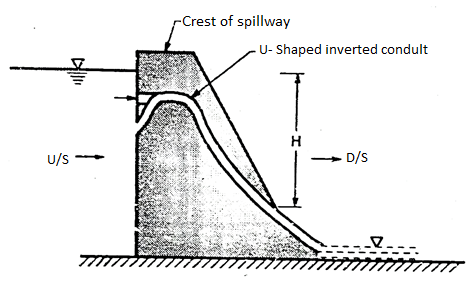
Fig 9: Siphon spillway
Tunnel spillway
- Definition: The tunnel spillway in which discharge of water can be conveyed by a closed channel around or under the dam. It is also called as conduit spillway.
- The closed channel can be in the form of the vertical shaft or inclined shaft or in the form of a horizontal tunnel.
- This type of spillway is designed so as to flow partly full because full flow due to siphonic action which may develop the negative pressure. In order to maintain free flow, the ratio of area of flow to the total conduit area is often limited to about 75 %. So as to avoid also unsteady flow through spillway, air vents are also provided at various critical points and junction.
Q13) Explain stepped and saddle spillway.
A13)
Stepped spillway
This type of spillway has been used for over 3000 years. Now a days new construction material like RCC gabions and design technique have increased the interest of stepped spillways and chutes. The steps in spillway produce considerable energy dissipation along chute.
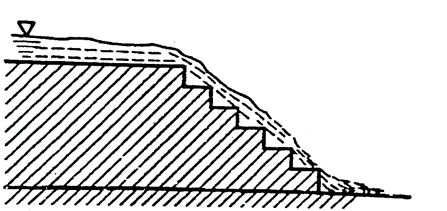
Fig 10: Stepped Spillway
Saddle spillway
- There may be one or more natural depressions or saddles providing spillway in some basins formed by a dam.
- A site which has a saddle is very desirable and economical, if the saddle is suitable for locating the spillway.
- Fig. shows saddle spillway. This type of spillway are constructed when any of the above type of spillway is not possible. It is usually necessary for the saddle to be on firm rock.
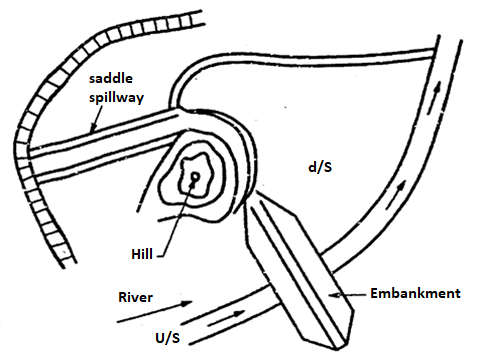
Fig 11: Saddle spillway