Unit - 1
Introduction to LTI elements
Q1) Write equation for given waveform
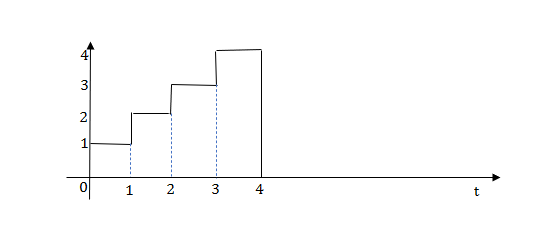
A1)
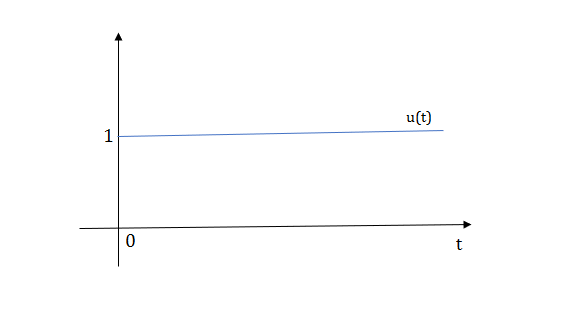
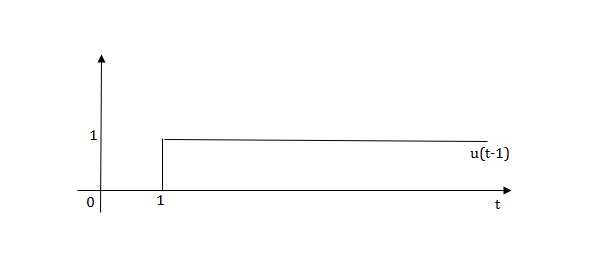
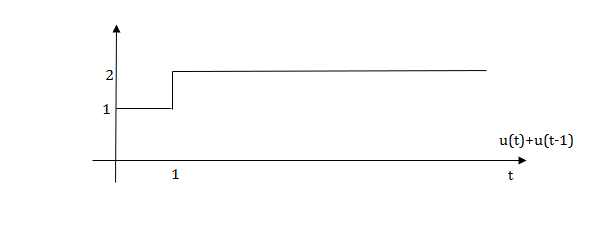
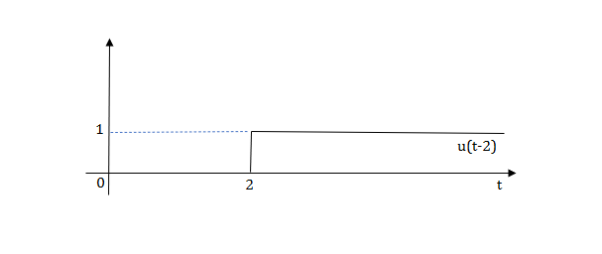
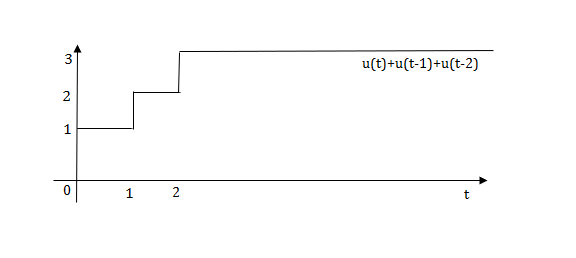

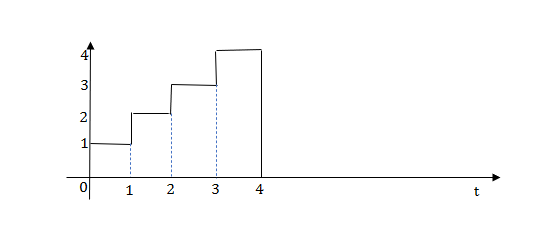
The final equation is=u(t)+u(t-1)+u(t-2)+u(t-3)-4u(t-4)
As the waveform is stopped at t=4 with amplitude 4,so we have to balance that using -4u(t-4).
Q2) Write the equation for the given waveform?
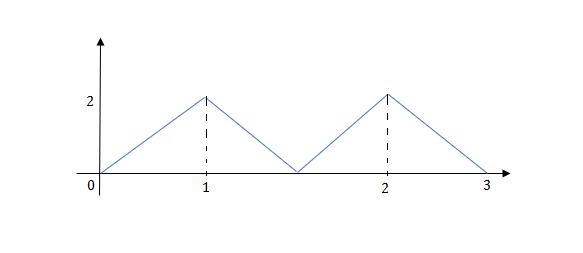
A2) Calculating slope of above waveform
Slope for (0,0) and (1,2)
a1 slope=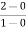 =2
=2
a2 slope=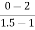 =-4
=-4
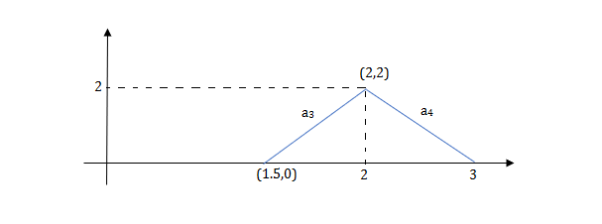
a3 slope =4 and a4= -2

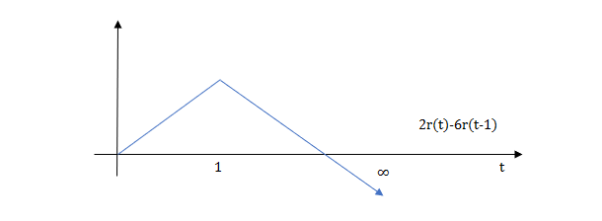
At t=1 slope changes from 2 to -4 so we need to add -6r(t-1) to 2r(t) to get the slope of -4.
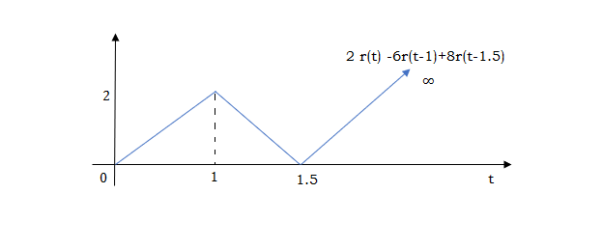
At t=1.5 slope changes from -4 to 4 so adding 8r(t-1.5) to get slope of 4
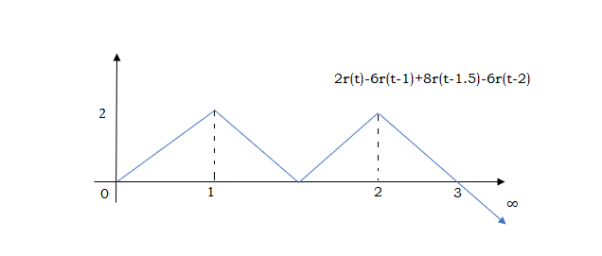
At t=2 slope changes from +4 to -2 so we add -6r(t-2). But we need to stop the waveform at t=3. Hence, we have to make slope 0. Which can be done by adding +2r(t-3). Final equation is given as 2r(t)-6r(t-1.5) +8r(t-1.5)-6r(t-2) +2r(t-3)
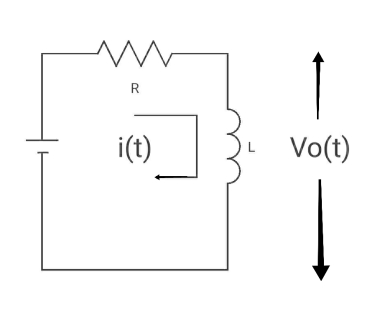
Q3) For given RL circuit find the differential equation for current i?
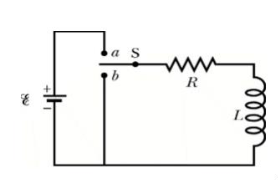
Fig: Series RL circuit
A3)
After switch is closed applying KVL
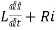 =0
=0
This is first order homogeneous differential equation so
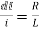 dt
dt
Integrating both sides
Ln i=  t+K
t+K
Taking antilog of both sides
i=k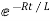
At t=0
i(0)= =I0
=I0
 =ke0
=ke0
The particular solution is given as
i= 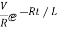 for t≥0
for t≥0
= for t<0
for t<0
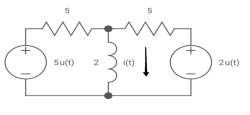
Q4) Find IL(0) for the given circuit below
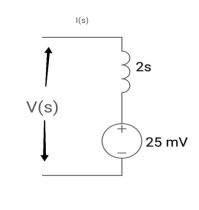
A4) From above circuit
L = 2H
LiL (0) = 25 mv
IL (0) = 12.5 m A
Q5) Find value across capacitor?
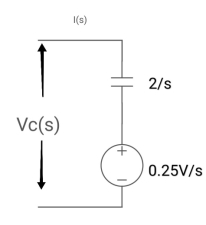
A5) From above circuit we can write
1/cs = 2/s
C=1/2f
Vc (0)/s = 0.25v/s
Vc(0)= .25v
Q6) Find voltage across capacitor?
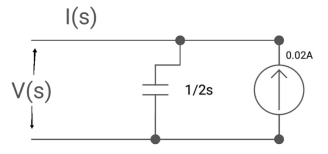
A6) 1/cs = 1/2S
C=2F
CVc (0) = 0.02
Vc(0)= 0.01V
Q7) For the following circuit shown below
(a) switch is at before moving to position = at t= 0, at t= 0+, i1(t) is
(a) –V/2R (b) –V/R (c) – V/4R
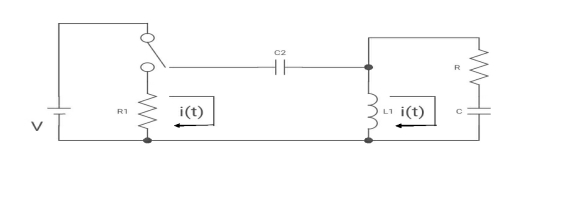
A7)
I1(t) L.T I1(s)
I2(t) L.T I2(s)
Then express in form
[ I1(s)/I2(s)] [::] = [:]
Drawing the ckl at t = 0-
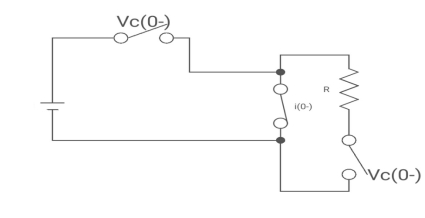
:. The capacitor is connected for long
Vc1(0-)= V
iL(0-) =0
Vc2(0-)=0
At t= 0+
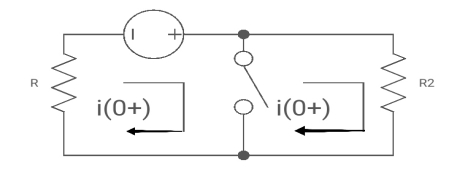
i1 (0+) = -V/2R
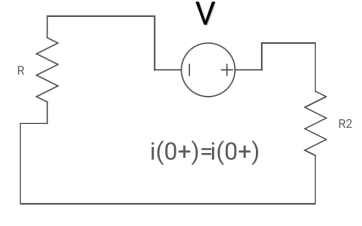
For t>0 the circuit is
Apply KVL
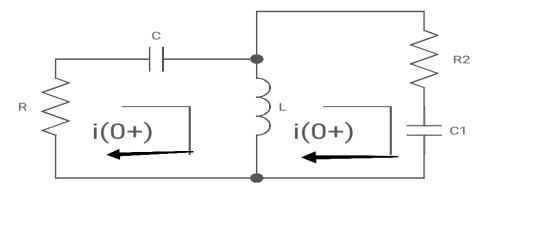
-R i1(t) -1/c  dt -L
dt -L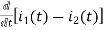 =0
=0
Also, we can deduce i1(t)- i2 (t) = iL(t)
-Ri1(t) -1/c  - L
- L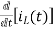 = 0
= 0
-RI1(s)-[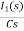 -
- ]-L[sI1(s)-iL(0-)]=0
]-L[sI1(s)-iL(0-)]=0
- RI1(s)-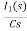 -
- 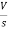 -s L I2(s)=0
-s L I2(s)=0
 - s L I2(s)= -
- s L I2(s)= - 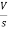 (1)
(1)
Again
-Ri2(t) ) -1/c 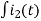 dt -L
dt -L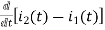 =0
=0
-Ri1(t) -1/c 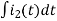 - L
- L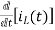 = 0
= 0
Taking Laplace Transform
-RI2(s)- [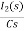 -
-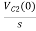 ]- L[s IL(s)- iL(0-)]=0
]- L[s IL(s)- iL(0-)]=0
-RI2(s)- 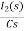 -
- Ls[ I1(s)- I2(s)]=0
Ls[ I1(s)- I2(s)]=0
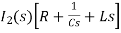 - s L I1(s)=0 (2)
- s L I1(s)=0 (2)
Hence in matrix representation
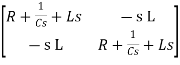
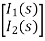 =
= 
Q8) All initial conditions are zero i(t) L.T, I(s), then find I(s)?
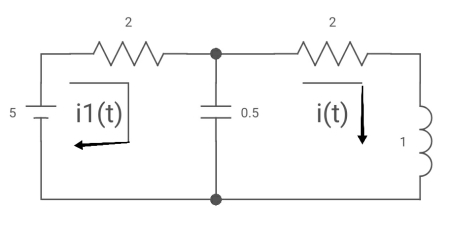
A8) Drawing Laplace circuit
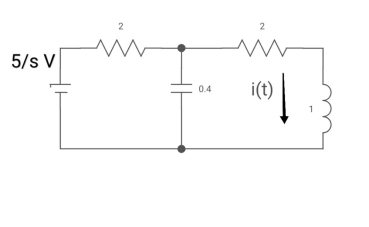
(2+S) 11 2/S
Zeq = [(2+S)2/S]/[2+S+2/S]=[2(S+2)]/[S2+2s+2]
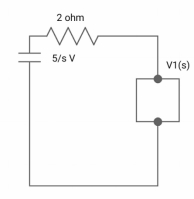
V1(s) = [5/S{2(S+2)/S2+2S+2}]/[2+{2(S+2)/ S2+2S+2}]
V1(s) = [5(S+2)/S]/[S2+ 3S +4]
I(s) = V1(s)/(S+2) = (5/S)/(S2+35+4)
Q9) The switch is at before moving to position = at t= 0, at t= 0+, i1(t) is
(a) –V/2R (b) –V/R (c) – V/4R (d) 0
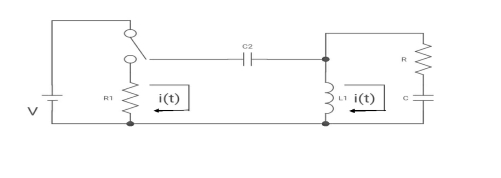
A9)
I1(t) L.T I1(s)
I2(t) L.T I2(s)
Then express in form
[ I1(s)/I2(s)] [::] .[:]
Drawing the ckt at t = 0-
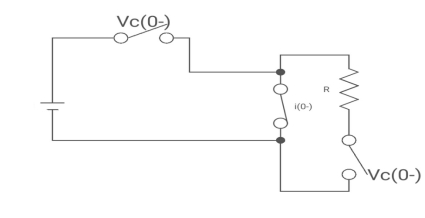
:. The capacitor is connected for long
Vc1(0-)= V
iL(0-) =0
Vc2(0-)=0
At t= 0+
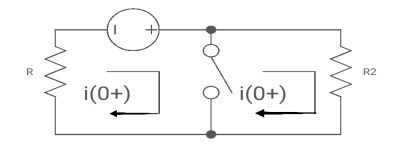
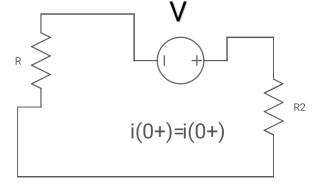
Fig: Circuit at t=0+
i1 (0+) = -V/2R
For t>0 the circuit is
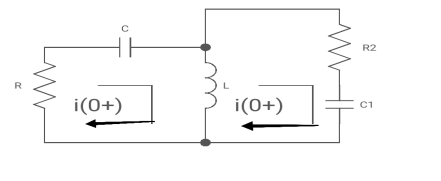
Fig: KVL in Circuit
Apply KVL
-R i1(t) -1/c 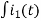 dt -L
dt -L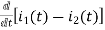 =0
=0
Also, we can deduce i1(t)- i2 (t) = iL(t)
-Ri1(t) -1/c 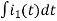 - L
- L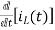 = 0
= 0
-RI1(s)-[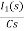 -
-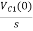 ]-L[sI1(s)-iL(0-)]=0
]-L[sI1(s)-iL(0-)]=0
- RI1(s)- -
- 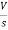 -s L I2(s)=0
-s L I2(s)=0
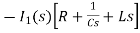 - s L I2(s)= -
- s L I2(s)= - 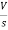 (1)
(1)
Again
-Ri2(t) ) -1/c 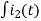 dt -L
dt -L =0
=0
-Ri1(t) -1/c 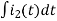 - L
- L = 0
= 0
Taking Laplace Transform
-RI2(s)- [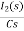 -
- ]- L[s IL(s)- iL(0-)]=0
]- L[s IL(s)- iL(0-)]=0
-RI2(s)- 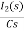 -
- Ls[ I1(s)- I2(s)]=0
Ls[ I1(s)- I2(s)]=0
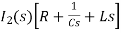 - s L I1(s)=0 (2)
- s L I1(s)=0 (2)
Hence in the matrix representation
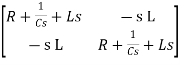
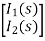 =
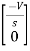
= 
Q10) All initial conditions are zero i(t) I(s), then find I(s)?
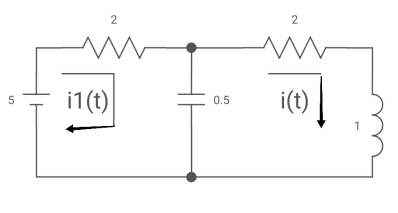
A10) Drawing Laplace circuit
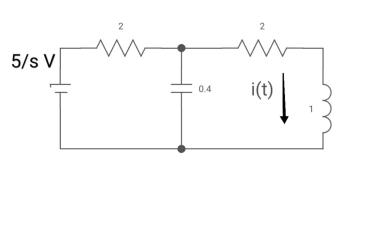
(2+S) 11 2/S
Zeq = [(2+S)2/S]/[2+S+2/S]=[2(S+2)]/[S2+2s+2]
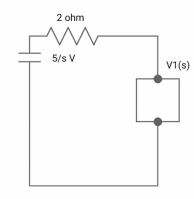
V1(s) = [5/S{2(S+2)/S2+2S+2}]/[2+{2(S+2)/ S2+2S+2}]
V1(s) = [5(S+2)/S]/[S2+ 3S +4]
I(s) = V1(s)/(S+2) = (5/S)/(S2+35+4)
Q11) There is no initial energy stored in this circuit. Find i1(t) and i2(t) for t>0?
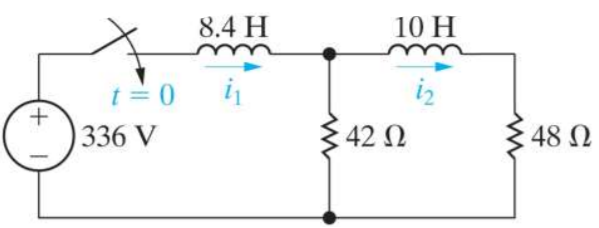
A11)
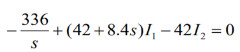
When circuit is closed the network is shown
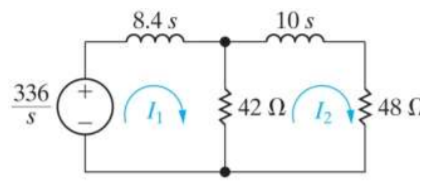
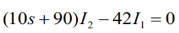
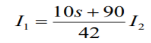


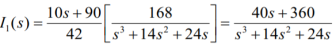
Q12) Find v0 (t) for t > 0.
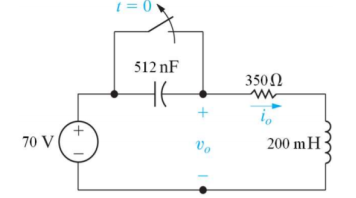
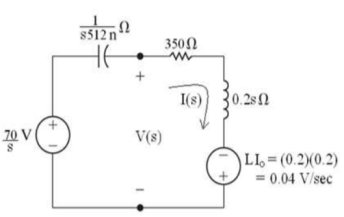
A12) Taking Laplace transform of above circuit we have,

Q13) There is no initial energy stored in this circuit. Find vo if ig = 5u(t) mA.
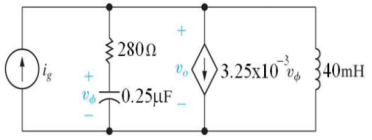
A13) Laplace Transform of above circuit we get
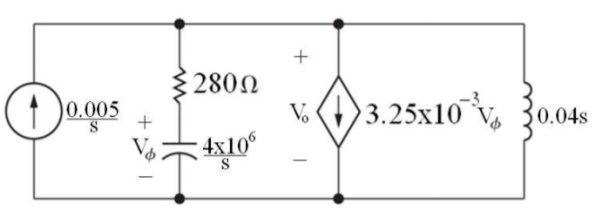

By voltage division we get
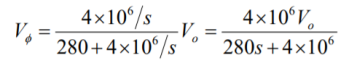
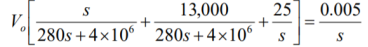
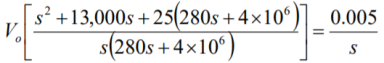
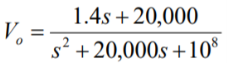
Q14) Find value of current i(t) for the given circuit?
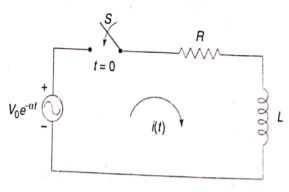
A14)
Applying KVL we get
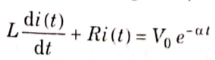
Taking Laplace transform of above equation we get
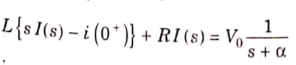
There is no initial current in inductor before closing the switch so i(0+)=0.
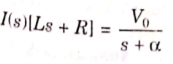
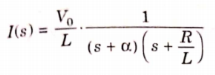
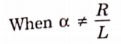
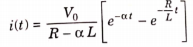
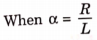
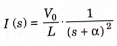
Taking ILT we get

Q15) For the circuit shown below find the value of i1(t) and i2(t) and output voltage across 5 Ohm resistor when the switch is closed also find initial and final values of current?
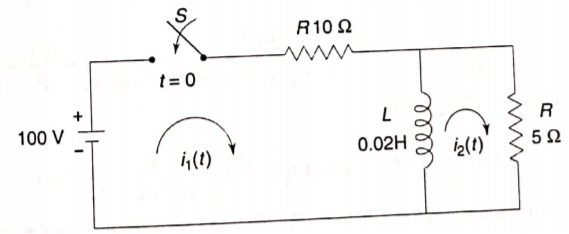
A15) By KVL we have
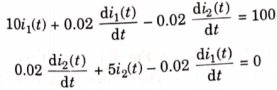
Taking LT of above equations, we get
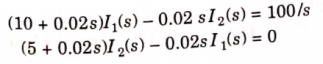
Solving above equation we get
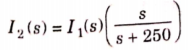
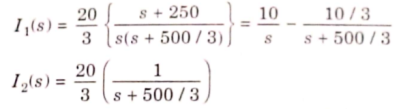
By inverse Laplace transform we get
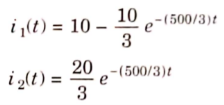
The voltage across 5 Ohm resistor is

The initial value of i1(t) is

The final value of i2(t) is

The initial value of i2(t) is
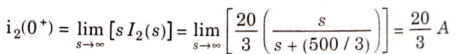
The Final value of i2(t) is

Q16) Find the inverse Laplace transform of
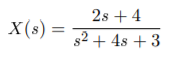
A16)
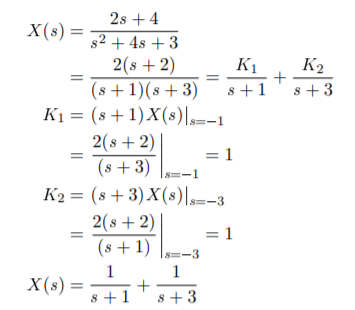
We know that
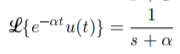
Hence,
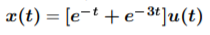
Q17) Find inverse Laplace transform of
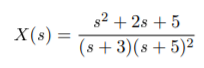
A17)

Taking inverse Laplace of above we get
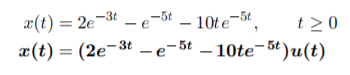
Q18) Find Inverse Laplace transform of
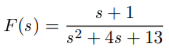
A18)
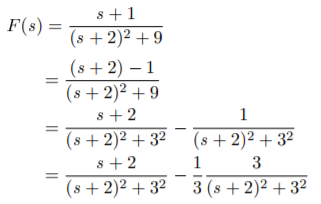

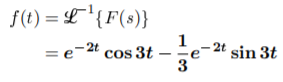
Q19) Find Inverse Laplace Transform of

A19)
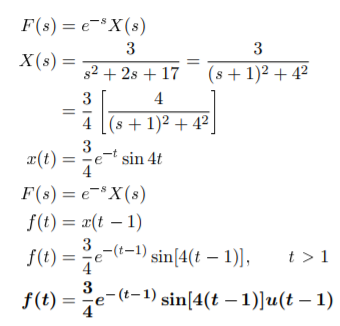
Q20) Write equation for initial and final value theorem?
A20) The initial value theorem

This theorem is valid if and only if f(t) has no impulse functions.
The final value theorem
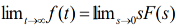
This theorem is valid if and only if all but one of the poles of F(s) are in the left-half of the complex plane, and the one that is not can only be at the origin.
Q21) V0 (t) = ? t =o if capacitor is uncharged?
A21) We know i(t) = i( )+[ i(0)- i(
)+[ i(0)- i( )]
)]
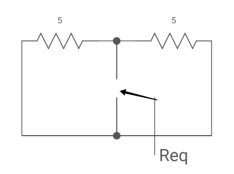
Req = R1R2 /R1+R2=(5x5)/(5+5)=5/2ohm
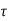 =L/Req=4/5 sec
=L/Req=4/5 sec
i(0)=0
i(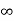 )=u(t)+
)=u(t)+ u(t)=1.4u(t)
u(t)=1.4u(t)
i(t)=1.4[1-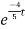 ]u(t)
]u(t)
Q22) Find Vo(t) for the circuit below?
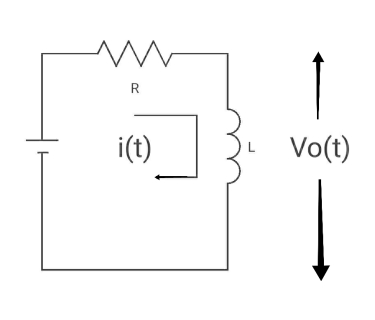
A22)
Time constant 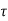 =L/Req = L/R
=L/Req = L/R
V (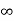 ) = 0, V (0) =VR (supply voltage)
) = 0, V (0) =VR (supply voltage)
i (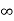 ) = VR/R, i(0) =0
) = VR/R, i(0) =0
By KVL,
VR=i(t) R + L di/dt(t)
On solving
V0(t)= VR e-tR/L
Q23) In network below switch is moved from 1 to 2 at t=0 a steady state is achieved already. Fond capacitor voltage Vc(t) and current i(t) through 200Ω?
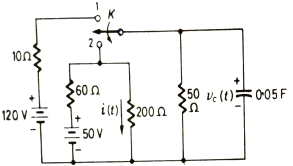
A23) The Voltage across capacitor is given by
Vc(t)= K1+K2 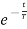
The steady state is reached when t= the above equation becomes
the above equation becomes
Vc(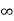 )= Lt t-->
)= Lt t-->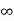 K = K1
K = K1
At t=0
Vc(0)= K1+K2
K2= Vc(0)- Vc(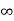 )
)
The final response for the circuit is given as
Vc(t)= Vc(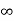 )-[Vc(
)-[Vc(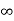 )-Vc(
)-Vc( )]
)]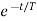
When switch is at position 1
Vc(0)= 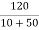 x 50 = 100V
x 50 = 100V
So, voltage of capacitor at t=0 and t=0+ will remain same.
TO find Req we replace voltage source by short circuit
Req = 60||200||50 = 24 Ω
The time constant will be T = ReqC = 24x0.05 = 1.2sec
Switch at position 2
The steady state voltage across capacitor is given by
 =
= 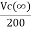 +
+ 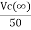
Vc(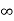 ) = 20V
) = 20V
The complete response will be
Vc(t)= Vc(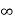 )-[Vc(
)-[Vc(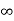 )-Vc(
)-Vc(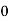 )]
)]
Vc(t)= 20 –[20-100]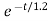
Vc(t)= 20+ 80 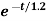
The value of current at switch position 1
I= 50/(200+60) = 0.192A
When switch is at 2
i(0+) = 100/200= 0.5A
i(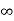 ) = Vc(
) = Vc(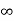 ) /200 = 0.1A
) /200 = 0.1A
The complete response of current is
i(t)= i(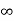 )-[i(
)-[i( )-i(
)-i(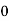 )]
)]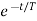
i(t)= 0.1-[0.1-0.5]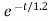
i(t)=0.1+0.4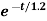
Q24) Find the value of V0(t) for circuit below?
A24)
Time constant, c= L/Req = L/R
V(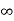 ) = 0
) = 0
V(0) = VR
i( ) = VR/R
) = VR/R
i(0) =0
By KVL,
VR=i(t) R + L di/dt(t)
On solving
V0(t)= VR e-tR/L
Q25) Find iL(t) for the circuit below. For t>0?
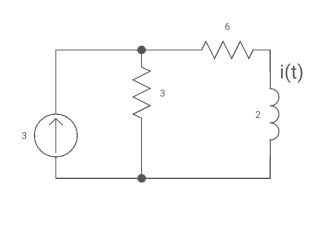
A25) The circuit for Req will be
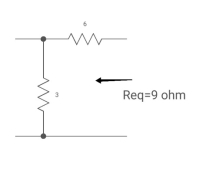
Req = 6+3
= 9ohm
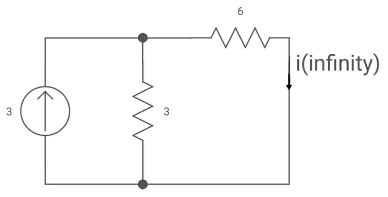
T= L/Req = 2/9 sec
i(0) =0
i( ) = 3*3/6+3 = 1A
) = 3*3/6+3 = 1A
i(t) = 1 [1-e4.5t]
Q26) Capacitor is initially uncharged find Vc (t); t >0
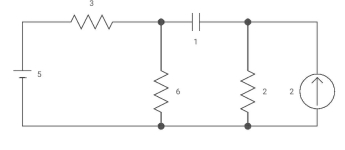
A26)
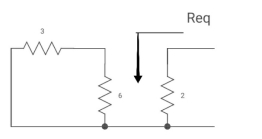
Req = (3116)+2
=2+2 = 4ohm
T= C Req= 2 sec
Clearly Vc(0) =0
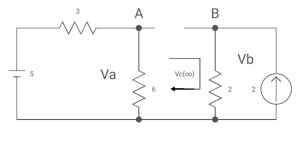
By voltage divides, VA = 5*6/3+B = 30 v/9
Clearly by ohms low
VB = 2*2 = 4v
Apply KVL, VA-Vc-VB =0
Vc(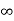 ) = 30/9 – 4 = -2/3 V
) = 30/9 – 4 = -2/3 V
Vc (t) = -2/3 [1- e0.25t]
CURVE:
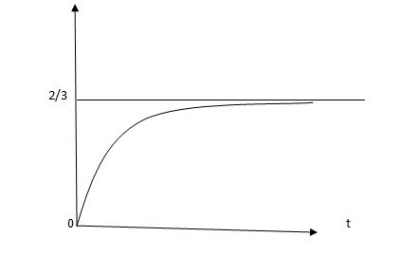
Vc(t) =2/3 [1-e-0.5t]
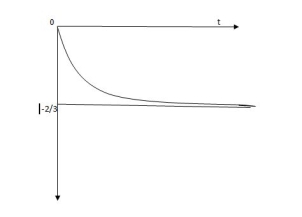
Vc(t) = -2/3 [1-e-0.5t]
Q27) Find i(t) for the given circuit below?
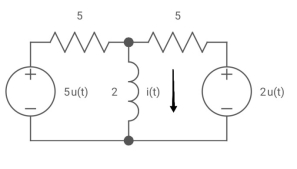
A27) We know i(t) = i ( ) +[i(0)- i(
) +[i(0)- i( )] e-t/T
)] e-t/T
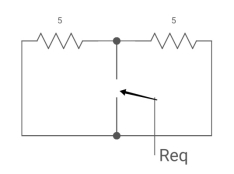
Req = 5*5/5+5 = 5/2 ohm
T=L/Req = 4/5 sec
Also
i(0) =0
i( ) = u(t) +2/5 u(t)
) = u(t) +2/5 u(t)
i(t) = 1.4 [1-e-5/4t)]u(t)
Q28) If switch ‘s’ closed for long time before opening at t=0-. Find Vx (0+)?
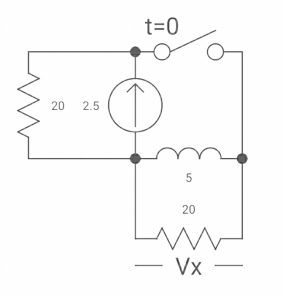
A28) At t= 0- switch was closed,
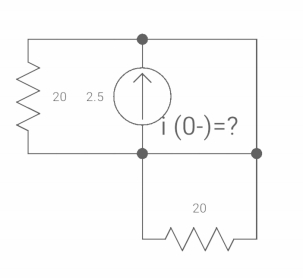
iL(0-) = 2.5A
At t= 0+
Inductor is initially charged so iL(0-) = iL(0+)
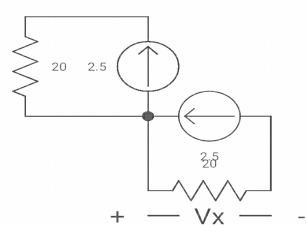
-Vx = 20x2.5
Vx = -50A
Q29) Find VR(0+) and dil/dt(t) = 0+ If switch is opened at t= 0?
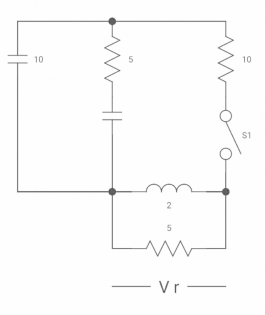
A29) At time t=0-
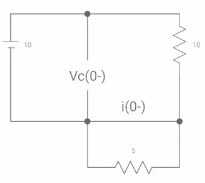
Vc(0-) = 10V
IL(0-) = 10/10 = 1 A
Also, iL(0-) = iL(0+) = 1A
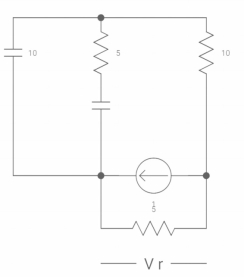
VR(0+) = 5V
Ldi(t)/dt = VL (t)
DiL(t)/dt = VL(t)/L
At t= 0+
d iL (0+) /dt = VL(0+)/L
-VL (0+)-VR =0
VL (0+) = -5V
DiL(t)/dt at t=0+
VL(0+)/L =-5/2
Dil/dt(o+) = 2.5 A/s
Q30) Find Vc(o+) and iR (o+) it switch‘s’ is closed at t=0?
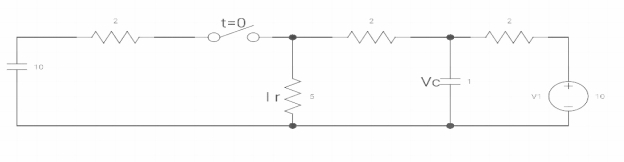
A30) At t=0-
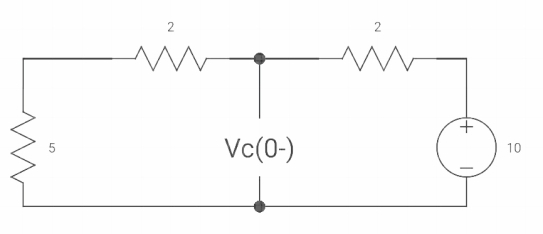
When switch opened at t=0
As capacitor is fully charged so acts as open circuit
Vc (0-) = 7*10/7+2 = 70/9v
At t=0+
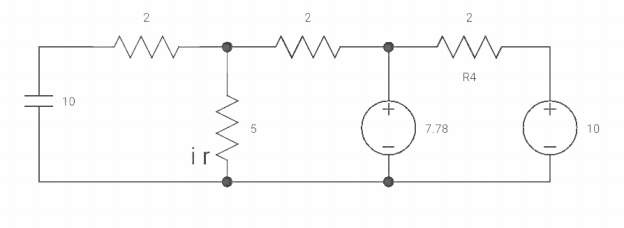
At t=0+ circuit
Vc(0+) = Vc (0) = 40/9v
By applying kcl at A,
VA-10/2+ VA/5+VA-7019/2 =0
VA [1/5+1/2+1/2] = 5+35/9
Va [6/5] = 80/9
Va= 400/54v
IR (0+) = Va/5 = 400/54*5 = 80/54 A
Q31) Find diL(t)/dt and dVc(t)/dt at t=0+. If switch is opened at t=0?
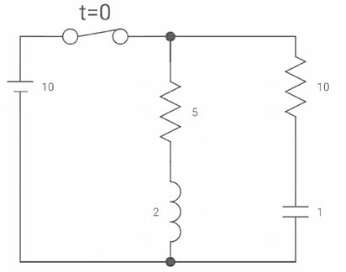
A31) At t=0-

Switch closed for long
Vc(0-) =10V = Vc(0+)
iL(0-) = 2A
DiL(t)/dt = VL(t)/L
At t=0+
DiL(0+)/dt = VL(0+)/L
Similarly, C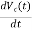 = ic(t)
= ic(t)
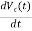 = ic(t)/C
= ic(t)/C
At t=0+
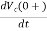 = ic(0+)/C
= ic(0+)/C
ic(0+) = -2A