Unit - 3
Transmission systems
Q1) What is transmission system?
A1)
It is the mechanism which transmits the power to the driving wheels which is developed by the engine of an automobile. It is also called Power Train. It constitutes:
• Tyres
• Propeller shaft
• The gear box
• Wheel
• Rear axle
• Universal joints
• Clutch
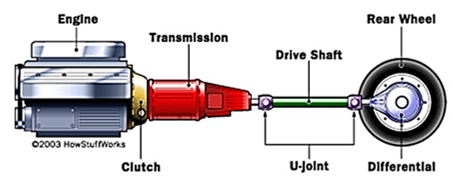
Fig 1. Components of Transmission system.
Q2) What is requirement of transmission system?
A2)
Requirements: -
• It can sustain the consequence of torque forces, driving thrust and braking force efficiently.
• It provides means to drive the driving wheels at dissimilar velocities when necessary.
• It enables flow of power at 90 (right) angles.
• It must enable transmission of power at different angles and lengths.
• It enables speed reduction between engine and the drive wheels in the ratio of 5:1.
• It offers ways to transmit power in opposed direction.
• It provides a varied leverage between the engine and the drive wheels
• It offers linking and de-linking of engine with other members of power train effortlessly and devoid of shock.
The main units of the transmission system according to the above requirements are as follow:
• Clutch
• Propeller Shaft and Universal Joints.
• Gear Box
• Transfer Case
• Final Drive
• Differential
• Torque Tube
• Road Wheel

Fig 2. Main units of Transmission System.
Q3) What is clutch?
A3)
- In phrases of mechanical engineering, a grab is that sort of tool which utilized by engineers to interact in addition to disengage transmission of electricity from a using shaft to a pushed shaft.
- In the mechanism of a grab, the using shaft is without delay linked to an engine while the alternative one or the pushed shaft offers the electricity output this is used by the consumer for working.
- Often instances clutches are used to restriction the movement or quantity of electricity transmission among components.
- A not unusual place instance of a grab is that it's far utilized in cars for enticing in addition to disengaging gearbox and the engine of the automobile.
Q4) What are the types of clutches?
A4)
Types of Clutches:
In mechanical engineering distinct sorts of clutches are present. Numerous sorts of clutches are utilized in a couple of functions through engineers, despite the fact that each kind has it is.
The running precept of various sorts of clutches is likewise distinct in nature this is why on this segment of this assessment, distinct sorts of clutches are mentioned in brief to offer an in depth view.
- Friction Clutch
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi Plate Clutch
- Cone Clutch
- Centrifugal Clutch
- Semi-centrifugal Clutch
- Diaphragm Clutch
- Dog and Spline Clutch
- Electromagnetic Clutch
- Vacuum Clutches
- Hydraulic clutch
- Freewheel Clutch
Q5) Write a note on cone clutch.
A5)
Cone clutch
Cone Clutch is a type of frictional capture. It is used to engage and disengage engine shaft to the transmission discipline shaft even as changing equipment ratio. Cone capture makes use of conical surfaces to transmit torque with the useful resource of the use of friction.
Cone capture is much less complex to engage and disengage in comparison to a pleasant displacement capture which modified into used in advance than cone clutches have been invented. Higher torque can be transferred using the cone capture than same period of plate capture due to greater contact area. The driving shaft and the driven shaft want to be perfectly coaxial for inexperienced functioning of the capture. This capture can be used wherein immoderate torque transmission is wanted at low rotating speed. So, this type of capture is extensively is heavy vehicles.

Fig 3. Cone Clutch
Parts of Cone Clutch:
1. Female Cone or Outer Cone:
It is the part of the cone grasp this is linked to the flywheel of the engine and additionally rotates with it. This component identity notification continually in rotating circumstance because the engine shaft rotates continuously. Female cone has internal slicing cone-fashioned groove which has friction lining over which the male cone interlocks and make frictional touch with it in an effort to have interaction the drive. This lady cone is installed over stable shaft.
2. Male Cone or Inner Cone:
This cone is hooked up to the transmission device or the gearbox. Inner cone has friction lining with inside the outer component which creates frictional touch with internal friction lining of the outer cone. By default, internal cone stays in touch with the outer cone with the assist of strain springs that is located at the back of the internal cone. When the grasp pedal is pressed in situations like converting gear, the spring is compressed and the internal cone actions far from the outer cone and disengages from the outer cone and consequently the engine is disengaged from the transmission box. This internal cone has internal splines and actions over slices of shaft for to and from motion.
3. Springs:
Springs are positioned in the back of the male cone which can be used to hold the internal cone engaged with outer cone. When the seize pedal is pressed, the spring compresses and the internal cone disengages with outer cone and consequently the driving shaft is disconnected from pushed shaft.
4. Sleeves:
Sleeves are the part of the seize that is connected to the male cone and installed at the splines and those sleeves are used for back and forth movement of male cone.
5. Pedal:
A seize pedal is used to function the seize.
Q6) Explain the working of cone clutch.
A6)
Working:
By default, the male cone is engaged with the woman cone because of the strain of the spring that's gift at the back of the male cone. When the take hold of pedal is pressed so that it will extrude the tools or for a few different cause, the fulcrum that's connected to pedal rotates which in flip compresses the spring and additionally the male cone is pulled far from the woman cone. Thus the touch among the male cone and woman cone will break.
So, the engine shaft may be disengaged from transmission device and rotation of engine shaft or using shaft will now no longer be transferred to the transmission shaft or the pushed shaft. Now after the disengagement whilst the take hold of pedal is launched slowly with the aid of using the motive force after converting the gears, the fulcrum that's connected to the pedal rotates and the spring expands and the male cone begins off evolved transferring closer to the woman cone over splines.
After that, the male take hold of make touch with the woman take hold of and friction pressure act among the internal friction lining of outer cone and outer friction lining of internal cone. Now the cone take hold of is stated to be in have interaction role and the rotation of engine shaft or using shaft is transferred to the transmission shaft or pushed shaft and each the shaft begin rotating at equal speed. The stiffness with the aid of using the spring continues the male cone and woman cone of the cone take hold of in engaged role.
Advantages:
1) The ordinary pressure performing on touch floor is more than the axial pressure.
2) Higher torque may be transferred than the identical length of plate grab because of huge quantity of frictional pressure involved.
3) It creates much less noise than plate grab.
4) Less put on and tear compared to displacement grab.
Q7) What do you mean by single plate clutch?
A7)
Single Plate Clutch (SPC)
- The diagram of SPC is given below in Fig. 4, with the friction plate placed between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
- Springs are provided tangentially offering axial force keeping the clutch in the engaged position.
- The second friction plate is attached on a hub (split from the inside) and thus the gear box is free to slide on the shaft. Friction is encountered from the friction plate on either side to provide two annular friction surfaces for the transmission of power.
- Clutch pedal is also there which pulls the pressure plate against the spring force every time detachment is required. It usually continues to be in engaged position (Figure 4).
- As the pedal is depressed, the pressure plate moves to the right opposite to spring force. This is achieved through a suitable linkage (not shown in Figure 4) and a thrust bearing. As such, the friction plate and clutch are released.
- In real sense, the clutch construction varies. The plate (pressure), springs, releasing lever and cover forms a cover assembly, that can be fixed straightly to the engine block, with the clutch plate placed between the flywheel and the pressure plate.

Fig 4. Single Plate Clutch.
Q8) Explain multi plate clutch in detail.
A8)
Multiplate Clutch (MPC)
- This type of clutch is a modified version of SPC where friction and number of metallic plates are increased.
- Due to growth of frictional surfaces, the ability of the clutch to transmit torque increases.
- The overall diameter of the clutch is reduced for torque transmission similar to a single plate clutch. Hence, MPC is applicable where high torque transmission is required like various heavy automobiles and racing cars.
- This is also used in scooters and motorcycles, due to space limitation.
- The framework is comparable to the SPC, exception being that, the friction plates are in 2 pairs, i.e., one pair of plates slips into the groove on the flywheel and the other a pressure plate slides onto the hub splines. Alternative plates belong to each set.

Fig 5. Multiplate Clutch
Working of MPC is divided into 2 steps as discussed below:
Engagement
- As the paddle is pressed, the engagement takes place in the engine and the movements of the thrust springs is enhanced.
- Thrust springs offers pressure to the pressure plates making the pressure plate to move in forward direction.
- Also, the linings which are placed on the inner side of the pressure plate make contact with the flywheel, start its action.
- Consequently, the clutch engages.
Disengagement
- For disengagement of engine and clutch, the clutch pedals as well as the fins of inner splined sleeves are pressed.
- Thrust spring moves in backward direction releasing pressure from the pressure plates and plate also moves backward.
- Consequently, due to released pressure from the flywheel, plate and springs the clutch disengages.
Q9) What is diaphragm spring?
A9)
Diaphragm Spring:
Eaton gives an extensive kind of diaphragm spring clutches to match pretty much any business automobile application. Built to strict OEM best standards, they make sure first-rate overall performance and grab existence. Their strong and easy walking layout reduces idling noise and might notably lessen extreme vibrations, extending drivetrain thing existence and the sturdiness of transmission synchronizers.
Working:
Figure indicates the development information of the diaphragm take hold of. It includes a diaphragm spring that is supported on a fulcrum preserving ring i.e. pivot ring in order that any phase thru the spring may be appeared as a easy lever. In the engaged role, the spring pivots at the rear pivot jewellery as it's far held in a take hold of cowl in order that its outer rim contacts the stress plate.

Fig 6. Diaphragm clutch
Therefore, enough stress is exerted with the aid of using the spring creating a company touch among stress plate and take hold of plate in addition to the flywheel in its herbal conical role. To disengage the take hold of, the pedal is depressed to purpose the linkage to transport throw-out bearing toward the flywheel. As the bearing contacts the internal role of the conical spring, it movements ahead which reasons the rim to transport backward because the spring pivots at the front pivot ring. It eliminates the stress at the stress plate and releases the take hold of disc from touch with each using members.
Features:
- Available in plenty of sizes from 280 millimeters to 430 millimeters
- Engineered and synthetic to unique gadget specifications
- Single or dual plate designs
- Soft-price dampers assist defend in opposition to dangerous torsional vibrations and growth the sturdiness of transmission synchronizers and driveline components
- Smooth engagement and much less pedal effort Available pre-dampers cast off rattle at idle
Q10) Explain centrifugal clutch.
A10)
Centrifugal Clutch:
Centrifugal Clutch is a kind of grasp wherein centrifugal pressure is used to attach the engine pressure shaft with the shaft of the transmission. It is located in among the engine flywheel and the transmission system. Its important feature is to attach the engine shaft with the transmission shaft. It works extra successfully at better speeds.
Parts of centrifugal clutch:
- Shoes:
It includes friction lining on the stop and this friction lining makes touch with the drum for the duration of the engagement.
2. Spring:
Spring is used to disengage the snatch while the engine rotates at a slower speed.
3. Spider or publications:
The spiders are established at the driver (engine) shaft or motor shaft. The spiders are similarly spaced. Equally spaced means, if they may be 4 publications than every manual is separated from every different through ninety degree. The sliding footwear are saved in among those publications and every manual is maintaining a spring.
4. Friction lining:
The outer floor of sliding footwear has friction lining. It allows in creating a grip with the internal floor of the drum.
5. Drum:
The drum of the snatch act as housing which encloses all of the components of the snatch that consists of sliding footwear, publications, springs etc. It is attached to the pushed shaft of the transmission gadget or chains or belt.
Working:
- As the engine rotates, the interior meeting of the centrifugal snatch begins off evolved rotating however drum stays desk bound and no electricity is transmitted.
- At decrease pace, the centrifugal pressure produced isn't enough to triumph over the spring pressure. So the snatch stays disengaged. But as the velocity will increase, the centrifugal pressure additionally will increase and now the centrifugal pressure will become more than the spring pressure.
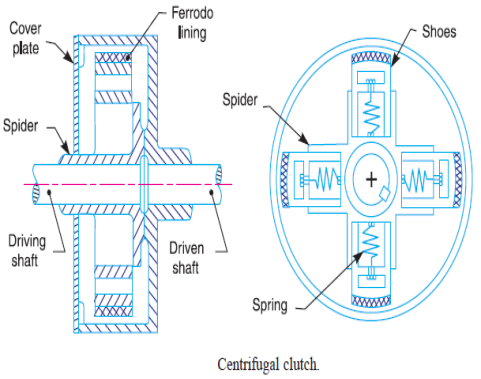
Fig 7. Centrifugal Clutch
- As the centrifugal pressure will become more than the spring pressure, this lets in the sliding footwear to transport outward in opposition to the spring and get engaged with the internal floor of the drum.
- The drum begins off evolved rotating and transfers the rotating electricity from the engine to the pushed shaft of the transmission. When the burden at the engine will increase, its pace decreases and disengages the snatch.
Q11) Write a note on electromagnetic clutch.
A11)
- The working precept of the actuator of electromagnetic snatch is an electromagnetic effect, however torque transmission is mechanical.
- The distinction among electromagnetic snatch and the everyday snatch is in how they manipulate the motion of strain plates.
- In the ordinary snatch, a spring used to interact the snatch while in EM snatch an electromagnetic area is used for engagement.
- The electromagnetic snatch comes numerous forms, such as magnetic particle snatch and multi-disc snatch.
- There are even no-touch clutches which include hysteresis snatch and eddy cutting-edge snatch. However, maximum broadly used shape is unmarried face friction snatch.
Construction:
Rotor:
Rotor is a primary a part of this snatch witch is hooked up at once to the riding shaft or engine shaft. It constantly rotate alongside the riding shaft.
Winding or Coil:
Winding coil is located at the back of the rotor and stays in desk bound function for the duration of snatch working. It is proven in figure. A excessive voltage DC deliver is hooked up with this winding which switch a excessive voltage present day into this winding and convert it into electromagnet.
Armature:
Armature is located at the front of the rotor. It is hooked up to the hub or stress plated with the assist or rivet or bolted joint.
Hub:
Hub or stress plate is bolted with the tools shaft or pushed shaft and rotates with it. It is located after the armature.
Friction Plate:
Friction plate is inserted among armature and rotor in keeping with the requirement.
Supply unit:
Supply unit consist snatch switch, battery, cord etc.
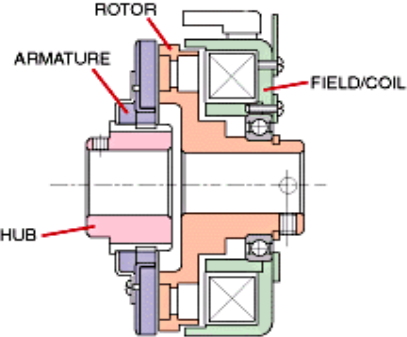
Fig 8: Electromagnetic Clutch
Working of electromagnetic clutch
- The predominant additives of EM take hold of are a coil shell, an armature, rotor, and hub.
- The armature plate is covered with friction coating. The coil is positioned at the back of the rotor.
- When the take hold of activated the electrical circuit energizes the coil, it generates a magnetic area. The rotor part of take hold of receives magnetized.
- When the magnetic area exceeds the air hole among rotor and armature after which it pulls the armature towards the rotor. The frictional pressure generated on the touch floor switch the torque.
- Engagement time relies upon at the electricity of magnetic fields, inertia, and air hole. When voltage is eliminated from the coil, the touch is gone.
Q12) Explain manual gear shift mechanism.
A12)
Manual Gear Shift Mechanism:
A guide transmission offers you a opportunity to shift gears manually. It consists of moving mechanism, synchronizers, intermediate, enter and output shafts, auxiliary shaft, casing and opposite equipment. The majority of gearboxes of this kind have 4 or 5 gears and one opposite.
As for the relaxation of advantages, right here they are: This kind stands proud for its enviable existence cycle. A guide transmission may even out survive the existence of the automobile’s engine.
- Excellent fuelling mileage.
- When in comparison with an automated transmission, the automobile with the guide one consumes 15% much less gasoline and has better acceleration dynamics.
- High efficiency – a guide transmission makes it viable to apply all to be had torque-wearing capacity.
- Ood vehicle behaviour – you could adjust the equipment moving system with the aid of using your own, deciding on the maximum snug using style. Low weight (decrease than that of an automated transmission).
- Possibility to begin up the engine regardless of the discharged battery and low-appearing ignition.
Possibility to tow a vehicle each via inflexible and bendy towline. Speaking approximately its disadvantages, it ought to be cited that the exploitation of forms of guide transmission may be pretty tough for beginners. A driving force will must use it in tandem with the clutch, so there may be a massive risk to disrupt it with the aid of using creating a rookie mistake. On pinnacle of that, in case you forgot to shift equipment, it is able to motive a few engine lug. Another component is that town using will make you shift gears manually all of the time.
Q13) Write a note on automatic gear shift mechanism.
A13)
Automatic Gear Shift Mechanism:
The production of all automated equipment bins is a long way extra complicated than that of guide ones. It includes extra gadgets and parts, so its purchase, installation, exploitation and restore don’t come cheap.
But this transmission is higher suitable for metropolis driving. It is exceedingly desired with the aid of using beginners, on the grounds that this form of gearbox in vehicle eliminates the need to tug the lever and use the seize all of the time.
The equipment pump is located among the planetary gear set and torque converter, wherein it pulls and pressurizer’s transmission fluid from a sump.
The pump enter leads at once to the housing of the torque converter connected to the flex plate of the engine. When the engine isn't always running, the transmission does now no longer have the oil strain had to function and as a result the car cannot be push-started.
The planetary equipment educate is a mechanical device wherein the gears are related with a hard and fast of bands and clutches.
When the driving force modifications gears, the bands maintain one equipment nonetheless at the same time as rotating some other to transmit torque from the engine and boom or lower gears.
Q14) Explain automatic transmission and its working.
A14)
In AT, the gear ration automatically as the automobile moves, meaning that the driver does not have to shift the gears manually.
Like other transmission systems on vehicles, it allows an internal combustion engine, best suited to run at a relatively high rotational speed, to provide a range of speed and torque outputs necessary for vehicular travel.
The most popular form found in automobiles is the hydraulic planetary automatic transmission. This system uses a fluid coupling in place of friction clutch, and accomplishes gear changes by hydraulically locking and unlocking a system of planetary gears.

Fig 9. Automatic Transmission System.
Working:
The turbine of the torque converter drives the ring gear of the first gear train through a free wheel. The drive to the ring gear of the second gear train is then taken from the planet carrier of the first train so that the two act in series. This arrangement gives three forward and one reverse speeds. For direct gear, clutch A is engaged. The second gear is obtained by engaging clutch B and applying brake BS. The application of both brakes BS and BF gives the first i.e., the lower most gear. For reverse gear only brake BR is applied.

Fig. 10 Working of Automatic transmission.
The selection of the particular gear and application of corresponding clutch and brake is done hydraulically. The hydraulic pressure is regulated by two factors:
(i) car speed that controls oil pressure on one side of the shift valve and
(ii) the throttle opening controlled by the driver through accelerator pedal, which controls oil pressure other side of the shift valve.
Q15) What is Fluid Flywheel? Explain in detail.
A15)
It is likewise referred to as Fluid take hold of or fluid coupling which couples the using member with the pushed member via a media of fluid. It includes contributors wherein one is a using member and the opposite one is pushed member as proven in Figure.
Among them, the using member is hooked up with the engine flywheel and the pushed member is hooked up with the transmission shaft. These contributors aren't made to touch with every other. The pushed member is unfastened to slip on splines furnished at the transmission shaft. The rotors are full of a fluid of required viscosity. Radial ribs are furnished to shape some of passages to keep away from the formation of eddies.
They additionally manual the fluid to float withinside the favoured direction.
When the engine is started, the using member known as the impeller begins offevolved to transport in the housing containing oil. Pockets of transferring using contributors are absolutely full of oil.
Due to this, the centrifugal pressure forces the oil outward radially. The wallet are designed in this type of manner that the splashed oil will strike the wallet or vanes of the pushed member.
Then the engine velocity increases. The oil that's popping out from the pocket of the using member moves the wallet of the pushed member with extra pressure. Thus, it has a tendency the pushed member to rotate on the equal velocity.
Characteristics of a Fluid Flywheel:
Stall velocity the stall velocity is described as the best velocity at which the pump can flip while the output turbine is locked and the most enter electricity is applied.
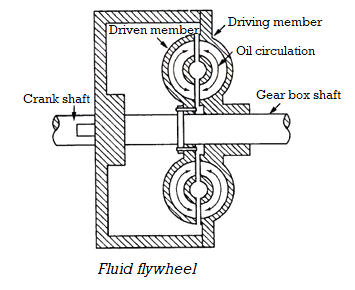
Fig. 11 Fluid flywheel
Under stall situations all the engine’s electricity could be dissipated withinside the fluid coupling as heat, probably main to damage.
Slip The runner velocity is nearly same to that of the impeller simplest while the performance of liquid coupling is highest.
But typically the runner velocity is much less than that of the impeller.
The (velocity) lag of the runner at the back of the impeller is referred to as slip.
This (velocity) slip varies with many elements including engine velocity, car velocity, and engine and car load.
Slip is given as (N1-N2)/N1 in which N1, N2 are velocity of using and pushed
Advantages of Fluid Flywheel:
1. It offers smoother electricity take-up than the centrifugal kind while the engine IS accelerated.
2. The fluid withinside the coupling behaves as a cushioning agent among engine and gearbox so that you can soak up shocks at some point of braking or coasting down on incline.
3. No want of separate pedal or lever to operate.
4. The using member acts as a flywheel at the crankshaft. Thus. Its miles smoothened out the torque variation.
5. There isn't any any put on transferring parts.
6. No want of adjustment is needed.
7. No preservation is necessary. Besides retaining the desired oil level.
3. It is easy in design.
9. There isn't any any jerk on transmission while the equipment engages.
10. No ability is needed for operating.
11. Car may be stopped in equipment and moved off simply through urgent the accelerator pedal itself.
Disadvantages of Fluid Flywheel:
1. There is a drag at the equipment box-shaft even the slip is 100%.
2. It has the equipment converting hard with the normal crash kind gearbox.
The fluid flywheel is normally used with an epicyclical gearbox which avoids this difficulty.
Q16) Explain torque converter and its working.
A16)
• This is a hydraulic transmission drive which is used to increase the torque of the automobile and henceforth reducing its speed.
• Torque converter provides constant deviation in the ratio of low to high.
• The important feature of this device is its capability to double (multiply) torque when there is a noticeable difference b/w the I/P and O/P rotational speeds comparable to a reduction gear.
• Cars working on automatic transmission have no clutch for disconnecting the transmission from the engine. As such they use this device.
Working
- As the engine switches on, rotation of the impeller starts. High centrifugal forces are generated inside the impellor which forces the oil (hydraulic fluid) into the turbine, turbine is still motionless.
- The hydraulic fluid thus gains high kinetic energy from the engine and knocks the external edges of the turbine. The force of high KE fluid (oil) causes the turbine to rotate. This force gets increased as the engine speed increase.
- When this force become very high, the turbine starts rotating in fruitful manner and the automobile starts moving.
- The turbine blade angle is such that it changes the direction of oil flow so that when it comes out of the turbine at the center, its direction is effectively backwards.

Fig 12. Parts of Torque Convertor

Fig 13. Flow of fluid in torque converter (a) under low-speed condition the stator deflects the fluid flow back to the impeller, (b) under high-speed condition the stator free wheels and fluid flow is not deflected.
Q17) Explain Universal Joint.
A17)
• A U-joint (universal coupling) is basically a coupling used to connect two rigid rods having axes inclined with each other, and is applicable in shafts which transmits rotary motion.
• RWD automobiles have U-joints at each end of the drive shaft. U-joints linked to the yoke permits the drive shaft to move backward and forward as automobile passes any obstacles or sink in the road, effectively shortening or lengthening the shaft.
• FWD also use 2 joints i.e., constant velocity (or CV) joints which also compensate for steering changes.

Fig 14. Universal Joint

Fig 15. Universal Joint.

Fig 16. Constant Velocity Universal Joint
The most common type of U- joint is the hook joint (Figure 13) which is highly used as it is very simple and compact in construction and is equitably effective at small angles of propeller shaft movement up and down 18°.
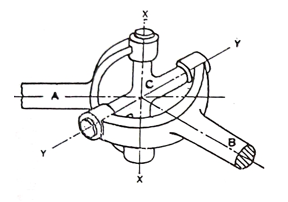
Fig 17. Hooke’s Joint
- The two opposite sides of the cross are supported on the shaft A's yoke, while the other two arms support the cross in the shaft B's yoke.
- The axes of shafts A and B intersect. Each of these shafts has a yoke. Cross four sides.
- Thus, shaft A can have axis XX and shaft B, angular rotation about axis YY. It is thus seen that with the addition of the hook it would be possible to have positive drive allowing angular momentum between shafts A and B.
Q18) Explain slip joint.
A18)
- A slip joint is a mechanical connection among factors that permits for movement however now no longer disconnection among the additives.
- This is executed to maintain the additives from turning into separated, despite the fact that they hold their personal separate functions.
- Even the swing palms in systems as massive as retractable stadium roofs use slip joints.
- Another feature that a slip joint is used for is to permit for a issue connected to every other with the aid of using a slip joint to be adjusted from one role in which it stays constant to a unique constant role.
- Such joints additionally permit for the automatic adjustment being made among pieces.
- These easier styles of slip joints are usually used to make a mechanical tool less difficult to move with the aid of using maintaining the factors of the tool from turning into separated at the same time as permitting them to lower in average size.
- Devices inclusive of tripod legs or objects inclusive of telescopes appoint the usage of those easy slip joints.
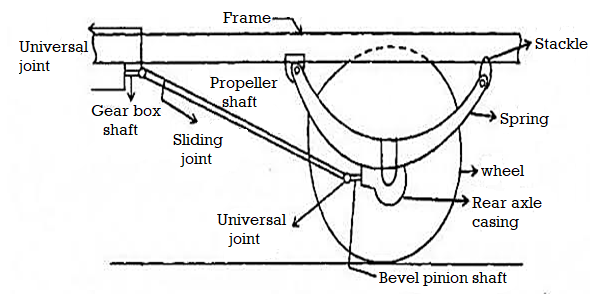
Q19) What are the functions and types of Propeller shaft?
A19)
- As torque is carried via way of means of the driveshaft, it's far subjected to torsion or shear pressure.
- So they need to be robust sufficient to undergo the pressure at the same time as averting an excessive amount of greater weight as this may growth their inertia.
- Driveshafts are used in a different way in one of a kind cars, with one of a kind configurations for front-wheel pressure, four-wheel pressure, and front-engine rear-wheel pressure in cars.
- The drive shafts also are utilized in cars like motorcycles, locomotives, and marine ships.
Functions of the Propeller
- Shaft In automobiles, the engine is on the front then the front wheels of the automobile are being driven.
- In addition, while the rear wheels meet unevenness with inside the road, the rear axle actions up and down, compressing and increasing with inside the suspension springs.
- Also, the period occupied with the aid of using the propeller shaft changes.
Types of Propeller Shaft
Following are the types of the propeller shaft:
- Single piece type
- Two or three piece type
- Single Piece type
This shaft is utilized in automobiles with a small distance among the engine and axle and in four-wheel-pressure automobiles. Friction welding is implemented with a view to will increase the strength, quality, and sturdiness of the shaft.
2. Two or Three Piece type
Two or 3-piece shafts are used as a part of automobiles with an extended distance among engine and axle, and four-wheel-pressure automobiles. Splitting the propeller shaft into or 3 elements reduces the range of revolutions.
Q20) Explain Differential axle.
A20)
The idea of the differential – that is, to permit wheels set up at the identical axle to rotate independently of every different – is an historic design, with the primary acknowledged example of its use recorded in China at some stage in the first millennium BC.
Although this turned into lengthy earlier than the discovery of the automobile, carts, wagons and chariots nonetheless suffered from the identical trouble of 1 wheel slipping or dragging whilst cornering, growing put on and detrimental roads.
The creation of engines powering the front or rear wheels to propel a car in place of simply dragging them thru horse brought a brand new trouble to triumph over – the way to permit impartial rotation even as nonetheless being capable of electricity each wheels.
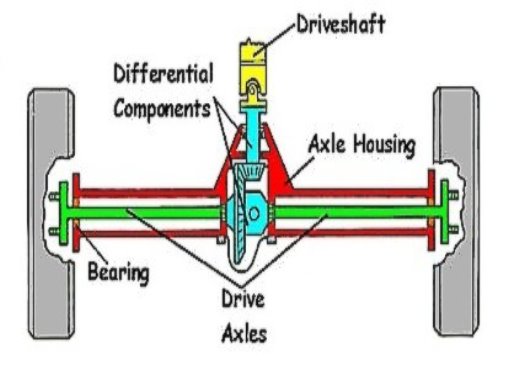
Fig 18: Differential Axle
The earliest cars didn’t hassle trying, they truly powered handiest one wheel on an independent axle. But this turned into some distance from perfect because it supposed they have been underpowered and encountered common troubles with traction on something apart from firm, degree ground.
Eventually this brought about the improvement of the Open Differential earlier than different extra complex sorts have been evolved to triumph over extra complicated using conditions.
Open differential:
A differential in its maximum fundamental shape contains halves of an axle with a equipment on every end, related collectively with the aid of using a 3rd equipment making up 3 facets of a square.
This is generally supplemented with the aid of using a fourth equipment for brought strength, finishing the square.
This fundamental unit is then in addition augmented with the aid of using a hoop equipment being brought to the differential case that holds the fundamental middle gears – and this ring equipment permits the wheels to be powered with the aid of using connecting to the pressure shaft.
Locked differential:
The locked or locking differential is a variation located on a few vehicles, by and large people who burst off road.
It is basically an open differential with the cap potential to be locked in area to create a set axle as opposed to an unbiased one.
The gain of a locked differential is it could benefit a substantially more quantity of traction than an open differential.
Because the torque isn't similarly cut up 50/50 it may channel greater torque to the wheel that has the higher traction - and isn't restricted with the aid of using the decrease traction of the alternative wheel at any given moment.
Because you're not likely to be journeying at pace and are generally journeying over choppy ground, the problem of tyre drag and put on round corners on a set axle is much less of a problem.