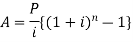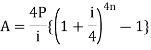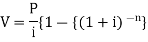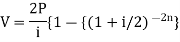BM
UNIT – IICommission Q1) The Price of a book is Rs. 15.75. A book seller sells 1200 books and pays Rs 17,860.50 to the book publisher after deducting his commission. Find the commission rate.A1)Here we have total commission, We have to find the total sale price of books. The total sale price of books = Number of Books 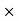 Price = 1200
Price = 1200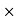 15.75 =18900Commission = Sale price – Amount paid to the Publisher = 18900-17860.5 = 1039.5Commission % = Commission
15.75 =18900Commission = Sale price – Amount paid to the Publisher = 18900-17860.5 = 1039.5Commission % = Commission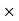 100 /Selling price = 1039.5
100 /Selling price = 1039.5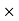 100/18900 = 5.5% Q2) Mahesh sold his car for Rs.68,000 with the help of an agent. If the commission paid by Mahesh is Rs 2550. Find rate of commission, and the net amount received by the Mahesh.A2)Commission % = Commission
100/18900 = 5.5% Q2) Mahesh sold his car for Rs.68,000 with the help of an agent. If the commission paid by Mahesh is Rs 2550. Find rate of commission, and the net amount received by the Mahesh.A2)Commission % = Commission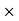 100 /Selling price = 2550
100 /Selling price = 2550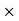 100/68000 = 3.75%Net amount received by farmer = Sale price – Commission = 68000-2550 = Rs65, 450 Q3) An agency pays 15% commission to a notebook distributor. The price of each notebook is Rs 3. If he sells 50 copies of notebook every day, find how much commission he receives in a month and also net amount received by the Agency?A3)Price of each news paper = Rs 3.Sale price for a day = Number copies sold in day
100/68000 = 3.75%Net amount received by farmer = Sale price – Commission = 68000-2550 = Rs65, 450 Q3) An agency pays 15% commission to a notebook distributor. The price of each notebook is Rs 3. If he sells 50 copies of notebook every day, find how much commission he receives in a month and also net amount received by the Agency?A3)Price of each news paper = Rs 3.Sale price for a day = Number copies sold in day  price of Cost of news paper = 50
price of Cost of news paper = 50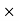 3 = Rs 150Sale price for a year = Number of days
3 = Rs 150Sale price for a year = Number of days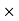 Sale price for a day = 30
Sale price for a day = 30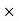 150 = 450 RsCommission = Commission%
150 = 450 RsCommission = Commission%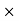 Selling price/100 = 15
Selling price/100 = 15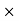 450/100 = 67.5 Rs.Net amount received by agency = selling price – commission = 450 -67.5 = 382.5 Rs Q4) Suppose the profit percentage is 80% of the cost. If the cost further increases by 20% but the selling price remains the same, how much is the decrease in profit percentage?A4) Let us supposeCP = Rs. 100.Then Profit = Rs. 80 and selling price = Rs. 180.The cost increases by 20% → New CP = Rs. 120, SP = Rs. 180.Profit % = 60/120
450/100 = 67.5 Rs.Net amount received by agency = selling price – commission = 450 -67.5 = 382.5 Rs Q4) Suppose the profit percentage is 80% of the cost. If the cost further increases by 20% but the selling price remains the same, how much is the decrease in profit percentage?A4) Let us supposeCP = Rs. 100.Then Profit = Rs. 80 and selling price = Rs. 180.The cost increases by 20% → New CP = Rs. 120, SP = Rs. 180.Profit % = 60/120 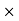 100 = 50%.Therefore, Profit decreases by 30%. Q5) A dishonest shopkeeper sells his grocery using weights 15% less than the true weights and makes a profit of 20%. Find his total gain percentage.A5) Suppose 1 kg of grocery bag. Its actual weight is 85% of 1000 gm = 850 gm.Let the cost price of each gram be Re. 1. Then the CP of each bag = Rs. 850.SP of 1 kg of bag = 120% of the true CPTherefore, SP = 120/100
100 = 50%.Therefore, Profit decreases by 30%. Q5) A dishonest shopkeeper sells his grocery using weights 15% less than the true weights and makes a profit of 20%. Find his total gain percentage.A5) Suppose 1 kg of grocery bag. Its actual weight is 85% of 1000 gm = 850 gm.Let the cost price of each gram be Re. 1. Then the CP of each bag = Rs. 850.SP of 1 kg of bag = 120% of the true CPTherefore, SP = 120/100 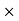 1000 = Rs. 1200Gain = 1200 – 850 = 350Hence Gain % = 350/850
1000 = Rs. 1200Gain = 1200 – 850 = 350Hence Gain % = 350/850  100 = 41.17% Q6) A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on the selling price. On a special sale day, he offers an extra 25% off coupon after the first discount. If the article was sold for Rs. 3600, find the marked price of the articleA6) Let the marked price of the article be x.First a 20% discount was offered, on which another 25% discount was offered.So, 75% of 80% of x = 360075/100
100 = 41.17% Q6) A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on the selling price. On a special sale day, he offers an extra 25% off coupon after the first discount. If the article was sold for Rs. 3600, find the marked price of the articleA6) Let the marked price of the article be x.First a 20% discount was offered, on which another 25% discount was offered.So, 75% of 80% of x = 360075/100 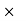 80/100
80/100 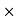 x = 3600 → x = 6000.So the article was marked at Rs. 6000. Q7) The cost price of 30 articles is equal to the selling price of 40 articles. What is the profit or loss percentage?A7) CP of 30 articles = SP of 40 articles Or, CP/SP = 30/40 =3/4
x = 3600 → x = 6000.So the article was marked at Rs. 6000. Q7) The cost price of 30 articles is equal to the selling price of 40 articles. What is the profit or loss percentage?A7) CP of 30 articles = SP of 40 articles Or, CP/SP = 30/40 =3/4
Or, 1 – CP/SP = 1- 3/4 = 1/4So, Loss percentage
= (l – CP/SP) x 100 = 1/4x 100 = 25% Q8) Sweety purchases a set of toys that lists for Rs. 950 and it has a trade discount of 30%, then find the net price.A8) As we know that-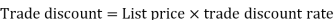
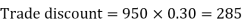 Then Net price = 950 – 285 = 665 Q9) If Raheem will buy a table that lists for Rs. 2000 and it has a trade discount of 50%. Then how much will he pay?A9) As we know that-
Then Net price = 950 – 285 = 665 Q9) If Raheem will buy a table that lists for Rs. 2000 and it has a trade discount of 50%. Then how much will he pay?A9) As we know that-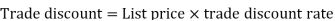
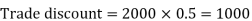 Then Net price = 2000 – 1000 = 1000 Q10) A person received an invoice for Rs. 3,000 dated 22 November 2019 with terms [2/10, n/30]. He paid the whole amount on 30 November 2019. How much did he effectively paid for the bill?A10)
Then Net price = 2000 – 1000 = 1000 Q10) A person received an invoice for Rs. 3,000 dated 22 November 2019 with terms [2/10, n/30]. He paid the whole amount on 30 November 2019. How much did he effectively paid for the bill?A10)Date of Invoice: 22nd November 2019 Day 1 of the cash discount period. : 23rd November 2019 Last day of the Cash discount period: 31st November 2019 Date of payment: 30th November 2019 Cash discount.= Price  Discount rate = Rs. 3,000
Discount rate = Rs. 3,000  2/100 = Rs. 60Amount effectively paid by the person = Bill value - Cash discount = 3,000 - 60 = Rs. 2,940 Q11) If a sweater has a total cost of $54 after tax, what is the cost of the sweater before tax, if the sales tax is 4.5%?A11)The total cost of the sweater is the original cost plus a 4.5% tax, which can be expressed in the equation:TC=C+TWhere TC is the total cost, C is the original cost, and T is the tax. Now, we will plug in the information we know. Since the original cost of the sweater is unknown, we will use the variable x. 54=x+.045x.045 is the decimal expression of 4.5%. Now, solve for x. Consolidate the x variable.54=1.045xDivide both sides by 1.045.51.67=x$51.67 is the cost of the sweater before tax. Q12) Kylie buys an article for $ 10000 and pays 7% tax. He sells the same article for $ 13000 and charges 9% tax. Find the VAT paid by Kylie.A12)Cost of the article = 10000Tax paid by Kylie = 7% of $ 10,000 = $ 7/100 × 10000 = $ 700Selling price of the article = $ 13000Tax charged at 9% = 9% of 13000 = $ 9/100 × 13000 = $ 1170Therefore, VAT = tax recovered on sale - Tax paid on purchase. = $ 1170 - $ 700 = $ 470Therefore, VAT = $ 470 Q13) A retailer buys an article from the wholesaler at $80 and the wholesaler charges a sales tax at the prescribed rate of 8%. The retailer fixes the price at $ 100 and charges sales tax at the same rate. Apply value added tax system of sales tax calculation to answer the following questions.(i) What is the price that a consumer has to pay to buy the article?(ii) Find the input tax and output tax for the retailer.(iii) How much VAT does the retailer pay to the government?A13)(i) Here, the price P = $100, the rate of sales tax r% = 8%Therefore, cost price for the consumer = P(1 + r/100) = $100 × (1 + 8/100) = $100 × 108/100 = $108(ii) Input tax = tax paid by the retailer to the wholesaler = 8% of $80 = 8/100 × $80 = $64/10 = $6.40Output tax = tax realised by the retailer from the consumer = 8% of $100 = 8/100 × $100 = $8(iii) Value added tax paid by the retailer = output tax – input tax = $8 - $6.40 = $1.60 Q14) A shopkeeper sells an article at its marked price $ 7500 and charges sales-tax at the rate of 12% from the customer. If the shopkeeper pays a VAT of $ 180, calculate the price inclusive of tax paid by the shopkeeper.A14)Since, the shopkeeper sells the article for $ 7500 and charges sales-tax at the rate of 12%.Therefore, the tax charged by the shopkeeper = 12% of $ 7500 = 1210012100 × 7500 = $ 900Since, VAT = Tax charged – Tax paidOr, $ 180 = $ 900 – Tax paidOr, Tax paid by the shopkeeper = $ 900 - $ 180 = $ 720If the shopkeeper buys the article for $ xTax on it = 12% of x = $ 720Or, 1210012100 × x = $ 720Or, x = $ 6000Therefore, the price inclusive of tax paid by the shopkeeper = $ 6000 + $ 720 = $ 6720 Q15) A manufacturer printed the price of his goods as $120 per article. He allowed a discount of 30% to the wholesaler who in his turn allowed a discount of 20% on the printed price to the retailer. If the prescribed rate of sales tax on the goods is 10% and the retailer sells it to the consumer at the printed price then find the value added tax paid by the wholesaler and the retailer.A15)For the manufacturer, the price of the article at which it is sold = Printed price – discount of the wholesaler= $ 120 – 30% of $ 120= $ 120 - $ 120 × 30/100= $ 120 - $ 36= $ 84Therefore, input tax for the wholesaler = 10% of 84 = 10/100 × $ 84 = $ 8.40For the wholesaler, the price of the article at which it is sold = Printed price – discount to the retailer= $ 120 - 20% of 120= $ 120 - $ 120 × 20/100= $ 120 - $ 24= $ 96Therefore, output tax for the wholesaler = 10% of 96 = 10/100 × $ 96 = $ 9.60Therefore, VAT payable for the wholesaler = output tax – input tax = $ 9.60 - $ 8.40 = $ 1.20For the retailer, the price of the article at which it is sold = printed price = $ 120Therefore, output tax for the retailer = 10% of 120 = 10/100 × $ 120 = $ 12.Input tax for the retailer = output tax for the wholesaler = $ 9.60Therefore, VAT payable by the retailer = output tax – input tax = $ 12 - $ 9.60 = $ 2.40Therefore, VAT paid by the wholesaler is $ 1.20 and that paid by retailer is $ 2.40 Q16) Aakash wants to invest a part of Rs. 12000 at Rs. 120 in 12% stock. He wants to invest the remaining amount at Rs. 125 in 15% stock. The total dividend he receives per year is Rs. 1360. Find the amount that Aakash should invest in 12% stock at Rs. 120.A16) Suppose the investment that Aakash should do is Rs. X. So, the second investment by him will be 12000 – X.Income on 1st share will be, 12/120 x X = X/10Income for 2nd share, 15/125 x (12000 – X) = 3(12000 – X)/25=> 3(12000 – X)/25 + X/10 = 1360So, 72000 + 5X – 6X = 1360 x 50=> X = 40000So, the required answer is Rs. 40000. Q17) Michael buys shares of face value $ 50 of a company which pays 10 % dividend. At what price did he buy each share from the market if his profit is 16 % on his investment?A17)Let the market value (M.V.) of each share be x.The dividend is calculated on nominal value.The dividend on one share = 10% of $ 50 = $ 5.Therefore, he earned $ 5 on an investment of x.A profit of 16 % on x = 1610016100 × x = 4x254x25Therefore, 4x254x25 = $ 5⟹ x = $25×5425×54⟹ x = $12541254⟹ x = $ 31.25Therefore, Michael bought each share at $ 31.25 from the market.Q18) Jackson buys $ 40 shares in a company, which pays 10% dividend. Jackson buys the share at such a price that his profit is 16% on his investment. At what price did Jackson buy the share?A18)Dividend (profit) given by the company on 1 share = 10% of $ 40 = $ 4.Suppose the man buys one share for x.Therefore, Jackson’s profit = 16% of $ x = $ 16x10016x100According to the problem, 16x10016x100 = 4⟹ x = $ 25Jackson bought the share at $ 25. Q19) Robert bought shares of 6% $ 100 shares at $ 120. Adrian bought shares of 8% $ 20 shares at $ 30. Whose investment was better?A19)6% $ 100 shares at $ 120i.e., the annual income from 1 share of nominal value $ 100 is $ 6, investment for 1 share being $ 120.Therefore, profit percentage = 61206120 × 100 % = 5%Therefore, Robert’s shares give him a profit of 5%8 % $ 20 shares at $ 30i.e., the annual income from 1 share of nominal value $ 20 is $ 8×201008×20100 = $ 8585, investment for 1 share being $ 30.Profit percentage = $85$30$85$30 × 100 % = 163163 % = 51313%Therefore, Adrian’s shares give him a profit of 51313%Therefore, Adrian’s investment was better. Q20) Explain annuities with examples.A20) Annuity-An annuity is a sequence of equal payment or a sequence of regular payment at regular intervals or in other words, An annuity is a fixed sum paid at regular intervals under certain conditions.The length of time during which the annuity is paid can either be until the death of the recipient or for a guaranteed minimum term of years, irrespective of whether the annuitant is alive or not.The time between payments is called the payment interval, and the time which the money is to be paid is called the term of the annuity. Amount of an annuity:Amount of an annuity is the total of all the installments left unpaid together with the compound interest of each payment for the period it remains unpaid. The formulas to find the amount of annuity are given below-
2/100 = Rs. 60Amount effectively paid by the person = Bill value - Cash discount = 3,000 - 60 = Rs. 2,940 Q11) If a sweater has a total cost of $54 after tax, what is the cost of the sweater before tax, if the sales tax is 4.5%?A11)The total cost of the sweater is the original cost plus a 4.5% tax, which can be expressed in the equation:TC=C+TWhere TC is the total cost, C is the original cost, and T is the tax. Now, we will plug in the information we know. Since the original cost of the sweater is unknown, we will use the variable x. 54=x+.045x.045 is the decimal expression of 4.5%. Now, solve for x. Consolidate the x variable.54=1.045xDivide both sides by 1.045.51.67=x$51.67 is the cost of the sweater before tax. Q12) Kylie buys an article for $ 10000 and pays 7% tax. He sells the same article for $ 13000 and charges 9% tax. Find the VAT paid by Kylie.A12)Cost of the article = 10000Tax paid by Kylie = 7% of $ 10,000 = $ 7/100 × 10000 = $ 700Selling price of the article = $ 13000Tax charged at 9% = 9% of 13000 = $ 9/100 × 13000 = $ 1170Therefore, VAT = tax recovered on sale - Tax paid on purchase. = $ 1170 - $ 700 = $ 470Therefore, VAT = $ 470 Q13) A retailer buys an article from the wholesaler at $80 and the wholesaler charges a sales tax at the prescribed rate of 8%. The retailer fixes the price at $ 100 and charges sales tax at the same rate. Apply value added tax system of sales tax calculation to answer the following questions.(i) What is the price that a consumer has to pay to buy the article?(ii) Find the input tax and output tax for the retailer.(iii) How much VAT does the retailer pay to the government?A13)(i) Here, the price P = $100, the rate of sales tax r% = 8%Therefore, cost price for the consumer = P(1 + r/100) = $100 × (1 + 8/100) = $100 × 108/100 = $108(ii) Input tax = tax paid by the retailer to the wholesaler = 8% of $80 = 8/100 × $80 = $64/10 = $6.40Output tax = tax realised by the retailer from the consumer = 8% of $100 = 8/100 × $100 = $8(iii) Value added tax paid by the retailer = output tax – input tax = $8 - $6.40 = $1.60 Q14) A shopkeeper sells an article at its marked price $ 7500 and charges sales-tax at the rate of 12% from the customer. If the shopkeeper pays a VAT of $ 180, calculate the price inclusive of tax paid by the shopkeeper.A14)Since, the shopkeeper sells the article for $ 7500 and charges sales-tax at the rate of 12%.Therefore, the tax charged by the shopkeeper = 12% of $ 7500 = 1210012100 × 7500 = $ 900Since, VAT = Tax charged – Tax paidOr, $ 180 = $ 900 – Tax paidOr, Tax paid by the shopkeeper = $ 900 - $ 180 = $ 720If the shopkeeper buys the article for $ xTax on it = 12% of x = $ 720Or, 1210012100 × x = $ 720Or, x = $ 6000Therefore, the price inclusive of tax paid by the shopkeeper = $ 6000 + $ 720 = $ 6720 Q15) A manufacturer printed the price of his goods as $120 per article. He allowed a discount of 30% to the wholesaler who in his turn allowed a discount of 20% on the printed price to the retailer. If the prescribed rate of sales tax on the goods is 10% and the retailer sells it to the consumer at the printed price then find the value added tax paid by the wholesaler and the retailer.A15)For the manufacturer, the price of the article at which it is sold = Printed price – discount of the wholesaler= $ 120 – 30% of $ 120= $ 120 - $ 120 × 30/100= $ 120 - $ 36= $ 84Therefore, input tax for the wholesaler = 10% of 84 = 10/100 × $ 84 = $ 8.40For the wholesaler, the price of the article at which it is sold = Printed price – discount to the retailer= $ 120 - 20% of 120= $ 120 - $ 120 × 20/100= $ 120 - $ 24= $ 96Therefore, output tax for the wholesaler = 10% of 96 = 10/100 × $ 96 = $ 9.60Therefore, VAT payable for the wholesaler = output tax – input tax = $ 9.60 - $ 8.40 = $ 1.20For the retailer, the price of the article at which it is sold = printed price = $ 120Therefore, output tax for the retailer = 10% of 120 = 10/100 × $ 120 = $ 12.Input tax for the retailer = output tax for the wholesaler = $ 9.60Therefore, VAT payable by the retailer = output tax – input tax = $ 12 - $ 9.60 = $ 2.40Therefore, VAT paid by the wholesaler is $ 1.20 and that paid by retailer is $ 2.40 Q16) Aakash wants to invest a part of Rs. 12000 at Rs. 120 in 12% stock. He wants to invest the remaining amount at Rs. 125 in 15% stock. The total dividend he receives per year is Rs. 1360. Find the amount that Aakash should invest in 12% stock at Rs. 120.A16) Suppose the investment that Aakash should do is Rs. X. So, the second investment by him will be 12000 – X.Income on 1st share will be, 12/120 x X = X/10Income for 2nd share, 15/125 x (12000 – X) = 3(12000 – X)/25=> 3(12000 – X)/25 + X/10 = 1360So, 72000 + 5X – 6X = 1360 x 50=> X = 40000So, the required answer is Rs. 40000. Q17) Michael buys shares of face value $ 50 of a company which pays 10 % dividend. At what price did he buy each share from the market if his profit is 16 % on his investment?A17)Let the market value (M.V.) of each share be x.The dividend is calculated on nominal value.The dividend on one share = 10% of $ 50 = $ 5.Therefore, he earned $ 5 on an investment of x.A profit of 16 % on x = 1610016100 × x = 4x254x25Therefore, 4x254x25 = $ 5⟹ x = $25×5425×54⟹ x = $12541254⟹ x = $ 31.25Therefore, Michael bought each share at $ 31.25 from the market.Q18) Jackson buys $ 40 shares in a company, which pays 10% dividend. Jackson buys the share at such a price that his profit is 16% on his investment. At what price did Jackson buy the share?A18)Dividend (profit) given by the company on 1 share = 10% of $ 40 = $ 4.Suppose the man buys one share for x.Therefore, Jackson’s profit = 16% of $ x = $ 16x10016x100According to the problem, 16x10016x100 = 4⟹ x = $ 25Jackson bought the share at $ 25. Q19) Robert bought shares of 6% $ 100 shares at $ 120. Adrian bought shares of 8% $ 20 shares at $ 30. Whose investment was better?A19)6% $ 100 shares at $ 120i.e., the annual income from 1 share of nominal value $ 100 is $ 6, investment for 1 share being $ 120.Therefore, profit percentage = 61206120 × 100 % = 5%Therefore, Robert’s shares give him a profit of 5%8 % $ 20 shares at $ 30i.e., the annual income from 1 share of nominal value $ 20 is $ 8×201008×20100 = $ 8585, investment for 1 share being $ 30.Profit percentage = $85$30$85$30 × 100 % = 163163 % = 51313%Therefore, Adrian’s shares give him a profit of 51313%Therefore, Adrian’s investment was better. Q20) Explain annuities with examples.A20) Annuity-An annuity is a sequence of equal payment or a sequence of regular payment at regular intervals or in other words, An annuity is a fixed sum paid at regular intervals under certain conditions.The length of time during which the annuity is paid can either be until the death of the recipient or for a guaranteed minimum term of years, irrespective of whether the annuitant is alive or not.The time between payments is called the payment interval, and the time which the money is to be paid is called the term of the annuity. Amount of an annuity:Amount of an annuity is the total of all the installments left unpaid together with the compound interest of each payment for the period it remains unpaid. The formulas to find the amount of annuity are given below-
Present value of an annuity-Present value of an annuity is the sum of the present values of all payments (or installments) made at successive annuity periods The formulas to calculate present value ‘V’ of an annuity P are given below-
The future value is calculated as-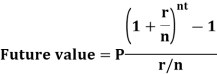 Example: Sundar decides to deposit 20,000rs. at the end of each year in a bank which pays 10% p.a. compound interest.If the installments are allowed to accumulate, what will be the total accumulation at the end of 9 years?Sol.Suppose A rs. be the total accumulation at the end of 9 years. Then we get-
Example: Sundar decides to deposit 20,000rs. at the end of each year in a bank which pays 10% p.a. compound interest.If the installments are allowed to accumulate, what will be the total accumulation at the end of 9 years?Sol.Suppose A rs. be the total accumulation at the end of 9 years. Then we get-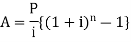 Here P = 20,000 rs., i = 10/100 = 0.1 and n = 9Then
Here P = 20,000 rs., i = 10/100 = 0.1 and n = 9Then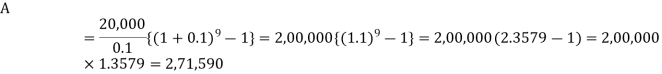 Hence the total required accumulation is 2,71,590 rs. Example: Rajeev purchased a flat valued at 3,00,000rs. He paid 2,00,000 rs. at the time of purchase and agreed to pay the balance with interest of 12% per annum compounded half yearly in 20 equal half yearly installments.If the first installment is paid after six months from the date of purchase, find the amount of each installment.[Given log 10.6 = 1.0253 and log 31.19 = 1.494]Sol.Here 2,00,000 has been paid at the time of purchase when cost of the flat was 3,00,000, we have toconsider 20 equated half yearly annuity payment P when 12% is rate of annual interest compounded halfyearly for present value of 1,00,000rs.So that-
Hence the total required accumulation is 2,71,590 rs. Example: Rajeev purchased a flat valued at 3,00,000rs. He paid 2,00,000 rs. at the time of purchase and agreed to pay the balance with interest of 12% per annum compounded half yearly in 20 equal half yearly installments.If the first installment is paid after six months from the date of purchase, find the amount of each installment.[Given log 10.6 = 1.0253 and log 31.19 = 1.494]Sol.Here 2,00,000 has been paid at the time of purchase when cost of the flat was 3,00,000, we have toconsider 20 equated half yearly annuity payment P when 12% is rate of annual interest compounded halfyearly for present value of 1,00,000rs.So that-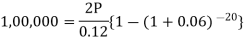 Or
Or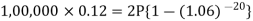
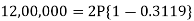
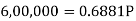 Then-
Then-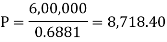 Hence the amount of each installment = 8,718.40Suppose,
Hence the amount of each installment = 8,718.40Suppose,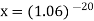 Taking log-
Taking log-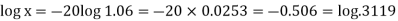 HenceX = 0.3119 Q21) Rohan invests Rs. 5,000 in a term deposit plan. The plan offers an interest rate of 6% p.a., compounded quarterly. How much interest will John earn after one year? Also, what is the effective rate of interest?A21) Here we have-P = 5000, i = 6% per annum or 0.06 p.a. or 0.015 per quarterCompounding period = n = 4
HenceX = 0.3119 Q21) Rohan invests Rs. 5,000 in a term deposit plan. The plan offers an interest rate of 6% p.a., compounded quarterly. How much interest will John earn after one year? Also, what is the effective rate of interest?A21) Here we have-P = 5000, i = 6% per annum or 0.06 p.a. or 0.015 per quarterCompounding period = n = 4 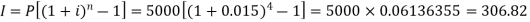 Rohan earns Rs. 306.82 interest after a yearNow the effective rate of interest is-
Rohan earns Rs. 306.82 interest after a yearNow the effective rate of interest is-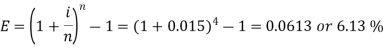 Q22) What is the effective rate of interest on a CD that has a nominal rate of 9.5 percent with interest compounded monthly?A22)Here we have,i = 9.5% or 0.095Now the effective rate of interest is-
Q22) What is the effective rate of interest on a CD that has a nominal rate of 9.5 percent with interest compounded monthly?A22)Here we have,i = 9.5% or 0.095Now the effective rate of interest is-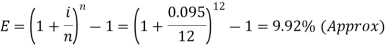 Q23) Amitabh invested Rs. 100 in a scheme that pays out a nominal annual interest rate of 10% compounded on a quarterly basis. Find the Effective Annual Rate.A23)Here we have,i = 10% or 0.1Now the effective rate of interest is-
Q23) Amitabh invested Rs. 100 in a scheme that pays out a nominal annual interest rate of 10% compounded on a quarterly basis. Find the Effective Annual Rate.A23)Here we have,i = 10% or 0.1Now the effective rate of interest is-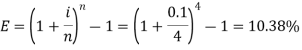 Q24) Sushmita invested 5000rs. At the rate of 8 per cent per annum then what will be the value of the amount she invested in 5 years.A24)Here P = 5000, i = 8/100 = 0.08, n = 5, now
Q24) Sushmita invested 5000rs. At the rate of 8 per cent per annum then what will be the value of the amount she invested in 5 years.A24)Here P = 5000, i = 8/100 = 0.08, n = 5, now 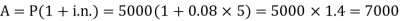 Hence the required amount is - 7000 Q25) Find out the simple interest on 5600 rs. At 12 percent per annum from July 15 to September 26, 2020.A25)Here we calculate the time-Total days from july 15 to sept 26 = 73 days or 73/365 = 1/5 yearsAnd P = 5600, i = 12/100 = 0.12Simple interest = P.i.n. = 5600
Hence the required amount is - 7000 Q25) Find out the simple interest on 5600 rs. At 12 percent per annum from July 15 to September 26, 2020.A25)Here we calculate the time-Total days from july 15 to sept 26 = 73 days or 73/365 = 1/5 yearsAnd P = 5600, i = 12/100 = 0.12Simple interest = P.i.n. = 5600 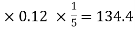 Hence the simple interest is – 134.40 Q26) Harpreet invests 1200rs. At 10 percent per annum for some time and it becomes 1560 then find the principal when that will become 2232 at 8 percent p.a. in the same time.A26)Here in first situation- P = 1200, A = 1560 and i = 0.10So that,
Hence the simple interest is – 134.40 Q26) Harpreet invests 1200rs. At 10 percent per annum for some time and it becomes 1560 then find the principal when that will become 2232 at 8 percent p.a. in the same time.A26)Here in first situation- P = 1200, A = 1560 and i = 0.10So that,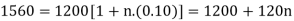
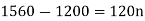
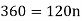
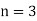 In second situation-A = 2232, n = 3, i = 0.08
In second situation-A = 2232, n = 3, i = 0.08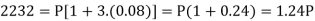
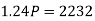
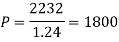 Q27) A sum of money invested at C.I. payable yearly amounts to 10, 816 rs. at the end of the second year and to 11,248.64 rs. at the end of the third year. Find the rate of interest and the sum.A27)Here A1 = 10,816, n = 2, and A2 = 11,248.64, n = 3We know that A = P (1 + i)n we get,10,816 =
Q27) A sum of money invested at C.I. payable yearly amounts to 10, 816 rs. at the end of the second year and to 11,248.64 rs. at the end of the third year. Find the rate of interest and the sum.A27)Here A1 = 10,816, n = 2, and A2 = 11,248.64, n = 3We know that A = P (1 + i)n we get,10,816 = 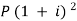 … (i)11,248.64 =
… (i)11,248.64 =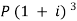 … (ii)Here on dividing equation (2) by (1)-
… (ii)Here on dividing equation (2) by (1)-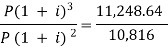 We get-
We get-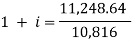
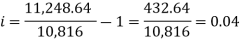 And
And 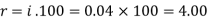 Hence the rate is 4 percent.Now from first equation-10,816 =
Hence the rate is 4 percent.Now from first equation-10,816 = 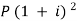 Or
Or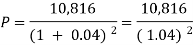 Now-
Now-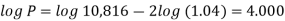 P = antilog 4.000 = 10,000Therefore they require answer- 10,000 Q28) Ronak deposited Rs. 10,000 in a bank for 3 years. Bank gives two offers either 10 percent compounded quarterly or 8% compounded continuously, then which offer is preferable for Ronak?A28)Balance after three years under first offer-
P = antilog 4.000 = 10,000Therefore they require answer- 10,000 Q28) Ronak deposited Rs. 10,000 in a bank for 3 years. Bank gives two offers either 10 percent compounded quarterly or 8% compounded continuously, then which offer is preferable for Ronak?A28)Balance after three years under first offer-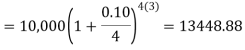 Balance after 3 years under second offer-
Balance after 3 years under second offer-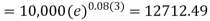 Q29) Suppose the profit percentage is 80% of the cost. If the cost further increases by 20% but the selling price remains the same, how much is the decrease in profit percentage?A29)Let us supposeCP = Rs. 100.Then Profit = Rs. 80 and selling price = Rs. 180.The cost increases by 20% → New CP = Rs. 120, SP = Rs. 180.Profit % = 60/120
Q29) Suppose the profit percentage is 80% of the cost. If the cost further increases by 20% but the selling price remains the same, how much is the decrease in profit percentage?A29)Let us supposeCP = Rs. 100.Then Profit = Rs. 80 and selling price = Rs. 180.The cost increases by 20% → New CP = Rs. 120, SP = Rs. 180.Profit % = 60/120 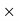 100 = 50%.Therefore, Profit decreases by 30%. Q30) A dishonest shopkeeper sells his grocery using weights 15% less than the true weights and makes a profit of 20%. Find his total gain percentage.A30)Suppose 1 kg of grocery bag. Its actual weight is 85% of 1000 gm = 850 gm.Let the cost price of each gram be Re. 1. Then the CP of each bag = Rs. 850.SP of 1 kg of bag = 120% of the true CPTherefore, SP = 120/100
100 = 50%.Therefore, Profit decreases by 30%. Q30) A dishonest shopkeeper sells his grocery using weights 15% less than the true weights and makes a profit of 20%. Find his total gain percentage.A30)Suppose 1 kg of grocery bag. Its actual weight is 85% of 1000 gm = 850 gm.Let the cost price of each gram be Re. 1. Then the CP of each bag = Rs. 850.SP of 1 kg of bag = 120% of the true CPTherefore, SP = 120/100 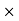 1000 = Rs. 1200Gain = 1200 – 850 = 350Hence Gain % = 350/850
1000 = Rs. 1200Gain = 1200 – 850 = 350Hence Gain % = 350/850  100 = 41.17% Q31) A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on the selling price. On a special sale day, he offers an extra 25% off coupon after the first discount. If the article was sold for Rs. 3600, find the marked price of the articleA31)Let the marked price of the article be x.First a 20% discount was offered, on which another 25% discount was offered.So, 75% of 80% of x = 360075/100
100 = 41.17% Q31) A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on the selling price. On a special sale day, he offers an extra 25% off coupon after the first discount. If the article was sold for Rs. 3600, find the marked price of the articleA31)Let the marked price of the article be x.First a 20% discount was offered, on which another 25% discount was offered.So, 75% of 80% of x = 360075/100 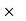 80/100
80/100 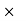 x = 3600 → x = 6000.So the article was marked at Rs. 6000. Q32) The cost price of 30 articles is equal to the selling price of 40 articles. What is the profit or loss percentage?A32)CP of 30 articles = SP of 40 articles Or, CP/SP = 30/40 =3/4
x = 3600 → x = 6000.So the article was marked at Rs. 6000. Q32) The cost price of 30 articles is equal to the selling price of 40 articles. What is the profit or loss percentage?A32)CP of 30 articles = SP of 40 articles Or, CP/SP = 30/40 =3/4
Or, 1 – CP/SP = 1- 3/4 = 1/4So, Loss percentage
= (l – CP/SP) x 100 = 1/4x 100 = 25% Q33) Sweety purchases a set of toys that lists for Rs. 950 and it has a trade discount of 30%, then find the net price.A33)As we know that-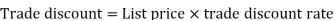
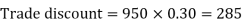 Then Net price = 950 – 285 = 665 Q34) If Raheem will buy a table that lists for Rs. 2000 and it has a trade discount of 50%. Then how much will he pay?A34)As we know that-
Then Net price = 950 – 285 = 665 Q34) If Raheem will buy a table that lists for Rs. 2000 and it has a trade discount of 50%. Then how much will he pay?A34)As we know that-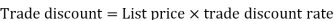
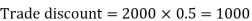 Then Net price = 2000 – 1000 = 1000 Q35) The Price of a book is Rs. 15.75. A book seller sells 1200 books and pays Rs 17,860.50 to the book publisher after deducting his commission. Find the commission rate.A35)Here we have total commission, We have to find the total sale price of books. The total sale price of books = Number of Books
Then Net price = 2000 – 1000 = 1000 Q35) The Price of a book is Rs. 15.75. A book seller sells 1200 books and pays Rs 17,860.50 to the book publisher after deducting his commission. Find the commission rate.A35)Here we have total commission, We have to find the total sale price of books. The total sale price of books = Number of Books 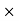 Price = 1200
Price = 1200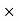 15.75 =18900Commission = Sale price – Amount paid to the Publisher = 18900-17860.5 = 1039.5Commission % = Commission
15.75 =18900Commission = Sale price – Amount paid to the Publisher = 18900-17860.5 = 1039.5Commission % = Commission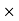 100 /Selling price = 1039.5
100 /Selling price = 1039.5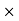 100/18900 = 5.5% Q36) Mahesh sold his car for Rs.68,000 with the help of an agent. If the commission paid by Mahesh is Rs 2550. Find rate of commission, and the net amount received by the Mahesh.A36)Commission % = Commission
100/18900 = 5.5% Q36) Mahesh sold his car for Rs.68,000 with the help of an agent. If the commission paid by Mahesh is Rs 2550. Find rate of commission, and the net amount received by the Mahesh.A36)Commission % = Commission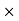 100 /Selling price = 2550
100 /Selling price = 2550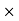 100/68000 = 3.75%Net amount received by farmer = Sale price – Commission = 68000-2550 = Rs65, 450 Q37) An agency pays 15% commission to a notebook distributor. The price of each notebook is Rs 3. If he sells 50 copies of notebook every day, find how much commission he receives in a month and also net amount received by the Agency?A37)Price of each newspaper = Rs 3.Sale price for a day = Number copies sold in day
100/68000 = 3.75%Net amount received by farmer = Sale price – Commission = 68000-2550 = Rs65, 450 Q37) An agency pays 15% commission to a notebook distributor. The price of each notebook is Rs 3. If he sells 50 copies of notebook every day, find how much commission he receives in a month and also net amount received by the Agency?A37)Price of each newspaper = Rs 3.Sale price for a day = Number copies sold in day  price of Cost of news paper = 50
price of Cost of news paper = 50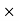 3 = Rs 150Sale price for a year = Number of days
3 = Rs 150Sale price for a year = Number of days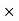 Sale price for a day = 30
Sale price for a day = 30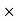 150 = 450 RsCommission = Commission%
150 = 450 RsCommission = Commission%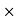 Selling price/100 = 15
Selling price/100 = 15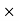 450/100 = 67.5 Rs.Net amount received by agency = selling price – commission = 450 -67.5 = 382.5 Rs
450/100 = 67.5 Rs.Net amount received by agency = selling price – commission = 450 -67.5 = 382.5 Rs
 Price = 1200
Price = 1200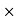 15.75 =18900Commission = Sale price – Amount paid to the Publisher = 18900-17860.5 = 1039.5Commission % = Commission
15.75 =18900Commission = Sale price – Amount paid to the Publisher = 18900-17860.5 = 1039.5Commission % = Commission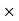 100 /Selling price = 1039.5
100 /Selling price = 1039.5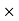 100/18900 = 5.5% Q2) Mahesh sold his car for Rs.68,000 with the help of an agent. If the commission paid by Mahesh is Rs 2550. Find rate of commission, and the net amount received by the Mahesh.A2)Commission % = Commission
100/18900 = 5.5% Q2) Mahesh sold his car for Rs.68,000 with the help of an agent. If the commission paid by Mahesh is Rs 2550. Find rate of commission, and the net amount received by the Mahesh.A2)Commission % = Commission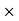 100 /Selling price = 2550
100 /Selling price = 2550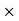 100/68000 = 3.75%Net amount received by farmer = Sale price – Commission = 68000-2550 = Rs65, 450 Q3) An agency pays 15% commission to a notebook distributor. The price of each notebook is Rs 3. If he sells 50 copies of notebook every day, find how much commission he receives in a month and also net amount received by the Agency?A3)Price of each news paper = Rs 3.Sale price for a day = Number copies sold in day
100/68000 = 3.75%Net amount received by farmer = Sale price – Commission = 68000-2550 = Rs65, 450 Q3) An agency pays 15% commission to a notebook distributor. The price of each notebook is Rs 3. If he sells 50 copies of notebook every day, find how much commission he receives in a month and also net amount received by the Agency?A3)Price of each news paper = Rs 3.Sale price for a day = Number copies sold in day  price of Cost of news paper = 50
price of Cost of news paper = 50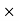 3 = Rs 150Sale price for a year = Number of days
3 = Rs 150Sale price for a year = Number of days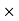 Sale price for a day = 30
Sale price for a day = 30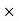 150 = 450 RsCommission = Commission%
150 = 450 RsCommission = Commission% Selling price/100 = 15
Selling price/100 = 15 450/100 = 67.5 Rs.Net amount received by agency = selling price – commission = 450 -67.5 = 382.5 Rs Q4) Suppose the profit percentage is 80% of the cost. If the cost further increases by 20% but the selling price remains the same, how much is the decrease in profit percentage?A4) Let us supposeCP = Rs. 100.Then Profit = Rs. 80 and selling price = Rs. 180.The cost increases by 20% → New CP = Rs. 120, SP = Rs. 180.Profit % = 60/120
450/100 = 67.5 Rs.Net amount received by agency = selling price – commission = 450 -67.5 = 382.5 Rs Q4) Suppose the profit percentage is 80% of the cost. If the cost further increases by 20% but the selling price remains the same, how much is the decrease in profit percentage?A4) Let us supposeCP = Rs. 100.Then Profit = Rs. 80 and selling price = Rs. 180.The cost increases by 20% → New CP = Rs. 120, SP = Rs. 180.Profit % = 60/120  100 = 50%.Therefore, Profit decreases by 30%. Q5) A dishonest shopkeeper sells his grocery using weights 15% less than the true weights and makes a profit of 20%. Find his total gain percentage.A5) Suppose 1 kg of grocery bag. Its actual weight is 85% of 1000 gm = 850 gm.Let the cost price of each gram be Re. 1. Then the CP of each bag = Rs. 850.SP of 1 kg of bag = 120% of the true CPTherefore, SP = 120/100
100 = 50%.Therefore, Profit decreases by 30%. Q5) A dishonest shopkeeper sells his grocery using weights 15% less than the true weights and makes a profit of 20%. Find his total gain percentage.A5) Suppose 1 kg of grocery bag. Its actual weight is 85% of 1000 gm = 850 gm.Let the cost price of each gram be Re. 1. Then the CP of each bag = Rs. 850.SP of 1 kg of bag = 120% of the true CPTherefore, SP = 120/100  1000 = Rs. 1200Gain = 1200 – 850 = 350Hence Gain % = 350/850
1000 = Rs. 1200Gain = 1200 – 850 = 350Hence Gain % = 350/850  100 = 41.17% Q6) A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on the selling price. On a special sale day, he offers an extra 25% off coupon after the first discount. If the article was sold for Rs. 3600, find the marked price of the articleA6) Let the marked price of the article be x.First a 20% discount was offered, on which another 25% discount was offered.So, 75% of 80% of x = 360075/100
100 = 41.17% Q6) A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on the selling price. On a special sale day, he offers an extra 25% off coupon after the first discount. If the article was sold for Rs. 3600, find the marked price of the articleA6) Let the marked price of the article be x.First a 20% discount was offered, on which another 25% discount was offered.So, 75% of 80% of x = 360075/100  80/100
80/100  x = 3600 → x = 6000.So the article was marked at Rs. 6000. Q7) The cost price of 30 articles is equal to the selling price of 40 articles. What is the profit or loss percentage?A7) CP of 30 articles = SP of 40 articles Or, CP/SP = 30/40 =3/4
x = 3600 → x = 6000.So the article was marked at Rs. 6000. Q7) The cost price of 30 articles is equal to the selling price of 40 articles. What is the profit or loss percentage?A7) CP of 30 articles = SP of 40 articles Or, CP/SP = 30/40 =3/4Or, 1 – CP/SP = 1- 3/4 = 1/4So, Loss percentage
= (l – CP/SP) x 100 = 1/4x 100 = 25% Q8) Sweety purchases a set of toys that lists for Rs. 950 and it has a trade discount of 30%, then find the net price.A8) As we know that-
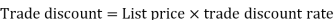
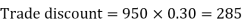 Then Net price = 950 – 285 = 665 Q9) If Raheem will buy a table that lists for Rs. 2000 and it has a trade discount of 50%. Then how much will he pay?A9) As we know that-
Then Net price = 950 – 285 = 665 Q9) If Raheem will buy a table that lists for Rs. 2000 and it has a trade discount of 50%. Then how much will he pay?A9) As we know that-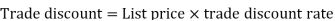
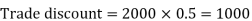 Then Net price = 2000 – 1000 = 1000 Q10) A person received an invoice for Rs. 3,000 dated 22 November 2019 with terms [2/10, n/30]. He paid the whole amount on 30 November 2019. How much did he effectively paid for the bill?A10)
Then Net price = 2000 – 1000 = 1000 Q10) A person received an invoice for Rs. 3,000 dated 22 November 2019 with terms [2/10, n/30]. He paid the whole amount on 30 November 2019. How much did he effectively paid for the bill?A10)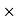 Discount rate = Rs. 3,000
Discount rate = Rs. 3,000  2/100 = Rs. 60Amount effectively paid by the person = Bill value - Cash discount = 3,000 - 60 = Rs. 2,940 Q11) If a sweater has a total cost of $54 after tax, what is the cost of the sweater before tax, if the sales tax is 4.5%?A11)The total cost of the sweater is the original cost plus a 4.5% tax, which can be expressed in the equation:TC=C+TWhere TC is the total cost, C is the original cost, and T is the tax. Now, we will plug in the information we know. Since the original cost of the sweater is unknown, we will use the variable x. 54=x+.045x.045 is the decimal expression of 4.5%. Now, solve for x. Consolidate the x variable.54=1.045xDivide both sides by 1.045.51.67=x$51.67 is the cost of the sweater before tax. Q12) Kylie buys an article for $ 10000 and pays 7% tax. He sells the same article for $ 13000 and charges 9% tax. Find the VAT paid by Kylie.A12)Cost of the article = 10000Tax paid by Kylie = 7% of $ 10,000 = $ 7/100 × 10000 = $ 700Selling price of the article = $ 13000Tax charged at 9% = 9% of 13000 = $ 9/100 × 13000 = $ 1170Therefore, VAT = tax recovered on sale - Tax paid on purchase. = $ 1170 - $ 700 = $ 470Therefore, VAT = $ 470 Q13) A retailer buys an article from the wholesaler at $80 and the wholesaler charges a sales tax at the prescribed rate of 8%. The retailer fixes the price at $ 100 and charges sales tax at the same rate. Apply value added tax system of sales tax calculation to answer the following questions.(i) What is the price that a consumer has to pay to buy the article?(ii) Find the input tax and output tax for the retailer.(iii) How much VAT does the retailer pay to the government?A13)(i) Here, the price P = $100, the rate of sales tax r% = 8%Therefore, cost price for the consumer = P(1 + r/100) = $100 × (1 + 8/100) = $100 × 108/100 = $108(ii) Input tax = tax paid by the retailer to the wholesaler = 8% of $80 = 8/100 × $80 = $64/10 = $6.40Output tax = tax realised by the retailer from the consumer = 8% of $100 = 8/100 × $100 = $8(iii) Value added tax paid by the retailer = output tax – input tax = $8 - $6.40 = $1.60 Q14) A shopkeeper sells an article at its marked price $ 7500 and charges sales-tax at the rate of 12% from the customer. If the shopkeeper pays a VAT of $ 180, calculate the price inclusive of tax paid by the shopkeeper.A14)Since, the shopkeeper sells the article for $ 7500 and charges sales-tax at the rate of 12%.Therefore, the tax charged by the shopkeeper = 12% of $ 7500 = 1210012100 × 7500 = $ 900Since, VAT = Tax charged – Tax paidOr, $ 180 = $ 900 – Tax paidOr, Tax paid by the shopkeeper = $ 900 - $ 180 = $ 720If the shopkeeper buys the article for $ xTax on it = 12% of x = $ 720Or, 1210012100 × x = $ 720Or, x = $ 6000Therefore, the price inclusive of tax paid by the shopkeeper = $ 6000 + $ 720 = $ 6720 Q15) A manufacturer printed the price of his goods as $120 per article. He allowed a discount of 30% to the wholesaler who in his turn allowed a discount of 20% on the printed price to the retailer. If the prescribed rate of sales tax on the goods is 10% and the retailer sells it to the consumer at the printed price then find the value added tax paid by the wholesaler and the retailer.A15)For the manufacturer, the price of the article at which it is sold = Printed price – discount of the wholesaler= $ 120 – 30% of $ 120= $ 120 - $ 120 × 30/100= $ 120 - $ 36= $ 84Therefore, input tax for the wholesaler = 10% of 84 = 10/100 × $ 84 = $ 8.40For the wholesaler, the price of the article at which it is sold = Printed price – discount to the retailer= $ 120 - 20% of 120= $ 120 - $ 120 × 20/100= $ 120 - $ 24= $ 96Therefore, output tax for the wholesaler = 10% of 96 = 10/100 × $ 96 = $ 9.60Therefore, VAT payable for the wholesaler = output tax – input tax = $ 9.60 - $ 8.40 = $ 1.20For the retailer, the price of the article at which it is sold = printed price = $ 120Therefore, output tax for the retailer = 10% of 120 = 10/100 × $ 120 = $ 12.Input tax for the retailer = output tax for the wholesaler = $ 9.60Therefore, VAT payable by the retailer = output tax – input tax = $ 12 - $ 9.60 = $ 2.40Therefore, VAT paid by the wholesaler is $ 1.20 and that paid by retailer is $ 2.40 Q16) Aakash wants to invest a part of Rs. 12000 at Rs. 120 in 12% stock. He wants to invest the remaining amount at Rs. 125 in 15% stock. The total dividend he receives per year is Rs. 1360. Find the amount that Aakash should invest in 12% stock at Rs. 120.A16) Suppose the investment that Aakash should do is Rs. X. So, the second investment by him will be 12000 – X.Income on 1st share will be, 12/120 x X = X/10Income for 2nd share, 15/125 x (12000 – X) = 3(12000 – X)/25=> 3(12000 – X)/25 + X/10 = 1360So, 72000 + 5X – 6X = 1360 x 50=> X = 40000So, the required answer is Rs. 40000. Q17) Michael buys shares of face value $ 50 of a company which pays 10 % dividend. At what price did he buy each share from the market if his profit is 16 % on his investment?A17)Let the market value (M.V.) of each share be x.The dividend is calculated on nominal value.The dividend on one share = 10% of $ 50 = $ 5.Therefore, he earned $ 5 on an investment of x.A profit of 16 % on x = 1610016100 × x = 4x254x25Therefore, 4x254x25 = $ 5⟹ x = $25×5425×54⟹ x = $12541254⟹ x = $ 31.25Therefore, Michael bought each share at $ 31.25 from the market.Q18) Jackson buys $ 40 shares in a company, which pays 10% dividend. Jackson buys the share at such a price that his profit is 16% on his investment. At what price did Jackson buy the share?A18)Dividend (profit) given by the company on 1 share = 10% of $ 40 = $ 4.Suppose the man buys one share for x.Therefore, Jackson’s profit = 16% of $ x = $ 16x10016x100According to the problem, 16x10016x100 = 4⟹ x = $ 25Jackson bought the share at $ 25. Q19) Robert bought shares of 6% $ 100 shares at $ 120. Adrian bought shares of 8% $ 20 shares at $ 30. Whose investment was better?A19)6% $ 100 shares at $ 120i.e., the annual income from 1 share of nominal value $ 100 is $ 6, investment for 1 share being $ 120.Therefore, profit percentage = 61206120 × 100 % = 5%Therefore, Robert’s shares give him a profit of 5%8 % $ 20 shares at $ 30i.e., the annual income from 1 share of nominal value $ 20 is $ 8×201008×20100 = $ 8585, investment for 1 share being $ 30.Profit percentage = $85$30$85$30 × 100 % = 163163 % = 51313%Therefore, Adrian’s shares give him a profit of 51313%Therefore, Adrian’s investment was better. Q20) Explain annuities with examples.A20) Annuity-An annuity is a sequence of equal payment or a sequence of regular payment at regular intervals or in other words, An annuity is a fixed sum paid at regular intervals under certain conditions.The length of time during which the annuity is paid can either be until the death of the recipient or for a guaranteed minimum term of years, irrespective of whether the annuitant is alive or not.The time between payments is called the payment interval, and the time which the money is to be paid is called the term of the annuity. Amount of an annuity:Amount of an annuity is the total of all the installments left unpaid together with the compound interest of each payment for the period it remains unpaid. The formulas to find the amount of annuity are given below-
2/100 = Rs. 60Amount effectively paid by the person = Bill value - Cash discount = 3,000 - 60 = Rs. 2,940 Q11) If a sweater has a total cost of $54 after tax, what is the cost of the sweater before tax, if the sales tax is 4.5%?A11)The total cost of the sweater is the original cost plus a 4.5% tax, which can be expressed in the equation:TC=C+TWhere TC is the total cost, C is the original cost, and T is the tax. Now, we will plug in the information we know. Since the original cost of the sweater is unknown, we will use the variable x. 54=x+.045x.045 is the decimal expression of 4.5%. Now, solve for x. Consolidate the x variable.54=1.045xDivide both sides by 1.045.51.67=x$51.67 is the cost of the sweater before tax. Q12) Kylie buys an article for $ 10000 and pays 7% tax. He sells the same article for $ 13000 and charges 9% tax. Find the VAT paid by Kylie.A12)Cost of the article = 10000Tax paid by Kylie = 7% of $ 10,000 = $ 7/100 × 10000 = $ 700Selling price of the article = $ 13000Tax charged at 9% = 9% of 13000 = $ 9/100 × 13000 = $ 1170Therefore, VAT = tax recovered on sale - Tax paid on purchase. = $ 1170 - $ 700 = $ 470Therefore, VAT = $ 470 Q13) A retailer buys an article from the wholesaler at $80 and the wholesaler charges a sales tax at the prescribed rate of 8%. The retailer fixes the price at $ 100 and charges sales tax at the same rate. Apply value added tax system of sales tax calculation to answer the following questions.(i) What is the price that a consumer has to pay to buy the article?(ii) Find the input tax and output tax for the retailer.(iii) How much VAT does the retailer pay to the government?A13)(i) Here, the price P = $100, the rate of sales tax r% = 8%Therefore, cost price for the consumer = P(1 + r/100) = $100 × (1 + 8/100) = $100 × 108/100 = $108(ii) Input tax = tax paid by the retailer to the wholesaler = 8% of $80 = 8/100 × $80 = $64/10 = $6.40Output tax = tax realised by the retailer from the consumer = 8% of $100 = 8/100 × $100 = $8(iii) Value added tax paid by the retailer = output tax – input tax = $8 - $6.40 = $1.60 Q14) A shopkeeper sells an article at its marked price $ 7500 and charges sales-tax at the rate of 12% from the customer. If the shopkeeper pays a VAT of $ 180, calculate the price inclusive of tax paid by the shopkeeper.A14)Since, the shopkeeper sells the article for $ 7500 and charges sales-tax at the rate of 12%.Therefore, the tax charged by the shopkeeper = 12% of $ 7500 = 1210012100 × 7500 = $ 900Since, VAT = Tax charged – Tax paidOr, $ 180 = $ 900 – Tax paidOr, Tax paid by the shopkeeper = $ 900 - $ 180 = $ 720If the shopkeeper buys the article for $ xTax on it = 12% of x = $ 720Or, 1210012100 × x = $ 720Or, x = $ 6000Therefore, the price inclusive of tax paid by the shopkeeper = $ 6000 + $ 720 = $ 6720 Q15) A manufacturer printed the price of his goods as $120 per article. He allowed a discount of 30% to the wholesaler who in his turn allowed a discount of 20% on the printed price to the retailer. If the prescribed rate of sales tax on the goods is 10% and the retailer sells it to the consumer at the printed price then find the value added tax paid by the wholesaler and the retailer.A15)For the manufacturer, the price of the article at which it is sold = Printed price – discount of the wholesaler= $ 120 – 30% of $ 120= $ 120 - $ 120 × 30/100= $ 120 - $ 36= $ 84Therefore, input tax for the wholesaler = 10% of 84 = 10/100 × $ 84 = $ 8.40For the wholesaler, the price of the article at which it is sold = Printed price – discount to the retailer= $ 120 - 20% of 120= $ 120 - $ 120 × 20/100= $ 120 - $ 24= $ 96Therefore, output tax for the wholesaler = 10% of 96 = 10/100 × $ 96 = $ 9.60Therefore, VAT payable for the wholesaler = output tax – input tax = $ 9.60 - $ 8.40 = $ 1.20For the retailer, the price of the article at which it is sold = printed price = $ 120Therefore, output tax for the retailer = 10% of 120 = 10/100 × $ 120 = $ 12.Input tax for the retailer = output tax for the wholesaler = $ 9.60Therefore, VAT payable by the retailer = output tax – input tax = $ 12 - $ 9.60 = $ 2.40Therefore, VAT paid by the wholesaler is $ 1.20 and that paid by retailer is $ 2.40 Q16) Aakash wants to invest a part of Rs. 12000 at Rs. 120 in 12% stock. He wants to invest the remaining amount at Rs. 125 in 15% stock. The total dividend he receives per year is Rs. 1360. Find the amount that Aakash should invest in 12% stock at Rs. 120.A16) Suppose the investment that Aakash should do is Rs. X. So, the second investment by him will be 12000 – X.Income on 1st share will be, 12/120 x X = X/10Income for 2nd share, 15/125 x (12000 – X) = 3(12000 – X)/25=> 3(12000 – X)/25 + X/10 = 1360So, 72000 + 5X – 6X = 1360 x 50=> X = 40000So, the required answer is Rs. 40000. Q17) Michael buys shares of face value $ 50 of a company which pays 10 % dividend. At what price did he buy each share from the market if his profit is 16 % on his investment?A17)Let the market value (M.V.) of each share be x.The dividend is calculated on nominal value.The dividend on one share = 10% of $ 50 = $ 5.Therefore, he earned $ 5 on an investment of x.A profit of 16 % on x = 1610016100 × x = 4x254x25Therefore, 4x254x25 = $ 5⟹ x = $25×5425×54⟹ x = $12541254⟹ x = $ 31.25Therefore, Michael bought each share at $ 31.25 from the market.Q18) Jackson buys $ 40 shares in a company, which pays 10% dividend. Jackson buys the share at such a price that his profit is 16% on his investment. At what price did Jackson buy the share?A18)Dividend (profit) given by the company on 1 share = 10% of $ 40 = $ 4.Suppose the man buys one share for x.Therefore, Jackson’s profit = 16% of $ x = $ 16x10016x100According to the problem, 16x10016x100 = 4⟹ x = $ 25Jackson bought the share at $ 25. Q19) Robert bought shares of 6% $ 100 shares at $ 120. Adrian bought shares of 8% $ 20 shares at $ 30. Whose investment was better?A19)6% $ 100 shares at $ 120i.e., the annual income from 1 share of nominal value $ 100 is $ 6, investment for 1 share being $ 120.Therefore, profit percentage = 61206120 × 100 % = 5%Therefore, Robert’s shares give him a profit of 5%8 % $ 20 shares at $ 30i.e., the annual income from 1 share of nominal value $ 20 is $ 8×201008×20100 = $ 8585, investment for 1 share being $ 30.Profit percentage = $85$30$85$30 × 100 % = 163163 % = 51313%Therefore, Adrian’s shares give him a profit of 51313%Therefore, Adrian’s investment was better. Q20) Explain annuities with examples.A20) Annuity-An annuity is a sequence of equal payment or a sequence of regular payment at regular intervals or in other words, An annuity is a fixed sum paid at regular intervals under certain conditions.The length of time during which the annuity is paid can either be until the death of the recipient or for a guaranteed minimum term of years, irrespective of whether the annuitant is alive or not.The time between payments is called the payment interval, and the time which the money is to be paid is called the term of the annuity. Amount of an annuity:Amount of an annuity is the total of all the installments left unpaid together with the compound interest of each payment for the period it remains unpaid. The formulas to find the amount of annuity are given below-
| When annuity is payable annually and interest is also compounded annually |
| annuity is payable half-yearly and interest is also compounded half-yearly |
| annuity is payable quarterly and interest is also compounded quarterly |
| When V of an annuity P payable annually |
| When V of an annuity P payable half-yearly |
| When V of an annuity P payable quarterly |
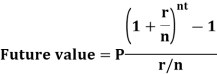 Example: Sundar decides to deposit 20,000rs. at the end of each year in a bank which pays 10% p.a. compound interest.If the installments are allowed to accumulate, what will be the total accumulation at the end of 9 years?Sol.Suppose A rs. be the total accumulation at the end of 9 years. Then we get-
Example: Sundar decides to deposit 20,000rs. at the end of each year in a bank which pays 10% p.a. compound interest.If the installments are allowed to accumulate, what will be the total accumulation at the end of 9 years?Sol.Suppose A rs. be the total accumulation at the end of 9 years. Then we get-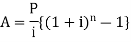 Here P = 20,000 rs., i = 10/100 = 0.1 and n = 9Then
Here P = 20,000 rs., i = 10/100 = 0.1 and n = 9Then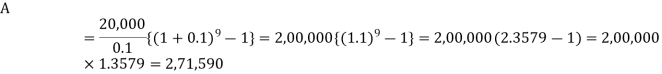 Hence the total required accumulation is 2,71,590 rs. Example: Rajeev purchased a flat valued at 3,00,000rs. He paid 2,00,000 rs. at the time of purchase and agreed to pay the balance with interest of 12% per annum compounded half yearly in 20 equal half yearly installments.If the first installment is paid after six months from the date of purchase, find the amount of each installment.[Given log 10.6 = 1.0253 and log 31.19 = 1.494]Sol.Here 2,00,000 has been paid at the time of purchase when cost of the flat was 3,00,000, we have toconsider 20 equated half yearly annuity payment P when 12% is rate of annual interest compounded halfyearly for present value of 1,00,000rs.So that-
Hence the total required accumulation is 2,71,590 rs. Example: Rajeev purchased a flat valued at 3,00,000rs. He paid 2,00,000 rs. at the time of purchase and agreed to pay the balance with interest of 12% per annum compounded half yearly in 20 equal half yearly installments.If the first installment is paid after six months from the date of purchase, find the amount of each installment.[Given log 10.6 = 1.0253 and log 31.19 = 1.494]Sol.Here 2,00,000 has been paid at the time of purchase when cost of the flat was 3,00,000, we have toconsider 20 equated half yearly annuity payment P when 12% is rate of annual interest compounded halfyearly for present value of 1,00,000rs.So that-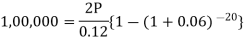 Or
Or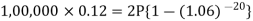
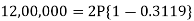
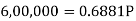 Then-
Then-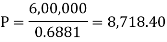 Hence the amount of each installment = 8,718.40Suppose,
Hence the amount of each installment = 8,718.40Suppose,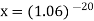 Taking log-
Taking log-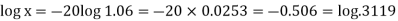 HenceX = 0.3119 Q21) Rohan invests Rs. 5,000 in a term deposit plan. The plan offers an interest rate of 6% p.a., compounded quarterly. How much interest will John earn after one year? Also, what is the effective rate of interest?A21) Here we have-P = 5000, i = 6% per annum or 0.06 p.a. or 0.015 per quarterCompounding period = n = 4
HenceX = 0.3119 Q21) Rohan invests Rs. 5,000 in a term deposit plan. The plan offers an interest rate of 6% p.a., compounded quarterly. How much interest will John earn after one year? Also, what is the effective rate of interest?A21) Here we have-P = 5000, i = 6% per annum or 0.06 p.a. or 0.015 per quarterCompounding period = n = 4 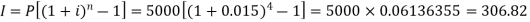 Rohan earns Rs. 306.82 interest after a yearNow the effective rate of interest is-
Rohan earns Rs. 306.82 interest after a yearNow the effective rate of interest is-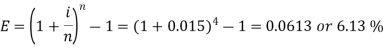 Q22) What is the effective rate of interest on a CD that has a nominal rate of 9.5 percent with interest compounded monthly?A22)Here we have,i = 9.5% or 0.095Now the effective rate of interest is-
Q22) What is the effective rate of interest on a CD that has a nominal rate of 9.5 percent with interest compounded monthly?A22)Here we have,i = 9.5% or 0.095Now the effective rate of interest is-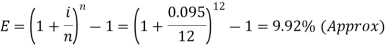 Q23) Amitabh invested Rs. 100 in a scheme that pays out a nominal annual interest rate of 10% compounded on a quarterly basis. Find the Effective Annual Rate.A23)Here we have,i = 10% or 0.1Now the effective rate of interest is-
Q23) Amitabh invested Rs. 100 in a scheme that pays out a nominal annual interest rate of 10% compounded on a quarterly basis. Find the Effective Annual Rate.A23)Here we have,i = 10% or 0.1Now the effective rate of interest is-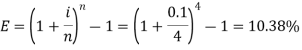 Q24) Sushmita invested 5000rs. At the rate of 8 per cent per annum then what will be the value of the amount she invested in 5 years.A24)Here P = 5000, i = 8/100 = 0.08, n = 5, now
Q24) Sushmita invested 5000rs. At the rate of 8 per cent per annum then what will be the value of the amount she invested in 5 years.A24)Here P = 5000, i = 8/100 = 0.08, n = 5, now 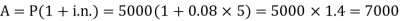 Hence the required amount is - 7000 Q25) Find out the simple interest on 5600 rs. At 12 percent per annum from July 15 to September 26, 2020.A25)Here we calculate the time-Total days from july 15 to sept 26 = 73 days or 73/365 = 1/5 yearsAnd P = 5600, i = 12/100 = 0.12Simple interest = P.i.n. = 5600
Hence the required amount is - 7000 Q25) Find out the simple interest on 5600 rs. At 12 percent per annum from July 15 to September 26, 2020.A25)Here we calculate the time-Total days from july 15 to sept 26 = 73 days or 73/365 = 1/5 yearsAnd P = 5600, i = 12/100 = 0.12Simple interest = P.i.n. = 5600 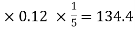 Hence the simple interest is – 134.40 Q26) Harpreet invests 1200rs. At 10 percent per annum for some time and it becomes 1560 then find the principal when that will become 2232 at 8 percent p.a. in the same time.A26)Here in first situation- P = 1200, A = 1560 and i = 0.10So that,
Hence the simple interest is – 134.40 Q26) Harpreet invests 1200rs. At 10 percent per annum for some time and it becomes 1560 then find the principal when that will become 2232 at 8 percent p.a. in the same time.A26)Here in first situation- P = 1200, A = 1560 and i = 0.10So that,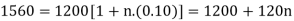
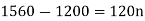
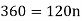
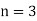 In second situation-A = 2232, n = 3, i = 0.08
In second situation-A = 2232, n = 3, i = 0.08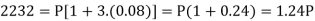
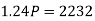
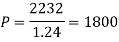 Q27) A sum of money invested at C.I. payable yearly amounts to 10, 816 rs. at the end of the second year and to 11,248.64 rs. at the end of the third year. Find the rate of interest and the sum.A27)Here A1 = 10,816, n = 2, and A2 = 11,248.64, n = 3We know that A = P (1 + i)n we get,10,816 =
Q27) A sum of money invested at C.I. payable yearly amounts to 10, 816 rs. at the end of the second year and to 11,248.64 rs. at the end of the third year. Find the rate of interest and the sum.A27)Here A1 = 10,816, n = 2, and A2 = 11,248.64, n = 3We know that A = P (1 + i)n we get,10,816 = 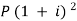 … (i)11,248.64 =
… (i)11,248.64 =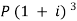 … (ii)Here on dividing equation (2) by (1)-
… (ii)Here on dividing equation (2) by (1)-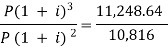 We get-
We get-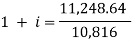
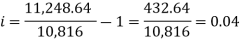 And
And 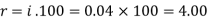 Hence the rate is 4 percent.Now from first equation-10,816 =
Hence the rate is 4 percent.Now from first equation-10,816 = 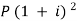 Or
Or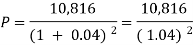 Now-
Now-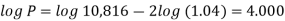 P = antilog 4.000 = 10,000Therefore they require answer- 10,000 Q28) Ronak deposited Rs. 10,000 in a bank for 3 years. Bank gives two offers either 10 percent compounded quarterly or 8% compounded continuously, then which offer is preferable for Ronak?A28)Balance after three years under first offer-
P = antilog 4.000 = 10,000Therefore they require answer- 10,000 Q28) Ronak deposited Rs. 10,000 in a bank for 3 years. Bank gives two offers either 10 percent compounded quarterly or 8% compounded continuously, then which offer is preferable for Ronak?A28)Balance after three years under first offer-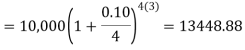 Balance after 3 years under second offer-
Balance after 3 years under second offer-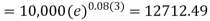 Q29) Suppose the profit percentage is 80% of the cost. If the cost further increases by 20% but the selling price remains the same, how much is the decrease in profit percentage?A29)Let us supposeCP = Rs. 100.Then Profit = Rs. 80 and selling price = Rs. 180.The cost increases by 20% → New CP = Rs. 120, SP = Rs. 180.Profit % = 60/120
Q29) Suppose the profit percentage is 80% of the cost. If the cost further increases by 20% but the selling price remains the same, how much is the decrease in profit percentage?A29)Let us supposeCP = Rs. 100.Then Profit = Rs. 80 and selling price = Rs. 180.The cost increases by 20% → New CP = Rs. 120, SP = Rs. 180.Profit % = 60/120 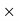 100 = 50%.Therefore, Profit decreases by 30%. Q30) A dishonest shopkeeper sells his grocery using weights 15% less than the true weights and makes a profit of 20%. Find his total gain percentage.A30)Suppose 1 kg of grocery bag. Its actual weight is 85% of 1000 gm = 850 gm.Let the cost price of each gram be Re. 1. Then the CP of each bag = Rs. 850.SP of 1 kg of bag = 120% of the true CPTherefore, SP = 120/100
100 = 50%.Therefore, Profit decreases by 30%. Q30) A dishonest shopkeeper sells his grocery using weights 15% less than the true weights and makes a profit of 20%. Find his total gain percentage.A30)Suppose 1 kg of grocery bag. Its actual weight is 85% of 1000 gm = 850 gm.Let the cost price of each gram be Re. 1. Then the CP of each bag = Rs. 850.SP of 1 kg of bag = 120% of the true CPTherefore, SP = 120/100 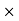 1000 = Rs. 1200Gain = 1200 – 850 = 350Hence Gain % = 350/850
1000 = Rs. 1200Gain = 1200 – 850 = 350Hence Gain % = 350/850  100 = 41.17% Q31) A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on the selling price. On a special sale day, he offers an extra 25% off coupon after the first discount. If the article was sold for Rs. 3600, find the marked price of the articleA31)Let the marked price of the article be x.First a 20% discount was offered, on which another 25% discount was offered.So, 75% of 80% of x = 360075/100
100 = 41.17% Q31) A shopkeeper offers a discount of 20% on the selling price. On a special sale day, he offers an extra 25% off coupon after the first discount. If the article was sold for Rs. 3600, find the marked price of the articleA31)Let the marked price of the article be x.First a 20% discount was offered, on which another 25% discount was offered.So, 75% of 80% of x = 360075/100 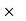 80/100
80/100 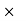 x = 3600 → x = 6000.So the article was marked at Rs. 6000. Q32) The cost price of 30 articles is equal to the selling price of 40 articles. What is the profit or loss percentage?A32)CP of 30 articles = SP of 40 articles Or, CP/SP = 30/40 =3/4
x = 3600 → x = 6000.So the article was marked at Rs. 6000. Q32) The cost price of 30 articles is equal to the selling price of 40 articles. What is the profit or loss percentage?A32)CP of 30 articles = SP of 40 articles Or, CP/SP = 30/40 =3/4Or, 1 – CP/SP = 1- 3/4 = 1/4So, Loss percentage
= (l – CP/SP) x 100 = 1/4x 100 = 25% Q33) Sweety purchases a set of toys that lists for Rs. 950 and it has a trade discount of 30%, then find the net price.A33)As we know that-
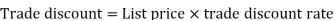
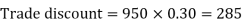 Then Net price = 950 – 285 = 665 Q34) If Raheem will buy a table that lists for Rs. 2000 and it has a trade discount of 50%. Then how much will he pay?A34)As we know that-
Then Net price = 950 – 285 = 665 Q34) If Raheem will buy a table that lists for Rs. 2000 and it has a trade discount of 50%. Then how much will he pay?A34)As we know that-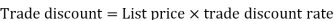
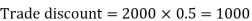 Then Net price = 2000 – 1000 = 1000 Q35) The Price of a book is Rs. 15.75. A book seller sells 1200 books and pays Rs 17,860.50 to the book publisher after deducting his commission. Find the commission rate.A35)Here we have total commission, We have to find the total sale price of books. The total sale price of books = Number of Books
Then Net price = 2000 – 1000 = 1000 Q35) The Price of a book is Rs. 15.75. A book seller sells 1200 books and pays Rs 17,860.50 to the book publisher after deducting his commission. Find the commission rate.A35)Here we have total commission, We have to find the total sale price of books. The total sale price of books = Number of Books 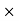 Price = 1200
Price = 1200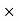 15.75 =18900Commission = Sale price – Amount paid to the Publisher = 18900-17860.5 = 1039.5Commission % = Commission
15.75 =18900Commission = Sale price – Amount paid to the Publisher = 18900-17860.5 = 1039.5Commission % = Commission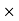 100 /Selling price = 1039.5
100 /Selling price = 1039.5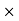 100/18900 = 5.5% Q36) Mahesh sold his car for Rs.68,000 with the help of an agent. If the commission paid by Mahesh is Rs 2550. Find rate of commission, and the net amount received by the Mahesh.A36)Commission % = Commission
100/18900 = 5.5% Q36) Mahesh sold his car for Rs.68,000 with the help of an agent. If the commission paid by Mahesh is Rs 2550. Find rate of commission, and the net amount received by the Mahesh.A36)Commission % = Commission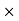 100 /Selling price = 2550
100 /Selling price = 2550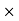 100/68000 = 3.75%Net amount received by farmer = Sale price – Commission = 68000-2550 = Rs65, 450 Q37) An agency pays 15% commission to a notebook distributor. The price of each notebook is Rs 3. If he sells 50 copies of notebook every day, find how much commission he receives in a month and also net amount received by the Agency?A37)Price of each newspaper = Rs 3.Sale price for a day = Number copies sold in day
100/68000 = 3.75%Net amount received by farmer = Sale price – Commission = 68000-2550 = Rs65, 450 Q37) An agency pays 15% commission to a notebook distributor. The price of each notebook is Rs 3. If he sells 50 copies of notebook every day, find how much commission he receives in a month and also net amount received by the Agency?A37)Price of each newspaper = Rs 3.Sale price for a day = Number copies sold in day  price of Cost of news paper = 50
price of Cost of news paper = 50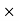 3 = Rs 150Sale price for a year = Number of days
3 = Rs 150Sale price for a year = Number of days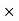 Sale price for a day = 30
Sale price for a day = 30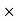 150 = 450 RsCommission = Commission%
150 = 450 RsCommission = Commission%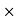 Selling price/100 = 15
Selling price/100 = 15 450/100 = 67.5 Rs.Net amount received by agency = selling price – commission = 450 -67.5 = 382.5 Rs
450/100 = 67.5 Rs.Net amount received by agency = selling price – commission = 450 -67.5 = 382.5 Rs 0 matching results found