Unit 1
Introduction to Statistics
Question Bank
- Define Statistics
Answer: The term “statistics” is defined in two senses: - in singular and in Plural senses.
Firstly, in plural sense, statistics means systematic collection of numerical facts. Secondly in singular sense, the term statistics means the various methods used for collection, analysis and interpretation of numerical facts. It is described as statistical method. In our study we are more concerned with the second meaning of statistics.
Wallis and Roberts has defined Statistics as “Statistics is a body of methods for making wise decisions on the face of uncertainty.”
Edward N. Dubois has defined Statistics as “Statistics is a body of methods for obtaining and analyzing numerical data in order to make better decisions in an uncertain world.”
2. Discuss the scope of Statistics
Answer: Statistics has become indispensible in every area today. There is hardly any field where statistics didn’t enter. Statistics is used right from the education till in aeronautical engineering. However, a few identified areas can be depicted as regards use of statistics:
- Statistics is used by Government, Banks, Financial Institutions in order to have knowledge about the economy, industrial performance and so on.
- In industry, statistics is used widely for quality control for the products manufactured.
- In education, statistics is so essential for the academicians for conducting research.
- In the field of Medical Science also Statistics plays an important role to test the efficiency of a new drug or medicine.
- In space research even statistics is used to conduct research and quality control.
3. State the functions of Statistics
Answer: Statistics is a body of methods for obtaining and analyzing numerical data in order to make better decisions in an uncertain world The functions of statistics can be enumerated as under:
- Expression of facts in numbers – One of the important function of statistics is to express facts in definite form i.e., in the form of numbers. The results expressed in definite form are more convincing than the result expressed on the basis of quality.
- Presentation of facts – Statistics helps in presenting the complex data in a simple form, so that it becomes easy to understand. Statistical methods present data in the form of graph, diagram, average, coefficient, etc.
- Comparison – After simplifying the data, it can be correlated and compared. Comparing data relating to fact is one of the functions of statistics as absolute figures convey less meaning.
- It helps other science- Many laws of economic, law of demand, law of supply have been verified with the help of statistics.
- Forecasting – Statistics also predicts future course of action. On the basis of estimates with the help of statistics we can make future policies.
- Policy making – Statistics helps in formulating favorable policies. Based on the forecast the government makes policies.
4. Explain the nature of Statistics.
Answer: Statistics are numerical statements of facts capable of some meaningful analysis and interpretation, and in singular sense, it relates to the collection, classification, presentation and interpretation of numerical data. It is the science of data collection and analysis.
The nature of statistics can be enumerated as under:
i) Aggregate of facts: Statistics are aggregate of facts as the data collected are facts and figures gathered from various authentic sources and field survey. When the data collected are presented, they are presented in an understandable manner. A single figure like 40 years or 50 years is not statistics. It needs collection of facts and figures to be statistics.
Ii) Numerically expressed: The facts and figures collected are expressed numerically so that it can be measured. Qualitative descriptions don’t have any room in statistics.
Iii) Enumerated or Estimated: The data collected are estimated or enumerated where actual enumeration is not possible. In that case, facts are expressed in terms like ‘good’, ‘average’, ‘excellent’, etc.
Iv) Statistics are affected by a marked extent by multiplicity of causes: Statistics is affected by a number of causes in case of any field of enquiry. For example, In production statistics is affected by soil, climate, raw material, soil fertility and so on.
v) Collected on a systematic manner: The data collected in statistics are presented in a systematic manner after going through a series of procedures. The data collected is in a raw form. Hence it needs to be tabulated, organized, analyzed and then presented in an understandable form.
Vi) Pre determined purpose: The reason behind which statistics are used have a purpose or objective which is pre determined. Whenever a sort of problem is identified, the reason to investigate crops us. Data is collected and accordingly reason is determined.
Vii) Capable of being placed in relation to each other: The data collected in statistics should be comparable and connected with the same department as regards the inquiry. For example, heights and weights of students should be compared with the heights and weights of students in the same class.
5. Enumerate the advantages and disadvantages of Statistics.
Answer: Statistics are numerical statements of facts capable of some meaningful analysis and interpretation, and in singular sense, it relates to the collection, classification, presentation and interpretation of numerical data. It is the science of data collection and analysis. The advantages or importance of Statistics can be identified as under:
- Importance for administrator administration – With the help of statistics, finance minister makes the use of revenue and expenditure data to prepare budget. Also, it helps in taking decision regarding taxes.
- Importance for businessman – statistics helps in providing relevant data. Thus, with the help of those data a business man can estimate demand and supply of the commodity.
- Importance in economics – statistics helps in measuring economics such as gross national output, consumption, saving, investment, expenditures, etc
- Importance for politician – Politician use statistics in formulating economic, social and educational policies of the country
- Importance in the field of education – statistics has wide application in education for determining the reliability and viability to a test, factor analysis, etc.
Besides various advantages, certain disadvantages are also identified which are as under:
- Study of numerical facts only – statistical method does not study quantitative phenomena such as honesty, wisdom, etc. So, experiments are done to measure the reaction of man through data.
- Study of aggregates only – statistics study only aggregates of quantitative facts. It does not study any particular unit.Prof. Horace Sacrist defined statistics, “By statistics we mean aggregates of facts…. And placed in relation to each other”
- It does not depict the entire story of phenomena – Any phenomena happen, due to many causes. But all the cause is not expressed in numbers. So, correct conclusion cannot be drawn. Analyzing quantitative data and ignoring qualitative data cannot give 100% conclusion.
- Homogeneity of data – To compare the data, it is essential that whatever statistics are collected, the same must be uniform in quality.
- It is liable to be miscued – As W.I. King points out, “One of the short-comings of statistics is that do not bear on their face the label of their quality.” Thus, the data collected by inexperienced person may be dishonest or biased. So, to get correct conclusion data must be used in caution.
- Too many methods to study a problem –to find a single result many statistical methods are used. All the methods result vary in each case. “It must not be assumed that the statistics is the only method to use in research, neither should this method of considered the best attack for the problem.” —Croxten and Cowden
6. Write short note on distrust of statistics.
Answer: The authenticity of statistical report fully depends on the statistical investigator who collects and compiles the data. It on his discretion how much with integrity he has done the survey without room for biasness. Many statisticians present the facts with wrong data due to not maintaining integrity. Hence the validity and reliability of statistical data completely depends on the honesty of the statistical investigator. The person who is the statistician might be inexperienced, lack of knowledge or liar. Hence the data may be mishandled and the result would be disastrous. The statisticians should be expert and experienced which can help in producing relevant and authentic information. Just for instance, if in case of medicines which are meant for curing people, but if they are handled by inefficient persons, they may prove fatal to the patients.
We cannot say that the medicine is bad; it is the person who did handle the research and presented wrong reports. Similarly, if a child gets burnt, it’s not the child to blame but the person who was not careful in keeping hot bowl in proper place.
7. What do you mean by census and sample survey?
Answer: A well-organized procedure of gathering, recording and analyzing information regarding the members of the population is called a census. Under method census each and every unit of the universe is included in the collection of data. Huge amount of finance, time and labor are required for gathering information. This method is useful to find out the ratio of male to female, the ratio of literate to illiterate people, the ratio of people living in urban areas to the people in rural areas.
The sample is a small segment considered for study which represents the standard of entire population. The selection of sample should give justifiable conclusion about the whole population. When the population size is very large and it is difficult to consider all members then sampling method is used. Under this method selection of appropriate representative sample is utmost important. On the basis of data collected from sample, conclusion is drawn for the whole population.
8. What are the different types of data?
Answer: Data are the raw facts and figures collected for investigation purposes either field survey or published sources. There are two types of sources of data: Primary Data and Secondary data.
Primary data is the information collected through original or firsthand research. Primary data is more reliable and authenticate as the data is nor changed or altered by any human beings. Also, the data is not published yet. Primary data is gathered by any authorized organization, investigator, and enumerator.
According to Horace Secrist “Data which are gathered originally for a certain purpose are known as primary data.”
Secondary data are public information that has been collected by others. The data collected from primary research and used by other is referred as secondary data. The secondary data may be obtained from various sources like industry surveys, database and information system, etc.
According to Blair, “The data which are used in an investigation, but which have been gathered originally by someone else for some other purpose are known as secondary data.”
9. What do you mean by classification? What are its types?
Answer: Classification of data is the process of arranging the data into homogenous groups according to their common characteristics. Raw data cannot be easily understood and not fit for analysis and interpretation. Therefore, arrangement of data helps the user in comparison and analysis. Example- population of a state can be grouped according to sex, age, etc
According to Prof. Secrist, “Classification is the process of arranging data into sequences according to their common characteristics or separating them into different related parts.”
The different types of classification are:
- Geographical classification – when the data classified according to the geographical location or regions (like states, cities, regions, zones, areas, etc). It is called geographical classification. It is also known as a real or spatial classification.
Ex- production of food grains are classified in different states in India
S.No | Name of states | Total food grains (000’ tones) |
1 | Andhra Pradesh | 1093.00 |
2 | Bihar | 12899.09 |
3 | Karnataka | 1834.70 |
4 | Punjab | 41289.00 |
5 | Orissa | 3600 |
2. Chronological classification – classification of data on the basis of time (like months, years, etc) of their occurrence are called chronological classification. This type of classification is suitable for data which takes place in course of time such as population, production, sales, etc.
Ex – profit of a company from 2001 to 2005
S.No | Year | Profits (in 000 Rs) |
1 | 2001 | 77 |
2 | 2002 | 88 |
3 | 2003 | 89 |
4 | 2004 | 94 |
5 | 2005 | 99 |
3. Qualitative classification – under this classification, the data are classified on the basis of some attributes or quality such as sex, color, literacy, honesty, intelligence, religion, etc. In this the attributes cannot be measured. This sort of classification is known as descriptive classification.
For example, Population can be divided on the basis of marital status as married or unmarried etc.
4. Quantitative classification – quantitative classification states that classification of data according to some characteristics that can be measured such as height, weight, income, sales, profit, etc.
Ex – students are classified according to weights
S.No | Weight | No. Of students |
1 | 30-40 | 77 |
2 | 40-50 | 60 |
3 | 50-60 | 50 |
4 | 60 - 70 | 20 |
5. Alphabetical classification – when data are arranged according to alphabetical order is called alphabetical classification
Ex – state wise classification of population in alphabetical order
S.No | Name of states | Population |
1 | Andhra Pradesh | 157 |
2 | Bihar | 150 |
3 | Karnataka | 200 |
4 | Punjab | 700 |
5 | Orissa | 450 |
10. What is tabulation? Explain the different parts of tabulation.
Answer: Tabulation is a systematic & logical presentation of numeric data in rows and columns, to facilitate comparison and statistical analysis. The method of placing organized data in tabular form is known as tabulation. Tabulation simplifies complex data and facilitates comparison.
According to Prof. L.R Connor, “Table involves the orderly and systematic presentation of numerical data in a form designed to elucidate the problem under consideration”
11. Discuss the various types of Sampling Techniques.
Answer: The sample is a small segment considered for study which represents the standard of entire population. The selection of sample should give justifiable conclusion about the whole population. When the population size is very large and it is difficult to consider all members then sampling method is used. Under this method selection of appropriate representative sample is utmost important. On the basis of data collected from sample, conclusion is drawn for the whole population.
Types of sampling method
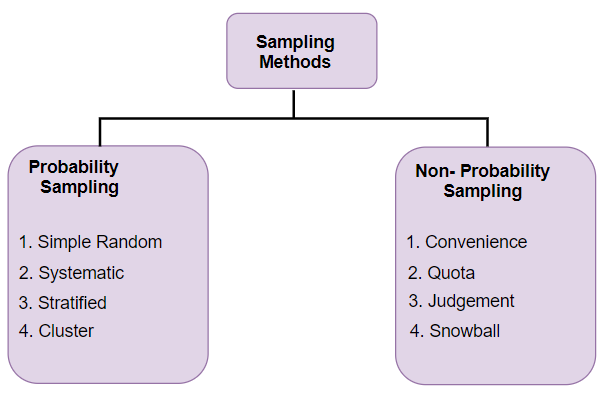
- Probability sampling
It is also called as random sampling. Random sampling is one of the simplest sampling techniques in which each sample has an equal chance of being chosen from the population. It is an unbiased representation of the population
Types of random sampling
- Simple random sampling – It is one of the basic and easiest form of random sampling. Simple random sampling assures that every member have an equal chance of being included in the sample.
- Stratified random sampling – It is also known as proportional random sampling. In this sampling technique, the populations are split into different groups. The overall sample selected randomly from different groups. These techniques guarantee that each group will be represented in sample.
- Systematic random sampling – systematic random sampling refers to selecting sample on a system of interval in a numbered population.
- Cluster random sampling – under cluster sampling, the researcher divide the population into separate groups known as cluster. Here each cluster represents the population as a whole. The researcher randomly selects the cluster for his analysis.
b. Non random sampling
It is also called as non probability sampling. Non random sampling is one of the sampling techniques in which each sample does not have an equal chance of being chosen from the population. It is a biased representation of the population
Types of non-random sampling
- Convenience sampling – under this technique, the samples are selected because they are easily accessible to the researcher. This technique is easiest, cheapest and less time consuming
- Consecutive sampling – It is similar like convenience sampling. Under this technique all subjects that are available as a part of sample are included which result a better presentation of the entire population
- Quota sampling – Under quota sampling, the samples are selected on the same proportions of individuals as the entire population depending on characteristics, traits as the basis of quota.
- Judgmental sampling - Judgmental sampling is more commonly known as purposive sampling. The researcher keeps a specific purpose in mind and selects the subject for sampling process. The researcher believes that some subjects are fit for the research compared to other individuals.
- Snowball sampling – this technique is used when the population size is small. Under snowball sampling, the researcher ask initial subject to identify another potential subject who meets the criteria of research. Thus, this technique hardly represents the population.