|
|
|
|
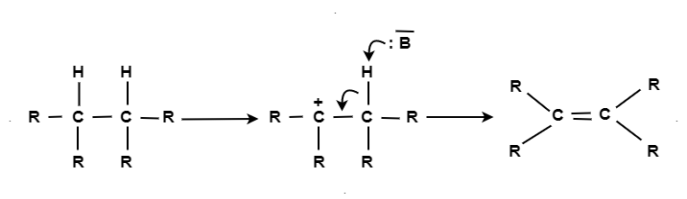
A6) When a reactant A-B reacts; C comes out as the leaving group i.e.; it has taken a place of B or in other words it has substitution reaction. In other words a substitution reaction is a part of one molecular replaced by other atom or group without causing a change a change in rest of the molecule. E.g. A-B + C A-C + B CH4 + Cl2 CH3Cl + HCl CH3Cl + Cl2 CH2Cl2 + HCl CH2Cl2 + Cl2 CHCl3 + HCl CHCl3 + Cl2 CCl4 + HCl The substitution reaction may be brought by free radical nucleophilic or electrophilic reagent. Mechanism: The substitution reaction may be completed through following steps: Chain Initiation: The formation of chlorine free radical took place by the presence of sunlight or ultraviolet rays. Cl : Cl Clo + Clo
Chain Propagation: The Cl2 free radical replaces H2 atom forming an other free radical which can later again formed Cl2 free radical & thus this chain goes on till all the H2 atoms are reduced by the chlorine. Clo + H:CH3 HCl + oCH3 oCH3 + Cl:Cl CH3Cl + oCl oCl + H:CH2Cl HCl + oCH2Cl oCH2Cl + Cl:Cl CH2Cl2 + oCl oCl + H:CH2Cl2 HCl + oCHCL2 oCHCL2 + Cl:Cl CHCl3 + oCl oCl + H:CCl3 HCl + oCCl3 oCCl3 + Cl:Cl CCl4 + oCl
Chain Termination: When all hydrogen atom are replaced by Cl than finally 2Cl free radical combines & chains terminates to form Cl molecule. Clo + oCl Cl:Cl |
|
|
|
|