MRSPTU
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
UNIT 10
Orthographic Projection
Question bank
- What is Orthographic projections with a help of a neat sketch?
Let us suppose that a transparent plane has been set up between an object and the station point of an observer's eye . The intersection of this plane with the rays formed by lines of sight from the eye to all points of the object would give a picture that is practically the same as the image formed in the eye of the observer. This is perspective projection.
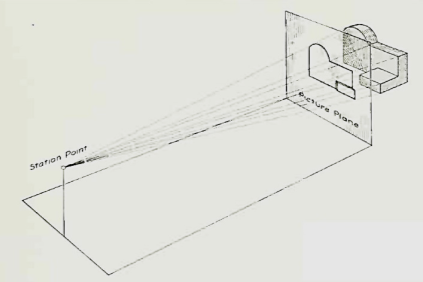
Perspective projection. The rays of the projection converge at the station point from which the object is observed.
If the observer would then walk backward from the station point until he reached a theoretically infinite distance, the rays formed by lines of sight from his eye to the object would grow longer and finally become infinite in length, parallel to each other, and perpendicular to the picture plane. The image so formed on the picture plane is what is known as "orthographic projection." See Fig.
2.
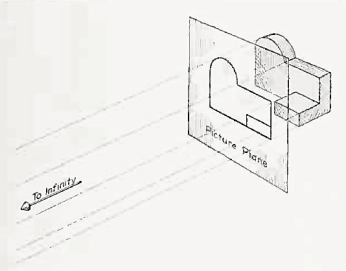
Orthographic projection.
Basically, orthographic projections could be defined as any single projection made by dropping perpendiculars to a plane. However, it has been accepted through long usage to mean the combination of two or more such views, hence the following definition has been put forward: Orthographic projection is the method of representing the exact shape of an object by dropping perpendiculars from two or more sides of the object to planes, generally at right angles to each other; collectively, the views on these planes describe the object completely. (The term "orthogonal" is sometimes used for this system of drawing.)
2. What are the different types of Orthographic views?
The rays from the picture plane to infinity may be discarded and the picture, or "view," thought of as being found by extending perpendiculars to the plane from all points of the object, This picture, or projection on a frontal plane, shows the shape of the object when viewed from the front, but it does not tell the shape or distance from front to rear. Accordingly, more than one projection are required to describe the object.

The frontal plane of projection. This produces the front view of the object.
In addition to the frontal plane, imagine another transparent plane placed horizontally above the object The projection on this plane, found by extending perpendiculars to it from the object, will give the appearance of the object as if viewed from directly above and will show the distance from front to rear.
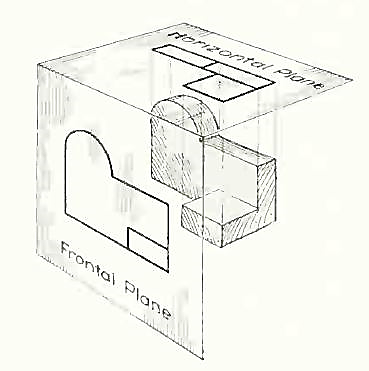
The frontal and horizontal planes of projections. Projection on the horizontal plane produces the top view of the object.
If this horizontal plane is now rotated into coincidence with the frontal plane, the two views of the object will be in the same plane, as if on a sheet of paper.
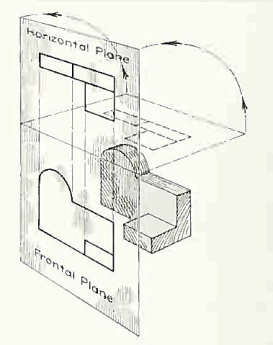
The horizontal plane rotated into the same plane as the frontal plane.
Now imagine a third plane, perpendicular to the first two. This plane is called a "profile plane," and a third view can be projected on it. This view shows the shape of the object when viewed from the side and the distance from bottom to top and front to rear.
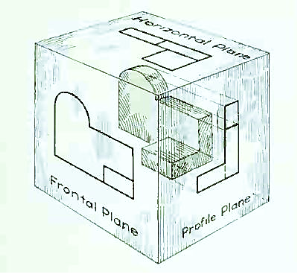
The three planes of projection: frontal, horizontal and profile. Each is perpendicular to other two.
The horizontal and profile planes are shown rotated into the same plane as the frontal plane (again thought of as the plane of the drawing paper). Thus, related in the same plane, they give correctly the three-dimensional shape of the object.
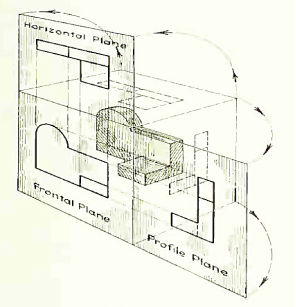
The horizontal and profile planes rotated into the same plane as the frontal plane. This makes it possible to draw three views of the object.
In orthographic projection the picture planes are called "planes of projection"; and the perpendiculars, "projecting lines" or "projectors."
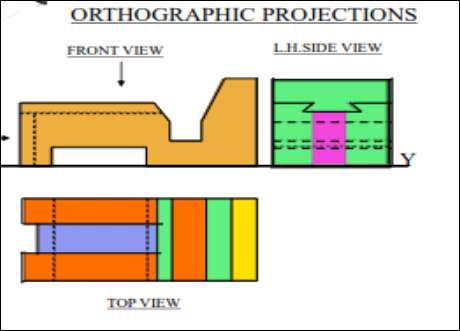
3. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method?
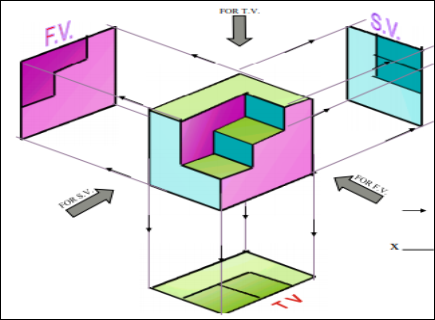
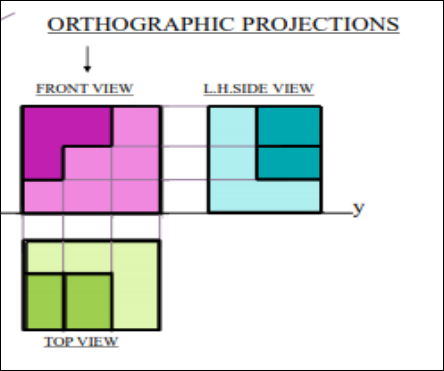
4. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method?
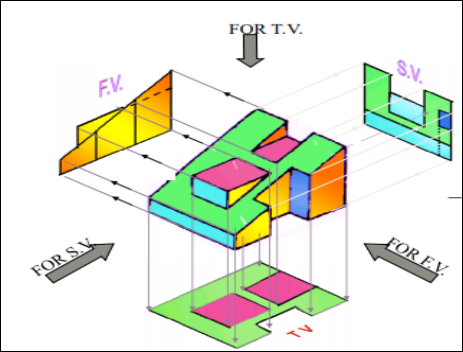
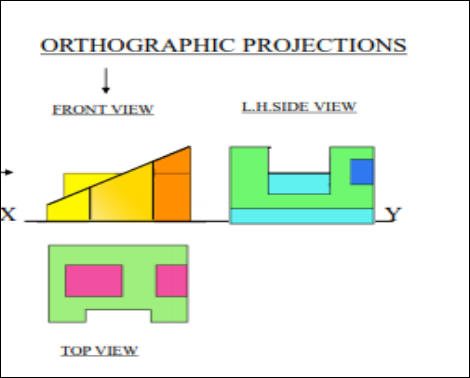
5. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method?
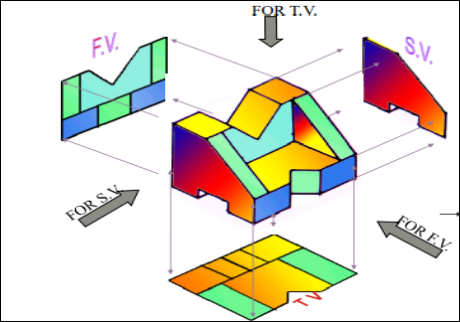
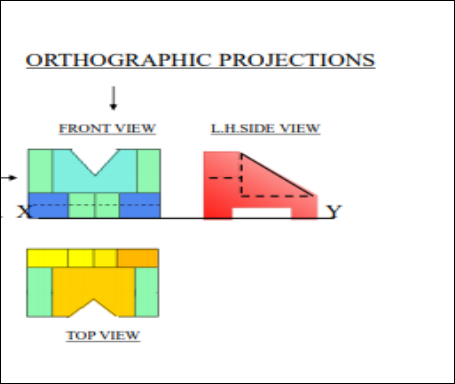
6. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method
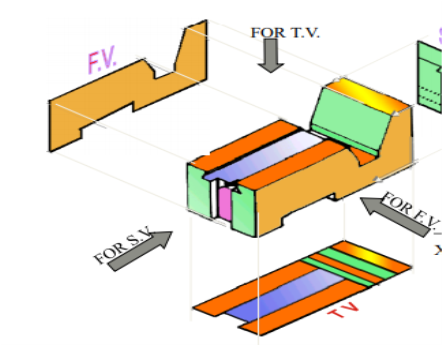
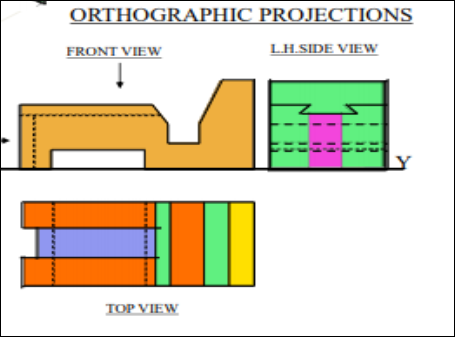
7. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method
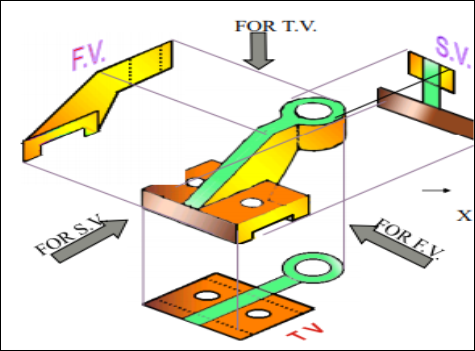
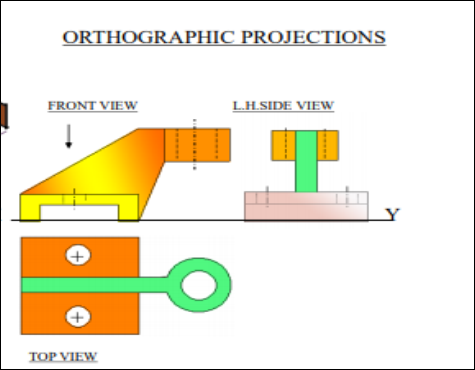
8. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Fv And Tv Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method
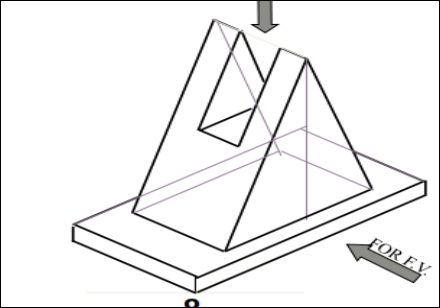
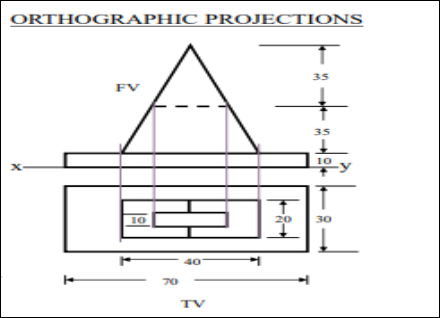
9. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method

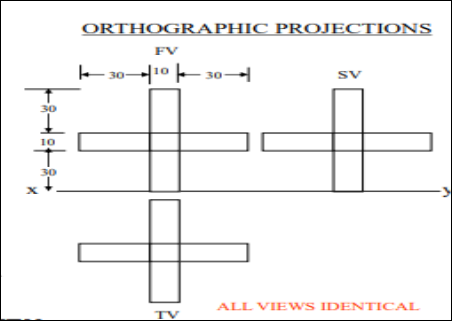
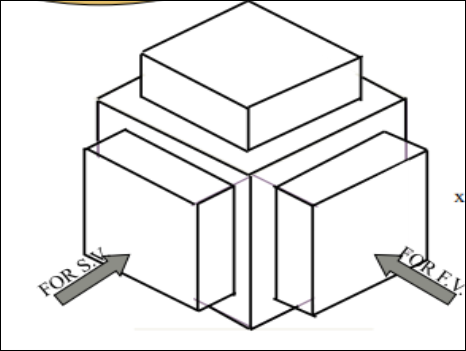 8. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method
8. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method
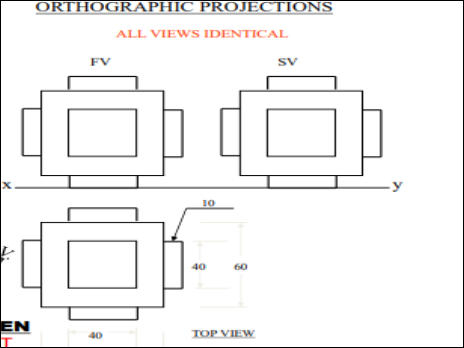
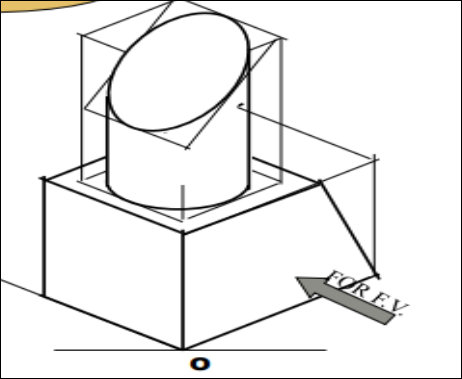 9. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method
9. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Three Views Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method

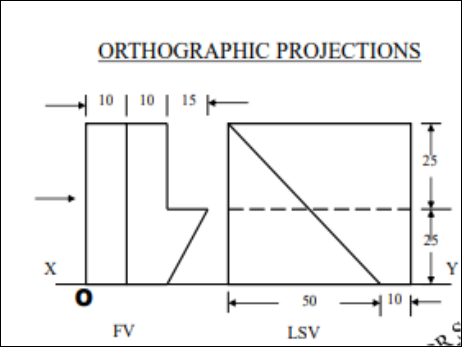
10. Pictorial Presentation Is Given Draw Fv And Lsv Of This Object By First Angle Projection Method