Unit I
Business Finance
Question bank
Q1) What is Business Finance? Write the features of it. 8
A1. Business proprietors want exclusive kinds of investment to develop and hold their enterprise. The begin of an enterprise starts with a top notch want for capital possibilities. Business finance is a extensive umbrella that covers the financial possibilities and prices for companies to buy enterprise capital claims, reply to deliver and call for issues, coins fluctuations, and make investments withinside the equipment and gadget had to begin a enterprise.
The want for credit score is a hallmark of a thriving economy. The wind of extrude is heading closer to extrude withinside the country's highbrow and business elite, as entrepreneurial insects are making present day adolescents better. SMEs want an amazing and dependable manner to elevate money. Top mortgage carriers provide the quality hobby price and tenure alternatives to satisfy the enterprise wishes of small enterprise humans and tech entrepreneurs.
Nature of Business finance
The nature of enterprise finance has unfolded a scenario this is an essential component that no person can challenge. Financing wishes and necessities start at start and keep via the quilt of the enterprise / business enterprise. Corporate Finance / Business Finance are an area of finance that works with economic selection making withinside the company world. Understand the character of enterprise finance withinside the following ways:
Throughout the business enterprise journey, it is truly born, grows, and dies. Funding is wanted at each stage. But finance that is not anything greater than a supervisory disposition, probable does now no longer remedy the hassle of the scenario. I even have come to recognise the character of enterprise finance, this is, how finance should be used.
- Business finance is effectively to be had from numerous sources; however the prices / hobby / compensation phrases related to the character of enterprise finance are exclusive. The situations that want to be taken into consideration close to different factors are probably to verify the character of enterprise finance and pick whether or not it's far clever to reap enterprise finance from a number of the to be had sources. Interest in finance is the fee of its capabilities or benefits.
b. The nature of enterprise finance additionally suggests the outlook for lenders, who can also additionally locate the borrower possibly unsafe. Short-time period or long-time period financing similarly determines elements withinside the nature of an enterprise's financing. Financial control is continually approximately considering the reason for which finance is wanted. It may be a completely long-time period funding or a short-time period funding in liquid or constant assets. Here are a few associated questions on the character of finance.
c. The essential reason of finance is to make sure the price of a business enterprise. What this indicates is that enterprise finance assesses danger and unearths the quality finance gain. There are many thoughts approximately the character of enterprise finance. That is, there are a few elements of studies that everybody wishes to have a take an observe all elements of finance earlier than making apparent choices.
d. As an example, making an investment is associated with fairness and the way to take into account liabilities in preference to paying dividends or having to provide greater inventory. Liquid assets, coins, liabilities, inventories, and enterprise financing are all worried in making within your means choices. Companies, even at the inventory exchange, should invest in others to assist them appreciably boom their holdings. Some groups use buyers to elevate, nurture and circulate forward.
e. The position of the Treasury Manager / Treasury Department is to allocate finance to different departments and additionally offer recommendation at the right use of enterprise finance. The nature of enterprise and economic control has passed through sizable adjustments in lots of elements. Example: Various authorities’ regulations and new regulations are one in every of them.
f. Competition is every other vicinity this is important to financial decisions. Your opposition determines whether or not your ongoing enterprise is in advance or behind. To live in advance, there are folks that are informed sufficient to stability among an excessive amount of debt and growth. Consumers are a part of the financial equation; however a few groups have minimum client revenue. Finance is likewise essential approximately debt and the way to keep away from the economic debt dilemma. Budgeting, accounting, and lots greater all ought to do with enterprise finance.
g. Financial control presupposes the character that creates that it's far because of the economic market. For example, the supply of enterprise finance has elevated sufficiently towards this sizable extrude, converting the character of finance control. Simple financing and its use at the moment are the essence of economic control.
Q2) Write the scope of Business Finance. 5
A2. Scope of Business Finance:
Business Finance researches, analyses, researches, and allocates price range and plenty of different regions protected in the scope of enterprise finance functions. Let's check a number of them:
1. Financial declaration evaluation and research:
Analysing monetary statements is every other scope of enterprise. However, it analyses the scenario that may be a monetary trouble which can arise withinside the marketing and marketing of an enterprise. The monetary statements encompass elements associated with administrative problems in branding and growth of latest companies and changes required for hard enterprise rehabilitation.
2. Financial making plans and control:
Every enterprise or enterprise should manipulate and carry out financially sound evaluation. The monetary supervisor should have understanding of the enterprise's modern-day monetary function that allows you to nicely plan and manipulate those monetary statements. Based in this monetary information, you furthermore might want to make true plans for destiny monetary situations associated with your enterprise. Fiscal price range is a crucial location for coping with monetary making plans. Based on price range, etc., agencies locate deviations among plans in the course of overall performance and try and enhance them. Therefore, the scope of enterprise finance includes monetary making plans and control.
3. Capital shape control:
Financial choices associated with long-time period property are referred to as long-time period funding choices or capital budgets. Business finance notes on this variety relate to funding proposals from many of the many applicable alternatives provided to the enterprise. Here, a capital shape control technique is used to degree the price of this funding suggestion and examine uncertainty and danger. This is due to the fact the go back from the funding suggestion will amplify into the destiny.
4. Financing:
Creating capital possibilities might be one of the maximum crucial and crucial regions of enterprise finance. Business finance calls for financing from agencies with the aid of stocks, company bonds, banks, monetary institutions, lenders and more. Companies can also select to promote their stocks to stocks whilst elevating long-time period investment for the enterprise's growth. Strengthen finances. Balancing enterprise price range is a sensitive act.
5. Capital funding:
There are styles of company finance: operating capital and glued capital. As the call implies, operating capital is commonly used to manipulate each day constant fees which includes uncooked cloth purchases and salaries and overheads. Fixed capital, on the opposite hand, may be used to buy constant property which includes land, buildings, equipment and actual estate. A funding selection is like ends of the identical coin.
6. Finance and danger control / monitoring:
Financial oversight is a generation and there may be virtually a solution. It's in no way a easy task. It calls for quite a few equipment and techniques. Corporate finance wishes to manipulate and manipulate the finance of the enterprise. You want to reduce the danger of your funding and on the identical time assure the most go back at the capital used.
7. Financial control:
Financing control is every other crucial location of enterprise finance. Financial control is worried approximately the enterprise's property or the mixture of systems related to them. Companies want to nicely blend capital and debt finance ratios in the course of their funding. The capital shape is the ratio of fairness capital to debt capital. Currently, a capital shape which includes suitable ratios and capital is diagnosed because the top-quality capital shape.
8. Working capital control:
Making monetary choices almost about modern-day or short-time period property is nicely referred to as operating capital control. Short-time period fulfilment is a want for long-time period fulfilment, and this may be a crucial location of enterprise finance. Therefore, the performance of coping with paintings price range ensures stability among profitability and liquidity.
9. Dividend control:
Business Finance additionally analyzes dividends, books and depreciation policies. All dividend alternatives are primarily based totally at the enterprise's investment choices. The enterprise wishes to determine how lots of its profits may be disbursed to shareholders as dividends and what sort of may be retained as profits. Here, monetary regulators want to increase sound dividend policies.
Q3) What do you mean by Financial Management? Write its nature. 8
A3. Financial Management is managerial activity which is concerned with the planning and controlling of the firm’s financial resources. Financial management also refers to the effective planning, organising, and controlling of monetary resources. Financial management primarily includes decisions and considerations regarding the size of investments, sources and range of use for capital, and the extent of profit earned from the same. It generally involves applying different management techniques to an enterprise’s financial resources to maximise profits.
Definitions:
Howard and Uptron define Financial Management “as an application of general managerial principles to the area of financial decision-making”.
Weston and Brighem define Financial Management “as an area of financial decision making, harmonizing individual motives and enterprise goal”.
Nature of financial management
The nature of financial management includes the following –

- Estimates capital requirements
Financial management helps in anticipation of funds by estimating working capital and fixed capital requirements for carrying business activities.
2. Decides capital structure
Proper balance between debt and equity should be attained, which minimizes the cost of capital. Financial management decides proper portion of different securities (common equity, preferred equity and debt).
3. Select source of fun
Source of fund is one crucial decision in every organisation. Every organisation should properly analyse various source of funds (shares, bonds, debentures etc.) and must select appropriate funds which involves minimal risk.
4. Selects investment pattern
Before investing the amount, the investment proposal should be analysed and properly evaluates its risk and returns.
5. Raises shareholders value
It aims to increase the amount of return to its shareholders by decreasing its cost of operations and increase in profits.
Finance manager should focus on raising the funds from different sources and invest them in profitable avenues.
6. Management of cash
Finance manager observes all cash movements (inflow and outflow) and ensures they should face any deficiency or surplus of cash.
7. Apply financial controls −
Implying financial controls helps in keeping the company actual cost of operation within limits and earning the expected profits.There different approaches involved like developing certain standards for business in advance, comparing the actual cost or performances with pre-established standards and taking all require remedial measures.
Q4) State the scope of Financial Management. 5
A4. Scope of financial management
Financial management is applicable in different areas of management that facilitates effective management of fund in the organisation. The scope of financial management is discussed below-
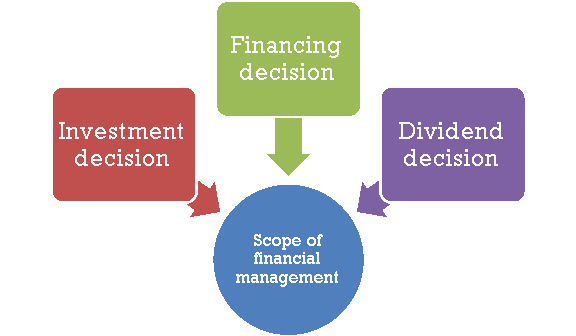
Figure: Scope of financial management
- Investment decision –
Investment decision is also known as capital budgeting. Investment decisions are related to investment in fixed assets. It may be long term and short term.
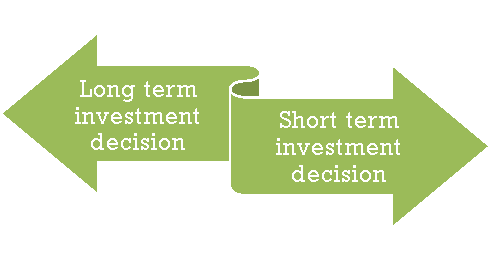
Figure: Types of investment decision
- Long-term investment decisions allow committing funds towards resources like fixed assets. Long-term investment decisions determine the performance of a business and its ability to achieve financial goals over time.
- Short-term investment decisions or working capital financing decisions mean committing funds towards resources like current assets. It occupies funds for a shorter period, including investments in inventory, liquid cash, etc. Short-term investment decisions directly affect the liquidity and performance of an organisation.
- Financing decision –
Financing decision involves the possible sources of raising finances. The financial manager estimates the requirement of funds and accordingly determines the sources of raising the required funds. They are of 2 different types –

Figure: Financial decisions
- Financial planning decisions attempt to estimate the sources and possible application of accumulated funds. A proper financial planning decision is crucial to ensure the availability of funds whenever required.
- Capital structure decisions involve identifying various sources of funds. It involves decisions regarding the combination of owned capital and borrowed capital. It facilitates the selection of the best external sources for short or long-term financial requirements.
3. Dividend decision –
It involves decisions taken with regards to net profit distribution profits. It involves decisions regarding-
- Dividend for the shareholders.
- Retained profits (usually depends on a particular company’s expansion and diversification plans).
Q5) Explain the two main objectives of Financial Management. 8
A5. There are mainly two objectives of financial management-
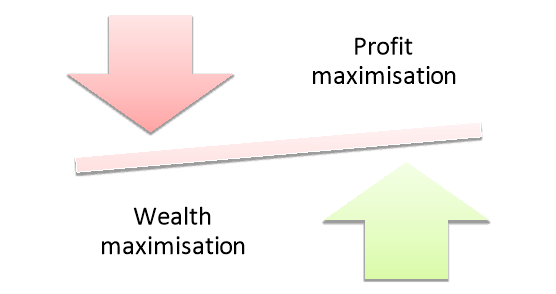
Figure: Objectives of financial management
(1) Profit Maximization:
According to this approach, all activities which increase profits should be undertaken and which decrease profits should be avoided. Profit maximization implies that the financial decision making should be guided by only one test, which is, select those assets, projects and decisions which are profitable and reject those which are not.
The following arguments are advanced in favour of this approach:
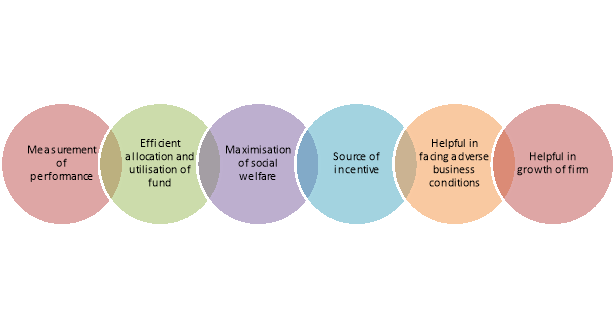
(i) Measurement of Performance
Profit is a test of economic efficiency of a business. It is a yardstick by which the economic performance of a business can be judged.
(ii) Efficient Allocation and Utilisation of Resources
Profit maximization leads to efficient allocation and utilisation of scarce resources of the business because sources tend to be directed to uses from less profitable projects to more profitable projects.
(iii) Maximisation of Social Welfare
Profitability is essential for fulfilling the goal of social welfare also. Maximization of profits leads to the maximization of social welfare.
(iv) Source of Incentive
Profit acts as a motivator or incentive which induces a business organisation to work more efficiently. If profit motive is withdrawn the pace of development will be reduced.
(v) Helpful in Facing Adverse Business Conditions
Economic and business conditions go on changing from time to time. There may be adverse business conditions like recession, severe competition etc. Under adverse circumstances a business will be able to survive only if it has some past earnings to rely upon. Hence, a business should maximize its profits when the circumstances are favourable.
(vi) Helpful in the Growth of the Firm
Profits are the major source of finance for the growth of a firm.
However, the profit maximization approach has been criticised on several grounds:
(2) Wealth Maximization:
This approach is now universally accepted as an appropriate criterion for making financial decisions as it removes all the limitations of profit maximization approach. It is also known as net present value (NPV) maximization approach. According to this approach the worth of an asset is measured in terms of benefits received from its use less the cost of its acquisition. Benefits are measured in terms of cash flows received from its use rather than accounting profit which was the basis of measurement of benefits in profit maximization approach. Measuring benefits in terms of cash flow avoids the ambiguity in respect of the meaning of the term profit. Another important feature of this approach is that it also incorporates the time value of money. While measuring the value of future cash flows an allowance is made for time and risk factors by discounting or reducing the cash flows by a certain percentage. This percentage is known as discount rate. The difference between the present value of future cash inflows generated by an asset and its cost is known as net present value (NPV). A financial action (or an asset or a project) which has a positive NPV creates wealth for shareholders and, therefore, is undertaken. On the other hand, a financial action resulting in negative NPV should be rejected since it would reduce shareholder’s wealth. If one out of various projects is to be chosen, the one with the highest NPV is adopted. Hence, the shareholder’s wealth will be maximized if this criterion is followed in making financial decisions.
The NPV can be calculated with the help of the following formula:

Q6) What is Profit maximization? What are its disadvantages? 5
A6. : According to profit maximization approach, all activities which increase profits should be undertaken and which decrease profits should be avoided. Profit maximization implies that the financial decision making should be guided by only one test, which is, select those assets, projects and decisions which are profitable and reject those which are not
Disadvantages of profit maximisation
(i) Ambiguous:
One practical difficulty with this approach is that the term profit is vague and ambiguous. Different people take different meanings of term profit. For example, profit may be short-term or long-term, it may be before tax or after tax, and it may be total profit or rate of profit. Similarly, it may be returned on total capital employed or total assets or shareholders’ funds and so on.
(ii) Ignores the Time Value of Money:
This approach ignores the time value of money, i.e., it does not make a distinction between profits earned over the different years. It ignores the fact that the value of one rupee at present is greater than the value of the same rupees received after one year. Similarly, the value of profit earned in the first year will be more in comparison to the equivalent profits earned in later years.
(iii) Ignores Risk Factor:
This approach ignores the risk associated with the earnings. If the two firms have the same total expected earnings, but if earnings of one firm fluctuate considerably as compared to the other, it will be more risky.
Investors in general, have a preference for a lower income with less risk in comparison to high income with greater risk. But this approach does not pay any attention to the risk factor.
(iv) Ignores Future Profits:
The business is not solely run with the objective of maximising immediate profits. Some firms place more importance on growth of sales. They are willing to accept lower profits to achieve stability provided by a large volume of sales.
(v) Ignores Social Obligations of Business:
This approach ignores the social obligations of business to various social groups like workers, consumers, society, Government etc. A firm cannot exist for long when interests of social groups are ignored because these groups contribute to its smooth run.
(vi) Neglects the Effects of Dividend Policy on Market Price of the Shares:
Under this approach the firm may not think of paying dividends because retaining profit in the business may satisfy the goal of maximising the earning per share.
Q7) What is wealth maximization? What are its advantages? 5
A7. Wealth Maximization: This approach is now universally accepted as an appropriate criterion for making financial decisions as it removes all the limitations of profit maximization approach. It is also known as net present value (NPV) maximization approach. According to this approach the worth of an asset is measured in terms of benefits received from its use less the cost of its acquisition. Benefits are measured in terms of cash flows received from its use rather than accounting profit which was the basis of measurement of benefits in profit maximization approach. Measuring benefits in terms of cash flow avoids the ambiguity in respect of the meaning of the term profit. Another important feature of this approach is that it also incorporates the time value of money. While measuring the value of future cash flows an allowance is made for time and risk factors by discounting or reducing the cash flows by a certain percentage. This percentage is known as discount rate. The difference between the present value of future cash inflows generated by an asset and its cost is known as net present value (NPV). A financial action (or an asset or a project) which has a positive NPV creates wealth for shareholders and, therefore, is undertaken. On the other hand, a financial action resulting in negative NPV should be rejected since it would reduce shareholder’s wealth. If one out of various projects is to be chosen, the one with the highest NPV is adopted. Hence, the shareholder’s wealth will be maximized if this criterion is followed in making financial decisions.
It has the following advantages in its favour:
(1) It uses cash flows instead of accounting profits which avoids the ambiguity regarding the exact meaning of the term profit.
(2) It gives due importance to the time value of money by reducing the future cash flows by an appropriate discount or interest rate. If higher risk and longer time period are involved, higher rate of discount or interest will be used to find out the present value of future cash benefits. The discount or interest rate will be lower for the projects which involve low risk.
(3) It gives due importance to payment of regular dividends – In this approach financial decisions are taken in such a way that the shareholders receive the highest combination of dividends and increase in the market price of the shares.
(4) It gives due importance to risk factor and analyses risk and uncertainty so that the best course of action can be selected out of different alternatives.
(5) It gives due importance to social responsibilities of the business.
(6) It takes into consideration long-run survival and growth of the firm.
Q8) State the difference between profit maximization and wealth maximization. 8
A8. The differences between profit maximisation and wealth maximisation are highlighted below-
Sr. No. | Profit maximisation | Wealth maximisation |
| It is short term objective. | It is long term objective. |
2. Time value of money | It takes into account time value of money. | It does not take into account time value of money. |
3. Risk | It does not consider risk factor. | It considers the risk factor. |
4. Objective | It focuses on large of amount of profit. | Its objective is to achieve highest market value of common stock. |
5. Usage | It helps in achieving a larger value of a company’s worth, which may reflect in the increased market share of the company. | It helps in achieving efficiency in the company’s day-to-day operations to make the business profitable. |
Q9) What is Capital Budgeting? 5
A9. A capital expenditure budget or capital budget is the process of making decisions about investing in fixed assets that are not intended for sale, such as land, buildings, machinery, and furniture.
The term investment refers to the expenditure that must be made in connection with the acquisition and development of long-term facilities, including fixed assets. This refers to the process by which management selects investment proposals that are worth investing in the available funds. To this end, management is responsible for deciding whether to acquire, add, or replace fixed assets in the light of the company's overall purpose.
Fixed investment is a very difficult question to answer. The term capital expenditure is related to accounting. Capital spending is usually aimed at making a profit in the future. In other words, in contrast to income and expenditure, it is assumed that the profit will be used up within the year for more than one year.
Capital Budgeting is one of the appraising techniques of investment decisions. Capital Budgeting is defined as the firm‘s decision to invest its current funds most efficiently in long term activities in anticipation of an expected flow of future benefits over a series of years.
Definition
Charles. T. Horngreen defined capital budgeting as ― “Long term planning for making and financing proposed capital out lay”.
According to Keller and Ferrara, ― “Capital Budgeting represents the plans for the appropriation and expenditure for fixed asset during the budget period”.
Robert N. Anthony defined as ― “Capital Budget is essentially a list of what management believes to be worthwhile projects for the acquisition of new capital assets together with the estimated cost of each product.”
Q10) What do you mean by capital budgeting? Write the nature of it? 8
A10. A capital expenditure budget or capital budget is the process of making decisions about investing in fixed assets that are not intended for sale, such as land, buildings, machinery, and furniture.
The term investment refers to the expenditure that must be made in connection with the acquisition and development of long-term facilities, including fixed assets. This refers to the process by which management selects investment proposals that are worth investing in the available funds. To this end, management is responsible for deciding whether to acquire, add, or replace fixed assets in the light of the company's overall purpose.
Fixed investment is a very difficult question to answer. The term capital expenditure is related to accounting. Capital spending is usually aimed at making a profit in the future. In other words, in contrast to income and expenditure, it is assumed that the profit will be used up within the year for more than one year.
Capital Budgeting is one of the appraising techniques of investment decisions. Capital Budgeting is defined as the firm‘s decision to invest its current funds most efficiently in long term activities in anticipation of an expected flow of future benefits over a series of years.
Nature
Budgets should necessarily be integrated with corporate planning. The budget defines the goals of the entire company and each functional area concretely and quantitatively. It provides guidelines on how to achieve these goals. It is inherently administrative and compelling compared to corporate planning, and its preparation is the responsibility of the line manager.
Budgets typically cover a year with monthly or quarterly splits. The creation of such a budget also includes an analysis of the company's current capabilities (assets and personnel) and financial position, as well as economic conditions, competitor behaviour, and future demand in the current market.
Some organizations follow a "rolling budget system". The system removes the month or quarter that just ended and adds the next month or quarter at the end of each month or quarter. The biggest advantage of this budget over a regular budget is that it lets management think concretely about the next 12 months.
Under this system, the next 12-month plan is always available. However, a better system is to prepare a one-year budget, divide it into one-month budgets, and supplement the budget with rolling forecasts. Actual results should be compared with both budget goals and forecasts. Investigating the causes of variance compared to the budget provides better learning because it gives insights on where managers made mistakes in developing budget assumptions.
Q11) Discuss the importance of capital budgeting. 5
A11. Below are some points to explain the importance of capital budgets.
- Calculating future cash flows: The capital budgeting process takes into account the discounted rate of return and follows various techniques, such as calculating the net present value, to determine the expected future cash inflows and expected future cash outflows of the project. Consider. Internal Rate of Return, Payback Period, Profitability Index, and Accounting Rate of Return Thus, an organization uses the process of capital budgeting to get ideas about future totals and net rates of return for current investments. ..
- Helps the organization's long-term goals: The capital budgeting process not only helps the organization make long-term decisions because it provides ideas for future costs and growth that takes into account expected future cash flows. It also helps you set long-term goals. Setting long-term goals is one of the most important and delicate areas of any organization and making the wrong decisions in this area can negatively impact an organization's long-term profitability.
- Spending Management: The capital budgeting process provides ideas for expected future cash inflows and expected future cash outflows. Consider the investment cost of the project in consideration of other related costs such as R & D cost and running cost of the project. Therefore, this information can be used by organizations to monitor total costs and manage future costs. Proper management and management of total costs is a very important factor in terms of company growth and efficiency.
- Useful for lasting decisions: In general, capital-related decisions are permanent decisions made by an organization because of the large investment and funding involved. Once such a decision is made, it cannot be undone in the future. Therefore, the capital budgeting process helps organizations make effective decisions for such lasting decisions.
- Maximizing Wealth: The interests and investment decisions of a company's shareholders depend on long-term investment decisions. Appropriate and systematic investment of capital and other long-term investments by the company will increase shareholder confidence, increase interest in investing in the company and maximize the company's assets.
- Information flow within a department: The entire capital budgeting process involves many steps and ideas, and many decisions are made by different levels of the enterprise. This allows information to flow and exchange within different departments, improving connectivity between departments.
- Large-scale protection of funds involved: As mentioned above, the acquisition of capital assets involves a large amount of funds by the company. Therefore, the capital budgeting process protects some of the large financial investments or large amounts of money invested by the company from future uncertainties.
- Protection from future risks: There are various risks associated with the acquisition of capital by the company. All of this is related to future events and uncertainties. Therefore, the capital budgeting process assists the organization in pre-assessment of the associated risks, and the management of the company plans the protection of such risks well in advance to minimize its impact.
- New opportunities in the market: Introducing new projects in the market creates many employment opportunities for new employees as well as existing ones. This boosts individual morale and drives the country's economic growth.
- Understand the complexity of a project: With the help of the capital budgeting process, the management of a company has ideas about the different types of complexity or complexity that may be encountered or encountered during the development of a project. Therefore, management can have a ready and proactive strategy to deal with such future complexity that arises from the project.
Q12) What is capital budgeting? How to take capital budgeting decisions? 5
A12. A capital expenditure budget or capital budget is the process of making decisions about investing in fixed assets that are not intended for sale, such as land, buildings, machinery, and furniture.
The term investment refers to the expenditure that must be made in connection with the acquisition and development of long-term facilities, including fixed assets. This refers to the process by which management selects investment proposals that are worth investing in the available funds. To this end, management is responsible for deciding whether to acquire, add, or replace fixed assets in the light of the company's overall purpose.
Fixed investment is a very difficult question to answer. The term capital expenditure is related to accounting. Capital spending is usually aimed at making a profit in the future. In other words, in contrast to income and expenditure, it is assumed that the profit will be used up within the year for more than one year.
Capital Budgeting is one of the appraising techniques of investment decisions. Capital Budgeting is defined as the firm ‘s decision to invest its current funds most efficiently in long term activities in anticipation of an expected flow of future benefits over a series of years.
There are four majors techniques used for capital budgeting decision analysis in order to select the viable investment are as below:
- Payback Period Method
It is the most popular and widely recognized traditional methods of evaluating the investment proposals. It can be defined as the number of years to recover the original capital invested in a project. The payback period can be used as accept or reject criterion as well as a method of ranking projects. The payback period is the number of years to recover the investment made in a project. If the payback period calculated for a project is less than the maximum payback period set-up by the company, it can be accepted. As a ranking method it gives the highest rank to a project which has the lowest payback period, and the lowest rank to a project with the highest payback period. Whenever a company faces the problem of choosing among two or more mutually exclusive projects, it can select a project on the basis of payback period, which has shorter period than the other projects. The formula for calculation of payback period method is-
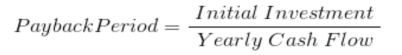
b. Accounting Rate of Return
This technique uses the accounting information revealed by the financial statements to measure the profitability of an investment proposal. It can be determined by dividing the average income after taxes by the average investment. According to Soloman, Accounting Rate of Return can be calculated as the ratio, of average net income to the initial investment. On the basis of this method, the company can select all those projects whose ARR is higher than the minimum rate established by the company. It can reject the projects with an ARR lower than the expected rate of return. This method also helps the management to rank the proposal on the basis of ARR.
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) = Original Investment Average Net Income
OR
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) = Average Investment Average Net Income
The following are the merits of ARR method:
(i) It is very simple to understand and calculate;
(ii) It can be readily computed with the help of the available accounting data;
(iii) It uses the entire stream of earnings to calculate the ARR.
c. Net Present Value (NPV)
The net present value method is a classic method of evaluating the investment proposals. It is one of the methods of discounted cash flow techniques, which recognizes the importance of time value of money. It correctly postulates that cash flows arising at time periods differ in value and are comparable only with their equivalents i.e., present values. It is a method of calculating the present value of cash flows (inflows and outflows) of an investment proposal using the cost of capital as an appropriate discounting rate. The net present value will be arrived at by subtracting the present value of cash outflows from the present value of cash inflows. Steps to compute net present value:
(i) Estimation of future cash inflows
(ii) An appropriate rate of interest should be selected to discount the cash flows. Generally, this will be the ―cost of capital‖ of the company, or required rate of return.
(iii) The present value of inflows and outflows of an investment proposal has to be computed by discounting them with an appropriate cost of capital.
(iv) The net value is the difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows.
The formula for the net present value can be written as:
NPV= C1 /(1+k)1 + C2 / (1+K)2 +C3 /(1+k)3 +…………. Cn /(1+K)n – I
Where,
C = Annual Cash inflows,
Cn = Cash inflow in the year n
K = Cost of Capital
I = Initial Investment
d. Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The internal rate of return method is also a modern technique of capital budgeting that takes into account the time value of money. It is also known as ‘time adjusted rate of return’ discounted cash flow’ ‘discounted rate of return,’ ‘yield method,’ and ‘trial and error yield method’.
In the net present value method, the net present value is determined by discounting the future cash flows of a project at a predetermined or specified rate called the cut-off rate. But under the internal rate of return method, the cash flows of a project are discounted at a suitable rate by hit and trial method, which equates the net present value so calculated to the amount of the investment.
Under this method, since the discount rate is determined internally, this method is called as the internal rate of return method. The internal rate of return can be defined as that rate of discount at which the present value of cash-inflows is equal to the present value of cash outflows.