Unit 1
Money
Q1) If you want to buy something you need money. Right? Explain Money and its functions. 8
A1) Goods time-honoured via way of means of standard consent as a medium of cash, financial trade. It is a medium wherein fee and fee are expressed. As a currency, it circulates anonymously from individual to individual and from united states of America to united states of America, hence facilitating trade, and it's miles a prime degree of wealth.
Money issues have involved humans from the time of Aristotle to the present. Paper categorized for $ 1, 10 Euros, one hundred Yuan, and 1,000 yen is a touch specific from paper of the equal length torn from newspapers and magazines, however the proprietor can order a few food. , Drinks, apparel and different family objects are handiest appropriate for lighting. What's the difference? The easy and accurate solution is that contemporary-day cash is a social ingenuity. People be given cash that manner due to the fact they understand that others do. This not unusual place feel makes a bit of paper precious due to the fact everybody thinks it's miles. Also, in my experience, cash has usually been time-honoured in trade for precious goods, assets, or services. After all, cash is a social exercise, however an uncommon power exercise that humans comply with even below intense provocation. Of course, the power of this treaty is that it permits governments to make cash via way of means of inflating (increasing) the currency. But it is now no longer indestructible. When the quantity of those papers will increase significantly, inclusive of at some stage in and after the war, cash can also additionally appear to be not anything extra than paper after all. If the social association to preserve cash as a medium of trade collapses, humans will search for options inclusive of cigarettes and cognac that have been briefly used as a medium of trade in Germany after World War II. In much less intense situations, new cash can also additionally update vintage cash. In many nations with records of excessive inflation, inclusive of Argentina, Israel and Russia, the fee of the greenback is extra solid than the neighbourhood currency, so charges can be anticipated in different currencies inclusive of America greenback. In addition, the greenback is widely known and the United States of America’s citizens be given the greenback as a medium of trade as it affords a extra solid shopping electricity than the neighbourhood currency.
Functions of Money:
Money performs various functions. Mainly the functions of money can be classified into three groups’ namely
(i) Primary functions (ii) Secondary function (iii) Contingent functions
1) Primary function: Primary functions are basic or fundamental function of money. In fact, they are the original functions of money which ensure smooth working of the economy. Following are the primary functions:
a) Medium of exchange: Money acts as an effective medium of exchange. It facilitates exchange of goods and services. Everything is bought and sold with help of money. By performing as the medium of exchange, money removes the difficulties of barter system.
b) Measure of value: Money serves as a common measure of value. The value of all goods and services are measured in terms of money. In other words, pieces of all goods and services are expressed in terms money.
2) Secondary function: Secondary functions are those functions which are derived from primary function.
a) Standard of deferred payment: Money acts as an effective standard of deferred payments. Deferred payments refer to payment to be made in future. Deferred payments have become the day to day activity in modern society. Money facilitates all kinds of credit transactions. Both, borrowings as well as lending are done in terms of money. All kinds of Hire purchase transactions are carried out in terms of money. As money enjoys the attributes of stability, Durability and General acceptability, it acts as a better standard of deferred payments.
b) Store of value: Money serves as a store of value. Savings were discouraged under the barter system due to lack of store of value. With inventions of money, it is possible to save. At present all savings are done in terms of money. Bank deposits represent the savings of the people. Moreover, money can be easily converted into any other Marketable assets like Land, Machinery, Plant, etc. Thus it facilitates capital accumulation. Money being the most liquid assets, it acts as a better store of value than any other assets.
c) Transfer of value: Money acts as a means of transferring purchasing power. Money facilitates transfer of value from one person to another person & one place to another place. As money enjoys general acceptability, a person can dispose of his property in Delhi and purchase new property at Mumbai. Instrument like cheques and bank drafts enable such transfer easy and quick.
3) Contingent function: In additions to the above functions, money has to performs certain special function known as contingent functions –
- Basis of credit: The modern business system is entirely linked to the credit system of the country. The credit system, on the other hand, derives its strength from money. In the absence of money, the credit instruments like cheque, bill of exchange, etc. are of no use. It is the quantity of money supply which determines the supply of credit in the country.
- Measurement & Distribution of national income: The national income is the result of efforts contributed by various factors of production. Money is helpful in measuring the contribution made by each factor of production and thus facilitates the distribution of national income between factors.
- Equalization of marginal utility: Every consumer is interested in spending his limited income in such a manner as to achieve maximum satisfaction (utility) for this purpose of achieving maximum satisfaction; he has to equalize marginal utilities from different goods. Money helps the consumer in equalizing marginal utilities.
- Liquidity: Money being the most liquid asset, it can be converted into any other assets quickly. An entrepreneur has to keep capital in liquid form for various purposes, such as transaction, Precautionary and speculative motives. Money provides such liquidity.
- Estimation of Macro Economic variables: Macro economic variables like Gross National Product, total savings, total investment etc. can be easily estimated in monetary terms. It also facilitates government tax collection, budgeting etc.
Q2) It refers to currencies issued by the Government of India and Reserve Bank of India. What does it refers to? What are its uses? 8
A2) High-powered plutocrat or strong plutocrat refers to currencies issued by the Government of India and the Reserve Bank of India. Some of this currency is stored with the general public and the rest is stored in reserve banks as wherewithal. So, we've the following equation
H = C R
Where H = strong plutocrat
C = Currency with the general public (bills coins)
R = Government and bank deposits by RBI
So, the sum of the Croesus deposited with the people and the bankroll of the bank is called strong Croesus. It's generally created by the central bank. Because corporate bank bankroll plays an important capacity in credit creation. So it's really important to study endowment. There are two types of reserves (i) legal reserves (RR) for banks associated with central banks and (ii) another reserves (ER).
So, H = C RR ER
High- powered plutocrat is also called collateralized plutocrat (RM) because the bank holds a reserve fund (R) and is created rested on this demand deposit (DD). High power plutocrat is called base plutocrat because the warp for creating credits is the Reserve Fund (R) and Ris is acquired as part of the High-Power Money (H) Security Fund.
Uses:
As mentioned anteriorly in this chapter, the following are vital factors in determining high power plutocrat
- Currency with the people
- Other deposits by RBI
- Cash with the bank
- Bank deposit by RBI.
High power Croesus (H) includes public currency (C), important marketable bank reserves, and other reserves (ER). So, the following equation is drawn.
Thus we get, the equation:
H=C+RR+ER
Supply of money (M) includes bank deposits (D) and currency with public©. Thus,
M=C+D
Dividing both the equations , we get
M÷H = C/D+D/D÷C+RR+ER
Now , dividing the numerator and the denominator by D we get:
M/H=C/D+C/D÷C/D+RR÷D+ER÷D
M/H= 1+ C÷D/C÷D+RR÷D+ER÷D
Presently, the demanded reserve proportion is RRr, the demanded reserve must proportion is RR/ D, and the else reserve proportion is ERr.
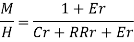

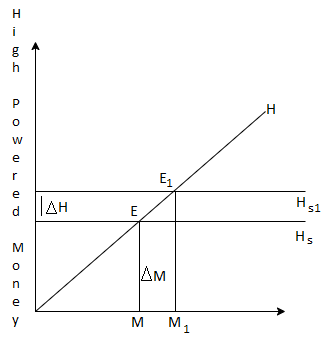
The enclosed figure shows that when the fund of high-power Croesus increases the AH, the Hs bend jumps to Hs and the fund and demand of high-power money in equilibrium at E. When the fund of high-power Croesus goes to Hs, the Croesus fund is turned on. The new equilibrium point is E, the Croesus fund in these two OMs. From the enclosed figure, it's also clear that when high- power Croesus increases AH, the Croesus fund increases to AM.
Q3) What are the sources of High Powered money? 5
A3) The following are influential sources of high-powered money:
(1) Reserve Bank of India claims; The Reserve Bank also lends to the government. The loan is in the form of a reserve bank investing in government bonds. After subtracting government deposits from the reserve bank loan volume, the volume of net bank credit to the government is calculated. It's also a significant source of plutocrat.
(2) Reserve Bank's Net Foreign Exchange. Wherewithal Arranging foreign exchange resources is the job of the Reserve Bank. When the reserve bank pays the public plutocrat to buy foreign securities, the volume of foreign exchange increases and the strong plutocrat increases. Conversely, when a reserve bank sells foreign securities, the volume of foreign exchange with the country's central bank losses. As a result, strong plutocrat is reduced.
(3) Government Monetary Responsibility to the People the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India is responsible for publishing 1-rupee notes and coins. This function is carried out through the government to fulfil its pecuniary liabilities to the people.
The volume of debt and plutocrat reservoir will increase, and the volume of high-powered plutocrat will also increase.
(4) Reserve Bank's Net Non-Monetary Debt Reserve Bank's non-monetary debt is in the form of capital introduced into public and statutory wherewithal. The main points are the Reserve Bank of India workers paid-in capital, reserve fund, donation fund and pension fund.
Reserve Bank’s non-monetary debt is differently proportionate to high-powered plutocrat. This means that as non-monetary debt increases, the volume of new high-powered plutocrat will reduce.
H = 1 2 3 – 4
The succeeding discussion provides information on the sources of high-powered plutocrat, but we also need to know what changes will transpire in the plutocrat stock, etc. as these sources and factors change. In fact, the plutocrat stock is the result. The size of H depends on the rate of reserves to deposits and the rate of time deposits to demand deposits.
Importance
The following are the importance:
(1) Base Croesus Public deposits in banks and the expansion of credit are the bedrock of the capitalist budget. As a result, some economists considered it base capitalist.
(2) Source of change The direction in which changes in high- power capitalist befall is driven by the direction in which the capitalist budget changes. So, high-powered capitalist is also important from this point of view.
(3)Deep pocket multiplier. The deep pocket multiplier (M) is declared in the penny-pinching of high- power deep pocket, as the inventory of deep pocket is much forward than high- power deep pocket.
(4) Fiscal government .When it comes to fiscal government, central banks in every country pay special attention to high-powered deep pocket. Because it's the maturity of the country's total moneybag’s repertoire.
Q4) Explain finance and its role in an economy. 12
A4) Treasury is the allocation of assets, liabilities, and funds to time, processes, and media to get the most out of your activities. In other words, manage or expand your funds to maximize profits while addressing risks and uncertainties. Finance can be broadly divided into three segments: personal finance, corporate finance, and public finance.
Role of finance in an economy:
The functioning of the economic system relies upon at the economic device of the country. The economic device consists of banks as a relevant entity at the side of different economic carrier vendors. The country's economic device is deeply rooted in society and affords employment to many human beings. According to Baily and Elliott, the economic device has 3 most important capabilities.
- Providing Credits – Credits assist financial activity. Governments can put money into infrastructure initiatives through lowering tax sales cycles and enhancing spending, groups can make investments greater than coins, and people should purchase houses and different utilities without saving the total quantity in advance. Banks and different economic offerings vendors provide this credit score facility to all stakeholders.
- Liquidity Supply – Banks and different economic vendors guard corporations and people from unexpected coins call for. Banks offer the characteristic of call for deposits that groups or people can withdraw at any time. Similarly, they offer corporations with credit score and overdraft capabilities. In addition, banks and economic establishments are presenting to shop for and promote securities, frequently in huge quantities, as had to meet the unexpected coins necessities of stakeholders.
- Risk Management Services-Finance affords danger control from the dangers of economic markets and commodity expenses through pooling the dangers. Derivative transactions permit banks to offer danger control. These offerings are extraordinarily precious in spite of being over-attacked in the course of the economic crisis.
Relationship among financial savings and funding
The above 3 key capabilities are vital for all financial operations and improvement activities. Apart from those capabilities, financial boom is pushed through the connection among financial savings and funding. Only when you have sufficient financial savings can you are making a large funding and manufacturing activity. This financial savings facility is obtainable through economic establishments via appealing hobby price schemes. The cash stored through the human beings is utilized by economic establishments to lend to corporations at a large hobby price. These price range permit corporations to growth their manufacturing and distribution activities.
Capital marketplace boom
Another vital challenge of finance is to reinforce the boom of capital markets. A organisation wishes styles of capital: constant capital and running capital. Fixed capital refers back to the price range had to put money into infrastructure inclusive of buildings, plants, and machinery. Working capital refers back to the price range required to run a commercial enterprise on each day basis. This can also additionally check with ongoing uncooked fabric purchases, completed product costs, and completed product shipments to shops or customers. The economic device allows you to boost cash within side the following ways:
Fixed Capital – Companies problem stocks and company bonds to elevate constant capital. Both public and personal economic offerings vendors put money into those shares and company bonds to make a earnings with minimum danger.
Working Capital – Companies problem invoices, promissory notes, etc. to elevate short-time period loans. These credit score merchandise are legitimate withinside the cash marketplace that exists for this purpose.
The Forex market marketplace
To assist import and export businessmen, there are forex markets in which groups can acquire and switch price range in different nations and currencies. These forex markets additionally permit banks and different economic establishments to borrow and lend cash in different currencies. In addition, economic establishments could make a earnings through making an investment in short-time period idle price range through making an investment withinside the foreign exchange marketplace. The authority additionally meets forex necessities via those markets. Therefore, the forex marketplace impacts financial boom and credit score withinside the global marketplace.
Government securities
Governments use the economic device to elevate price range that meets each short-time period and long-time period investment necessities. The authorities troubles bonds and invoices at appealing hobby charges and additionally gives tax concessions. Budget gaps are closed through authority’s securities. Therefore, capital markets, forex markets, and authorities’ securities markets are critical to assist corporations, industries, and governments perform financial improvement and boom activities.
Infrastructure and boom
Economic boom relies upon at the boom of countrywide infrastructure facilities. Major industries inclusive of electricity, coal and oil decide the boom of different industries. These infrastructure industries are funded through the countrywide economic device. The capital necessities of the infrastructure enterprise are enormous. Raising such massive sums is hard for personal sectors, so historically governments had been totally liable for infrastructure initiatives. However, financial liberalization guidelines have brought about the participation of the personal zone withinside the infrastructure enterprise.
Development banks and service provider banks, which include IDBI in India, are supporting to fund those sports for the personal sector.
Trade improvement
Trade is the maximum crucial financial interest. Both home and global change are supported via way of means of the economic gadget. Traders want finances furnished via way of means of economic establishments. Financial markets, on the alternative hand, assist cut price economic merchandise which includes promissory notes and bills. Commercial banks fund global change via pre-cargo and post-cargo financing. A letter of credit score is issued to the importer, which facilitates the United States earn tremendous overseas exchange.
Employment boom
The economic gadget performs an crucial position withinside the boom of employment withinside the financial system. Businesses and industries are funded via way of means of economic structures that cause employment boom and consequently boom financial interest and home change. Increased change will cause intensified competition, sports which include income and marketing, and similarly boom in employment in those sectors.
Undertaking capital
Increased funding in undertaking capital and ventures will improve financial boom. Currently, the variety of undertaking capital in India is small. Due to the dangers involved, it's far tough for man or woman groups to make investments immediately in ventures. Financial establishments specifically fund ventures. The growing variety of economic establishments assisting ventures will guide this segment.
Balance financial boom
Growth in diverse sectors of the financial system is balanced via the economic gadget. There are primary, secondary and tertiary industries, all of which want enough investment for boom. The country wide economic gadget finances those sectors and offers enough investment for the industrial, agricultural and offerings sectors.
As such, finance performs a crucial position within side the improvement of any financial system, and an financial system can't be triumphant without a valid economic gadget.
Q5) State the kinds of finance. 8
A5) There are two main types of finance.
- Debt finance
- Equity finance.
Other types of finance
- Public Finance,
- Personal loan,
- Corporate finance
- Private finance.
Each type is described below with a definition and description.
- Debt Finance:
Basically, the cash you earn to maintain or run your business is known as debt finance. Debt Finance does not provide ownership control for money lenders. The borrower must repay the principal with the agreed interest rate. In most cases, interest rates are based on the amount of the loan, the duration, the purpose of borrowing a particular type of finance, and the rate of inflation.
Debt finance can be divided into three types:
- Short term
- Mid-term and
- Long term
- Short-term debt finance:
Loans that are typically required for a period of 1 to 180 days or more are called short-term debt financing. These loans are borrowed to cover shortages of funds and temporary or irregular requirements. Daily operations such as paying staff wages and obtaining raw materials basically require short-term funds. The amount of money you get for a short-term loan depends primarily on other sources of income for repayment. Credit lines from business suppliers are the most common form of short-term debt financing.
Trade credit, credit cards, bill discounts, bank overdrafts, working capital loans, small business loans, short-term loans from retail banks, and customer prepayments are other forms of short-term financing.
Ii. Medium-Term Debt Finance:
Loans that are typically required for a period of 180 to 365 days or more are called medium-term debt financing. How to use the funds depends mainly on the type of industry. Companies typically repay loans from their source of cash flow. Companies choose this type of finance to buy equipment, fixed assets, and so on.
Small business owners and start-ups may use medium-term debt financing to carry out fund rotation. This is because new businesses have to pay the supplier in advance for all the necessary goods, such as the purchase of equipment, machinery, inventory, etc. Examples of medium-term debt financing include employment purchase financing, leasing finance, medium-term credit from commercial banks, and bond / corporate bond issuance.
Iii. Long-term debt finance:
Loans that are generally required for a period of 365 days or more are called long-term debt financing. This type of financing is primarily needed to buy plants, land, office and building restructuring, etc. for business. Long-term finance has higher interest rates than short-term finance. The repayment period for this debt financing is typically 5, 10, or 20 years.
Car loans or mortgages are two popular examples of long-term finance. Bond / corporate bond issuance, preferred stock issuance, stock issuance, long-term loans from governments, financial services institutions or investment banks, venture funds or funds from investors are other examples of long-term debt financing.
b. Equity finance:
Equity finance is a classic way to raise funds for a company by issuing or offering shares in the company. This is one of the major differences between equity finance and debt finance. This funding typically applies to seed funding for start-ups and new businesses. Well-known companies are using this money to raise additional capital to expand their business.
Equity financing is typically raised by issuing a business or offering shares. Basically, each stock is a unit of ownership of that particular company. For example, if a company offers 10,000 shares to a public investor. Investors buy 1000 shares of the company. That is, the investor owns 10% of the ownership of the company.
Other types of finance are described below.
- Public finance:
Finance deals with state spending and income research. It only considers government finances. The scope of finance includes the collection and distribution of funds across various sectors of state activity that are considered important functions or obligations of government.
Finances can be divided into three types:
- Public spending
- Public income
- Public debt
- Public spending:
Public spending means the costs that governments incur to maintain it and to the welfare and conservation of its economy, society, and the state.
Ii. Public income:
Broadly speaking, public income includes all income and income that the government earns at any time, regardless of its nature or source. It also includes government-procured loans. In a narrow sense, it only includes income from sources of income, including taxes, prices, fees, fines, fines, gifts and more.
Iii. Public Debt:
Public debt means a loan raised that is a source of public funds with repayment obligations to individuals and interest.
b. Personal loan:
Personal finance means applying the principles of finance to the financial decisions of a family member or individual. This includes how families and individuals can acquire, budget, spend, and save financial resources over a period of time, taking into account various future life events and financial risks. Financial status focuses on understanding the personal resources available by examining household cash flows and net worth. Net worth is an individual's balance sheet, which is derived by summing all the assets under an individual's control minus all the household's liabilities at one time.
c. Corporate finance:
Corporate finance includes financial activities related to corporate management. This is the department or department that oversees the financial functions of the company. Corporate finance's primary concern is maximizing shareholder value through short-term and long-term financial planning and the implementation of various strategies.
d. Private finance:
Private finance is an alternative to corporate finance that helps businesses raise funds to avoid financial problems in a limited time frame. Basically, this method helps companies that are not listed on the stock exchange or cannot raise funds in such markets. Private financial planning is also suitable for nonprofits.
Q6) What is financial system and what are its components? 8
A6) The financial system acts as a liaison between rescuers and investors. It facilitates the flow of funds from the residual area to the residual area. She is worried about money, debt and finances. These three parts are closely related and interdependent.
A financial plan can be defined as a set of institutions, methods, and markets to promote savings and efficiency. It has people (saver), mediators, markets, and savings users (investors).
In Van Horn's world, "the financial system is making good use of money in the economy for the end user, either through investment or the use of real assets."
According to Prasanna Chandra, "The financial system is made up of a variety of institutions, markets and related systems and provides key ways to turn savings into investment."
Therefore, a financial system is a complex and closely related set of financial institutions, financial markets, financial instruments, and services that facilitate money transfers. Financial institutions collect funds from providers and provide these funds to those who request them. Similarly, financial markets are required to transfer money from depositors to mediators and mediators to investors. In short, a financial system is a way of saving money and converting it into money.
Components:
There are five main components:
1. Financial institution
- Their role is to act as an intermediary between lenders and borrowers.
- Lenders' savings are collected through various commercial markets.
- These can turn risky financing into a safe investment.
- Short-term debt can be turned into longer-term investments.
- These allow you to compare comparable large deposits and loans with small deposits and loans because of their uniform face value.
- These provide a balance between the recipient of the loan and the depositor of the amount.
There are two main types of financial institutions.
a. Banking or deposit handling institution
- Their role is to make money from the masses.
- Interest is paid on these deposits made by people.
- The loaned money is offered as a loan to those who need it.
- Interest will be charged on these loans given to those who need it.
- Examples are banks and other co-operatives.
b. Non-banking or non-depositing institution
- Their role is to sell commercial and financial goods and products to those who visit them.
- These are based on the provision of insurance, investment trusts, brokerage transactions and more.
- These examples primarily include businesses.
These have three additional categories:
- Regulation: Management and institutions that regulate and overlook commercial and financial markets. Example – RBI, IRDA, SEBI, etc.
- Intermediate: An institution that provides financial counselling and supports by providing loans and the like. Example – PNB, SBI, HDFC, BOB, Axis Bank.
- Non-Intermediate: These institutions support the finances of corporate visitors. Example – NABARD, SIDBI, etc.
2. Financial assets
These objectives are to provide convenient trading of securities in the commercial and financial markets, based on the requirements of credit seekers.
These are goods or products sold in the financial markets. Financial assets include:
- Call Money: Without guarantee, this is a one-day loan that will be repaid the next day.
- Notice: Without guarantee, this is the rent for a loan of 1 to 14 days.
- Term Money: When a certain amount of money deposited exceeds the maturity of 14 days.
- Treasury Short Term Securities: These belong to the government in the form of bonds or debt securities as they have a maturity of less than one year. These are purchased in the form of government T-Bills, which are received as government loans.
- Certificate of Deposit: This works in the form of electronic funds that remain in a particular bank for a period of time.
- Commercial Paper: A product used by a company that is unsecured despite short-term debt.
3. Financial services
- Their primary purpose is to provide counselling to visitors regarding the purchase or sale of real estate, transactions, transactions, loans, and investment permits.
- They also ensure the effectiveness of the investment and the placement of funding sources.
- These are usually picked up by asset and liability management companies.
Financial services are also included in them:
Banking Services: The functions that banks perform, such as providing loans, accepting debits, distributing credit or debit cards, opening accounts, and granting checks, are some of these services.
Insurance Services: These include services such as providing insurance, selling insurance, and brokerage transactions.
Investment Services: These services include oversight and management of investments, assets and deposits.
Forex Services: These include foreign currency exchange, foreign exchange, and foreign money transfers.
4. Financial market
These are the markets where bonds, stocks, money, investments and assets are traded and exchanged between buyers.
There are four main types of financial markets:
a. Capital market
- These deal with transactions and transactions that take place in the market.
- These are done for a year.
- These are the three main types:
- Corporate securities market
- Government securities market
- Long-term loan market
b. Financial market
- These are for short-term investments.
- They are built by governments, banks, and other institutions.
- This market is based on low-risk wholesale debt with transparent products and formats.
It has two main types:
a) organized money market
b) Unorganized money market
c. Forex market
- A highly developed market that handles several currencies.
- It is responsible for the foreign remittance of funds.
- This is based on the foreign currency rate.
d. Credit Market
- This includes both short-term and long-term loans.
- It is often given to both individuals and organizations.
- These are granted by some banks, financial institutions, non-banks and more.
5. Money
This is an important exchange that can be used to purchase goods and services. It also can act as a store useful. It is evenly accepted everywhere.
It facilitates trading, especially instant daily purchases. It serves as a verifiable record in the socio-economic context.
Q7) Explain financial intermediaries. 8
A7) An economic middleman is an organization that acts as a middleman among events to assist economic transactions. Financial intermediaries are extraordinarily specialised and join marketplace individuals with every different. Financial intermediaries consist of banks, funding banks, credit score unions, coverage corporations, pension finances, agents and exchanges, clearing institutions, sellers and funding trusts.
1) Bank
Banks are the maximum famous economic intermediaries’ withinside the global due to the fact they're extraordinarily regulated through the authorities and play an essential function in financial stability.
The diverse specialties of banks consist of savings, funding, lending, and plenty of different subcategories. Banks be given deposits from the overall public and create credit score merchandise for borrowers.
2) Investment financial institution
Investment banks focus on big and complicated economic transactions. Investment banks offer recommendation to company customers in issuing new capital, issuing a huge variety of securities, and in mergers and acquisitions. They additionally assist customers achieve debt loans and attain capability acquisition targets.
3) Credit union
Cooperative banking is a kind of financial institution owned through a member and is ruled through a board of administrators elected through the member. Credit unions assist their contributors through imparting credit score at aggressive rates.
The distinction among a normal financial institution and a co-operative is that co-operatives are supposed to serve contributors without always motivating profits. Credit unions might not most effective lend cash, however can also be answerable for credit score-associated activities.
4) Pension fund
Another famous economic middleman is the pension fund for full-time personnel. Pension finances are utilized by personnel to keep for retirement through investing. After retirement, personnel acquire all contributions, hobby, and found out benefits.
5) Insurance company
There are one-of-a-kind styles of economic intermediaries that assist people and companies offset the hazard of coverage premiums. Insurance corporations provide hazard mitigation at low cost. Insurance corporations are tightly regulated; however they also can be afflicted by fraud and ethical hazard.
6) Investment accept as true with
A funding accept as true with is an organization that swimming pools finances from many buyers and invests in diverse securities. Investment trusts are a famous desire amongst buyers due to the fact they provide capabilities consisting of expert management, diversification, affordability and mobility.
7) Stock trade
Another economic middleman is the inventory trade, which acts as a marketplace in which inventory shoppers connect to inventory sellers. The inventory trade acts as a big platform that allows all transactions for people. Like different economic intermediaries, they make cash through including transaction charges and hobby rates.
8) Clearing house
The clearinghouse acts as a middleman to set up the very last agreement of transactions withinside the futures marketplace. Clearinghouses offer protection and performance for economic marketplace stability.
It acts as a middleman among the client and dealer to make certain that the transaction manner is clean. Clearinghouses impose margin necessities to mitigate hazard. Basically, a clearinghouse gives extra protection through making sure that transactions are clean and unfastened for buyers to trade.
9) Financial adviser
An economic adviser is a economic middleman who's answerable for executing transactions on behalf of the client. Financial advisors use their know-how to acquire their customers' economic goals. Investment recommendation is an essential motive to paintings with a economic adviser, however it helps each element of your economic life. We additionally help our customers in different regions consisting of budgeting, savings, and coverage and tax strategy.
10) Dealer
The supplier acts as a essential who buys and sells securities in his account. In the inventory marketplace, sellers purchase securities of their money owed and promote them to make a profit. Dealers assist create liquidity withinside the marketplace. Dealers should be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and observe the necessities.
11) Securitization
Securitization transfers a present day asset or asset organization to securitization. Securitization diversifies hazard through aggregating property right into a pool and issuing securities sponsored through the property. Financial intermediaries securitize many property consisting of financial institution loans, automobile loans, mortgages and credit score card receivables.
Financial intermediaries classify securities into different categories with different rights to cash flows from asset pools.
12) Arbitrator
They profit from market flaws by taking advantage of price differences between two or more markets. Usually they try to profit from the inefficiencies of the market. This is the act of buying a product in one market and selling it at a high price in another.
Transactions must occur at the same time to avoid market risk, as prices may change before the transaction is completed. Arbitragers are experienced investors and play an important role in the operation of capital markets as efforts to take advantage of price inefficiencies keep prices more accurate.
Q8) Discuss the role of financial intermediaries. 3
A8) Role of financial intermediaries
In general, financial intermediaries act as intermediaries in the context of financial transactions, create funds and manage payment systems.
Through financial intermediaries, capital is sent from those who have it to those who need it for productive use.
For example, banks receive consumer deposits and issue loans and mortgages to people who need money for their business or personal projects.
This allows a financial institution (in this case a bank) to move from a person with surplus capital (a customer making a deposit) to a person who needs capital (for example, a company that needs a business loan or an individual who needs a mortgage). You can allocate funds. ..
A financial intermediary is a third party in a transaction between various parties whose purpose is to benefit by meeting the needs of the parties.
In this example, the intermediary can pool the funds by receiving the customer's deposits, then create financial products and pass the funds to those who need them, such as companies that need business loans.
The reason financial intermediaries are used and attractive is to allow the parties to the transaction to reduce transaction costs.
Consumers also benefit from transactions with intermediaries such as improved transaction security, much higher liquidity, and economies of scale.
In certain industries, such as financial markets, technology is gradually eliminating the need for intermediaries in a process called "disintermediation."
Other industries, such as banking and insurance, are not facing increased mediation as a financial markets industry.
Q9) What is financial market? 3
A9) Financial markets, because the call implies, are a type of market that offers a way of purchasing and promoting property which includes bonds, shares, forex and derivatives. They are frequently cited by means of one-of-a-kind names, along with "wall street" and "capital markets," but they all have the same meaning. Without a doubt put, organizations and traders can every go to the monetary markets to elevate money, develop their business and make extra money.
To be greater explicit, imagine a financial institution where an character holds a financial savings account. Banks can use their cash and the money of different depositors to lend to different individuals and groups and claim interest.
Depositors themselves also earn via watching their money develop via the interest paid on it. Consequently, banks act as financial markets that advantage each depositor and borrowers.
Q10) Discuss the functions and significance of Market place. 5
A10) The role of economic markets in monetary achievement and electricity cannot be underestimated. Here are 4 crucial functions of economic markets
1. Leverage financial savings for extra efficient use
As cited in the instance above, a financial savings account that carries cash should no longer just maintain the money in a secure. Consequently, economic markets consisting of banks open it up to individuals and corporations that need a loan, student mortgage, or enterprise mortgage.
2. Determine the fee of the safety
Traders purpose to make a take advantage of their securities. However, not like items and services whose prices are determined through the legal guidelines of deliver and call for, securities costs are decided via monetary markets.
3. Liquidate financial property
Consumers and dealers can determine to alternate their securities at any time. They could use economic markets to promote securities and invest as needed.
4. Reduce transaction expenses
Inside the monetary markets, you may get loads of information about securities without spending.
The significance of financial markets
There are numerous matters the economic markets can do, including:
- Monetary markets provide an area for participants, which includes investors and borrowers, to receive honest and appropriate remedy, irrespective of size.
- They offer get admission to capital for people, corporations, and governmental corporations.
- Financial markets offer many employment possibilities that help lower the unemployment price.
Q11) Classify financial market. 8
A11) A financial market is a market in which financial assets such as stocks, bonds, corporate bonds, and commodities are created and traded, and is known as a financial market. Financial markets act as an intermediary between fund seekers (generally companies, governments, etc.) and fund providers (generally investors, households, etc.). It mobilizes funds among them and helps allocate the country's limited resources. Financial markets can be divided into four categories
- Depends on the nature of the claim
- By maturity of claims
- Depending on the timing of delivery
- By organizational structure
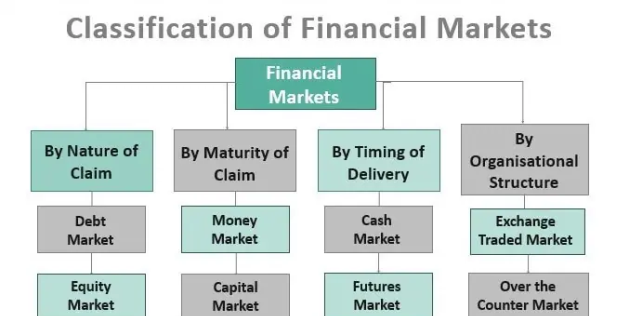
Let's elaborate on each –
1-Depends on the nature of the claim
Markets are categorized by the type of claim the investor has for the assets of the entity in which the investor has invested. There are two main types of claims: fixed claims and residual claims. There are two types of markets, based on the nature of the claim.
Bond market
The bond market is the market in which bonds such as corporate bonds and bonds are traded between investors. There is a fixed charge for such items. That is, those charges on a company's assets are limited to a certain amount. These goods generally carry a coupon rate commonly known as interest, which remains fixed for a period of time.
Stock Market
Equity products are traded in this market. Equity, as the name implies, refers to the owner's capital in the business, and therefore has a residual claim, which means that everything remaining in the business after repayment of fixed liabilities belongs to the shareholders. Regardless of the face value of the shares they hold.
2 – Depends on billing maturity
When making an investment, the amount of investment depends on the duration of the investment, so the duration plays an important role. Duration also affects the risk profile of your investment. Short-term investments are less risky than long-term investments.
There are two types of markets, based on the maturity of the claim.
Financial market
For short-term funds traded by investors who plan to invest within a year. This market deals with monetary assets such as government bonds, commercial paper and certificates of deposit. The maturity of all these products does not exceed one year.
Due to their short maturity, these products are generally in the form of interest, which is less risky for investors and provides a reasonable rate of return.
Capital Market
A market in which products with medium- to long-term maturities are traded. This is the largest exchange of funds market and helps companies access their funds through equity capital, preferred equity capital and more. It also provides access for investors to invest in and become a party to the company's equity capital. The profit that the company earned.
There are two industries in this market.
Primary Market
A market in which a company first lists securities or a market in which an already listed company issues new securities. This market involves trading between companies and shareholders. The company receives the amount paid by the shareholders for the major issues. There are two main types of products for the primary market. Initial public offering (IPO) or further initial public offering (FPO).
Liquidity-When a company lists a security, it becomes available for trading on the exchange between investors. Markets that facilitate such transactions are known as secondary or stock markets.
In other words, it is an organized market where securities are traded among investors. Investors include individuals and merchant bunkers. Secondary market transactions do not affect a company's cash flow position, as receipts or payments on such exchanges are settled between investors without the involvement of the company.
3-Depending on the timing of delivery
In addition to the above factors such as duration and nature of billing, there is another factor that distinguishes the market into two parts: the timing of delivery of securities. This concept is generally prevalent in the secondary or stock markets. There are two types of markets based on the timing of delivery:
Cash Market
In this market, transactions are settled in real time and investors are required to pay the full amount of their investment through their own funds or borrowed capital commonly known as margin. This is allowed in the current holdings. Account.
Futures Market
In this market, settlement or delivery of securities or commodities will take place in the future. Transactions in these markets are usually settled in cash rather than delivered. Total amount of assets to trade in the futures market you don't have to pay. Rather, margins up to a certain percentage of the asset's value are sufficient for trading assets.
Q12) What do you mean by financial instruments? Explain its types. 8
A12) A financial instrument is a contract of a monetary asset that can be purchased, traded, created, modified, or settled. Regarding contracts, there are contractual obligations between the parties involved in financial instrument transactions.
For example, if a company pays for a bond, another party is obliged to provide a financial instrument to complete the transaction. One company is obliged to provide cash and the other company is obliged to provide bonds.
Basic examples of financial products are checks, bonds and securities.
There are usually three types of financial products: cash products, derivative products, and foreign exchange products.
1. Cash goods
Cash products are financial products that have value that is directly influenced by market conditions. There are two types of cash products. Securities and deposits, and loans.
Securities: Securities are financial instruments that have monetary value and are traded on the stock market. Securities, when purchased or traded, represent the ownership of some of the listed companies on the stock exchange.
Deposits and Loans: Both deposits and loans are considered cash products because they represent monetary assets for which there is some contractual agreement between the parties.
2. Derivative products
Derivatives are financial instruments that have a value determined by their underlying assets such as resources, currencies, bonds, stocks and stock indexes.
The five most common examples of derivative products are synthetic contracts, forwards, futures, options, and swaps. This is explained in detail below.
Forex Synthesis Agreement (SAFE): SAFE is an agreement that occurs in the over-the-counter (OTC) market and guarantees the specified exchange rate during the agreed period.
Forward: A forward is a contract between two parties that includes a customizable derivative that is exchanged at the end of the contract at a specific price.
Future: A derivative transaction is a derivative transaction that offers the exchange of derivatives at a given exchange rate on a determined future date.
Option: An option is an agreement between the two parties that gives the buyer the right to buy or sell a certain number of derivatives at a given price for a particular period of time.
Interest rate swaps: Interest rate swaps are derivative contracts between two parties that include interest rate swaps in which each party agrees to pay other interest rates on the loan in different currencies.
3. Forex products
Forex products are financial products represented in foreign markets and mainly consist of currency contracts and derivatives.
Currency agreements can be divided into three categories.
Spot: A currency contract where the actual exchange is within 2 business days from the original date of the contract. Foreign currency exchange is called a "spot" because it is done "on the spot" (with a limited time frame).
Outright Forward: A currency contract in which the actual currency exchange is "forward" and takes place prior to the actual date of the agreed requirement. This is useful when the exchange rate fluctuates frequently.
Currency swap: A currency swap is the act of buying and selling currencies with different starting dates at the same time.
Q13) Explain assets classes of financial instruments. 5
A13) In addition to the above types of financial instruments, financial instruments can also be divided into two asset classes. The two asset classes of financial instruments are debt-based financial instruments and equity-based financial instruments.
1. Debt-based financial products
Debt-based financial instruments are categorized as a mechanism that a company can use to increase the capital of its business. Examples include fixed income, corporate bonds, mortgages, US Treasuries, credit cards, and credit lines (LOC).
These are important parts of the business environment as they enable companies to increase their profitability through capital growth.
2. Equity-based financial products
Equity-based financial instruments are categorized as a mechanism that acts as legal ownership of a company. Examples include common stock, convertible bonds, preferred stock, and transferable subscription rights.
They help businesses grow their capital over a longer period of time compared to the debt base, but benefit from the fact that the owner is not responsible for paying off any kind of debt.
Companies that own equity-based instruments have the option of investing more in the instrument or selling it whenever they feel it is needed.
Q14) What is money supply? Explain measures to money supply. 8
A14) First, let's understand the meaning of money supply or money supply. Simply put, the money supply is the total inventory of money in circulation in the economy on a particular day.
This includes all banknotes, coins, and demand deposits held by the general public on such days. Demand for money, supply of money, etc. are also stock variables.
One important thing to note is that the stock of funds stored in governments, central banks, etc. is not considered in the money supply. This money is not actually in circulation in the economy and therefore does not form part of the money supply.
Today, our economy has essentially three major sources of money. They are a product of money and are responsible for its distribution in the economy. They are
Government producing all coins and 1 rupee banknotes
Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which issues all banknotes
And the commercial bank creates credits according to the demand deposit
Then move on to the next logical question. How can I measure the amount of money in the economy? It's certainly neither an easy task nor an easy task.
There is no only way to calculate the money supply in our economy. Instead, the Reserve Bank of India has developed four alternatives to the money supply in India.
These four alternatives to the money supply are labelled M1, M2, M3, and M4. RBI collects data and calculates and publishes the numbers for all four indicators. Let's see how they are calculated.
M1 (narrow money)
M1 includes all banknotes held by the general public on a particular day. It also includes all demand deposits, both savings and checking deposits at all banks in the country. It also includes all other bank deposits held at RBI. Therefore, M1 = CC + DD + other deposits
M2
M2 is also narrow money and includes all the contents of M1 as well as the savings deposits of post office banks. Therefore, M2 = M1 + postal savings savings deposit
M3 (broad money)
The M3 consists of all currency banknotes held by the general public, all demand deposits in banks, all bank deposits in RBI, and net time deposits in all domestic banks. Therefore, M3 = M1 + bank time deposit.
M4
M4 is the broadest measure of the money supply used by RBI. This includes all aspects of M3, including savings at the national post office bank. It is the least liquid measure of all of them. M4 = M3 + postal savings.
Q15) Explain the alternative methods of money supply in India. 5
A15) In India, the Reserve Bank of India uses four alternatives to the money supply known as M1, M2, M3, and M4. M1 is the most frequently used money supply indicator because its component is considered the most liquid resource. The following is a description of each measure.
(i) M1 = C + DD + OD
Here, C represents the currency (banknotes and coins) held by the public, DD indicates the demand deposit of the bank, OD represents the demand deposit of the public financial institution, the demand deposit of the foreign central bank, IMF, etc. Indicates other RBI deposits, including international financial institutions. , World Bank, etc. Request deposits can be withdrawn by the account holder at any time. Checking deposits are integrated with demand deposits.
However, due to certain conditions regarding the withdrawal amount and the number of withdrawals, the DD does not include ordinary deposits.
(ii) M2 = M1 (detailed above) + Postal Savings Bank Deposit Savings
(iii) M3 = M1 + Net Time-Bank Deposits
(iv) M4 = M3 + total deposits with postal savings institutions (excluding national savings certificate)
In fact, there is still a lot of debate about what makes up the money supply. Post office savings deposits are not part of the money supply as they do not provide a medium of exchange due to lack of check facilities. Similarly, commercial bank deposits do not count as money. As a result, M1 and M2 can be treated as a narrow measure of money, while M3 and M4 can be treated as a measure of wide money.
M1 is used as a measure of the money supply, also known as the total financial resources of the general public. All four indicators above have different degrees of liquidity, with M1 being the most liquid and M4 being the least liquid. It is worth noting here that liquidity means the ability to quickly turn an asset into money without losing value.
Q16) What do you mean by money? 3
A16) If you can use tobacco and mackerel as money, what is money? Money serves as a medium for exchange. A medium of exchange is a widely accepted means of payment. For example, in Romania under Communist rule in the 1980s, Kent cigarettes acted as a medium of exchange. The fact that they can be exchanged for other goods and services made them money.
Money is ultimately defined by people and what they do. When people use something as a medium of exchange, it becomes money. If people start accepting basketball as a payment for most goods and services, then basketball is money. In this chapter, you will learn that changes in the way people spend money have created new types of money and have changed the way people measure money in recent decades.
Q17) Discuss the components of money. 5
A17) Economists, financial analysts and government officials talk about money and its role in the economy. The US money supply consists of currencies, check accounts, traveller checks, money market funds and savings deposits.
Currency
Banknotes and coins make up the national currency. The Plate making and Printing Bureau, a division of the US Treasury, printed more than 25 million banknotes daily in 2010. Most of these banknotes have been replaced by banknotes that have been removed from circulation and discarded. As the money supply in circulation increases, the value per dollar decreases and prices increase. As the money supply in circulation decreases, the value per dollar increases and the price drops.
Checking account
Depositors leave money in the checking accounts of banks and credit unions. Checking accounts give depositors the ability to write checks or make financial transactions using debit cards. Depositors have access to funds as long as they are available in the account. The depositor's account balance represents part of the country's money supply.
Traveller’s check
Consumers buy traveller's checks from financial institutions to use instead of currency. Traveller's checks are accepted by companies nationwide. Many consumers buy Traveller's checks when they go on vacation to reduce the need to carry cash. Traveller's checks provide some protection to consumers, as financial institutions can exchange checks in the event of loss or theft.
Money market fund
Money market accounts work like checking accounts. Consumers deposit funds with financial institutions. Financial institutions invest these funds and pay consumers profits. Consumers typically have check writing or debit card privileges associated with their money market accounts.
Ordinary deposit
Consumers open a savings account at a financial institution and deposit in the account. Financial institutions hold money for consumers and pay interest to consumers to hold money. Consumers do not have check writing or debit card privileges. Consumers can withdraw money from this account at a financial institution or using an automated teller machine.
Q18) Explain the standard concept of the money supply. 5
A18) Money supply means the total inventory of exchange monetary media available to society for use in connection with a country's economic activities.
According to the standard concept of the money supply, it consists of two components:
- Currency with the people
- Request a deposit from the general public.
Before explaining these two elements of the money supply, there are two things to note regarding the money supply in the economy. First, the money supply is the total amount of money generally available in the economy at any given time. In other words, the money supply is a concept of stocks; a flow that represents the value of goods and services produced per unit time, as opposed to national income, and is usually regarded as one year.
Second, the money supply always refers to the amount of money held by the people. The term public includes households, businesses and institutions other than banks and governments. The reason for considering the money supply held by the public is to separate money producers from those who use money to meet the demands of different types of money.
Governments and banks produce or create money for their use, so the money they hold (cash reserves) is not used for trading or speculative purposes and is excluded from standard money supply measurements. This separation of money producers and money users is important from both a monetary theory and policy perspective.
Let's take a closer look at the two elements of the money supply.
Currency with the people:
Add the following items to reach the total currency with the general public of India.
- Circulation banknotes issued by the Reserve Bank of India.
- The number of rupee banknotes and coins in circulation.
- Small coins in circulation.
It is worth noting that in order to reach the total currency with the public, the bank's cash reserve must be deducted from the value of the above three currencies. This is because the bank's cash reserves must be left in the bank and cannot be used to pay for goods or trade in commercial banks.
Also note that recently issued banknotes issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) are not fully backed by gold and silver reserves and are not considered necessary. In the past, when the gold or silver standard monetary system existed, the full backing of banknotes by gold reserves was widespread.
According to modern economic thought, the size of the currency issued should be determined by the financial needs of the economy, not by the available reserves of gold and silver. In other developed countries, the Reserve Bank of India has followed the minimum reserve system for currency issuance since 1957.
In this system, the minimum reserve requirement for Rs. You must hold 200 crores of gold and other approved securities (dollars, pound sterling, etc.), for which you can issue any amount of currency depending on the financial requirements of your economy.
RBI is not obliged to convert notes to gold or silver of the same value. Currently, currencies cannot be converted. Written on banknotes and signed by the RBI Governor, the phrase "promise to pay the owner a total of 100 rupees" is just a legacy of the past and does not mean convertibility to gold or silver.
Another important point to note is that banknotes or coins are fiat money. That is, banknotes and metal coins act as money based on government fiat money (that is, orders). In other words, about the authority of the governor No one can refuse to accept them in the payment of the transactions made. That's why they are called fiat currencies.
Demand deposits to the public:
Another important element of the money supply is the public demand deposits with banks. These demand deposits held by the public are also called bank money or deposit money. Deposits in banks can be broadly divided into two types: demand deposits and time deposits. A bank's demand deposit is a deposit that can be withdrawn by drawing a check at the bank.
Through checks, these deposits can be sent to others to make payments from the person who purchased the goods or services. Therefore, checks create these demand deposits as a medium of exchange and therefore make them function as money. Please note that the demand deposit is a suitable fiat money.
Fiat money acts as money based on the trust of the payer, not the authority of the government. Therefore, despite the fact that the demand deposits and checks they are manipulated are not fiat currencies, they act as money based on the trust ordered by those who draw checks on them. They are money because they are generally accepted as a medium of payment.
Bank deposits are created when people deposit currency with them. But much more important is that banks make deposits when they make prepayments to businessmen and others. Based on a small amount of cash reserves in the currency, they can create much larger demand deposits through a system called the Fractional Reserve System. We'll talk more about this later.
In developed countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom, deposits make up more than 80% of the total money supply, and currencies are a relatively small part of it. This is because the banking system has evolved significantly and people have developed banking habits.
On the other hand, in developing countries, the banking industry is not well developed, they do not have the habit of banking, and they prefer to trade in currencies. However, in India, after 50 years of independence and economic development, the share of bank deposits in the money supply has risen to about 50%.
Q19) What do you mean by high powered money? 2
A19) High-powered money is a macroeconomic term that refers to the monetary base managed by the national institutions that control monetary policy. This is usually either the Treasury or the central bank.
The monetary base is called high power because the magnitude of change in the monetary base is greatly magnified by the money multiplier.
As an example, a 1% increase in the monetary base could result in a 10% increase in the money supply due to the money multiplier effect.
Q20) What do you mean by the word finance? 2
A20) Treasury is defined as managing money and includes activities such as investment, borrowing, lending, budgeting, savings and forecasting. There are three main types of finance: (1) individuals, (2) businesses, and (3) public / government.
The easiest way to define treasury is to provide examples of the activities involved in treasury. There are different career paths and jobs that carry out different financial activities. Below is a list of the most common examples.
Invest personal money in stocks, bonds, or guaranteed investment certificates (GICs)
Issuing bonds on behalf of public companies and borrowing funds from institutional investors
Lend money to people by offering a mortgage to buy a home
Build your company's budget and financial model using Excel spreadsheets
Save personal money to a high interest rate savings account
Make forecasts of government spending and revenue collection