CHEM
UNIT-4CHEMICAL FUELS Q1) Define fuels and classify them?A1) Coal, is nothing but the primary fossil fuel, that is rich in carbon, coal is usually black or brown in colour, and occur in stratified sedimentary depositsChemical fuels, by a process called combustion react with substances around them to release energy. The chemical energy produced during combustion is not stored in the chemical bonds of the fuel but is stored in the weak double bond of molecular oxygen. Classification of chemical fuelsChemical fuels are divided in two ways. First, based on their physical properties, as a solid, liquid or gas. Secondly, on the basis of their occurrence: primary (natural fuel) and secondary (artificial fuel). Thus, a general classification of chemical fuels is:
Solid fuel refers to different types of solid material that are used as fuel to produce energy and provide heating, that is released by combustion., Solid fuels include fuel tablets, wood, charcoal, peat and pellets made from wood, rye, grains, wheat. Solid rocket fuel technology also uses solid fuel. Solid fuels have been used by humanity for many years to create fireLiquid fuels need to take the shape of the container; the fumes of liquid fuels are flammable. These fuels are combustible or energy-generating molecules that can be used to produce mechanical energy usually kinetic energy.Most of the liquid fuels are produced from the fossil remains of the dead animals and plants when exposed to the heat and pressure inside the Earth’s crust, there are however other types of liquid fuels like hydrogen fuel, jet fuel, ethanol and bio-diesel.Fuel gas is in gaseous form under ordinary conditions, many fuels are composed of hydrocarbons (like methane and propane) carbon monoxide, hydrogen or may exist in the form of mixtures. Gaseous fuels are potential sources of heat and light energy. And can be distributed and transmitted through pipes from the beginning to directly to the place of consumption. Fuel gas is contrasted with solid and liquid fuels, though some fuel gases are liquified for storage purposes Q2) Explain solid fuels?A2) Coal, is nothing but the primary fossil fuel, that is rich in carbon, coal is usually black or brown in colour, and occur in stratified sedimentary deposits.The key difference between proximate and ultimate analysis of coal is that proximate analysis is the technique used to analyse the moisture content, ash content and fixed carbon of coal whereas ultimate analysis is the technique used to analyse the chemical composition of coal.The technique of proximate analysis involves the determination of the different compounds present in a mixture. Ultimate analysis, on the other hand, involves the determination of the number and types of different chemical elements present in a particular compound. Therefore, these two techniques are related to each other.Proximate analysis of coal is the process of determining the presence of different compounds and their amounts in coal. The technique of proximate analysis was developed by Henneberg and Stohmann (German scientists) in 1860. This analysis technique involves the partitioning of compounds into different categories depending on the chemical properties of these compounds. Mainly, there are six categories of compounds as moisture, ash, crude protein, crude lipid, crude fibre, and nitrogen-free extracts. In the process of proximate analysis of coal, the moisture content of coal, ash content of coal and the fixed carbon content of coal are determined.The ultimate analysis of coal is the process of determining different chemical elements present in coal. This technique allows us to get more comprehensive results compared to the proximate analysis process.In this analysis technique, we test moisture, ash, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulphur and oxygen content of the sample to determine the elemental composition of the coal sample. Therefore, each and every chemical element in the sample is analysed through chemical routes and then we can express the contents as percentages with respect to the total mass of the sample. Mostly, this analysis technique is useful in the coal and coke industry. Q3) Explain the fractionation of Petroleum?A3) According to the boiling point of petroleum the separation or fractionation of components takes place. Fractionation is performed in oil refineries is the first step of refining of petroleum and also the production of petroleum products. The concept of the process includes petroleum capacity to be heated to a vapor phase that differs in composition from the liquid phase. The fractions that are obtained are usually mixtures of hydrocarbons. Repeated fractional distillation can be can be implemented for separated Various individual hydrocarbonsPetroleum fractionation can be a single, one-time process, that is called equilibrium distillation, or a gradual, step-by-step vaporization known as fractional distillation. The fractionation process can be further distilled or rectified the vaporizing agent is the water vapour obtained on being heated whereas fractionation is carries out under atmospheric pressure or whereas the same heating temperature, the equilibrium distillation separates the fraction less precisely than fractional distillation, the yield of petroleum is more. In labs the batch fractional distillation is extensively used for rectification of the vapour phase.The refining industry uses the combination of equilibrium distillation and rectification of the vapour and also liquid phases, this method allows the distillation of petroleum in plants that operate continuously, this combination shows a lot of accuracy in the separation and economises on the amount of fuel consumed to heat the petroleum. The use of water vapor helps in lowering the operation of temperatures and results in higher yields as well as higher concentrations of high-boiling constituents in the residue.
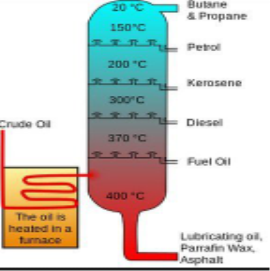
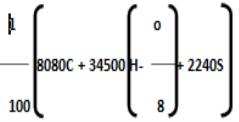
Q4) Write the composition and uses of kerosene?A4) The chemical composition of kerosene depends on its source, kerosine usually consists different hydrocarbons, each of the hydrocarbon contain 10-16 carbon atoms per molecule. The main constituents of kerosine are saturated straight-chain and branched-chain paraffins, as well as ring-shaped cycloparaffins (also known as naphthene’s). Kerosene is less volatile than gasoline.UsesKerosene forms the light and lamping fuel, people in villages and campers prefer kerosine lamps due to its longevity, and easy for transportation, the flame can be easily adjusted accordingly. Kerosine heaters don’t require electricity, it’s a versatile heating oil and easily portable. Kerosine I s also used as a jet fuel, it is highly combustible and meets the demand of the jet. Stage effects, circus performers, and other live performances that include fire use kerosine because of its low flame temperature.it is also used as an alternative for other flame sources As it is a derivative of petroleum, it is used as a solvent and chemical lubricant. Q5) Explain cracking and its importance?A5) Cracking, is a process in petroleum refining. In this process heavy molecules of hydrocarbon are broken down into lighter molecules by heat, pressure and sometimes catalysts. It is a very important process for the commercial production of gasoline and diesel oil.The process of cracking yields light oil, middle oils that is used in diesel fuel, heavy residual oils and also solid carbonaceous product like coke etc. Gases such as methane, ethane. Ethylene, propane, propylene and butylene are also produced during cracking. The end product formed in the process can directly go into fuel blending or can be subjected to future process, until oils of desired weight are produced. The gases can be used in the refinery’s fuel system, Certain raw materials are also produced from the petrochemical plants, where a large number of end products can be obtained from them like synthetic rubber, plastic and also agricultural products.Catalytical Cracking by moving bed methodCracking of petroleum yields light oils at different ranges (corresponding to gasoline), the middle-range oils used in diesel fuel, and the residual heavy oils, a solid carbonaceous product known as coke, and such gases as butylene, propylene, propane ethane and methane. Based on the product that is formed the oil could go directly into blending or may further undergo cracking reactions or other refinery process, until the oils of desired weight are obtained. the gases formed can be used in the refinery, for the petrochemical plants they form an important raw material. From the raw materials huge end products are formed that range from synthetic rubber and agricultural chemicals.An improved process of Catalytic cracking was done in 1940, the process involved using powdered catalyst or a fluidised one. During the 1950s, fuels used in automobile and jets were in much demand. Thus, hydrocracking was applied to petroleum refining. This process uses hydrogen gas to improve the hydrogen-carbon ratio in the cracked molecules and to arrive at a broader range of end products, such as gasoline, kerosine (used in jet fuel), and diesel fuel. Q6) What do you understand by Octane and Cetane numbers?A6) Octane and Cetane numbersOctane Number and Cetane Number are the standards to measure the tendency of fuel to ignite spontaneously. The performance of gasoline is measured by the Octane number on the other hand the cetane number measures the performance of diesel. The reason why petrol can’t be used in diesel engine and diesel can’t be used in a petrol engine is that when the fuel that has high octane number will have low cetane number and high cetane number fuel has low octane number.As per the Standard operating conditions the Octane number of a fuel defines the percentage of Iso-butene present in a mixture of Iso-octane and heptane. When used in a gasoline engine the Octane rating signifies the ability to resist auto ignition. As air and fuel are compressed together, gasoline tends to ignite a spark at the end of compression by a spark plug. If gasoline with low octane number is used it creates problems during ignition and tends to adapt to auto combustion easily due to excess of heat and pressure effects on the other hand, fuels that have high octane value takes more time to burn but provides maximum efficiency to the gasoline engine.Cetane is a type of chemical compound known as a Hexadecane. Cetane number is opposite to octane number, and measures how quickly the engine burns inside a compressed engine. Cetane compounds tend to ignite spontaneously under compression, therefore they are assigned as cetane number of hundred. Cetane number of a fuel can be defined as the percentage volume of n-hexadecane in the mixture of n-hexadecane and 1-methylnaphthalene which is responsible to provide ignition delay period. Q7) Write notes on Gasoline?A7) CNG is mainly composed of ethane and is obtained by compressing natural gas, to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at Standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored and distributed in hard containers at a pressure of 20–25 MPa (2,900–3,600 psi), usually in spherical or cylindrical shapes. UsesCNG burns cleaner as compared to diesel and petrol, the carbon monoxide emissions are less y 80% and shows 44% hydrocarbons are produced in vehicles that use gasoline. Natural Gas still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, in case of leakage, CNG is not a threat as they are nontoxic and do not show any form of contamination to ground water CNG cars also run quieter producing less noise, thereby reducing noise pollution. than gasoline and diesel vehicles. Safety CNG is less flammable that has a flammability rating of approximately 5 percent - 15 percent, and is safe compared to other fuels. In cases of collision CNG cylinders are safe in terms of size, structure and location, comparatively they are less dangerous than gasoline and diesel tanks. These cylinders that show higher pressure and temperature have safety devices which are designed to release the gases. The maintenance cost will be drastically reduced as the oil changes and tune us will be less frequent. Q8) Explain the Determination of Calorific value using Dulong’s Formula?A8) Theoretical Calculation of Calorific Value Using Dulong’s formulaThe calorific value of a fuel can be theoretically determined by using Dulong’s formula. It is assumed that heat evolved comes from the combustion of carbon, hydrogen, and sulphur present in the fuel. The total heat evolved is equal of heat evolved by the combustion of individual constituent’s present. The calorific value of hydrogen = 34500 cal/gm. Calorific value of carbon = 8080 cal/gm Calorific value of sulphur = 2240 cal/gm.Then, Dulong’s formula is HCV =
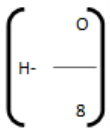
Where, C, H, O, S are percentage fractional weight of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and sulphur respectively obtained from the analysis of 1 gm of the fuel.
represents the available hydrogen. It is assumed that oxygen present in fuel combines with hydrogen to form water. 8 parts by weight of oxygen combines with one part by weight of hydrogen, to form water. So actual heating value of hydrogen is obtained by above expression.A sample of coal has following composition by mass C = 70 %, O = 8 %, H = 10 %, N = 3 %, S = 2%, Ash = 7 %. Calculate H.C.V. and L.C.V. using Dulong formula [Difficulty level-high]Solution: HCV = 1/100[8080 C+34500(H-O/8) +2240 S] = 1/100[8080 + 70+34500(10-8/8) +2240 X 2] = 1/100 [565600 + 34500 (10-1) X 4480] = 1/100 [565600 + 310500 + 4480] = 1/100 [880580] = 8805.80kcal/kg LCV = [ HCV- 9/100 H X 587] kcal/kg = [8805.80-9/100 x 587] = [8805.80- 528.30] = 8277.80 kcal/kg Answer: HCV/GCV = 8805.80kcal/kg
LCV/NCV = 8277.80 kcal/kg Q9) Write the importance of Coal ranking?A9) Coal and its rankingThe classification of coal is based on its ranking, that refers to the degree of coalification. The ranking of coal is determined by depth of burial and to which the coal was subjected over time, as the temperature increases, peat gets converted to lignite which is a very soft and low ranked coal.as temperature increases lignite is transformed into subbituminous coal and then into bituminous coal.at higher temperatures, that accompanies deformation intensely following the folding and faulting of the earth’s crust. The highest rank of coal is produced the Anthracites. The increase in coal corresponds to the increase in the amount of fixed carbon and decrease in the amount of moisture and other volatile material in coal. generally, the calorific (heat) value of coal is increased in ranking from lignite through bituminous coal. In addition, the terms used for various coal ranks vary from country to country.Q10) Define the ideal temperature of a fuel?A10) Ignition temperature when it is low, the substance catches fire, therefore if the temperature of the fuel is lower than the room temperature, then is catches fire very easily andMay cause many hazards, therefore for an ideal fuel, the ignition temperature should be higher than the room temperature.
General types of chemical fuels | ||
| Primary (natural) | Secondary (artificial) |
Solid fuels | Coal, peat, dung wood etc. | Coke and charcoal |
Liquid fuels | Petroleum | Diesel, ethanol, naphtha, diesel tar, coal gasoline, kerosine |
Gaseous fuels | Natural gas | Coke, gas. CNG, propane, methane water gas. Hydrogen, oven gas, coal gas. |
|
|
|
LCV/NCV = 8277.80 kcal/kg Q9) Write the importance of Coal ranking?A9) Coal and its rankingThe classification of coal is based on its ranking, that refers to the degree of coalification. The ranking of coal is determined by depth of burial and to which the coal was subjected over time, as the temperature increases, peat gets converted to lignite which is a very soft and low ranked coal.as temperature increases lignite is transformed into subbituminous coal and then into bituminous coal.at higher temperatures, that accompanies deformation intensely following the folding and faulting of the earth’s crust. The highest rank of coal is produced the Anthracites. The increase in coal corresponds to the increase in the amount of fixed carbon and decrease in the amount of moisture and other volatile material in coal. generally, the calorific (heat) value of coal is increased in ranking from lignite through bituminous coal. In addition, the terms used for various coal ranks vary from country to country.Q10) Define the ideal temperature of a fuel?A10) Ignition temperature when it is low, the substance catches fire, therefore if the temperature of the fuel is lower than the room temperature, then is catches fire very easily andMay cause many hazards, therefore for an ideal fuel, the ignition temperature should be higher than the room temperature.
0 matching results found