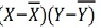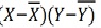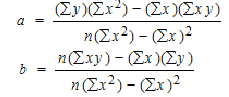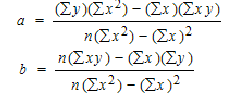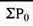Unit – 3
Correlation
Q1) Compute Pearsons coefficient of correlation between advertisement cost and sales as per the data given below:
Advertisement cost | 39 | 65 | 62 | 90 | 82 | 75 | 25 | 98 | 36 | 78 |
sales | 47 | 53 | 58 | 86 | 62 | 68 | 60 | 91 | 51 | 84 |
A1)
X | Y |
|
|
|
| |
39 | 47 | -26 | 676 | -19 | 361 | 494 |
65 | 53 | 0 | 0 | -13 | 169 | 0 |
62 | 58 | -3 | 9 | -8 | 64 | 24 |
90 | 86 | 25 | 625 | 20 | 400 | 500 |
82 | 62 | 17 | 289 | -4 | 16 | -68 |
75 | 68 | 10 | 100 | 2 | 4 | 20 |
25 | 60 | -40 | 1600 | -6 | 36 | 240 |
98 | 91 | 33 | 1089 | 25 | 625 | 825 |
36 | 51 | -29 | 841 | -15 | 225 | 435 |
78 | 84 | 13 | 169 | 18 | 324 | 234 |
650 | 660 |
| 5398 |
| 2224 | 2704 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
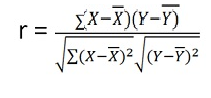
r = (2704)/√5398 √2224 = (2704)/(73.2*47.15) = 0.78
Thus Correlation coefficient is positively correlated
Q2) Compute correlation coefficient from the following data.
Hours of sleep (X) | Test scores (Y) |
8 | 81 |
8 | 80 |
6 | 75 |
5 | 65 |
7 | 91 |
6 | 80 |
A2)
X | Y |
|
|
|
| |
8 | 81 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 2.3 | 5.4 | 3.1 |
8 | 80 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
6 | 75 | -0.7 | 0.4 | -3.7 | 13.4 | 2.4 |
5 | 65 | -1.7 | 2.8 | -13.7 | 186.8 | 22.8 |
7 | 91 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 12.3 | 152.1 | 4.1 |
6 | 80 | -0.7 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 1.8 | -0.9 |
40 | 472 |
| 7 |
| 361 | 33 |

X = 40/6 =6.7

Y = 472/6 = 78.7
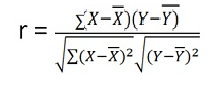
r = (33)/√7 √361 = (33)/(2.64*19) = 0.66
Thus Correlation coefficient is positively correlated
Q3) Calculate coefficient of correlation between X and Y series using Karl pearson shortcut method.
X | 14 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 16 | 15 |
Y | 13 | 11 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 9 | 14 | 17 |
A3)
Let assumed mean for X = 15, assumed mean for Y = 14
X | Y | dx | dx2 | dy | dy2 | dxdy |
14 | 13 | -1.0 | 1.0 | -1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
12 | 11 | -3.0 | 9.0 | -3.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 |
14 | 10 | -1.0 | 1.0 | -4.0 | 16.0 | 4.0 |
16 | 15 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
16 | 15 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
17 | 9 | 2.0 | 4.0 | -5.0 | 25.0 | -10.0 |
16 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
15 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 |
120 | 104 | 0 | 18 | -8 | 62 | 6 |
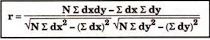
 r = 8 *6 – (0)*(-8)
r = 8 *6 – (0)*(-8)
√8*18-(0)2 √8*62 – (-8)2
r = 48/√144*√432 = 0.19
Q4) Calculate coefficient of correlation between X and Y series using Karl pearson shortcut method.
X | 1800 | 1900 | 2000 | 2100 | 2200 | 2300 | 2400 | 2500 | 2600 |
F | 5 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 9 |
A4)
Assumed mean of X and Y is 2200, 6
X | Y | dx | dx (i=100) | dx2 | dy | dy2 | dxdy |
1800 | 5 | -400 | -4 | 16 | -1.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 |
1900 | 5 | -300 | -3 | 9 | -1.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 |
2000 | 6 | -200 | -2 | 4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
2100 | 9 | -100 | -1 | 1 | 3.0 | 9.0 | -3.0 |
2200 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
2300 | 8 | 100 | 1 | 1 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 |
2400 | 6 | 200 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.0 |
2500 | 8 | 300 | 3 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 6.0 |
2600 | 9 | 400 | 4 | 16 | 3 | 9 | 12.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 0 | 60 | 9 | 29 | 24 |
Note – we can also proceed dividing x/100
 r = (9)(24) – (0)(9)
r = (9)(24) – (0)(9)
√9*60-(0)2 √9*29– (9)2
r = 0.69
Q5) Calculate Spearman rank-order correlation.
Test 1 | 8 | 7 | 9 | 5 | 1 |
Test 2 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 5 |
A5)
Here, highest value is taken as 1
Test 1 | Test 2 | Rank T1 | Rank T2 | d | d2 |
8 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
7 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
9 | 7 | 1 | 3 | -2 | 4 |
5 | 4 | 4 | 5 | -1 | 1 |
1 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
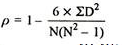
R = 1 – (6*8)/5(52 – 1) = 0.60
Q6) Calculate Spearman rank-order correlation.
English | 56 | 75 | 45 | 71 | 62 | 64 | 58 | 80 | 76 | 61 |
Maths | 66 | 70 | 40 | 60 | 65 | 56 | 59 | 77 | 67 | 63 |
A6)
Rank by taking the highest value or the lowest value as 1.
Here, highest value is taken as 1
English | Maths | Rank (English) | Rank (Math) | d | d2 |
56 | 66 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 25 |
75 | 70 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
45 | 40 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 |
71 | 60 | 4 | 7 | -3 | 9 |
62 | 65 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 1 |
64 | 56 | 5 | 9 | -4 | 16 |
58 | 59 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
80 | 77 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
76 | 67 | 2 | 3 | -1 | 1 |
61 | 63 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
| 54 |
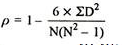
 R = 1-(6*54)
R = 1-(6*54)
10(102-1)
R = 0.67
Therefore this indicates a strong positive relationship between the ranks individuals obtained in the math and English exam.
Q7) Find Spearman's rank correlation coefficient between X and Y for this set of data:
X | 13 | 20 | 22 | 18 | 19 | 11 | 10 | 15 |
Y | 17 | 19 | 23 | 16 | 20 | 10 | 11 | 18 |
A7)
X | Y | Rank X | Rank Y | d | d2 |
13 | 17 | 3 | 4 | -1 | 1 |
20 | 19 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
22 | 23 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
18 | 16 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
19 | 20 | 6 | 7 | -1 | 1 |
11 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
10 | 11 | 1 | 2 | -1 | 1 |
15 | 18 | 4 | 5 | -1 | 1 |
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
R =
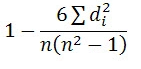
 R = 1 – 6*8/8(82 – 1) = 1 – 48 = 0.90
R = 1 – 6*8/8(82 – 1) = 1 – 48 = 0.90
504
Q8) Find Spearman's rank correlation coefficient:
Commerce | 15 | 20 | 28 | 12 | 40 | 60 | 20 | 80 |
Science | 40 | 30 | 50 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 30 | 60 |
A8)
C | S | Rank C | Rank S | d | d2 |
15 | 40 | 2 | 6 | -4 | 16 |
20 | 30 | 3.5 | 4 | -0.5 | 0.25 |
28 | 50 | 5 | 7 | -2 | 4 |
12 | 30 | 1 | 4 | -3 | 9 |
40 | 20 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 16 |
60 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 36 |
20 | 30 | 3.5 | 4 | -0.5 | 0.25 |
80 | 60 | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
|
|
|
|
| 81.5 |
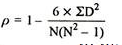
R = 1 – (6*81.5)/8(82 – 1) = 0.02
Q9) Explain regression analysis.
A9)
Regression analysis is a technique of studying the dependence of one variable called dependent variable, on one or more variable called explanatory variable, with a view to estimate or predict the average value of the dependent variables in terms of the known or fixed values of the independent variables.
Regression analysis includes several variations, such as linear, multiple linear, and nonlinear. The most common models are simple linear and multiple linear.
Nonlinear regression analysis is commonly used for more complicated data sets in which the dependent and independent variables show a nonlinear relationship.
Linear model assumption -
Importance
Regression Analysis, a statistical technique, is used to evaluate the relationship between two or more variables. Regression analysis helps an organisation to understand what their data points represent and use them accordingly with the help of business analytical techniques in order to do better decision-making. In this analysis, you will understand how the typical value of the dependent variable changes when one of the independent variables is varied, while the other independent variables are held fixed. Business analysts and data professionals use this powerful statistical tool for removing the unwanted variables and select the important ones.
Q10) How to find a linear regression equation.
Subject | X | Y |
1 | 43 | 99 |
2 | 21 | 65 |
3 | 25 | 79 |
4 | 42 | 75 |
5 | 57 | 87 |
6 | 59 | 81 |
|
|
|
A10)
Subject | X | Y | Xy | X2 | Y2 |
1 | 43 | 99 | 4257 | 1849 | 9801 |
2 | 21 | 65 | 1365 | 441 | 4225 |
3 | 25 | 79 | 1975 | 625 | 6241 |
4 | 42 | 75 | 3150 | 1764 | 5625 |
5 | 57 | 87 | 4959 | 3249 | 7569 |
6 | 59 | 81 | 4779 | 3481 | 6521 |
Total | 247 | 486 | 20485 | 11409 | 40022 |
To find a and b, use the following equation
Find a:
((486 × 11,409) – ((247 × 20,485)) / 6 (11,409) – 247*247)
484979 / 7445
=65.14
Find b:
(6(20,485) – (247 × 486)) / (6 (11409) – 247*247)
(122,910 – 120,042) / 68,454 – 2472
2,868 / 7,445
= .385225
y’ = a + bx
y’ = 65.14 + .385225x
Q11) Calculate linear regression analysis.
Students | X | Y |
1 | 95 | 85 |
2 | 85 | 95 |
3 | 80 | 70 |
4 | 70 | 65 |
5 | 60 | 70 |
A11)
students | X | Y | X2 | y2 | xy |
1 | 95 | 85 | 9025 | 7225 | 8075 |
2 | 85 | 95 | 7225 | 9025 | 8075 |
3 | 80 | 70 | 6400 | 4900 | 5600 |
4 | 70 | 65 | 4900 | 4225 | 4550 |
5 | 60 | 70 | 3600 | 4900 | 4200 |
total | 390 | 385 | 31150 | 30275 | 30500 |
To find a and b, use the following equation
Find a:
((385 × 31150) – ((390 × 30500)) / 5 (31150) – 152100)
97750 / 3650
=26.78
Find b:
(5(30500) – (390 × 385)) / (5 (31150) – 152100)
2,350 / 3650
= .0.64
y’ = a + bx
y’ = 26.78 + .0.64x
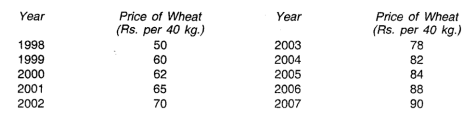
Q12) From the following data of wholesale prices of wheat for ten years construct index number taking a) 1998 as base and b) by chain base method.
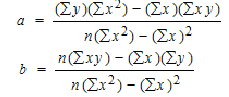

Q13) From the following data calculate the index numbers using the Chain Index Numbers method.
Year 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018
Prices 120 124 130 144 150 160 164 170
A13)
Construction of Chain Index Numbers
Year | Price | Link Relatives | Chain indices |
2011 | 120 | 100 | 100 |
2012 | 124 | 120/124 x 100 = 103.33 | 103.33 ×100/100 = 103.33 |
2013 | 130 | 124/130 x 100 = 104.83 | 104.83 ×103.33/100 = 108.32 |
2014 | 144 | 130/144 x 100 = 110.76 | 110.76×108.32 /100= 119.98 |
2015 | 150 | 144/150 x 100 = 104.16 | 104.16 ×119.98/100 = 124.97 |
2016 | 160 | 150/160 x 100 = 106.66 | 106.66×124.97/100 = 133.29 |
2017 | 164 | 160/164 x 100 = 102.5 | 102.5 ×133.29/100 = 136.62 |
2018 | 170 | 164/170 x 100 = 103.65 | 103.65 ×136.62/100 = 141.61 |
Q14) Compute the chain base index numbers-
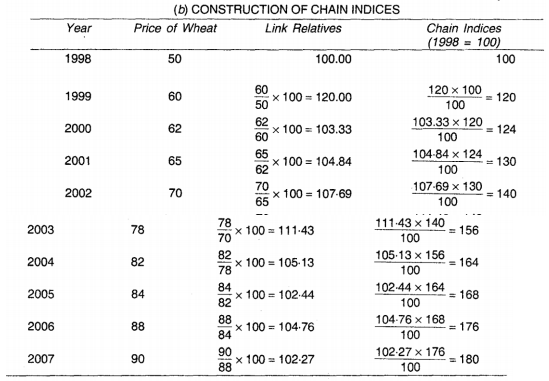
A14)

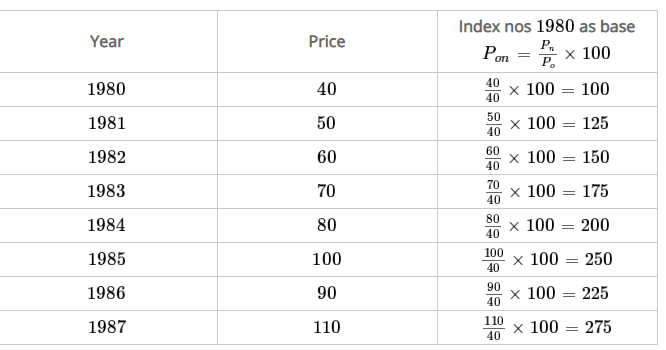
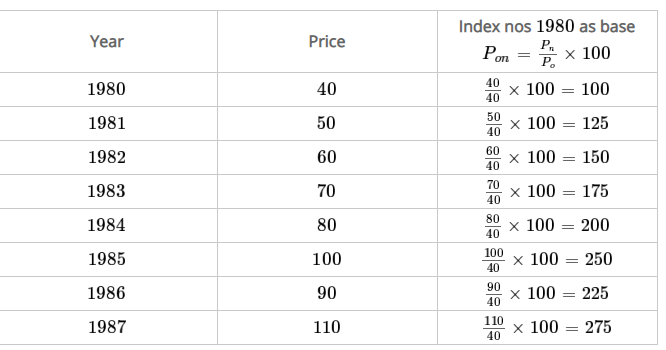
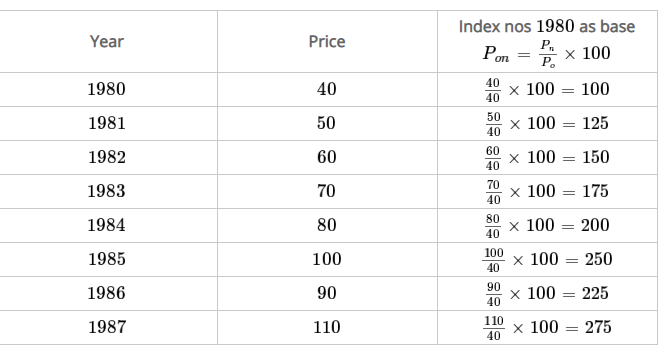
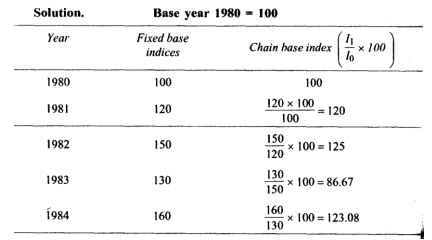
Q15) Find index numbers for the following data taking 1980 as the base year.
Year | 1980 | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 1985 | 1986 | 1987 |
Price | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 100 | 90 | 110 |
A15)
Q16) Find the index number from the data given below.
Commodities | Units | Price in 2007 | Price in 2008 |
Sugar | Quintal | 2200 | 3200 |
Milk | Quintal | 18 | 20 |
Oil | Liter | 68 | 71 |
Wheat | Quintal | 900 | 1000 |
Clothing | Meter | 50 | 60 |
|
|
|
|
A16)
Commodities | Units | Price in 2007 | Price in 2008 |
Sugar | Quintal | 2200 | 3200 |
Milk | Quintal | 18 | 20 |
Oil | Liter | 68 | 71 |
Wheat | Quintal | 900 | 1000 |
Clothing | Meter | 50 | 60 |
|
|
|
|
Index number ( P01 ) = 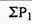
P01 = (4351/3236)*100 = 134.45
It means the price in 2008 were 34% more than the price in 2007
Q17) Construct the price index for 2003, taking the year 2000 as base year.
Commodities | Price in 2000 | Price in 2003 |
A | 60 | 80 |
B | 50 | 60 |
C | 70 | 100 |
D | 120 | 160 |
E | 100 | 150 |
|
|
|
A17)
Commodities | Price in 2000 - P 0 | Price in 2003 - P 1 |
A | 60 | 80 |
B | 50 | 60 |
C | 70 | 100 |
D | 120 | 160 |
E | 100 | 150 |
|
|
|
Index number ( P01 ) = 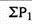
P01 = (550/400)*100 = 137.5
Therefore there is an increase of 37.5% in the prices in 2003 as against 2000.
Q18) Prepare simple aggregative price index.
Commodities | Price in 1995 - P 0 | Price in 2003 - P 1 |
Wheat | 100 | 140 |
Rice | 200 | 250 |
Pulses | 250 | 350 |
Sugar | 14 | 20 |
Oil | 40 | 50 |
A18)
Commodities | Price in 1995 - P 0 | Price in 2003 - P 1 |
Wheat | 100 | 140 |
Rice | 200 | 250 |
Pulses | 250 | 350 |
Sugar | 14 | 20 |
Oil | 40 | 50 |
|
|
|
Simple aggregative index number = (810/604)*100 = 134.1
Q19) Using simple average of price relative method find price index for 2010, taking 2009 as base year for the following data.
Commodities | Price (2009) | Price(2010) |
A | 60 | 80 |
B | 50 | 60 |
C | 60 | 72 |
D | 50 | 75 |
E | 25 | 37 .5 |
F | 20 | 30 |
A19)
Commodities | Price (2009) | Price(2010) | Price relatives |
A | 60 | 80 | 133.33 |
B | 50 | 60 | 120 |
C | 60 | 72 | 120 |
D | 50 | 75 | 150 |
E | 25 | 37 .5 | 150 |
F | 20 | 30 | 150 |
N = 6 |
|
| 823.33 |
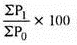
= 823.33/6 = 137.22
Q20) Calculate the price indices from the following data by applying (1) Laspeyre’s method (2) Paasche’s method and (3) Fisher ideal number by taking 2010 as the base year.
Commodity | 2010 | 2011 | ||
PO | QO | P1 | Q1 | |
A | 20 | 10 | 25 | 13 |
B | 50 | 8 | 60 | 7 |
C | 35 | 7 | 40 | 6 |
D | 25 | 5 | 35 | 4 |
A20)
Commodity | 2010 | 2011 |
|
|
|
| ||
PO | QO | P1 | Q1 | Poqo | P1qo | Poq1 | P1q1 | |
A | 20 | 10 | 25 | 13 | 200 | 250 | 260 | 325 |
B | 50 | 8 | 60 | 7 | 400 | 480 | 350 | 420 |
C | 35 | 7 | 40 | 6 | 245 | 280 | 210 | 240 |
D | 25 | 5 | 35 | 4 | 125 | 175 | 100 | 140 |
|
|
|
|
| 970 | 1185 | 920 | 1125 |
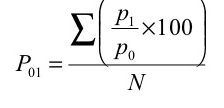
P 01 = (1185/970)*100 = 122.16
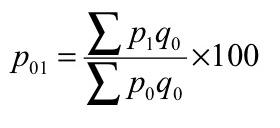
P 01 = (1125/920)*100 = 122.28
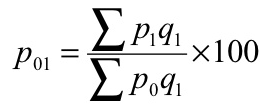
 P 01 = √ = ((1185/970) + (1125/920)) *100 = 120.55
P 01 = √ = ((1185/970) + (1125/920)) *100 = 120.55