Unit – 5
Pictorial View
Q1) What is isometric?
A1) It is defined as 3D objects drawn with no perspective i.e., Lines have no vanishing points is termed as isometric.
Q2) What is Perspective?
A2) It is defined as 3D objects drawn with 1 or more vanishing points is called as Perspective
Q3) What are the fundamental of building information modelling?
A3) 5 fundamentals of BIM are: -
1. Visualization
2. Quantification
3. Communication
4. Coordination
5. Simulation
Q4) Define BIM?
A4) Building Information Modelling (BIM) is an intelligent 3D model-based process that gives architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) professionals the insight and tools to more efficiently plan, design, construct, and manage buildings and infrastructure
Q5) What is BIM include?
A5)
Q6) What is the isometric projection?
A6) It’s a pictorial orthographic projection of an object where a transparent cube containing the object is tilted before one of those solid diagonals of the cube becomes perpendicular to the vertical plane along with the three axes are equally inclined to this vertical plane
Q7) Write the perspective principles?
A7) The main principle that are responsible for linear perspective are
1) size of forms,
2) overlap of forms,
3) placement of forms and
4) Convergence of lines.
All four principles can and should be used together to best interpret perspective.
Size of Forms
The largest of similar forms will appear closest to the viewer. With this scene, the square on the right appears closest because it is largest of the three. The square on the left appears to be the farthest away because it is the smallest.
Overlap of Forms
The square at the top looks bigger because it is overlapping the square at the bottom.
Placement of Forms
Forms placed farthest from the horizon appear closest to the viewer. The square on the right is farther from the horizon than the other two boxes, causing it to look closer to the viewer, whereas the other boxes are closer to the horizon, making them appear farther away.
Convergence of Lines
Parallel lines converge in the distance. In this scene, the road lines (orthogonal lines) meet as they recede into the distance, giving the appearance of depth. A vanishing point is formed where the orthogonal lines meet. The principle of convergence of lines shares the concept of depth expressed through size in that the width of the path decreases with distance.
Q8) Write the types of perspective drawing?
A8) There are typically three types of perspective drawing:
Q9) What is the relation between lines in isometric?
A9) 1. Line those are parallel to object are parallel at isometric projection.
2. Vertical lines at object seen vertical at isometric projection.
3. Horizontal lines on body are drawn at an angle of 30owith horizontal at isometric projection.
4. Lines parallel to an isomeric axis term as isometric line and by fore shortened to 82%.
5. Lines which are not parallel to any isometric axis is term as non-isometric line.
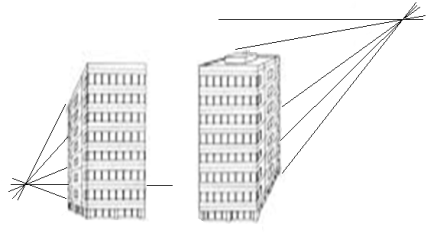
Q10) Draw perspective view of building?
A10)