Unit - 7
Psychrometry and psychometric charts
Q1)Explain the main part of vapour compression refrigeration cycles?
A1)
The Main Parts Of Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycles:
- Evaporator Its function is to provide a heat transfer surface through which heat can pass from the refrigerated space into the vaporizing refrigerant. This is generally a Fin & Tube (Hair-Pin type) heat exchanger, similar to Air- Cooled Condensers.
- Suction Line It carries the low-pressure vapour from the evaporator to suction inlet of the compressor.
- Compressor The function of the compressor is to draw refrigerant vapour from the evaporator and to raise Its temperature and pressure to such a print to that it may be easily condensed with normally available condensing media. It also maintains a continuous flow of the refrigerant through the system.
Compression Ratio = Absolute Discharge Pressure / Absolute Suction Pressure
The Capacity of a Compressor is determined by its Mass Flow rate (Lb/Min) and not by Volume Flow (CFM).
The most common compressors used in chillers are reciprocating, rotary screw, centrifugal, and scroll compressors. Each application prefers one or another due to size, noise, and efficiency and pressure issues.
4. Discharge Line It conveys the high pressure and high-temperature refrigerant from the compressor to the condenser.
5. Condenser The function of the condenser is to provide a heat transfer surface through which heat passes from the refrigerant to the condensing medium which is either water or air.
Types of Condensers:
• Air-Cooled
• Water-Cooled
6. Liquid Receiver It acts as, a reservoir that stores the liquid refrigerant coming from the condenser and supplies it to the evaporator according to the requirement.
7. Liquid Line It carries the liquid refrigerant from the receiver and conveys it to the expansion valve.
8. Expansion valve Function Of This valve is to Supply a proper amount of refrigerant to the evaporator after reducing its pressure considerably so that the refrigerant may take sufficient amount of heat from the refrigerating space during evaporation
The Metering Device converts the High Pressure and High-Temperature Liquid from Condenser to Low Pressure and Low-Temperature Liquid-Vapour mixture, which will be fed to the Evaporator.
An expansion valve is a component in refrigeration and air conditioning systems that control the amount of refrigerant flow into the evaporator thereby controlling the superheat at the outlet of the evaporator.
Types of Expansion devices
- Thermostatic EV
- Capillary tube
- Hand operated EV
- Automatic or Constant Pressure EV
- Float expansion
Q2) Name the different type of vapour compression cycle?
A2)
The vapour compression cycle essentially consists of compression, condensation, throttling and evaporation. Many scientists have focused their attention to increase the coefficient of performance of the cycle. Through there are many cycles, but There are mainly 5 types of Vapour Compression Cycles
1. Cycle with dry saturated vapour after compression,
2. Cycle with wet vapour after compression,
3. Cycle with superheated vapour after compression,
4. Cycle with superheated vapour before compression.
5. Cycle with under cooling or sub cooling of refrigerant
Q3) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of vapour compression cycle?
A3)
Advantages of Vapour Compression System :
- It has a smaller size for the given capacity of refrigeration.
- It has less running cost.
- It can be employed over a large range of temperatures.
- The coefficient of performance is quite high.
- Less time required to produce refrigerant effects.
Disadvantages of Vapour Compression System:
- The initial cost is high.
- The prevention of leakage of the refrigerant is the major problem in the vapour compression system.
- More wear and tear and noise due to Moving Parts
- Liquid droplets in suction line may damages.
Q4) what is multi staging in vapour compression system?
A4)
Multi-Stage: In the case of a Refrigeration system very low-pressure refrigerant vapours (Evaporator pressure) are to be compressed to very high-pressure refrigerant vapours (Condenser pressure). As this pressure ratio is very high the size and work done required in case of a single-stage is more, thus COP decreases to increase COP and reduce work done multi staging is needed.
Advantages of multi-staging in vapour compression system:
1. Work done per kg of refrigerant is reduces by using an intercooler
2. Volumetric efficiency of compressor increases
3. It reduces leakage of refrigerant
4. It gives uniform torque, therefore, the smaller flywheel may be used
5. Effective lubrication can be done
6. Cost of compressor reduces
Q5) Explain practical absorption refrigeration cycle?
A5)
Practical Absorption Refrigeration Cycle:
The replacement of the compressor by the simple arrangement of Fig is not very economical in practice. In order to make improvements certain additional auxiliary items are provided in the system. They include analyzer, a rectifier, and two heat exchangers. The practical absorption cycles as developed after incorporating these auxiliaries is shown in Fig.
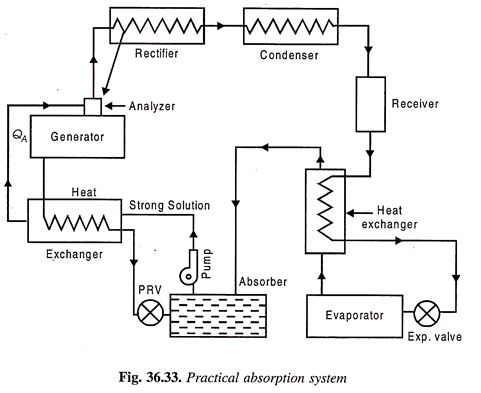
Fig 1 Practical absorption system
(a) Analyzer:
The ammonia vapours leaving the generator may contain certain moisture, and therefore it should be freed from any trace of water vapour before passing on to the condenser and then to the expansion valve, otherwise the water vapour is likely to freeze in the small valve passage and choke the flow.
The function of the analyzer is to remove the moisture as far as possible. It is open types of cooler and forms an integral part of the generator, mounted on its top. Both the strong aqua-ammonia solution from the absorber and the condensate removed in rectifier are introduced from the top and flow downwards.
The hot rising vapour of ammonia therefore comes in contact with the same and gets cooled. Thus most of the water vapour is condensed and drips back into the generator. This helps in salvaging a certain portion of heat in outgoing vapour which would otherwise have been rejected out through the condenser.
(b) Rectifier:
It is a closed type of cooler and is actually a miniature condenser where any traces of water vapour left in the ammonia vapour, are removed by condensation .The cooling is achieved by circulating water as is done in an ordinary condenser. The condensed aqua is drained back to the generator through the analyser.
(c) Heat Exchangers:
Two heat exchangers are provided to internally exchange heat from the higher temperature fluid to the lower temperature fluid so that one is cooled and the other is heated.
One heat exchanger is provided between liquid receiver and evaporator so that the liquid is sub-cooled and vapour is heated up. Another heat exchanger is located between generator and absorber so that the strong aqua is heated up before going on to the analyser and weak aqua is cooled before entering the absorber.
Q6) where is the Industrial air conditioning system used?
A6)
Industrial Air Conditioning -
The objective of this is to provide favourable surrounding conditions so that the required processes can be carried out and required products can be produced.
It should also provide at least a partial measure of comfort to the people working in the industries.
Industrial air conditioning examples-
- Textile industries
- Printing industries
- Manufacturing of precision parts
- Semi-conductor industries
- Pharmaceutics
- Photographic materials
- Computer rooms
- Mines, power plants, etc.
Q 7) what are the important issues to be considered in the design of refrigeration systems?
A7)
Refrigeration systems are used in a wide variety of applications. Each application has specific requirements of temperature, moisture content, capacity, operating duration, availability of resources etc. Hence, refrigeration system design must be done for each application based on the specific requirements. Since refrigeration systems are cost and energy intensive, it is important to design the systems to achieve low initial and running costs. Reliability of the systems is also very important as the failure of the refrigeration systems to perform may lead huge financial losses. Of late, issues related to environment have attracted great attention; hence the refrigeration systems should be as far as possible environment friendly.
Q7) what is the relation between refrigeration and air conditioning?
A8).
Air conditioning involves control of temperature and moisture content. One of the most common requirements of air conditioning systems is cooling and dehumidification of air. Refrigeration systems are required for cooling and dehumidification. Refrigeration systems can also be used for heating of air by utilizing the heat rejected at the condenser that is by running them as heat pumps.
Q8) Explain the importance of cold storages?
A9)
Preservation of perishable products using cold storages equalizes the prices throughout the year and makes these products available round the year. Without them, the prices would be very low at the time of harvest and very high during the off-season. With storage facilities, it would also be possible to make the products available in areas where they are not grown. That is the main importance of cold storage.
Q9) A Carnot air conditioner takes heat from a room at 21oC and transfers it to the outdoors, which is at 35oC. For every two joules of electric energy required operating the air conditioner, how many joules are removed from the room in the form of heat?
A10)
Given,
The temperature of the hot reservoir TH=308K
The temperature of the cold reservoir TC=284K
The work required to operate the refrigerator W=2J
The coefficient of performance of a general refrigerator is,
K=QC / W
In particular, for a Carnot air conditioner, which is a Carnot engine operating in reverse, the coefficient of performance is,
K=TC / TH−TC
Then, combining both expressions,
QC / W=TC / TH−TC
The heat removed from the room is,
QC=TC x W / TH−TC
=284K x 2J / 308K−284K
=23.7J
For every two joules of electric energy required 23.7j of heat are removed from the room.