Module 3
Vector calculus
Q1. Calculate the curl for the following vector field.
F⃗ =x3y2 i⃗ +x2y3z4 j⃗ +x2z2 k⃗
Sol: In order to calculate the curl, we need to recall the formula.
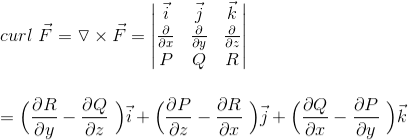
where P, Q, and R correspond to the components of a given vector field: F⃗ =Pi⃗ +Qj⃗ +Rk⃗
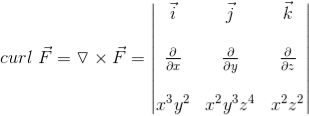
=(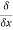 (x2z2)−
(x2z2)−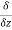 (x2y3z4) )i⃗ +(
(x2y3z4) )i⃗ +(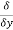 (x3y2)−
(x3y2)−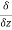 (xz2) )j⃗ +(
(xz2) )j⃗ +(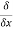 (x2y3z4)−
(x2y3z4)−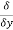 (x3y2) )k⃗
(x3y2) )k⃗
=(0−4x2y3z3)i⃗ +(0−2xz2)j⃗ +(2xy3z4−2x3y)k⃗
Thus the curl is
=(−4x2y3z3)i⃗ +(−2xz2)j⃗ +(2xy3z4−2x3y)k⃗
Q2. Find the directional derivative of Θ=x2y cos z at (1,2,π/2) in the direction of a = 2i+3j+2k.
Sol : ∇ϕ = i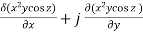 + k
+ k 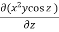
= 2xy cos zi+ x2 cos zj -x2y sin zk
At (1,2,π/2) ∇ϕ = 0i +0j-2k
Directional directive in the direction of 2i+3j+2k.
=(0i+0j-2k).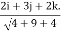 =-
=- 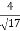
Q3. In what direction from the point (2,1,-1) is the directional derivative of ϕ=x2yz3 maximum? What is its magnitude?
Solution :∇ϕ= i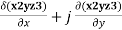 + k
+ k 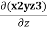
= -4i-4j+12k
Directional derivative is maximum in the direction of ∇Θ. Hence, directional derivative is maximum in the direction of -4i-4j+12k
Its magnitude =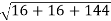 =4
=4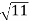
Q4. Prove that ͞͞͞F = [y2 cos x +z3] i +(2y sin x – 4) j +(3xz2 + 2) k is a conservative field. Find (i) scalar potential for͞͞͞F (ii) the work done in moving an object in this field from (0, 1, -1) to ( / 2,-1, 2)
/ 2,-1, 2)
 Sol. : (a) The field is conservative if cur͞͞͞͞͞͞F = 0.
Sol. : (a) The field is conservative if cur͞͞͞͞͞͞F = 0.
 Now, cur͞͞͞F =
Now, cur͞͞͞F = 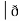 ̷̷
̷̷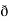 X
X 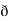 /
/ 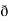 y
y 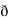 /
/ 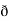 z
z
i j k
Y2COS X +Z3 2y sin x-4 3xz2 +2
; Cur 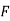 = (0-0) – (3z2 – 3z2) j + (2y cos x- 2y cos x) k = 0
= (0-0) – (3z2 – 3z2) j + (2y cos x- 2y cos x) k = 0
; F is conservative.
(b) Since F is conservative there exists a scalar potential ȸ such that
F = ȸ
 (y2 cos x +z3) i + (2y sin x-4) j + (3xz2 + 2) k
(y2 cos x +z3) i + (2y sin x-4) j + (3xz2 + 2) k
= 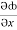 i +
i + 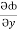 j +
j + 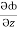 k
k
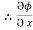 = y2 cos x + z3,
= y2 cos x + z3, 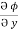 = 2y sin x – 4,
= 2y sin x – 4, 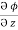 = 3xz2 + 2
= 3xz2 + 2
Now, 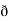 =
= 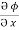 dx +
dx + 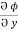 dy +
dy + 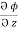 dz
dz
= (y2 cos x + z3) dx +(2y sin x – 4)dy + (3xz2 + 2)dz
= (y2 cos x dx + 2y sin x dy) +(z3dx +3xz2dz) +(- 4 dy) + (2 dz)
=d(y2 sin x + z3x – 4y -2z)
 ȸ = y2 sin x +z3x – 4y -2z
ȸ = y2 sin x +z3x – 4y -2z
(c) now, work done =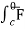 .d ͞r
.d ͞r
= 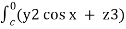 dx + (2y sin x – 4) dy + ( 3xz2 + 2) dz
dx + (2y sin x – 4) dy + ( 3xz2 + 2) dz
= 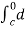 (y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z) (as shown above)
(y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z) (as shown above)
= [ y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z ]( 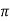 /2, -1, 2)
/2, -1, 2)
= [ 1 +8  + 4 + 4 ] – { - 4 – 2} =4
+ 4 + 4 ] – { - 4 – 2} =4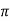 + 15
+ 15
Q5. If 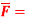 x2zi – 2y3z3j + xy2z2k find dvi
x2zi – 2y3z3j + xy2z2k find dvi  and curl
and curl  at (1,-1, 1)
at (1,-1, 1)
Sol: div 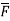 = ∇.
= ∇.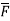 =
= 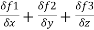 =
=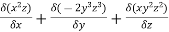
= 2xz – 6y2z3 + 2xy2z =(2-6+2) = -2

 Curl
Curl 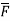 =
= 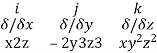
=i(2xyz2 + 6y3z2) – j(y2z2- x2) + k(0-0)
=-8 at (1,-1,1)
Q6. Find the angle between the normal to the surface xy = z2 at the points (1,4,2) and (-3,-3,3)
Sol: let ϕ = xy-z2
∇ϕ= i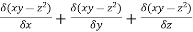 =yi + xj -2zk =4i + j -4k
=yi + xj -2zk =4i + j -4k
∇ϕ = 3i – 3j-6k
But these are the normal to the surface at given points. Angle between two vectors is given by (4i + j -4k).( 4i + j -4k)= |4i + j- 4k|.|-3i-3j -6K|cos θ.
If θ is the angle between then cos θ= 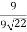 =
= 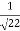 .
.
7. Evaluate 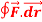 where F= cos y.i-x siny j and C is the curve y=
where F= cos y.i-x siny j and C is the curve y=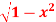 in the xy plae from (1,0) to (0,1)
in the xy plae from (1,0) to (0,1)
Sol : The curve y=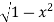 i.e x2+y2 =1. Is a circle with centre at the origin and radius unity.
i.e x2+y2 =1. Is a circle with centre at the origin and radius unity.
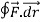 =
= 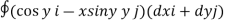
= 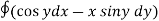
=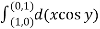 =-1
=-1
8. Evaluate 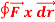 where
where  = (2xy +z2) I +x2j +3xz2 k along the curve x=t, y=t2, z= t3 from (0,0,0) to (1,1,1).
= (2xy +z2) I +x2j +3xz2 k along the curve x=t, y=t2, z= t3 from (0,0,0) to (1,1,1).
Sol: F x dr = 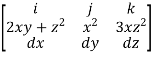
Put x=t, y=t2, z= t3
Dx=dt ,dy=2tdt, dz=3t2dt.
F x dr = 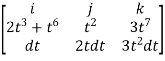
=(3t4-6t8) dt i – ( 6t5+3t8 -3t7) dt j +( 4t4+2t7-t2)dt k
=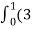 t4-6t3)dti –(6t5+3t8-3t7)dt j+(4t4 + 2t7 – t2)dt k
t4-6t3)dti –(6t5+3t8-3t7)dt j+(4t4 + 2t7 – t2)dt k
=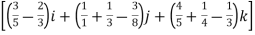
=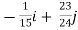 +
+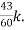
9. Prove that ͞͞͞F = [y2 cos x +z3] i +(2y sin x – 4) j +(3xz2 + 2) k is a conservative field. Find (i) scalar potential for͞͞͞F (ii) the work done in moving an object in this field from (0, 1, -1) to ( / 2,-1, 2)
/ 2,-1, 2)
Sol. : (a) The field is conservative if cur͞͞͞͞͞͞F = 0.

 Now, curl͞͞͞F =
Now, curl͞͞͞F = 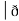 ̷̷
̷̷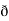 X
X 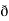 /
/ 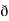 y
y 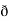 /
/ 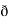 z
z
Y2COS X +Z3 2y sin x-4 3xz2 + 2
; Cur 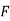 = (0-0) – (3z2 – 3z2) j + (2y cos x- 2y cos x) k = 0
= (0-0) – (3z2 – 3z2) j + (2y cos x- 2y cos x) k = 0
; F is conservative.
(b) Since F is conservative there exists a scalar potential ȸ such that
F = ȸ
 (y2 cos x=z3) i + (2y sin x-4) j + (3xz2 + 2) k =
(y2 cos x=z3) i + (2y sin x-4) j + (3xz2 + 2) k = 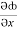 i +
i + 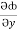 j +
j + 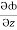 k
k
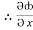 = y2 cos x + z3,
= y2 cos x + z3, 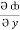 = 2y sin x – 4,
= 2y sin x – 4, 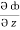 = 3xz2 + 2
= 3xz2 + 2
Now, 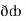 =
= 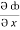 dx +
dx + 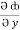 dy +
dy + 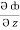 dz
dz
= (y2 cos x + z3) dx +(2y sin x – 4)dy + (3xz2 + 2)dz
= (y2 cos x dx + 2y sin x dy) +(z3dx +3xz2dz) +(- 4 dy) + (2 dz)
=d(y2 sin x + z3x – 4y -2z)
 ȸ = y2 sin x +z3x – 4y -2z
ȸ = y2 sin x +z3x – 4y -2z
(c) now, work done =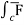 .d ͞r
.d ͞r
= 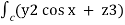 dx + (2y sin x – 4) dy + ( 3xz2 + 2) dz
dx + (2y sin x – 4) dy + ( 3xz2 + 2) dz
= 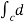 (y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z) (as shown above)
(y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z) (as shown above)
= [ y2 sin x + z3x – 4y + 2z ]( 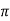 /2, -1, 2)
/2, -1, 2)
= [ 1 +8  + 4 + 4 ] – { - 4 – 2} =4
+ 4 + 4 ] – { - 4 – 2} =4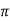 + 15
+ 15
10. Verify green’s theorem for 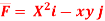 and C is the triangle having verticles A (0,2 ) , B (2,0 ) , C (4,2 ).
and C is the triangle having verticles A (0,2 ) , B (2,0 ) , C (4,2 ).
SOL:By green theorem.
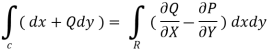
Here ,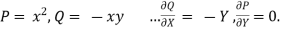
(a) Along AB , since the equation of AB is
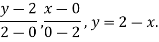
Putting 
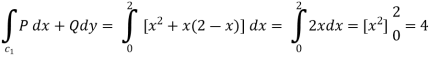
Along BC , since the equation of BC , 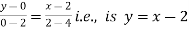 .
.
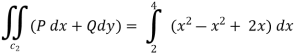
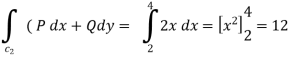
Along CA , since the equation of CA, is y = 2 , dy = 0.
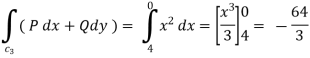
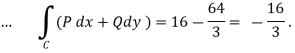
(b) 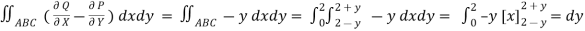
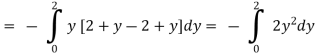
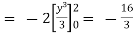 .
.
From (1) and (2) , the theorem is verified .