Unit - 1
Introduction
Q1) What is Artificial Intelligence?
A1) In today's world, technology is growing very fast, and we are getting in touch with different new technologies day by day.
Here, one of the booming technologies of computer science is Artificial Intelligence which is ready to create a new revolution in the world by making intelligent machines. The Artificial Intelligence is now all around us. It is currently working with a variety of subfields, ranging from general to specific, such as self-driving cars, playing chess, proving theorems, playing music, Painting, etc.
AI is one of the fascinating and universal fields of Computer science which has a great scope in future. AI holds a tendency to cause a machine to work as a human.
Artificial Intelligence is composed of two words Artificial and Intelligence, where Artificial defines "man-made," and intelligence defines "thinking power", hence AI means "a man-made thinking power."
So, we can define AI as:
"It is a branch of computer science by which we can create intelligent machines which can behave like a human, think like humans, and able to make decisions."
Artificial Intelligence exists when a machine can have human based skills such as learning, reasoning, and solving problems With Artificial Intelligence you do not need to pre-program a machine to do some work, despite that you can create a machine with programmed algorithms which can work with own intelligence, and that is the awesomeness of AI.
It is believed that AI is not a new technology, and some people says that as per Greek myth, there were Mechanical men in early days which can work and behave like humans.
Q2) Why Artificial Intelligence?
A2) Before Learning about Artificial Intelligence, we should know that what is the importance of AI and why should we learn it. Following are some main reasons to learn about AI:
● With the help of AI, you can create such software or devices which can solve real-world problems very easily and with accuracy such as health issues, marketing, traffic issues, etc.
● With the help of AI, you can create your personal virtual Assistant, such as Cortana, Google Assistant, Siri, etc.
● With the help of AI, you can build such Robots which can work in an environment where survival of humans can be at risk.
● AI opens a path for other new technologies, new devices, and new Opportunities.
Q3) What are the Goals of Artificial Intelligence?
A3) Following are the main goals of Artificial Intelligence:
- Replicate human intelligence
- Solve Knowledge-intensive tasks
- An intelligent connection of perception and action
- Building a machine which can perform tasks that requires human intelligence such as:
- Proving a theorem
- Playing chess
- Plan some surgical operation
- Driving a car in traffic
- Creating some system which can exhibit intelligent behavior, learn new things by itself, demonstrate, explain, and can advise its user.
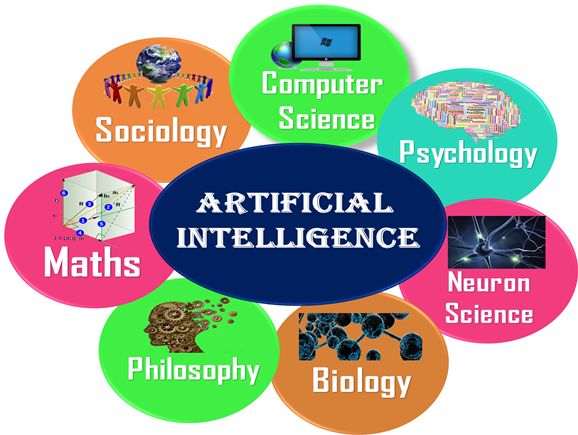
Q4) What Comprises Artificial Intelligence?
A4) Artificial Intelligence is not just a part of computer science even it's so vast and requires lots of other factors which can contribute to it. To create the AI first we should know that how intelligence is composed, so the Intelligence is an intangible part of our brain which is a combination of Reasoning, learning, problem-solving perception, language understanding, etc.
To achieve the above factors for a machine or software Artificial Intelligence requires the following discipline:
● Mathematics
● Biology
● Psychology
● Sociology
● Computer Science
● Neurons Study
● Statistics
Q5) Write the advantages of AI?
A5) Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Following are some main advantages of Artificial Intelligence:
● High Accuracy with less errors: AI machines or systems are prone to less errors and high accuracy as it takes decisions as per pre-experience or information.
● High-Speed: AI systems can be of very high-speed and fast-decision making, because of that AI systems can beat a chess champion in the Chess game.
● High reliability: AI machines are highly reliable and can perform the same action multiple times with high accuracy.
● Useful for risky areas: AI machines can be helpful in situations such as defusing a bomb, exploring the ocean floor, where to employ a human can be risky.
● Digital Assistant: AI can be very useful to provide digital assistant to the users such as AI technology is currently used by various E-commerce websites to show the products as per customer requirement.
● Useful as a public utility: AI can be very useful for public utilities such as a self-driving car which can make our journey safer and hassle-free, facial recognition for security purpose, Natural language processing to communicate with the human in human-language, etc.
Q6) What are the disadvantages of AI?
A6) Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Every technology has some disadvantages, and the same goes for Artificial intelligence. Being so advantageous technology still, it has some disadvantages which we need to keep in our mind while creating an AI system. Following are the disadvantages of AI:
● High Cost: The hardware and software requirement of AI is very costly as it requires lots of maintenance to meet current world requirements.
● Can't think out of the box: Even we are making smarter machines with AI, but still they cannot work out of the box, as the robot will only do that work for which they are trained, or programmed.
● No feelings and emotions: AI machines can be an outstanding performer, but still it does not have the feeling so it cannot make any kind of emotional attachment with human, and may sometime be harmful for users if the proper care is not taken.
● Increase dependency on machines: With the increment of technology, people are getting more dependent on devices and hence they are losing their mental capabilities.
● No Original Creativity: As humans are so creative and can imagine some new ideas but still AI machines cannot beat this power of human intelligence and cannot be creative and imaginative.
Q7) Explain the history of AI?
A7) Artificial Intelligence is not a new word and not a new technology for researchers. This technology is much older than you would imagine. Even there are the myths of Mechanical men in Ancient Greek and Egyptian Myths. Following are some milestones in the history of AI which defines the journey from the AI generation to till date development.
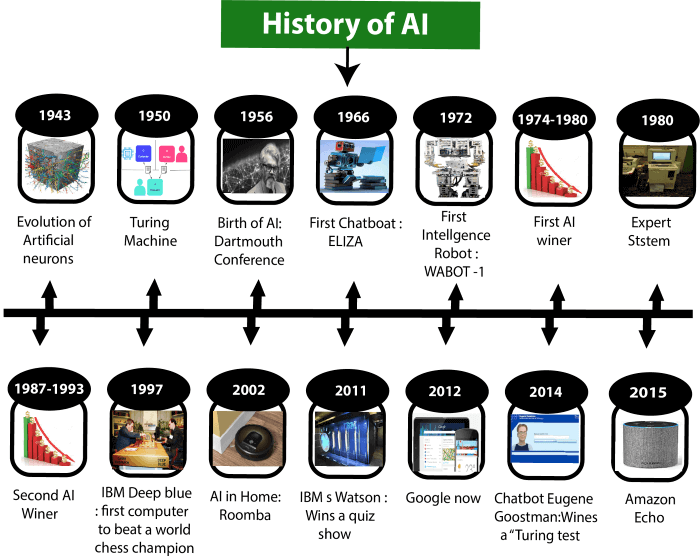
Maturation of Artificial Intelligence (1943-1952)
- Year 1943: The first work which is now recognized as AI was done by Warren McCulloch and Walter pits in 1943. They proposed a model of artificial neurons.
- Year 1949: Donald Hebb demonstrated an updating rule for modifying the connection strength between neurons. His rule is now called Hebbian learning.
- Year 1950: The Alan Turing who was an English mathematician and pioneered Machine learning in 1950. Alan Turing publishes "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" in which he proposed a test. The test can check the machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to human intelligence, called a Turing test.
The birth of Artificial Intelligence (1952-1956)
- Year 1955: An Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon created the "first artificial intelligence program "Which was named as "Logic Theorist". This program had proved 38 of 52 Mathematics theorems, and find new and more elegant proofs for some theorems.
- Year 1956: The word "Artificial Intelligence" first adopted by American Computer scientist John McCarthy at the Dartmouth Conference. For the first time, AI coined as an academic field.
At that time high-level computer languages such as FORTRAN, LISP, or COBOL were invented. And the enthusiasm for AI was very high at that time.
The golden years-Early enthusiasm (1956-1974)
- Year 1966: The researchers emphasized developing algorithms which can solve mathematical problems. Joseph Weizenbaum created the first chatbot in 1966, which was named as ELIZA.
- Year 1972: The first intelligent humanoid robot was built in Japan which was named as WABOT-1.
The first AI winter (1974-1980)
- The duration between years 1974 to 1980 was the first AI winter duration. AI winter refers to the time period where computer scientist dealt with a severe shortage of funding from government for AI researches.
- During AI winters, an interest of publicity on artificial intelligence was decreased.
A boom of AI (1980-1987)
- Year 1980: After AI winter duration, AI came back with "Expert System". Expert systems were programmed that emulate the decision-making ability of a human expert.
- In the Year 1980, the first national conference of the American Association of Artificial Intelligence was held at Stanford University.
The second AI winter (1987-1993)
- The duration between the years 1987 to 1993 was the second AI Winter duration.
- Again, Investors and government stopped in funding for AI research as due to high cost but not efficient result. The expert system such as XCON was very cost effective.
The emergence of intelligent agents (1993-2011)
- Year 1997: In the year 1997, IBM Deep Blue beats world chess champion, Gary Kasparov, and became the first computer to beat a world chess champion.
- Year 2002: for the first time, AI entered the home in the form of Roomba, a vacuum cleaner.
- Year 2006: AI came in the Business world till the year 2006. Companies like Facebook, Twitter, and Netflix also started using AI.
Deep learning, big data and artificial general intelligence (2011-present)
- Year 2011: In the year 2011, IBM's Watson won jeopardy, a quiz show, where it had to solve the complex questions as well as riddles. Watson had proved that it could understand natural language and can solve tricky questions quickly.
- Year 2012: Google has launched an Android app feature "Google now", which was able to provide information to the user as a prediction.
- Year 2014: In the year 2014, Chatbot "Eugene Goostman" won a competition in the infamous "Turing test."
- Year 2018: The "Project Debater" from IBM debated on complex topics with two master debaters and also performed extremely well.
- Google has demonstrated an AI program "Duplex" which was a virtual assistant and which had taken hairdresser appointment on call, and lady on other side didn't notice that she was talking with the machine.
Now AI has developed to a remarkable level. The concept of Deep learning, big data, and data science are now trending like a boom. Nowadays companies like Google, Facebook, IBM, and Amazon are working with AI and creating amazing devices. The future of Artificial Intelligence is inspiring and will come with high intelligence.
Q8) What do you mean by state of the art?
A8) Researchers now have access to new tools that can help them achieve critical objectives, and these technologies are excellent starting points in and of themselves. The following are some specific domains that have been achieved in recent years:
● Machine learning;
● Reinforcement learning;
● Deep learning;
● Natural language processing.
Machine learning
Machine learning is a subtype of artificial intelligence that employs statistical approaches to enable machines to absorb data without being explicitly instructed to do so. This is referred to as 'training' a 'model' with a learning 'algorithm,' which improves performance on a given task over time. Researchers have been inspired to push further on the accelerator as a result of their triumphs in this field.
The capacity of machines to learn how to create molecules is one of these achievements. It was feasible to train the computers with roughly 12.4 million reactions using a system made up of three neural networks and a search tree technique dubbed 'Monte Carlo,' which solved various retrosynthetic studies. This process is far faster than the current one, which involves computerised molecular synthesis planning. In fact, it solves more than 80% of a single molecular test, with a maximum time restriction of 5 seconds as a target for each unique molecule being examined.
Research on improving techniques like hyperparameters and neural networks, which are fixed parameters provided to computers as beginning values for learning, is also continuing. By reducing the complexity and size of the calculation, new algorithms can help to maximise network performance. LEAF (Learning Evolutionary AI Framework) is an example of this, since it uses these methods to precisely optimise hyperparameters and network designs by welding together smaller, more effective networks.
Reinforcement Learning (RL)
Reinforcement learning is a branch of machine learning that deals with software agents that learn 'goal-oriented' behaviour by attempting and failing in settings that reward them for their actions (called 'Policy') toward accomplishing the goals.
This is the field that has piqued the interest of researchers the most in the recent decade. In 2018, OpenAI, a non-profit artificial intelligence research organisation dedicated to promoting and creating friendly AI, achieved significant results in the game Montezuma's Revenge. A technique called Random Network Distillation (RND) was used to achieve superhuman performance by encouraging the RL agent to explore unanticipated states. The graph below demonstrates how far this strategy outperformed the game's other AI algorithms.
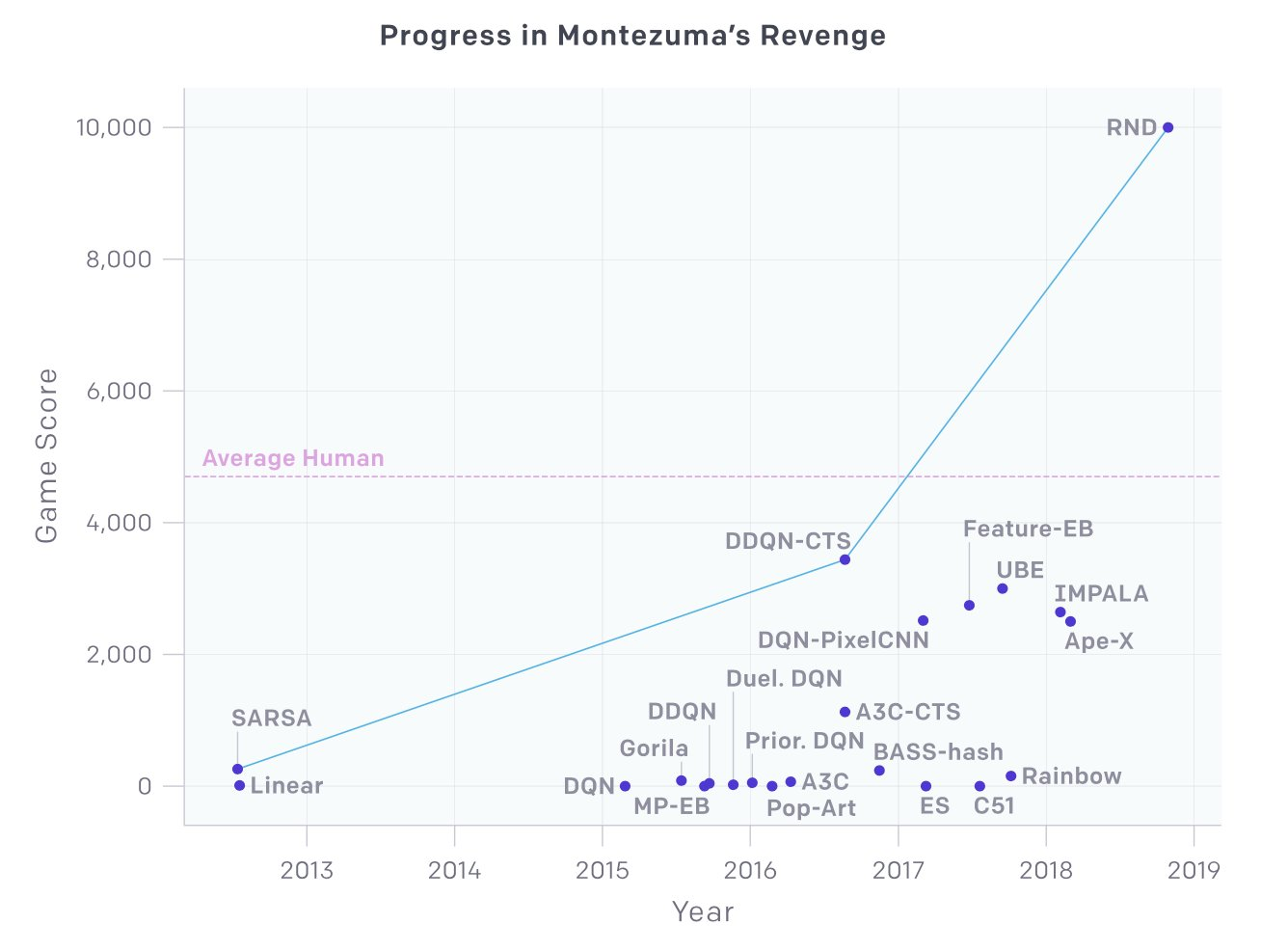
This is only one of a number of examples of findings received in 2019. DeepMind's AlphaStar is another AI worth considering. It used multi-agent algorithm training to defeat the five-time world champion in the real-time strategy game StarCraft 2. It began by forcing agents to compete against one another, allowing it to learn about the vast strategic space. Later, a new agent was created that integrated the greatest methods that people had devised. Multiple agents that independently learnt and operated together to compete against one another achieved a level of performance equal to humans in Quake 3 Arena.
Deep Learning
Deep learning, another type of machine learning, is inspired by the action of neurons in the brain to learn how to discern complicated patterns from taught data. This is because algorithms, mostly statistical calculations, are used. The term 'deep' alludes to the huge number of levels of neurons that ML models at the same time, allowing for the acquisition of rich data representations and performance increases.
The year 2019 marked a watershed moment for deep learning and its applications in a variety of fields, particularly medicine. For example, a technique known as "two phases" has resulted in expert-level diagnosis and therapy prescriptions for a variety of eye illnesses. The first stage used a computerised 3D scanner to reconstruct an eye tissue map, and the second stage used this map to make predictions about the severity of the condition. A deep learning model that was employed in 54 thousand ECG traces is another example. It can identify 12 different types of arrhythmias.
Even more significant is what the researchers hope future research will reveal, namely the possibility of recovering speech in paralysed patients and movement in quadriplegics.
In the first case, Columbia University researchers were able to synthesise voice with a vocoder employing ways of analysing the brain activity of five epileptic patients. Although the system has achieved 75 percent accuracy, a deep learning model has shown a 65 percent improvement in voice comprehensibility.
In the second, even more astonishing example, researchers implanted a microelectrode in a paraplegic patient's hand and arm portion of the left side of the primary motor cortex. They told the neural network to use the voltage signals inside the patient's skull to forecast what the patient's arm movement intentions would be. Without monitoring, the patient was able to maintain a high-accuracy resuscitation of his paralysed forearm with functional electrical stimulation for almost a year.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) is the process by which computers learn to interpret, comprehend, and alter textual material. With Google AI's BERT and Transformer, Allen Institute's ELMo, OpenAI's Transformer, Ruder and Howard's ULMFit, and Microsoft's MT-DNN, 2019 was a banner year for NPL. All of these studies have demonstrated that pre-taught language models can increase performance on a wide range of NLP tasks.
Take the OpenAI GPT-2 pre-educated language model for example:
INPUT: Miley Cyrus was busted shoplifting on Hollywood Boulevard from Abercrombie and Fitch.
OUTPUT (written totally by machine on the second attempt): Security guards were recorded on camera escorting the 19-year-old singer out of the store. The singer was dressed in a black hoodie with the labels 'Blurred lines' and 'Fashion Police' on the front and back, respectively. The video can be found by scrolling below.
Miley Cyrus was busted shoplifting today on Hollywood Boulevard from Abercrombie & Fitch (pictured).
Q9) Write down the risks of AI?
A9) Artificial intelligence is dreaded by many experts and ordinary individuals alike, despite being heralded as a gift for humanity by tech pundits. This dread has been shown on film countless times in the shape of dystopian futures generated by AI computers that have taken over the world. The Matrix and the Terminator are two of the most well-known examples.
AI is Unsustainable
Intelligent machines are known for their great computational power, which is provided by a slew of processors. Selenium, a rare earth metal, is a major component of these computer chips. Furthermore, such robots' batteries are made of Lithium, another rare element found in the earth's crust. Increased mining of these materials is rapidly and irreversibly harming our ecosystem. Furthermore, they consume a large amount of power to operate, putting a strain on our power plants and, once again, damaging the environment.
Lesser Jobs
Machines, without a doubt, perform routine and repetitious activities far better than people. Many firms would prefer machines replace humans in order to boost their profits, lowering the number of employment available for humans.
A threat to Humanity
Elon Musk is widely regarded as one of the most intelligent people working on artificial intelligence today. He has also stated openly that artificial intelligence is the greatest future threat to human civilisation. This suggests that the dismal future depicted in science fiction films is not implausible. In addition, Stephen Hawking has long expressed his opposition to AI advancements.
The most serious danger connected with AI is that computers will develop consciousness and turn against humans if they become self-aware.
Q10) What are the benefits of AI?
A10) Artificial Intelligence is a computer program's ability to learn and think. Everything that includes a programme doing something that we would ordinarily associate with human intelligence is termed artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence applications offer huge benefits and have the potential to disrupt any industry. Let's take a look at a few of them.
1) Reduction in Human Error:
Because humans make mistakes from time to time, the term "human error" was coined. Computers, on the other hand, do not make these errors if they are correctly programmed. Artificial intelligence makes choices based on previously obtained data and a set of algorithms. As a result, errors are decreased, and the prospect of achieving better precision and accuracy is increased.
For example, AI has removed the majority of human mistake in weather forecasting.
2) Takes risks instead of Humans:
One of the most significant advantages of artificial intelligence is this. By constructing an AI Robot that can do the risky tasks for us, we can transcend many of humanity's risky limits. It can be utilised effectively in every type of natural or man-made disaster, whether it is going to Mars, defusing a bomb, exploring the deepest regions of the oceans, mining for coal and oil.
Have you heard about the explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear power facility in Ukraine? There were no AI-powered robots available at the time to assist us in minimising the effects of radiation by controlling the fire early on, as any human who came close to the core died in minutes. They eventually used helicopters to drop sand and boron from a safe distance.
AI Robots can be utilised in situations when human intervention is risky.
3) Available 24x7:
Without breaks, an average human will labour for 4–6 hours every day. Humans are created in such a way that they can take time off to replenish themselves and prepare for a new day at work, and they even have weekly off days to keep their professional and home lives separate. But, unlike humans, we can use AI to make machines work 24 hours a day, seven days a week with no breaks, and they don't get bored.
For example, educational institutions and helpline centres receive a large number of requests and difficulties that AI can successfully address.
4) Helping in Repetitive Jobs:
We will be doing a lot of repetitious labour in our day-to-day work, such as writing thank-you emails, double-checking documents for flaws, and so on. We can use artificial intelligence to efficiently automate these monotonous operations and even remove "boring" duties from humans' schedules, allowing them to be more creative.
For example, at banks, we frequently see numerous document verifications in order to obtain a loan, which is a time-consuming task for the bank's owner. The owner can use AI Cognitive Automation to speed up the process of document verification, which will benefit both the customers and the owner.
5) Digital Assistance:
Digital assistants are used by some of the most modern enterprises to engage with people, reducing the requirement for human personnel. Many websites also use digital assistants to supply things that users seek. We can discuss what we're searching for with them. Some chatbots are created in such a way that it's difficult to tell whether we're conversing with a machine or a human.
For example, we all know that businesses have a customer service team that is responsible for answering customers' questions and concerns. Organizations can use AI to create a voice bot or a chatbot that can assist customers with all of their questions. Many firms have already begun to implement them on their websites and mobile applications.
6) Faster Decisions:
We can make computers make decisions and carry out activities faster than humans by combining AI with other technologies. While a human will consider numerous aspects, both emotionally and practically, before making a decision, an AI-powered machine will focus on what it has been designed to do and will produce results more quickly.
For instance, we've all played Chess games on Windows. Because of the AI in the game, beating the CPU in hard mode is practically impossible. According to the algorithms utilised, it will take the best feasible step in the shortest amount of time.
7) Daily Applications:
Apple's Siri, Microsoft's Cortana, and Google's OK Google are all commonplace in our daily lives, whether it's for finding a location, taking a selfie, making a phone call, or responding to an email.
For example, when we wanted to go somewhere 20 years ago, we used to ask someone who had already been there for instructions. All we have to do now is ask Google, "OK Google, where is Visakhapatnam?" It will show you the location of Visakhapatnam on a Google map as well as the best route between you and Visakhapatnam.
8) New Inventions:
Many technologies in practically every domain are powered by AI, which will aid humans in solving the majority of complicated problems.
For instance, using powerful AI-based technologies, clinicians can now identify breast cancer in women at an early stage.
Q11) Write about agent and environment and intelligent agent?
A11) Agents in Artificial Intelligence
An AI system can be defined as the study of the rational agent and its environment. The agents sense the environment through sensors and act on their environment through actuators. An AI agent can have mental properties such as knowledge, belief, intention, etc.
What is an Agent?
An agent can be anything that perceive its environment through sensors and act upon that environment through actuators. An Agent runs in the cycle of perceiving, thinking, and acting. An agent can be:
● Human-Agent: A human agent has eyes, ears, and other organs which work for sensors and hand, legs, vocal tract work for actuators.
● Robotic Agent: A robotic agent can have cameras, infrared range finder, NLP for sensors and various motors for actuators.
● Software Agent: Software agent can have keystrokes, file contents as sensory input and act on those inputs and display output on the screen.
Hence the world around us is full of agents such as thermostat, cell phone, camera, and even we are also agents.
Before moving forward, we should first know about sensors, effectors, and actuators.
Sensor: Sensor is a device which detects the change in the environment and sends the information to other electronic devices. An agent observes its environment through sensors.
Actuators: Actuators are the component of machines that converts energy into motion. The actuators are only responsible for moving and controlling a system. An actuator can be an electric motor, gears, rails, etc.
Effectors: Effectors are the devices which affect the environment. Effectors can be legs, wheels, arms, fingers, wings, fins, and display screen.
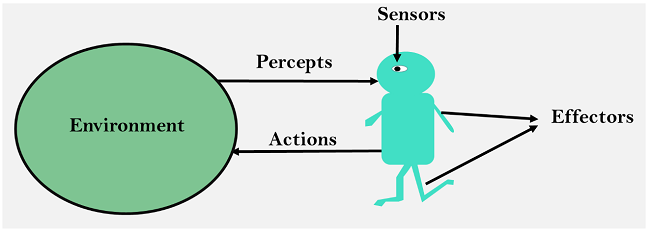
Intelligent Agents:
An intelligent agent is an autonomous entity which act upon an environment using sensors and actuators for achieving goals. An intelligent agent may learn from the environment to achieve their goals. A thermostat is an example of an intelligent agent.
Following are the main four rules for an AI agent:
● Rule 1: An AI agent must have the ability to perceive the environment.
● Rule 2: The observation must be used to make decisions.
● Rule 3: Decision should result in an action.
● Rule 4: The action taken by an AI agent must be a rational action.
Rational Agent:
A rational agent is an agent which has clear preference, models uncertainty, and acts in a way to maximize its performance measure with all possible actions.
A rational agent is said to perform the right things. AI is about creating rational agents to use for game theory and decision theory for various real-world scenarios.
For an AI agent, the rational action is most important because in AI reinforcement learning algorithm, for each best possible action, agent gets the positive reward and for each wrong action, an agent gets a negative reward.
Note: Rational agents in AI are very similar to intelligent agents.
Rationality:
The rationality of an agent is measured by its performance measure. Rationality can be judged on the basis of following points:
● Performance measure which defines the success criterion.
● Agent prior knowledge of its environment.
● Best possible actions that an agent can perform.
● The sequence of percepts.
Note: Rationality differs from Omniscience because an Omniscient agent knows the actual outcome of its action and act accordingly, which is not possible in reality.
Structure of an AI Agent
The task of AI is to design an agent program which implements the agent function. The structure of an intelligent agent is a combination of architecture and agent program. It can be viewed as:
Agent = Architecture + Agent program
Following are the main three terms involved in the structure of an AI agent:
Architecture: Architecture is machinery that an AI agent executes on.
Agent Function: Agent function is used to map a percept to an action.
f:P* → A
Agent program: Agent program is an implementation of agent function. An agent program executes on the physical architecture to produce function f.
PEAS Representation
PEAS is a type of model on which an AI agent works upon. When we define an AI agent or rational agent, then we can group its properties under PEAS representation model. It is made up of four words:
● P: Performance measure
● E: Environment
● A: Actuators
● S: Sensors
Here performance measure is the objective for the success of an agent's behavior.
PEAS for self-driving cars:

Let's suppose a self-driving car then PEAS representation will be:
Performance: Safety, time, legal drive, comfort
Environment: Roads, other vehicles, road signs, pedestrian
Actuators: Steering, accelerator, brake, signal, horn
Sensors: Camera, GPS, speedometer, odometer, accelerometer, sonar.
Example of Agents with their PEAS representation
Agent | Performance measure | Environment | Actuators | Sensors |
1. Medical Diagnose | ● Healthy patient ● Minimized cost | ● Patient ● Hospital ● Staff | ● Tests ● Treatments | Keyboard |
2. Vacuum Cleaner | ● Cleanness ● Efficiency ● Battery life ● Security | ● Room ● Table ● Wood floor ● Carpet ● Various obstacles | ● Wheels ● Brushes ● Vacuum Extractor | ● Camera ● Dirt detection sensor ● Cliff sensor ● Bump Sensor ● Infrared Wall Sensor |
3. Part -picking Robot | ● Percentage of parts in correct bins. | ● Conveyor belt with parts, ● Bins | ● Jointed Arms ● Hand | ● Camera ● Joint angle sensors. |
Q12) What is rationality?
A12) The state of being reasonable, sensible, and having a good sense of judgment is known as rationality.
Rationality is concerned with the actions and consequences that can be foreseen based on the agent's views. Taking actions with the objective of obtaining useful knowledge is a fundamental part of reason.
The rationality of an agent is determined by its performance metric. To determine reasonableness, utilize the following criteria:
● The success criterion is defined by a performance metric.
● The agent has prior knowledge of its surroundings.
● The most effective activities that an agent can take.
● The order in which percepts appear.
Q13) What do you mean by the Nature of Environments?
A13) Some programs operate in an entirely artificial environment, relying solely on keyboard input, databases, computer file systems, and character output on a screen.
On the other hand, some software agents (software robots or softbots) exist in rich, unlimited softbots domains. The simulator's environment is incredibly detailed and complex. The software agent must choose among a vast number of possibilities in real time. In both a real and an artificial setting, a softbot examines a customer's internet interests and offers appealing things to them.
The Turing Test is the most well-known artificial scenario, in which one real and other artificial agents are put to the test on an equal footing. Because a software agent cannot perform as effectively as a human, this is a challenging environment to work in.
Turing test
The Turing Test can be used to determine whether a system's intelligent behavior is successful.
Two humans will participate in the test, as well as a machine that will be checked. One of the two individuals is assigned to the role of tester. They're all in separate rooms. The tester has no way of knowing who is human and who is not. He types the questions and transmits them to both intelligences, who react with typed answers.
The goal of this test is to deceive the tester. The machine is deemed to be intelligent if the tester is unable to distinguish the machine's response from the human response.
Q14) Explain structure of agents?
A14) An intelligent agent (IA) is an entity that makes a decision that enables artificial intelligence to be put into action. It can also be described as a software entity that conducts operations in the place of users or programs after sensing the environment. It uses actuators to initiate action in that environment.
Characteristics of intelligent agents
Intelligent agents have the following distinguishing characteristics:
● They have some level of autonomy that allows them to perform certain tasks on their own.
● They have a learning ability that enables them to learn even as tasks are carried out.
● They can interact with other entities such as agents, humans, and systems.
● New rules can be accommodated by intelligent agents incrementally.
● They exhibit goal-oriented habits.
● They are knowledge-based. They use knowledge regarding communications, processes, and entities.
The structure of intelligent agents
The IA structure consists of three main parts: architecture, agent function, and agent program.
- Architecture: This refers to machinery or devices that consists of actuators and sensors. The intelligent agent executes on this machinery. Examples include a personal computer, a car, or a camera.
- Agent function: This is a function in which actions are mapped from a certain percept sequence. Percept sequence refers to a history of what the intelligent agent has perceived.
- Agent program: This is an implementation or execution of the agent function. The agent function is produced through the agent program’s execution on the physical architecture.
Categories of intelligent agents
There are 5 main categories of intelligent agents. The grouping of these agents is based on their capabilities and level of perceived intelligence.
Simple reflex agents
These agents perform actions using the current percept, rather than the percept history. The condition-action rule is used as the basis for the agent function. In this category, a fully observable environment is ideal for the success of the agent function.
Model-based reflex agents
Unlike simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents consider the percept history in their actions. The agent function can still work well even in an environment that is not fully observable. These agents use an internal model that determines the percept history and effect of actions. They reflect on certain aspects of the present state that have been unobserved.
Goal-based agents
These agents have higher capabilities than model-based reflex agents. Goal-based agents use goal information to describe desirable capabilities. This allows them to choose among various possibilities. These agents select the best action that enhances the attainment of the goal.
Utility-based agents
These agents make choices based on utility. They are more advanced than goal-based agents because of an extra component of utility measurement. Using a utility function, a state is mapped against a certain measure of utility. A rational agent selects the action that optimizes the expected utility of the outcome.
Learning agents
These are agents that have the capability of learning from their previous experience.
Learning agents have the following elements.
● The learning element: This element enables learning agents to learn from previous experiences.
● The critic: It provides feedback on how the agent is doing.
● The performance element: This element decides on the external action that needs to be taken.
● The problem generator: This acts as a feedback agent that performs certain tasks such as making suggestions (new) and keeping history.
Q15) How intelligent agents work?
A15) Intelligent agents work through three main components: sensors, actuators, and effectors. Getting an overview of these components can improve our understanding of how intelligent agents work.
● Sensors: These are devices that detect any changes in the environment. This information is sent to other devices. In artificial intelligence, the environment of the system is observed by intelligent agents through sensors.
● Actuators: These are components through which energy is converted into motion. They perform the role of controlling and moving a system. Examples include rails, motors, and gears.
● Effectors: The environment is affected by effectors. Examples include legs, fingers, wheels, display screen, and arms.