Unit 1
Introduction to Communication Systems
Q1) Draw and explain block diagram of communication system.
A1)
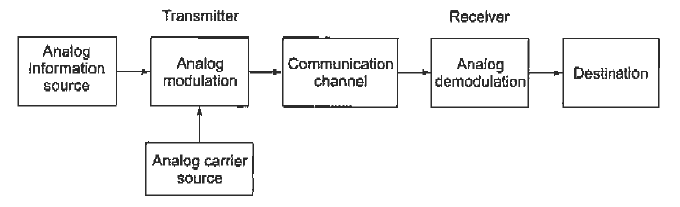
Fig. Block diagram of elements of communication (ref 3)
Information Source
It produces a message that is analog in nature, i.e., the output of the information source is a continuous signal.
Analog carrier source
Sine wave is used as a carrier signal which will help in analog modulation.
Analog modulation
The carrier signal is superimposed with the message signal and then the modulated signal is obtained which is also analog in nature.
Communication channel
The analog modulated signal is transmitted via the communication channel towards the receiver end after addition of the requisite power levels.
Analog demodulation
At the receiver end, the incoming modulated signal is passed through an analog demodulation process which extracts the analog message signal. The analog message is then passed onto the final destination.
Destination
The nature of signal starting from the information source till the final destination is analog.
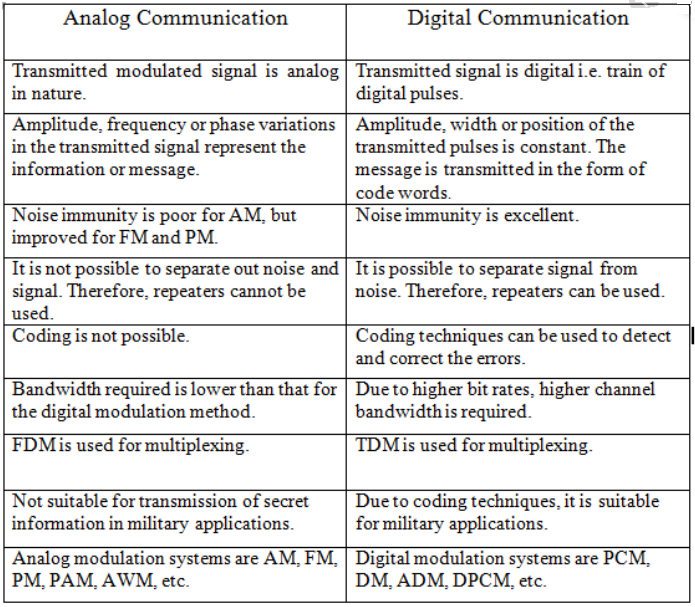
Q2) Compare analog and digital communication.
A2)
Q3) Explain modulation and its types.
A3)
Modulation is the process of having a baseband voice, video or digital signal modify another higher frequency signal called the carrier.
In AM, the baseband signal varies the amplitude of the higher frequency carrier signal.
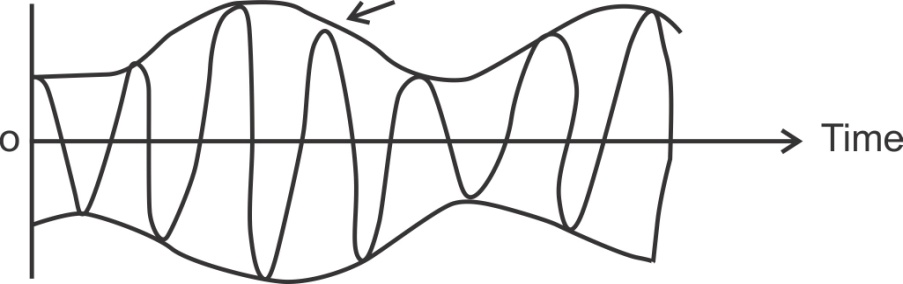
Fig.: AM wave
In FM the baseband signal varies the frequency of the carrier.
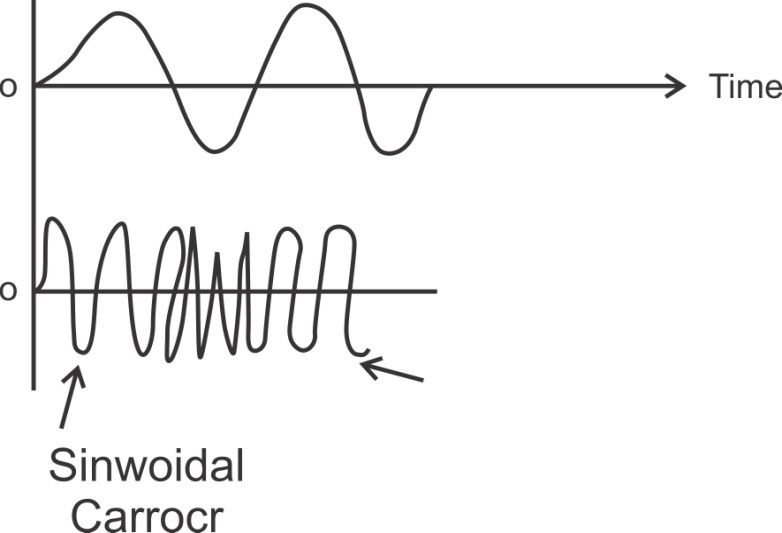
Fig: FM wave
Q4) Why audio signals are not transmitted by electromagnetic waves?
A4)
Audio signals are not transmitted by electromagnetic waves because
1> Antennas would be too long.
2> Simultaneous transmission would interfere.