Unit 5
Timing circuit
Q1) Explain Multivibrators and its types.
A1)
Multivibrators are sequential logic circuits that operate continuously between HIGH and LOW.
There are three types of clock pulse generation circuits:
- Astable – It has NO stable states but switches continuously between two states. This action results in a train of square wave pulses at a fixed frequency.
- Monostable – It has only ONE stable state and is triggered externally with it thus returning back to its first stable state.
- Bistable – It has TWO stable states that produces a single pulse either positive or negative.
Q2) Explain Monostable and Astable multivibrator.
A2)
Monostable Multivibrators or “one-shot” pulse generators are often used to convert short sharp pulses into wider ones for timing applications. They generate a single output pulse when a suitable external trigger signal or pulse T is applied.
Astable Multivibrators are the most commonly used multivibrator circuit. It is a free running oscillator that have no permanent state but are continually changing there output from (LOW) to (HIGH) and then back again. This continuous switching action produces a continuous and stable square wave output that switches abruptly between the two logic levels making it ideal for timing and clock pulse applications.
Q3) Write some features of LM555.
A3)
- It operates from +5 Volts to +18 Volts supply voltage.
- Sinking or sourcing 200 mA of load current.
- The duty cycle is adjustable.
- The maximum power dissipation per package is 600 mW.
Q4) Draw and explain pin diagram of LM555.
A4)
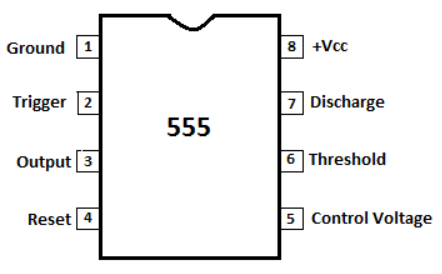
Fig.1:Pin Diag of LM555
- TRIG: It is an input pin. Output of the timer depends upon the amplitude of the external trigger voltage.
- OUT: This output is approximately 1.7 V below +Vcc.
- RESET: The timer does not start until RESET rises above approximately 0.7 volts. Overrides TRIG which overrides threshold.
- THR: The timing (OUT high) interval ends when the voltage at threshold is greater than that at CTRL.
- DIS: In phase with output, Open collector output may discharge a capacitor between intervals.
Q5) Explain working of LM555.
A5)
The 555 timer operates in 3 modes:
- A-stable
- Mono-stable
- Bi-stable modes.
Block Diagram:X
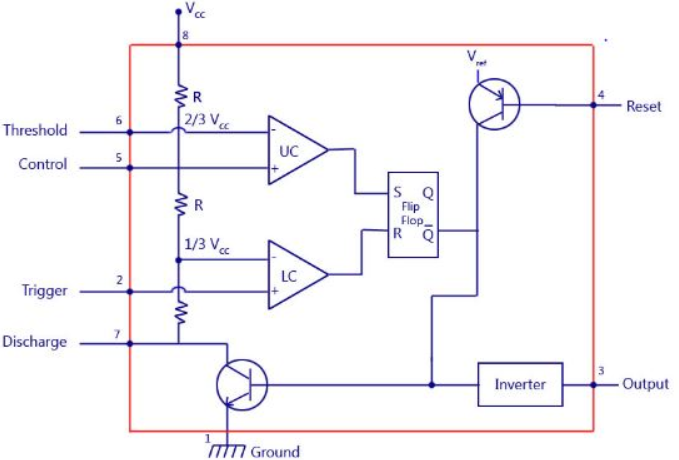
Fig.2:Block Diag of LM555