Unit – 2
System modelling in terms of differential equations
Q1)
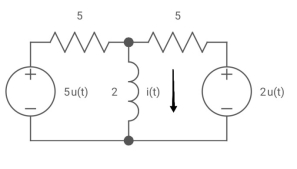
V0 (t) = ? t =o if capacitor is uncharged?
A1)
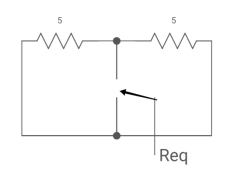
Req = R1R2 /R1+R2
V0(0)=0
V0 (infinity) = VR R2/R1+R2
V0 (t) = V0 (infinity) + [Vo (0) – V0 (infinity)] e-t/c
=VR R2/R1+R2 *[ 1- e+(R1+R2)/R1R2]
Q2)
A2)
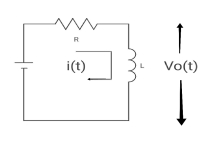
Time constant , c= L/Req = L/R
V(infinity) = 0
V(0) = VR
I(infinity) = VR/R, I (0) =0
By KVL,
VR=i(t) R + L di/dt(t)
On solving
V0(t)= VR e-tR/L
Q3) Find i(t)
For t>0?
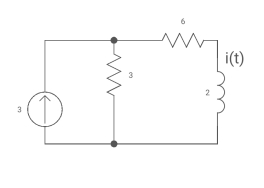
A3)
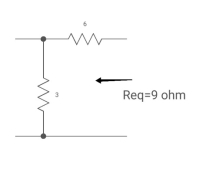
Req = 673
= 9ohm
Diagram
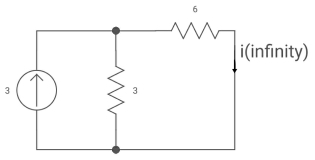
T= L/Req = 2/9 sec
I(0) =0
I(infinity) = 3*3/6+3 = 1A
i(+) = 1 [1-e4.51]
Q4) Capacitor is initially uncharged find
Vc (t); t >0
A4)
Diagram
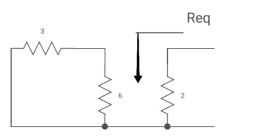
Req = (3116)+2
=2+2 = 4ohm
C= c Req
= 2 sec
Clearly Vc(0) =0
Diagram
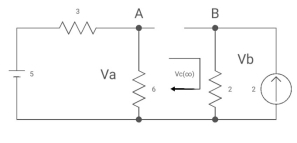
By voltage divides, VA = 5*6/3+B = 30 v/9
Clearly by ohms low
VB = 2*2 = 4v
Apply KVL, VA-Vc-VB =0
Vc(infinity) = 30/9 – 4 = -2/3 V
Vc (t) = -2/3 [1- e0.5t]
CURVE:-
Diagram
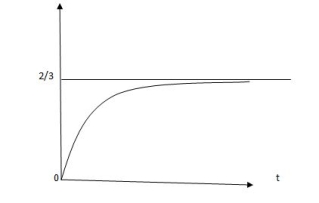
Vc(t) =2/3 [1-e-0.25]
Diagram
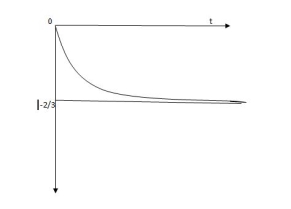
Vc(t) = -2/3 [1-e]
Q5) Find i(t)?
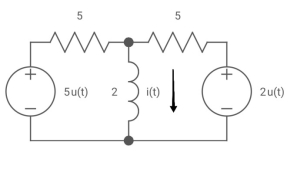
A5)
We know i(t) = I (infinity) +[i(0)- i(infinity0] e-t/c
Diagram
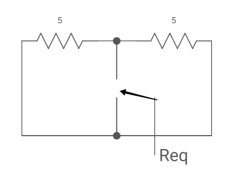
Req = 5*5/5+5 = 5?2 ohm
:. T=L/Req = 4/5 sec
Also, i( 0) =0
i(infinity) = u(t) +2/5 u(t)
:. I(t) = 1.4 [1-e-5/4t)]u(t)
Q6)
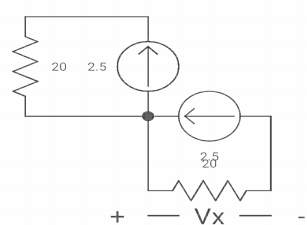
If switch ‘s’ closed at t= 0 find out the voltage across capacitor and current through capacitor at t= 0+?
A6)
At t= 0- switch was open so,
:. There is no potential so Vc(0-) = 0
At t= 0+, Vc (0-) = Vc(0+) = 0
Diagram
Isc = 10/5 = 2 A
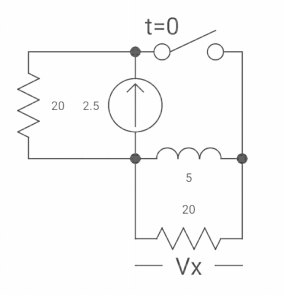
Q7)
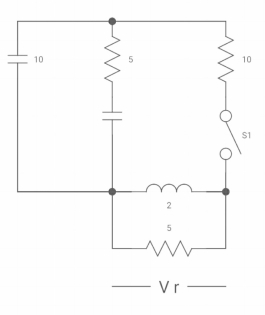
The switch was closed for long time before
Opening at t=0- find VX (0+) ?
(a) 25V (b) 50 V (c)-50V (d) 0V
A7)
At time t=0-
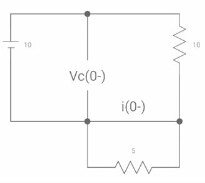
Clearly, il(0-) = 2.5 A
At t= 0+ , as inductor is initially charges
So il (0-) = il(0+)
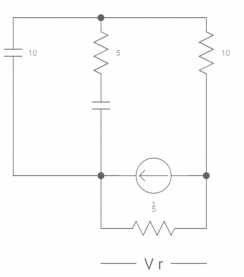
-VX= 20/2.5 20*2.5
VX= -50A
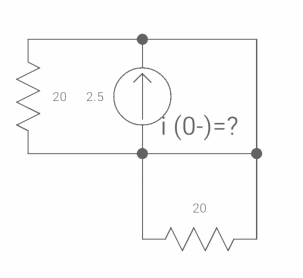
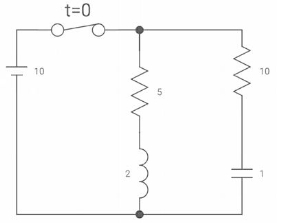
Q8)
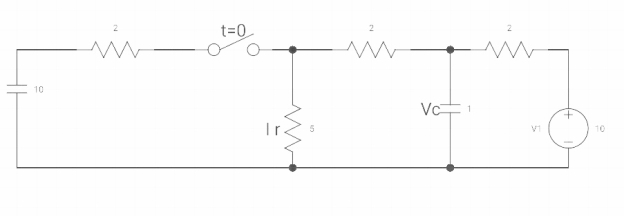
VR(0+)=
Dil/dt(t) = 0+ ?
If switch is opened at t= 0?
A8)
At t=0-
Vc(0-) = 10V
IL(0-) = 10/10 = 1 A
Also, iL(0-) = iL(0+) = 1A
VR(0+) = 5V
Ldi(t)/dt = VL (t)
DiL(t)/dt = VL(t)/L
At t= 0+
d/dt iL (0+) = VL(0+)/L
-VL (0+)-VR =0
VL (0+) = -5V
Dt(t) at t = ot = vl (ot)/L
=-5/2
dil/dt(o+) = 2.5 A/s
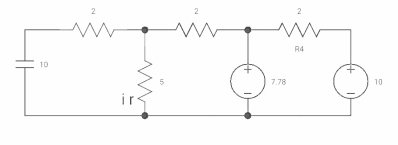
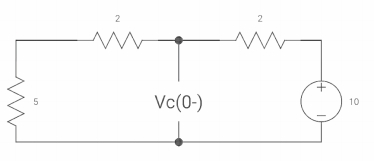
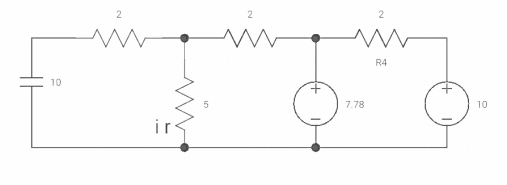
Vc(o+) and iR (o+) it switch ‘s’ is closed at t=0?
At t=0
As capacitor is fully charged so acts as
Vc (0-) = 7*10/7+2 = 70/9v
At t=0+
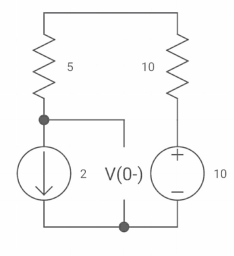
Vc(0+) = Vc (0) = 40/9v
By applying kcl at A,
VA-10/2+ VA/5+VA-7019/2 =0
VA [1/5+1/2+1/2] = 5+35/9
Va [6/5] = 80/9
Va= 400/54v
IR (0+) = Va/5 = 400/54*5 = 80/54 A
Q9)
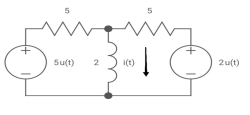
V0 (t) = ? t =o if capacitor is uncharged?
A9)
We know i(t) = i( )+[ i(0)- i(
)+[ i(0)- i( )]
)]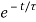
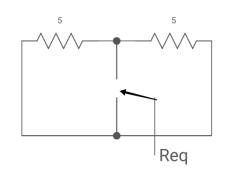
Req = R1R2 /R1+R2=(5x5)/(5+5)=5/2ohm
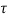 =L/Req=4/5 sec
=L/Req=4/5 sec
i(0)=0
i(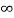 )=u(t)+
)=u(t)+ u(t)=1.4u(t)
u(t)=1.4u(t)
i(t)=1.4[1-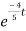 ]u(t)
]u(t)
Q10) Find V0(t)?
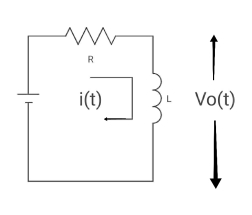
A10)
Time constant 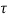 =L/Req = L/R
=L/Req = L/R
V(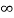 ) = 0, V(0)=VR(supply voltage)
) = 0, V(0)=VR(supply voltage)
i (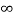 ) = VR/R, i(0) =0
) = VR/R, i(0) =0
By KVL,
VR=i(t) R + L di/dt(t)
On solving
V0(t)= VR e-tR/L
Q11) If V1=6cos2t, find i2 at steady state.
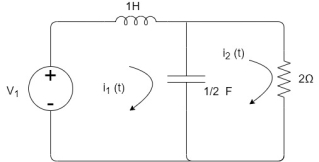
A11)
Apply KVL
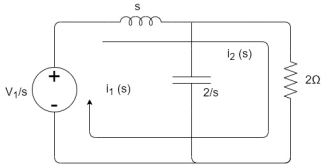
6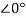 -sI1(s)-2I2(s)=0
-sI1(s)-2I2(s)=0
-2I2(s)-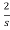 I2(s)+
I2(s)+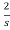 I1(s)=0
I1(s)=0
I2(s)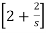 =
= I1(s)
I1(s)
I1(s)=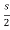 [
[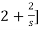 I2(s)
I2(s)
Substituting I1(s) in first equation
6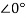 -s
-s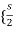 [
[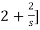 }I2(s)- 2I2(s)=0
}I2(s)- 2I2(s)=0
Solving above equation we get
I2(s)=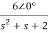
Replace s=jω, s=2j
I2(jω)=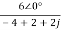 =
=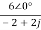 =
=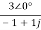
=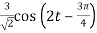
Q12) If V1=2sin2t, Va at steady state will be?
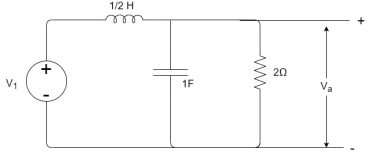
A12)
Zeq=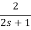
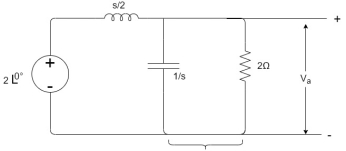
By voltage divider rule Va=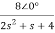
Replace s by jω , s=2j
Va=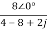 =
=
Va=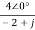 =
=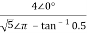
Va=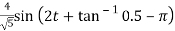
Q13) Write equation for given waveform
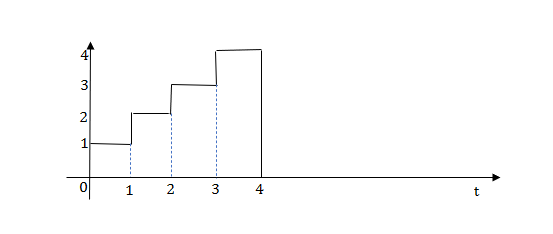
A13)
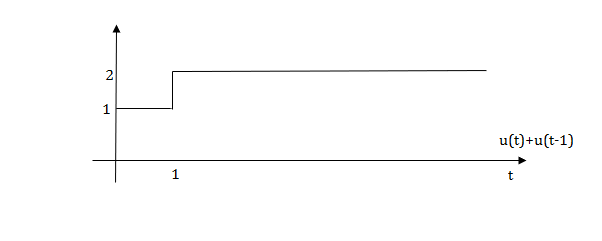
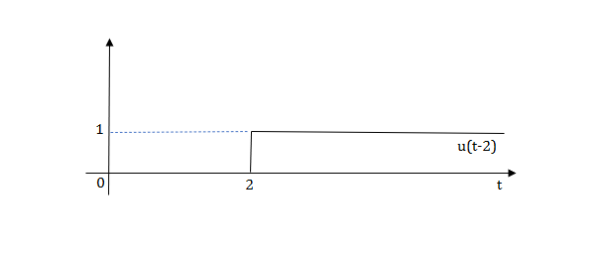
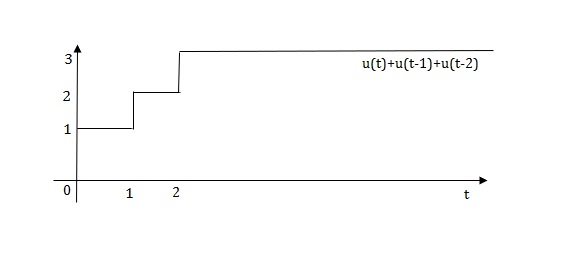
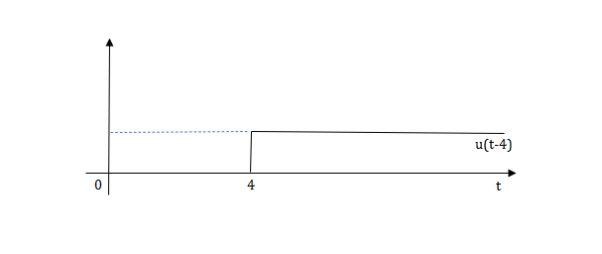
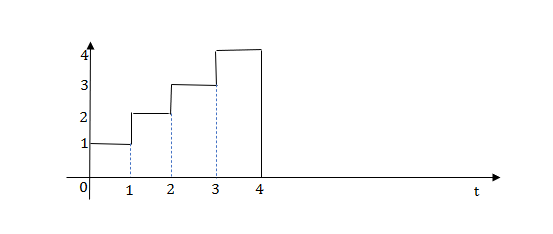
The final equation is=u(t)+u(t-1)+u(t-2)+u(t-3)-4u(t-4)
Q14) Write the equation for the given waveform?
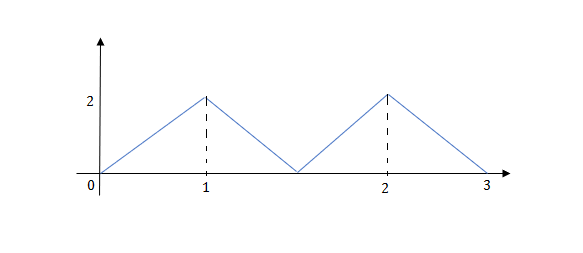
A14)
Calculating slope of above waveform
Slope for (0,0) and (1,2)
a1 slope=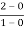 =2
=2
a2 slope=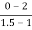 =-4
=-4
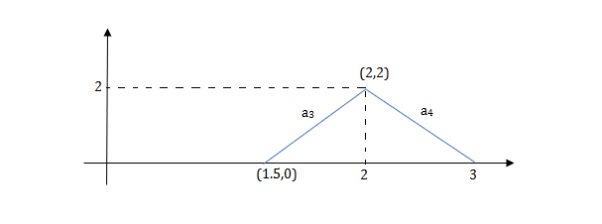
a3 slope =4 and a4= -2

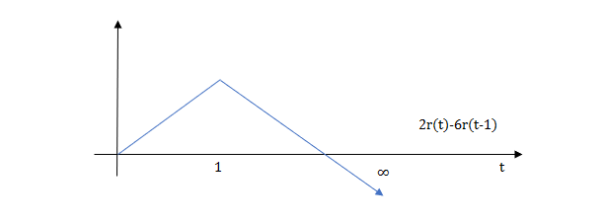
At t=1 slope changes from 2 to -4 so we need to add -6r(t-1) to 2r(t) to get the slope of -4.
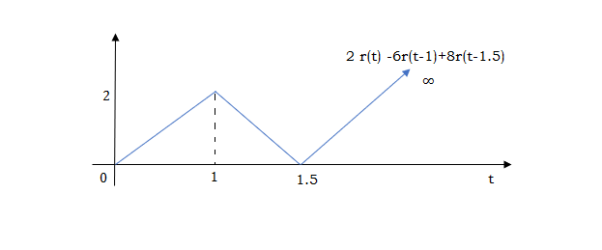
At t=1.5 slope changes from -4 to 4 so adding 8r(t-1.5) to get slope of 4
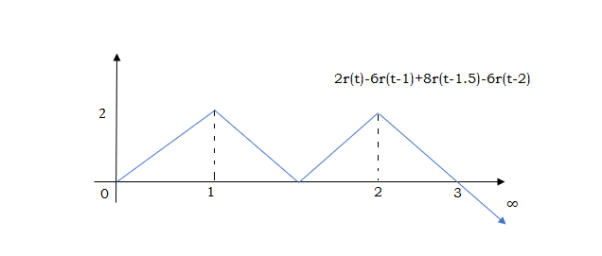
At t=2 slope changes from +4 to -2 so we add -6r(t-2). But we need to stop the waveform at t=3. Hence we have to make slope 0. Which can be done by adding +2r(t-3). Final equation is given as
2r(t)-6r(t-1.5)+8r(t-1.5)-6r(t-2)+2r(t-3)
Q15) Find IL(0)
Diagram
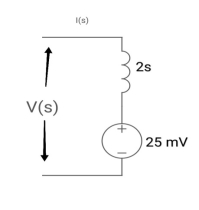
A15)
Comparing with ckf,
L = 2H
LiL (0) = 25 mv
IL (0) = 12.5 m A
Q16) Find voltage across capacitor?
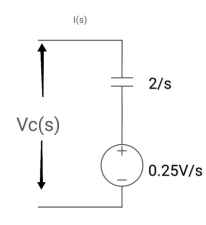
A16)
Comparing with circuit,
1/cs = 2/5
C=1/2f
Vc (0)/s = 0.25v/5
Vc(0)= .25v
Q17) Find Vc(0)?
Diagram
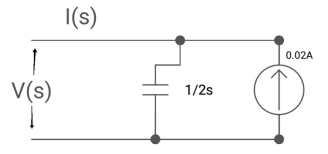
A17)
1/cs = 1/2S
C=2F
CVc (0) = 0.02
Vc(0)= 0.01