Unit - 4
Fuel supply systems in SI and CI engines
Q1) Explain fuel supply system.
A1)
Fuel Supply Systems:
In an engine, the combustion of gas with oxygen with inside the combustion chamber gives the strength important to power the piston. In a SI engine, the liquid gas and the air are usually combined previous to their arrival with inside the combustion chamber i.e., out of doors the engine cylinder. The technique of making ready this combination is known as carburetion. The fundamental gas deliver device in a petroleum engine includes a gas tank, furl lines, gas pump, gas filters, air cleaner, carburetor and inlet manifold. The device answerable for making ready the best combination of air and gas, and directing this combination to every of the cylinders is understood as "Induction System". The Intake manifold is the ducting or piping thru which the gas and air combination travels from the carburetor to the cylinder.
Conventional fuels
In a few instances nuclear substances along with uranium also are included. Some traditional reasserts normally used are fossil fuels, nuclear power, hydropower, and geothermal strength.
Fossil Fuels:
Clean coal technology mean tons more processing to lessen very last emissions.
Q2) Explain various terms used in fuel supply system
A2)
Hydropower:
The large hydropower dams are in place. Some need them removed, claiming that the power may be offset with the aid of using advanced performance and conservation. Smaller dams are being removed, but they will be mounted in different locations.
Nuclear:
Nuclear electricity has a social problem, and best now are new flowers being considered.
Geothermal:
Geothermal strength is viable in non-geyser regions wherein air con and heating can employ the floor warmth flux
Alternative fuels
Alternative fuels, called non-traditional or superior fuels, are any substances or materials that may be used as fuels, apart from traditional fuels.
Conventional fuels include:
Fossil fuels (petroleum (oil), coal, and herbal gas), in addition to nuclear substances which includes uranium and thorium, in addition to synthetic radioisotope fuels which can be made in nuclear reactors.
Bio-fuel:
Bio-fuels also are taken into consideration a renewable source. Although renewable strength is used basically to generate electricity, it's far frequently assumed that a few shape of renewable strength or a percent is used to create opportunity fuels. Biomass: Biomass with inside the strength manufacturing enterprise is residing and currently useless organic cloth which may be used as gasoline or for business manufacturing.
Q3) Explain algae based fuels, alcohol fuels and ammonia?
A3)
Algae-based fuels:
Algae-primarily based totally bio-fuels had been promoted with inside the media as a ability panacea to crude oil-primarily based totally transportation problems. Algae may want to yield greater than 2000 gallons of gasoline in line with acre in line with yr of production. Algae primarily based totally fuels are being efficiently examined via way of means of the U.S. Navy Algae-primarily based totally plastics display ability to lessen waste and the fee in line with pound of algae plastic is anticipated to be less expensive than conventional plastic prices.
Alcohol fuels:
These alcohols may be utilized in inner combustion engines as opportunity fuels. Butane has every other advantage: it's far the best alcohol-primarily based totally motor gas that may be transported easily via way of means of current petroleum-product pipeline networks, in place of best via way of means of tanker vans and railroad cars
Ammonia:
Ammonia (NH3) can be used as fuel. Benefits of ammonia include no need for oil, zero emissions, low cost, and distributed production reducing transport and related pollution
Carbon neutral fuel:
Carbon impartial gasoline is artificial gasoline—including methane, gasoline, diesel gasoline or jet gasoline made out of renewable or nuclear electricity used to hydrogenate waste carbon dioxide recycled from energy plant flue exhaust fuel line or derived from carbonic acid in seawater.
Q4) Explain fuel supply system in CI engine.
A4)
For the supply of fuel from fuel tank to engine cylinder following fuel feed systems are used:
- Gravity system
- Air pressure system
- Vacuum system (suction and gravity system)
- Pump feed system
- Fuel injection system
Gravity fuel feed system:
In this machine, the gas tank is set up at the very best factor of the SI engine. This machine is pretty easy and reasonably-priced because the gas drops into the go with the flow Chamber of the carburetor beneathneath Gravity. It's miles utilized in a small engine having low gas intake as enough head isn't evolved for big engine.
Air pressure feed system:
In this system, an hermetic gasoline tank is used and is positioned below the seat or close to the engine. The hand operated a pump or automatically operated pump elements the high-stress air to the gasoline tank for deliver the gasoline to the carburetor.
Vacuum feed system (Suction and Gravity system:
In this system, gasoline from the gasoline tank that's positioned close to the engine is sucked through suction from the induction manifold. Through gravity, the gasoline is provided to the waft of the carburetor.
Pump feed system:
In this system, a metallic pipe incorporates petrol to the gas pump which Pumps it into the glide Chamber of the carburetor thru the pipe. Right here we use a mechanical or electric or a diaphragm pump resources the gas from the gas tank is located at any appropriate area and is vented to the atmosphere.
This system is used in most vehicles in the present days.
Fuel injection system:
The petrol injection machine now comes to fashionable vehicles. The gasoline is atomized with the aid of an air injector nozzle then added into an air stream. There can be separate gasoline injectors are used for separate cylinder or one unmarried gasoline injector is used.
Q5) Explain fuel supply system in SI engine.
A5)
There are basically two types of injection systems: Air injection system and solid injection system.
1. Air Injection System:
In this gadget, gasoline is pressured into the cylinder with the aid of compressed air. This gadget is little used nowadays, as it calls for a cumbersome multi-degree air compressor. This reasons an growth in engine weight and decreases the brake energy output further. One gain this is claimed for the air injection gadget is ideal blending of gasoline with the air ensuing in better imply powerful pressure.
Another benefit is its cap potential to make use of fuels of excessive viscosity which might be much less high-priced than the ones utilized by the engines with strong injection systems. These blessings are off-set via way of means of the requirement of a multistage compressor thereby making the air-injection gadget obsolete.
2. Solid Injection System:
In this system the liquid fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber without the aid of compressed air. Hence, it is also called airless mechanical injection or solid injection system.
It can be classified into four types.
- Individual pump and nozzle system
- Unit injector system
- Common rail system
- Distributor system
Q6) Explain individual pump and nozzle system and unit injector system?
A6)
Individual Pump and Nozzle System:
In this system, every cylinder is supplied with one pump and one injector. A separate metering and compression pump is supplied for every cylinder. The pump can be located near the cylinder. The excessive stress pump plunger is actuated through a cam, and produces the gasoline stress important to open the injector valve at the perfect time. The quantity of gasoline injected relies upon at the powerful stroke of the plunger.
Unit Injector System:
A separate metering and compression pump is provided for each cylinder. The pump may be placed close to the cylinder. The immoderate strain pump plunger is actuated via a cam, and produces the gas strain crucial to open the injector valve at the best time. The amount of gas injected is based upon on the effective stroke of the plunger.
Common Rail System:
A robotically operated (via a push rod and rocker arm) valve lets in the gas to go into the right cylinder thru the nozzle.
Distributor System:
In this device the pump which pressurizes the gasoline additionally meters and instances it. The gasoline pump after metering the specified quantity of gasoline is furnished to a rotating distributor at the precise time for deliver to every cylinder. The wide variety of injection strokes consistent with cycle for the pump is same to the wide variety of cylinders. Since there may be one metering detail in every pump, a uniform distribution is routinely ensured. Not simplest that, the fee of the gasoline-injection device additionally reduces.
Q7) What is carburetor?
A7)
The carburetor works on Bernoulli's principle: the quicker air moves, the decrease its static strain, and the better its dynamic strain. Instead, it actuates carburetor mechanisms which meter the float of air being pulled into the engine. When carburetors are carried out in plane with piston engines, particular designs and abilties are had to save you fuel line hunger in the course of inverted flight.he carburetor works on Bernoulli's principle: the quicker air moves, the decrease its static strain, and better the dynamic strain is.Instead, it actuates carburetor mechanisms that meter the float of air being carried into the engine. The tempo of this float, and consequently its (static) strain, determines the quantity of fuel line drawn into the airstream.
When carburetors are utilized in plane with piston engines, unique designs and functions are had to save you gas hunger for the duration of inverted flight. Later engines used an early shape of gas injection called a strain carburetor.
Most manufacturing carbureted engines, in place of gas-injected, have a unmarried carburetor and an identical consumption manifold that divides and transports the air/gas aggregate to the consumption valves, eleven though a few engines (like motorbike engines) use more than one carburetors on break up heads.
Older engines used updraft carburetors, in which the air enters from underneath the carburetor and exits thru the top.
This had the gain of by no means flooding the engine, as any liquid gas droplets might fall out of the carburetor as opposed to into the consumption manifold; it additionally lent itself to apply of an oil tubtub air cleaner, in which a pool of oil underneath an detail underneath the carburetor is drawn up into the mesh and the air is drawn thru the oil-included mesh; this turned into an powerful gadget in a time whilst paper air filters did now no longer exist. Beginning with inside the past due 1930s, downdraft carburetors have been the maximum famous kind for automobile use with inside the United States. In Europe, the sidedraft carburetor changed downdraft as unfastened area with inside the engine bay reduced and the usage of the SU-kind carburetor (and comparable devices from different manufacturers) increased. Some small propeller-pushed plane engines nonetheless use the updraft carburetor design.
Q8) Explain the types of carburetors.
A8)
Types of carburetors
There are 3 popular styles of carburetors relying at the route of float of air. Hence, it need to be designed for particularly small blending tube and throat in order that even at low engine speeds the air speed is enough to boost and bring the gas debris along. Otherwise, the gas droplets have a tendency to split out supplying simplest a lean combination to the engine. On the opposite hand, the integration tube is finite and small then it can't deliver combination to the engine at a sufficiently speedy charge at excessive speeds.
It is positioned at a stage better than the inlet manifold and wherein the air and combination normally comply with a downward course. Hence, the integration tube and throat may be made huge which makes excessive engine speeds and excessive unique outputs possible.
Constant Choke Carburetor:
In the regular choke carburetor, the air and gas glide regions are continually maintained to be regular. But the stress distinction or depression, which reasons the glide of gas and air, is being various as in line with the call for at the engine.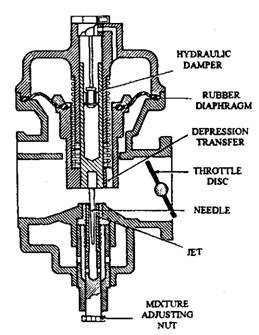
Fig: Constant Choke Carburetor
Constant Vacuum Carburetor:
In the regular vacuum carburetor, (from time to time referred to as variable choke carburetor) air and gas waft regions are being various as in keeping with the call for at the engine, at the same time as the vacuum is maintained to be usually same.
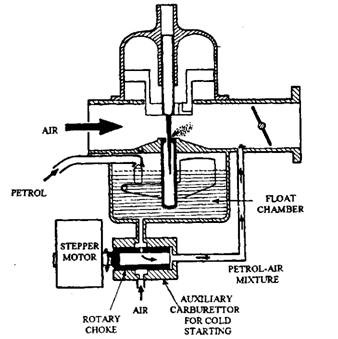
Fig: Constant vacuum carburetor
Multiple Venturi Carburetor:
Multiple venture gadget makes use of double or triple venturi. The raise venturi is placed concentrically in the fundamental venturi. The discharge fringe of the raise venturi is placed on the throat of the primary venturi. The raise venturi is placed upstream of the throat of the bigger fundamental venturi. Only a fragment of the whole air flows aleven though the raise venturi. Now the strain on the raise venturi go out equals the strain at the primary venturi throat. The gasoline nozzle is placed on the throat of the raise venturi.
Q9) Explain CD and CC carburetors in detail.
A9)
C.D. & C.C. Carburetors
Carter Carburetor:
This carburetor is an American make and utilized in jeep. It is a down draft kind and has 3 venturi (triple venturi diffusing sort of choke). The small venturi is saved above the drift chamber level, different beneath the petrol level, one beneath different.
The carburetor consists of following circuits.
1. Float Chamber Circuit.
2. Starting Circuit.
3. Idle and Low Speed Circuit.
4. Part and Full Throttle Circuit
5. Acceleration Circuit.
1. Float Chamber Circuit:
It includes a traditional flow and a flow chamber. Fuel enters the flow chamber from predominant supply. A needle valve keeps gas stage with inside the flow chamber. When the gas stage falls, the needle valve opens the inlet to confess extra gas.
2. Starting Circuit:
When the engine is completely choked (choke valve is closed), entire of engine suction is carried out at the principle nozzle, which then supplies fuel. As the air go with the drift is pretty small, the combination furnished may be very rich. Once the engine starts, the spring managed choke valve opens to offer accurate quantity of air for the duration of warming up period.
3. Idle and Low Speed Circuits:
In this carburetor separate idling passage is supplied with low pace port and idle port. For Idling wealthy combination is needed in small amount and throttle valve is sort of closed. The complete engine suction is now implemented on the idle port via which the air and gas are drawn for this reason offers wealthy combination. In low pace operation the throttle valve is opened further. The primary nozzle additionally begins offevolved providing the gas. In this degree gas is brought each through primary venturi and occasional pace port via idle passage.
4. Part and Full Throttle Circuit:
In component throttling, gas is added via way of means of the primary nozzle only. During complete throttling, most air is passing thru the venture.This is acquired via way of means of mechanical metering approach which makes use of a metering rod having some of steps of diameter sizes at its bottom.
5. Acceleration Circuit:
When accelerator pedal is pressed, pump actuates giving a further spurt of gasoline for acceleration. When the pedal is launched the pump piston actions up there with the aid of using sucking gasoline from waft chamber for subsequent operation.
Q10) What is fuel injection?
A10)
Port Fuel Injection:
Port Fuel injection is whilst gasoline (both fuel or diesel fuels) is injected previous to the valve and cylinder, wherein the combustion takes place.The consumption valve may have a gasoline injection machine that sprays gasoline into the air entering the engine. From there the spark plugs ignite the pressurized slurry of air and gasoline, pushing the cylinder head down and spinning the crankshaft. Now, that is going on at every of the cylinders, so when you have a V6 engine with port injection, and it takes place so fast which you won’t even word the cycle besides with the aid of using noise. With port gasoline injection, the cleansing impact of the consumption manifold ports and valves promotes better exhaust fuel line recirculation rates. Improved noise traits at low speeds. Increased limp-domestic capability. Port injection sprays gasoline into the consumption ports, wherein it mixes with the incoming air. When the consumption valve opens, the gasoline combination is pulled into the engine cylinder. With direct injection, the injectors are with inside the cylinder head and spray gasoline without delay into the combustion chamber, blending with the air charge.
Q11) Explain direct injection in detail.
A11)
Direct Injection
Firstly, Diesel Direct Injection (DI) is a fundamental sort of gasoline injection device which many in advance technology diesel engines used. The easy DI diesel engines inject the gasoline into the combustion chamber above the piston immediately. The compression of air with inside the combustion chamber increases its temperature above 400oC. Then, it ignites the diesel-gasoline injected into the combustion chamber. Hence, the diesel engines also are regarded as ‘Compression Ignition’ engines. Instead of getting the gasoline jumbled together with the air previous to the valve, direct injection places the slurry of gasoline immediately into the combustion chamber. This changed into a extensive development at the carburetor device and boasts greater electricity thru the device while not having an excessive amount of gasoline be utilized. While older gasoline injection structures may be automatically initiated in cars made with inside the 1900s, maximum injection structures at the moment are electronically managed thru an engine’s ECU (Electronic Control Unit) and feature greater green capabilities. Most structures now are closed loop (higher air/gasoline mixtures) structures with an Oxygen Sensor relaying records to an ECU which controls the real blend of air to gasoline. Most vehicles constructed for the reason that Nineteen Nineties have direct injection engines.
The fuel system of Direct Injection consists of following parts:
- Fuel Injection Pump (FIP)
- Injectors
- High-Pressure Lines
- Fuel feed pump
- Fuel Filter
- Governor
Advantages of conventional Direct Injection:
- Higher low-end torque
- Sturdiness
- Lower maintenance
- Longer engine life
Disadvantages of conventional Direct Injection:
- Higher NVH (Noise, Vibrations & Harshness) levels
- Sluggish in operation
- Lower engine speeds & BHP
- Heavier engine components
Q12) What is common rail injection?
A12)
A now no longer unusual place rail is one of the most crucial components in a diesel and gasoline direct injection tool. The important difference amongst an instantaneous and a favored injection is the delivery of fuel line and the way how this one mixes with incoming air. The now no longer unusual place rail is an prolonged metallic cylinder. Common rail engines require a totally short to no heating-up time, depending on the ambient temperature, and convey lower engine noise and emissions than older systems.
Diesel engines have historically used various styles of fuel line injection. Two now no longer unusual place kinds encompass the unit-injection tool and the distributor/inline-pump systems.
They are cam driven, and injection strain is proportional to engine velocity. This normally manner that the very best injection strain can best be done at the very best engine velocity and the most viable injection strain decreases as engine velocity decreases.
With unit or distributor structures, the injection strain is tied to the immediately strain of a unmarried pumping occasion without a accumulator, accordingly the connection is greater outstanding and troublesome.
They are confined with inside the wide variety and timing of injection activities that may be commanded at some stage in a unmarried combustion occasion. While more than one injection activities are viable with those older structures, it's miles plenty greater tough and luxurious to achieve.
Q13) Give note on common rail injection?
A13)
• Lower gasoline pump height torque necessities.
• As excessive velocity direct injection (HSDI) engines developed, greater of the power to combine the air with gasoline got here from the gasoline spray momentum in preference to the swirl mechanisms hired in older, IDI combustion structures.
• Only excessive strain gasoline injection structures had been capable of offer the combination power and appropriate spray practice wanted for low PM and HC emissions.
• To generate the power required to inject the gasoline in about 1 millisecond, the traditional distributor pump could ought to offer almost 1 kW of hydraulic strength in four (in a 4-cylinder engine) 1 ms bursts in line with pump revolution, accordingly setting extensive stress at the force shaft [Breitbach 2002].
This document was truncated here because it was created in the Evaluation Mode.