Unit 5
Special NDT techniques
Q1) Explain principle Eddy current inspection and its advantages.
A1) It is the technique which uses electromagnetic induction to detect defects in an electrically conductive material. In this technique, a conductive material carrying alternating current is bought in proximity to the test specimen, it generates eddy current.
The principle of eddy current inspection is as mentioned below:
- When magnetic flux through a conductor changes, induced currents are set –up in closed paths on the surface of the conductor.
- These currents are in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic flux and are called eddy currents.
- When an alternating current is passed through a coil, a magnetic field is set up around it.
- The direction of the magnetic field changes with a change in the direction of magnetic field during the cycles of alternating current.
- The induced eddy current produces its own magnetic field in a direction opposite to the inducing primary magnetic field.
- The secondary magnetic field due to the eddy current interacts with primary magnetic field and changes the overall magnetic field and the magnitude of the current following through the coil.
- This means that the impedance if the coil is altered due to the influence of the eddy current.
- During NDT, changes in impedance are displayed either on a meter or on a CRT screen.
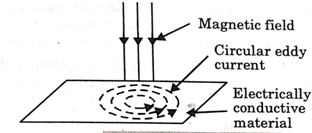
Fig.1: Eddy current
Advantages of ECI:
- Eddy current testing can detect very small cracks in or near the surface of the material, the surfaces need minimal preparation, and physically complex geometries can be investigated.
- It is also useful for making electrical conductivity and coating thickness measurements.
Q2) Explain the different method for ECT.
A2) There are three major methods for eddy current technique.
- The pulsed eddy current technique,
- Transmission method
- Reflection method
- The pulse eddy current technique:
- This technique uses a step function voltage to excite the probe.
- The advantage of using a step function voltage is that it contains a continuum of frequencies.
- Since the depth of penetration is dependent on the frequency of excitation, information from a range of depths can be obtained all at once.
- As a result, the electromagnetic response to several different frequencies can be measured with just a single step.
- To prove the strength and ease interpretation of the signal, a reference signal is usually collected, to which all other signals are compared.
- Flaws, conductivity and dimensional changes produced a change in the signal and difference between the reference signal and the measurement signal that is displayed.
- This technique can be used for the detection and quantification of corrosion and cracking in multilayer aluminium air craft structures.
2. Reflection methods:
- In this methods both primary coil, which excites the electromagnetic field and secondary coil, which detects the discontinuity, are arranged adjacent to each other on either the outside or inside wall of the tube.
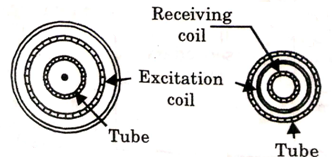
Fig.2: Reflection method
3. Transmission Method:
- When this method is employed, the exciting and receiving coils are placed at opposite walls either on outside or inside diameter
- With this method, the receiving coil is affected only by those electromagnetic fields that have fast through the entire wall of the tube.
Q3) Mention the important equipments used in Eddy Current Testing.
A3) Dedicated instruments:
- It includes crack detectors, thickness gauges and conductivity meters.
- These instruments are designed to perform specific operation only with much efficiency.
- Standard impedance Plane Display Instruments:
It is general purpose instrument which can perform variety of eddy current applications.
It displays the condition of material in a characteristics manner and shows variation in both inductive reactance and resistance during testing.
Working operation of impedance plane display instruments is controlled by following factors.
- Frequency
- Sensitivity
- Dot position (horizontal/Vertical)
- Rotation
- Filters, and
- Gates
C. Multi-frequency Instruments:
- They work on multiple frequency and elimination the drawbacks of the other instruments.
- It can display the activity of test at each frequency separately and can also show mixed output of different signals.
- These instruments provide following advantages:
- Suppression of undesirable variables.
- Optimization of frequency variables.
- Identification of signals by pattern
- Simultaneous operation of both absolute and differential mode.
Q4) Describe Sensitivity of Eddy current testing.
A4) The sensitivity of defect detection depends upon the test material, its structure, the type of type of defect, the orientation of the defect, the depth of the defect, material quality and surface condition that is surface roughness.
The detection sensitivity also depends upon the particular test technique, the type, magnitude and frequency of the excitation, and the type, size and performance of the sensors.
The encircling coils see a large surface area of the material under test and therefore, their sensitivity is intrinsically less than a point probe system.
In addition, the lift –off effect is inescapable and the ‘fit’ of the coils round the rest object is critical.
The greater the mismatch between the diameter of the coil and the diameter of and the diameter of the object, the lower will be sensitivity.
Increasing the amplification of the measurement signal will be partially overcome this problem but such amplification applies also to noise levels and the sensitivity is usually limited by this factor.
Q5) Explain pulsed eddy current testing and eddy current array method for eddy current testing.
A5) 1. Pulsed Eddy Current:
- Conventional ECT uses sinusoidal alternating current of a particular frequency to excite the probe.
- Pulsed eddy current testing uses a step function voltage to excite the probe.
- The advantage of using a step function voltage is that such a voltage contains a range of frequencies.
- As a result, the electromagnetic response to several different frequencies can be measured with just a single step.
- Since depth of penetration depends on the excitation frequency, information from a range depth can be obtained all at once.
- When comparing pulse eddy current testing with the conventional ECT, it must be regarded as a continuous wave method where propagation take place at a single frequency or, more precisely, over a very narrow frequency bandwidth.
- With PEC method, the frequencies are excited over a wide band, the extent of which varies inversely with the pulse length; this allows multi-frequency operation.
- The total amount of energy dissipated within a given period of time is considerably less for pulsed wave than for continuous wave of the same intensity, thus allowing higher input voltages to be applied to the exciting coil for PEC than conventional ECT.
- This way even high temperature inspections are possible.
- Eddy Current Array:
- Eddy Current Array (ECA) and conventional ECT share the same working principles.
- ECA technology provides the ability to electronically drive an array of coils arranged in specific pattern called a topology that generates a sensitivity profile suited to the target defects.
- Data acquisition is achieved by multiplexing the coils in special patterns to avoid mutual inductance between the individual coils.
- The benefits of ECA are:
- Faster inspections.
- Wider coverage
- Less operator dependence- array probes yield more consistent results compared to manual raster scans.
- Better detection capabilities.
- Easier analysis because of simpler scan patterns.
- Improved positioning and sizing because of encoded data.
- Array probes can easily be designed to be flexible or shaped to specifications, making hard-to-reach areas easier to inspect.
- ECA technology provides a remarkably powerful tool and saves significant time during inspections.
- ECA inspection in carbon steel welds is regulated by ASTM standard E3052.
Q6) Explain the scope, applications and limitation of Eddy current technique.
A6) Applications of ECT are:
- Testing of hot wire made of non ferrous materials and ferrous materials above the Curie point.
- Testing of casted, welded, forged, rolled and drawed products is possible.
- Detection of cracks of any discontinuity is possible.
- ECT can perform dimensional measurement of materials.
- Conductivity measurement can be done by using ECT.
- Conductive coating thickness measurement can be done.
- Inspection of railways components can be possible.
(b). Scope of ECT:
- Sensitivity to surface and sub-surface defect
- Portability of test equipment
- It can measure conductivity accurately.
- It can detect through the surface coatings.
- It do not require contact between probe and test specimen.
(c). Limitations of ECT:
- It is very susceptible to magnetic permeability changes.
- It can be used for inspection of conductive materials only.
- It has insensitive to defects a parallel to the surface.
- It requires skilled personnel for performing inspection.
- Distance between the probe and the test specimen is to be maintained.
Q7) Define absolute and differential probe.
A7) 1. Absolute probe:
- It consists of single test coil placed on the test specimen, which is used to generate the eddy current and a secondary coil called as balance load, which balances the bridge circuit.
- When an alternating current is passed through the test coil, a magnetic flux is generated around the coil.
- When coil is brought in proximity to conductive material, eddy currents are generated, which appears as a resistance to the coil.
- This results in change in impedance of the test coil and measuring this change one can use absolute coils for flaw detection, conductivity measurement, lift off measurement and thickness measurement
- Differential probes:
It consists of two active coils coupled to the test specimen with one portion of the test specimen being compared to another portion.
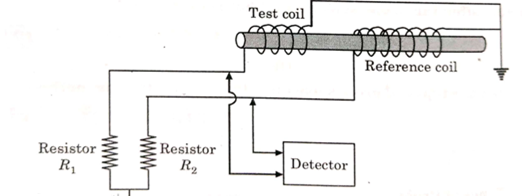
Fig.3: Differential probe
When a flaw less test specimen is tested using this probe, no differential signal is developed between these two active coils.
However when one coil is over flawed part of a test specimen and other one is over flawless part of the same test specimen, a differential signal is produced.
Q8) What is holography? Explain.
A8) The image of three dimensional object is recorded on a two dimensional photographic plate. When a photograph is recorded, the phase distribution at the plane of the photograph is lost because emulsion on the photographic plate is sensitive only to intensity variations. Hence, three dimensional characters are lost.
- A new method of recording optical images is known as holography.
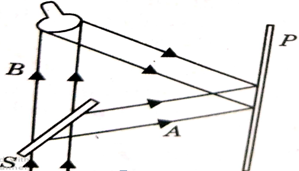
Fig.: Holography
- Holography means complete recording. In 1948, Dennis Galior gave an entirely new idea and proposed a method of recording not only the amplitude but also the phase of the wave.
- During recording process, there is superimposition of two waves, one emanating from the object and another coherent wave called the reference waves.
- The two waves produce interference fringes in the plane of the recording medium. The record is called hologram.
- It memorizes an encoded image of the object and contains much more information than ordinary photograph can record.
- Now the hologram is illuminated by the wave which is much similar to the reference wave known as reconstructive wave. The principle of holography was laid down by Gabor and attained practical importance due to lasers in 1960.
Principle of Holography:
The basic principle of holography can be explained in to two steps:
- Recording of the hologram:
Splitter s is used to divide a laser beam into two beams A and B.
The transmitted beam illuminates the object and the light scattered by the object impinges on a photographic plate. The reflected beam A falls on to the photographic plate. This beam is known as reference beam.
An interference pattern which we get due to superposition of two beams is recorded on the plate.
The developed plate is known as hologram. The hologram contains enough information to produce complete reconstruction of the object.
b. Reconstructing the image:
In the reconstruction process, the hologram is illuminated by a reconstruction wave, which in most cases is identical to the reference wave used for forming hologram.
The reconstruction wave after passing through the hologram produces two images. One of them appears at the original position occupied by the object (virtual image) and the other (real image) which can be photographed directly without using a lens.
The virtual image which is seen by looking through the hologram appears incomplete three dimensional forms. If one moves his eyes, it is possible to see the other sides of the object.
The real image has all the properties as in the case of virtual image and is form between the observer and the plates as shown in figure.
However, the real images reverse foreground and background, so the interest of the observer lies in the virtual image.
Q9) Explain Thermography.
A9) It is the example of infrared imaging science. Thermo graphic cameras usually detect radiation in the long infrared range of electromagnetic spectrum.
An infrared camera or monitor is used to observe the actual temperature or the variation over an area, of the surface of a plant item. Variations in heat transfers through the walls may be attributable to wall thinning or the build of a scale. It may indicate the presence of wet insulation and the potential conditions for corrosion under insulation (CUI). Alternatively, a heat source can be used to heat the surface and the dispersion of the heat observed.
Unexpected changes in the heat flow can be used to identify defects. For containers containing hot or cold liquid, it is possible to observe the level of liquid in the item non-invasively. The size of defect which can be detected will depend upon the optical parameters of the system and the resolution of the camera.
In accessing the results, the emissivity of any pants or coatings on the component need to be considered. Reflections of sunlight can also distort readings. The technique non-contacting and only line of sight to the surface under examination is required. It is quick and easy to apply but can only detect defects and or faults which cause a change in heat flow or the surface temperature of the item.
Q10) What is acoustic emission testing? Explain.
A10) The phenomenon of generating transient elastic waves during the release of energy from localised sources within a solid material is called acoustic emission (AE). Dislocations resulting from plastic deformations cause AE.
The elastic waves generated in this manner propagate in all directions and reach the surface of the material, where they are detected with the help of piezoelectric transducers.
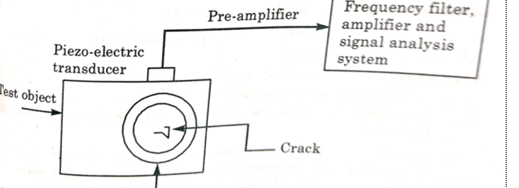
Fig.5: Acoustic emission testing
The piezoelectric transducer is directly attached to the test object with a coupling medium and secured with tape. The voltage output from the transducer is fed into the pre-amplifier, which is placed closed to the transducers.
The pre-amplifier eliminates mechanical, acoustical and background noise. However, it also generates electrical noise, which limits the sensitivity of the system.
The pre-amplifier signal is passed through a variable band pass filter to the main amplifier connected to a signal analysis system. The signal analysis system produces a signal each time the amplifier voltage signal exceeds a select threshold level.
The following parameters are used to identify AE events:
- Peak amplitude- the peak of the signal
- Arrival time- the time when the peak signal process the threshold signal.
- Duration time- the between the first threshold crossing and the peak amplitude.
- Ring count- the no. Of threshold crossing.