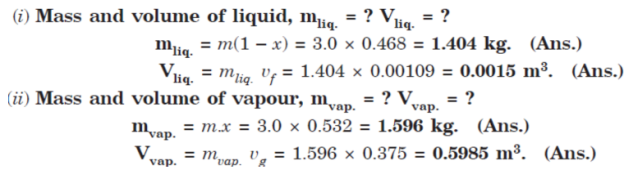Unit 3
Definition
Q1. Explain the various steps and heats involved in formation of steam.
A1. Formation of steam
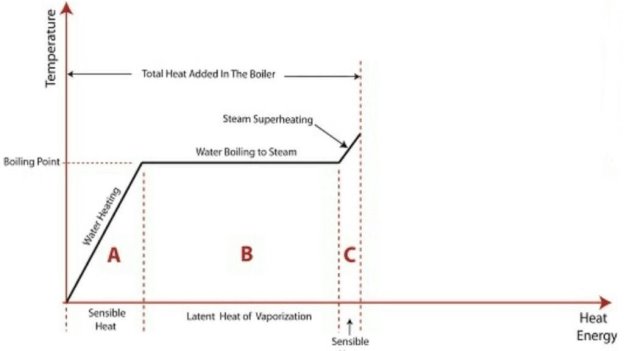
The above diagram shows the phase change occurring when water from and at 0°C is heated till is converted to steam and further to superheat it.
Temperature is plotted as ordinate and Enthalpy as abscissa.
Phase Change
hg = hf + hfg
hsup = hg + Cp (tsup - tsat)
tsup = temperature of superheated steam
tsat = temperature of saturation of steam
Cp = Specific heat of water at constant pressure.
Q2. Explain the critical point of water with the help of T-v diagram.
A2.
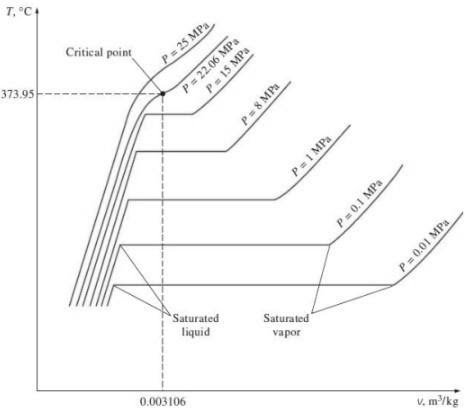
Critical Point
Q3. Explain triple point of water.
A3.
Triple point
Q4. Define dryness fraction.
A4. Dryness fraction is defined ratio of mass of dry steam to total mass of mixture of wet steam.
It is denoted by ‘x’.
It is very important property of steam and needs to be determined before the steam is fed to the boiler.
Q5. A mass of 200 g of saturated liquid water is completely vaporized at a constant pressure of 100 kPa. Determine
(a) the volume change and
(b) the amount of energy transferred to the water.
A5. Find Properties from Steam Table:
Psat = 100 kPa
a) The volume change:
vfg = vf – vg
=1.6941 - 0.001043
= 1.6931 m3/kg
b) the amount of energy transferred to the water.
The amount of energy needed to vaporize a unit mass of a substance at a given pressure is the enthalpy of vaporization at that pressure, which is
hfg= 2257.5 kJ/kg for water at 100 kPa.
Thus, the amount of energy transferred is
mhfg = (0.2 kg) (2257.5 kJ/kg) = 451.5 Kj
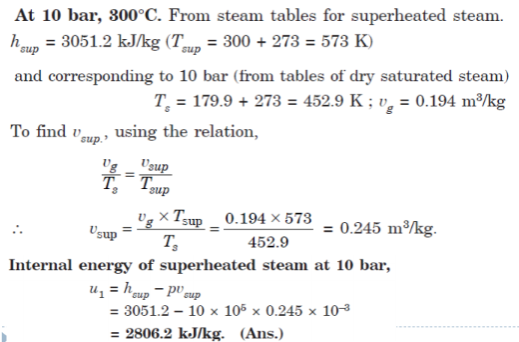
Q6. Calculate the internal energy per kg of superheated steam at a pressure of 10 bar and a temperature of 300°C. Also find the change of internal energy if this steam is expanded to 1.4 bar and dryness fraction 0.8.
A6.

Q7. In a steam power cycle, the steam supply is at 15 bar and dry and saturated. The condenser pressure is 0.4 bar. Calculate the Carnot and Rankine efficiencies of the cycle. Neglect pump work.
A7.


Q8. 1000 kg of steam at a pressure of 16 bar and 0.9 dry is generated by a boiler per hour. The steam passes through a superheater via boiler stop valve where its temperature is raised to 380°C. If the temperature of feed water is 30°C,
Determine:
(i) The total heat supplied to feed water per hour to produce wet steam.
(ii) The total heat absorbed per hour in the superheater.
Take specific heat for superheated steam as 2.2 kJ/kg K.
A8.

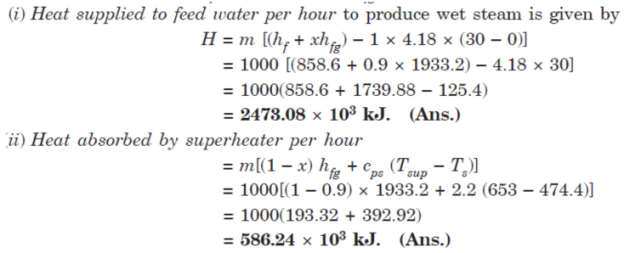
Q9. A vessel having a capacity of 0.05 m3 contains a mixture of saturated water and saturated steam at a temperature of 245°C. The mass of the liquid present is 10 kg.
Find the following:
(i) The pressure,
(ii) The mass,
(iii) The specific volume,
(iv) The specific enthalpy,
(v) The specific entropy, and
(vi) The specific internal energy.
A9.


Q10. A vessel having a volume of 0.6 m3 contains 3.0 kg of liquid water and water vapour mixture in equilibrium at a pressure of 0.5 MPa.
Calculate:
(i) Mass and volume of liquid;
(ii) Mass and volume of vapour.
A10.