EG
UNIT 6DEVELOPMENT OF LATERAL SURFACES 1. A pipe 40 mm diameter and 120 mm long (along the axis) is welded to thevertical side of a tank. Show the development of the pipe, if it makes anangle of 60° with the side to which it is welded, the other end of the pipemaking an angle of 30° with its own axis. Neglect thickness of the pipe. 2. The inside of a hopper of a floor mill is to be lined with tin sheet. The topand bottom of the hopper are regular pentagons with each side equal to450 mm and 300 mm respectively (internally). The height of the hopper is450 mm. Draw the shape to which the tin sheet is to be cut so as to fitin the hopper. Scale, 1:10. 3. A 50 mm cylindrical pipebranches off at 90° from a75 mm cylindrical main pipeas shown in fig.1. Drawthe developments of both thepipes at the joint. Assumesuitable lengths for the main pipeas well as for the branch pipe.
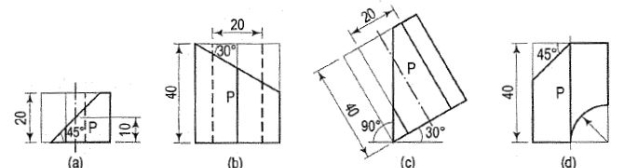
Figure 14. A cone of 90 mm diameter of base and 90 mm height stands on its baseon the ground. A semi-circular hole of 50 mm diameter is cut through thecone. The axis of the hole is horizontal and intersects the axis of the cone.It is 30 mm above the base of the cone. The flat surface of the hole containsthe axis of the cone and is perpendicular to the V.P. Draw three views ofthe cone and also develop the surface of the cone.5. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the part P of each of the solids,the front views of which are shown in fig. 2 and described below.(a) A cube, one vertical face inclined at 30° to the V.P.(b) A pentagonal prism, a side of the base parallel to the V.P.(c) A hexagonal prism, two faces parallel to the V.P.(d) A square prism, length of the side of the base 20 mm and all faces equallyinclined to the V.P.
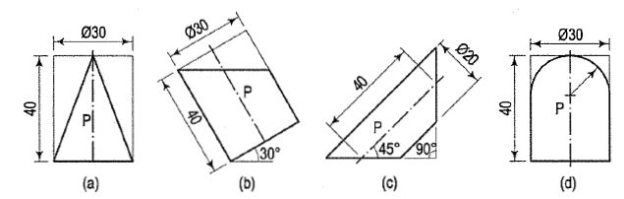
Figure 2 6. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the part P of each of the cylinders,the front views of which are shown in fig. 3.
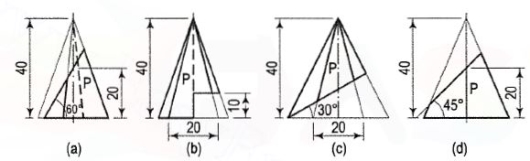
Figure 37. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the part P of each of the pyramids,the front views of which are shown in fig. 4 , and described below.(a) A square pyramid, side of the base 20 mm long and one side of the baseinclined at 30° to the V.P.(b) A pentagonal pyramid, one side of the base parallel to the V.P.© A hexagonal pyramid, two sides of the base parallel to the V.P.(d) A square pyramid, side of the base 20 mm long and all the sides of the baseequally inclined to the V.P.
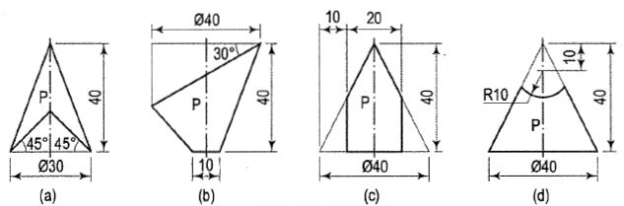
Figure 48. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the part P of each of the cones,front views of which are shown in fig. 5.
Figure 59. A vertical cone, base 100 mm diameter and height 125 mm is penetrated byanother cone, 50 mm diameter and axis 100 mm long. The axis of the penetratingcone is parallel to the H.P. and the V.P., 40 mm above the base and 10 mm fromthe axis of the vertical cone. It comes out equally on both sides of the cone. Drawthe projections showing curves of intersection.10. A cylinder, 50 mm diameter and axis vertical, penetrates a pentagonal pyramidhaving its base on the ground and one side of the base parallel to the V.P. Thediameter of the circumscribing circle of the base of the pyramid is 75 mm andits height is 100 mm. The two axes are 10 mm apart. Draw the projectionsshowing curves of intersection, when the plane containing the two axes is parallelto the V.P. Develop the surface of the pyramid.
|
|
|
|
|
0 matching results found