UNIT 1
Introduction
- What are data structure and its terminology?
Introduction
Data Structure can be defined as the group of data elements which provides an efficient way of storing and organising data in the computer so that it can be used efficiently. Some examples of Data Structures are arrays, Linked List, Stack, Queue, etc. Data Structures are widely used in almost every aspect of Computer Science i.e. Operating System, Compiler Design, Artifical intelligence, Graphics and many more.
Data Structures are the main part of many computer science algorithms as they enable the programmers to handle the data in an efficient way. It plays a vitle role in enhancing the performance of a software or a program as the main function of the software is to store and retrieve the user's data as fast as possible
Basic Terminology
Data structures are the building blocks of any program or the software. Choosing the appropriate data structure for a program is the most difficult task for a programmer. Following terminology is used as far as data structures are concerned
Data: Data can be defined as an elementary value or the collection of values, for example, student's name and its id are the data about the student.
Group Items: Data items which have subordinate data items are called Group item, for example, name of a student can have first name and the last name.
Record: Record can be defined as the collection of various data items, for example, if we talk about the student entity, then its name, address, course and marks can be grouped together to form the record for the student.
File: A File is a collection of various records of one type of entity, for example, if there are 60 employees in the class, then there will be 20 records in the related file where each record contains the data about each employee.
Attribute and Entity: An entity represents the class of certain objects. It contains various attributes. Each attribute represents the particular property of that entity.
Field: Field is a single elementary unit of information representing the attribute of an entity.
Need of Data Structures
As applications are getting complexed and amount of data is increasing day by day, there may arrise the following problems:
Processor speed: To handle very large amout of data, high speed processing is required, but as the data is growing day by day to the billions of files per entity, processor may fail to deal with that much amount of data.
Data Search: Consider an inventory size of 106 items in a store, If our application needs to search for a particular item, it needs to traverse 106 items every time, results in slowing down the search process.
Multiple requests: If thousands of users are searching the data simultaneously on a web server, then there are the chances that a very large server can be failed during that process
In order to solve the above problems, data structures are used. Data is organized to form a data structure in such a way that all items are not required to be searched and required data can be searched instantly.
2. What are the types of linear and nonlinear data structure?
Types of Linear Data Structures are given below:
Arrays: An array is a collection of similar type of data items and each data item is called an element of the array. The data type of the element may be any valid data type like char, int, float or double.
The elements of array share the same variable name but each one carries a different index number known as subscript. The array can be one dimensional, two dimensional or multidimensional.
The individual elements of the array age are:
Age[0], age[1], age[2], age[3],......... Age[98], age[99].
Linked List: Linked list is a linear data structure which is used to maintain a list in the memory. It can be seen as the collection of nodes stored at non-contiguous memory locations. Each node of the list contains a pointer to its adjacent node.
Stack: Stack is a linear list in which insertion and deletions are allowed only at one end, called top.
A stack is an abstract data type (ADT), can be implemented in most of the programming languages. It is named as stack because it behaves like a real-world stack, for example: - piles of plates or deck of cards etc.
Queue: Queue is a linear list in which elements can be inserted only at one end called rear and deleted only at the other end called front.
It is an abstract data structure, similar to stack. Queue is opened at both end therefore it follows First-In-First-Out (FIFO) methodology for storing the data items.
Non Linear Data Structures: This data structure does not form a sequence i.e. each item or element is connected with two or more other items in a non-linear arrangement. The data elements are not arranged in sequential structure.
Types of Non Linear Data Structures are given below:
Trees: Trees are multilevel data structures with a hierarchical relationship among its elements known as nodes. The bottommost nodes in the hierarchy are called leaf node while the topmost node is called root node. Each node contains pointers to point adjacent nodes.
Tree data structure is based on the parent-child relationship among the nodes. Each node in the tree can have more than one child except the leaf nodes whereas each node can have almost one parent except the root node. Trees can be classified into many categories which will be discussed later in this tutorial.
Graphs: Graphs can be defined as the pictorial representation of the set of elements (represented by vertices) connected by the links known as edges. A graph is different from tree in the sense that a graph can have cycle while the tree cannot have the one.
3. Explain Operations on data structure
1) Traversing: Every data structure contains the set of data elements. Traversing the data structure means visiting each element of the data structure in order to perform some specific operation like searching or sorting.
Example: If we need to calculate the average of the marks obtained by a student in 6 different subjects, we need to traverse the complete array of marks and calculate the total sum, and then we will divide that sum by the number of subjects i.e. 6, in order to find the average.
2) Insertion: Insertion can be defined as the process of adding the elements to the data structure at any location.
If the size of data structure is n then we can only insert n-1 data elements into it.
3) Deletion: The process of removing an element from the data structure is called Deletion. We can delete an element from the data structure at any random location.
If we try to delete an element from an empty data structure then underflow occurs.
4) Searching: The process of finding the location of an element within the data structure is called Searching. There are two algorithms to perform searching, Linear Search and Binary Search. We will discuss each one of them later in this tutorial.
5) Sorting: The process of arranging the data structure in a specific order is known as Sorting. There are many algorithms that can be used to perform sorting, for example, insertion sort, selection sort, bubble sort, etc.
6) Merging: When two lists List A and List B of size M and N respectively, of similar type of elements, clubbed or joined to produce the third list, List C of size (M+N), then this process is called merging
4. Explain Data object
Data Model is an abstract model that represents the data objects, data flow between these data objects, and the interrelationship between these data objects. It is a way of storing data on a computer so that it can be used in a more efficient manner for further purposes.
Data model or data structure consists of following fundamental elements:
1. Data object:
The data object is actually a location or region of storage that contains a collection of attributes or groups of values that act as an aspect, characteristic, quality, or descriptor of the object. A vehicle is a data object which can be defined or described with the help of a set of attributes or data.
Different data objects are present which are shown below:
- External entities such as a printer, user, speakers, keyboard, etc.
- Things such as reports, displays, signals.
- Occurrences or events such as alarm, telephone calls.
- Sales databases such as customers, store items, sales.
- Organizational units such as division, departments.
- Places such as manufacturing floor, workshops.
- Structures such as student records, accounts, files, documents.
2. Attributes:
Attributes define the properties of a data object. The attribute is a quality or characteristic that defines a person, group, or data objects. It is actually the properties that define the type of entity. An attribute can have a single or multiple or range of values as per our needs.
There are three types of attributes:
- Naming attributes –
To name an instance of a data object, naming attributes are used. User naming attributes identify user objects such as Login_names and User_Id for some security purpose. For example- Make and model are naming attributes in a vehicle data object. - Descriptive attributes –
These attributes are used to describe the characteristics or features or the relationship of the data object. Sometimes also referred to as relationship attributes. For example- In a vehicle, the color of a data object is a descriptive attribute that describes the features of the object. - Referential attribute –
These are the attributes that are used to formalize binary and associative relationships and in making reference to another instance in another table. For example- The data object is a referential attribute in a vehicle.
3. Relationship:
The relationship represents the connection or relation between different data objects and describes association among entities. Relationships are of three types: one-to-many, many-to-many, and many-to-one.
For example, toy and shopkeeper are two objects that share the following relationship:
- The Shopkeeper order toys.
- The shopkeeper sells toys.
- The shopkeeper shows toys.
- The Shopkeeper stocks toys.
5. What is Data Structure?
The data structure name indicates itself that organizing the data in memory. There are many ways of organizing the data in the memory as we have already seen one of the data structures, i.e., array in C language. Array is a collection of memory elements in which data is stored sequentially, i.e., one after another. In other words, we can say that array stores the elements in a continuous manner. This organization of data is done with the help of an array of data structures. There are also other ways to organize the data in memory. Let's see the different types of data structures.
The data structure is not any programming language like C, C++, java, etc. It is a set of algorithms that we can use in any programming language to structure the data in the memory.
To structure the data in memory, 'n' number of algorithms were proposed, and all these algorithms are known as Abstract data types. These abstract data types are the set of rules.
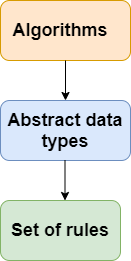
Types of Data Structures
There are two types of data structures:
- Primitive data structure
- Non-primitive data structure
Primitive Data structure
The primitive data structures are primitive data types. The int, char, float, double, and pointer are the primitive data structures that can hold a single value.
Non-Primitive Data structure
The non-primitive data structure is divided into two types:
- Linear data structure
- Non-linear data structure
Linear Data Structure
The arrangement of data in a sequential manner is known as a linear data structure. The data structures used for this purpose are Arrays, Linked list, Stacks, and Queues. In these data structures, one element is connected to only one another element in a linear form.
When one element is connected to the 'n' number of elements known as a non-linear data structure. The best example is trees and graphs. In this case, the elements are arranged in a random manner.
We will discuss the above data structures in brief in the coming topics. Now, we will see the common operations that we can perform on these data structures.
Data structures can also be classified as:
- Static data structure: It is a type of data structure where the size is allocated at the compile time. Therefore, the maximum size is fixed.
- Dynamic data structure: It is a type of data structure where the size is allocated at the run time. Therefore, the maximum size is flexible.
Major Operations
The major or the common operations that can be performed on the data structures are:
- Searching: We can search for any element in a data structure.
- Sorting: We can sort the elements of a data structure either in an ascending or descending order.
- Insertion: We can also insert the new element in a data structure.
- Updation: We can also update the element, i.e., we can replace the element with another element.
- Deletion: We can also perform the delete operation to remove the element from the data structure.
6. Which Data Structure?
A data structure is a way of organizing the data so that it can be used efficiently. Here, we have used the word efficiently, which in terms of both the space and time. For example, a stack is an ADT (Abstract data type) which uses either arrays or linked list data structure for the implementation. Therefore, we conclude that we require some data structure to implement a particular ADT.
An ADT tells what is to be done and data structure tells how it is to be done. In other words, we can say that ADT gives us the blueprint while data structure provides the implementation part. Now the question arises: how can one get to know which data structure to be used for a particular ADT?.
As the different data structures can be implemented in a particular ADT, but the different implementations are compared for time and space. For example, the Stack ADT can be implemented by both Arrays and linked list. Suppose the array is providing time efficiency while the linked list is providing space efficiency, so the one which is the best suited for the current user's requirements will be selected.
Advantages of Data structures
The following are the advantages of a data structure:
- Efficiency: If the choice of a data structure for implementing a particular ADT is proper, it makes the program very efficient in terms of time and space.
- Reusability: he data structures provide reusability means that multiple client programs can use the data structure.
- Abstraction: The data structure specified by an ADT also provides the level of abstraction. The client cannot see the internal working of the data structure, so it does not have to worry about the implementation part. The client can only see the interface.
7. Explain Primitive and Non-primitive data structures
Primitive Data Structures
Primitive Data Structures are the basic data structures that directly operate upon the machine instructions.
hey have different representations on different computers.
Integers, Floating point numbers, Character constants, String constants and Pointers come under this category.
Non-primitive Data Structures
Non-primitive data structures are more complicated data structures and are derived from primitive data structures.
They emphasize on grouping same or different data items with relationship between each data item.
Arrays, Lists and Files come under this category.
8. Differences between Linear Data Structures and Non-linear Data Structures.
Sr. No. | Key | Linear Data Structures | Non-linear Data Structures | |
1 | Data Element Arrangement | In linear data structure, data elements are sequentially connected and each element is traversable through a single run. | In non-linear data structure, data elements are hierarchically connected and are present at various levels. | |
2 | Levels | In linear data structure, all data elements are present at a single level. | In non-linear data structure, data elements are present at multiple levels. |
|
3 | Implementation complexity | Linear data structures are easier to implement. | Non-linear data structures are difficult to understand and implement as compared to linear data structures. |
|
4 | Traversal | Linear data structures can be traversed completely in a single run. | Non-linear data structures are not easy to traverse and needs multiple runs to be traversed completely. |
|
5 | Memory utilization | Linear data structures are not very memory friendly and are not utilizing memory efficiently. | Non-linear data structures uses memory very efficiently. |
|
6 | Time Complexity | Time complexity of linear data structure often increases with increase in size. | Time complexity of non-linear data structure often remain with increase in size. |
|
7 | Examples | Array, List, Queue, Stack. | Graph, Map, Tree. |
|
9. What is a Static Data structure?
In Static data structure the size of the structure is fixed. The content of the data structure can be modified but without changing the memory space allocated to it.
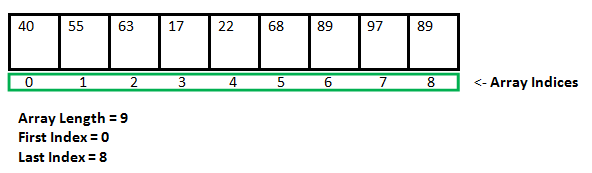
Example of Static Data Structures: Array
10. What is Dynamic Data Structure?
In Dynamic data structure the size of the structure in not fixed and can be modified during the operations performed on it. Dynamic data structures are designed to facilitate change of data structures in the run time.
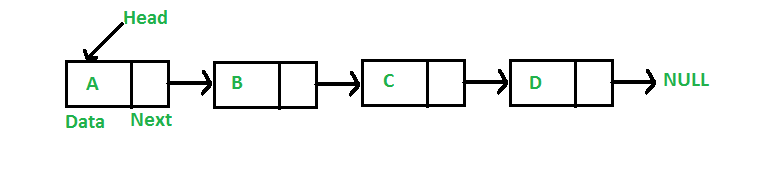
Example of Dynamic Data Structures: Linked List
Static Data Structure vs Dynamic Data Structure
Static Data structure has fixed memory size whereas in Dynamic Data Structure, the size can be randomly updated during run time which may be considered efficient with respect to memory complexity of the code. Static Data Structure provides more easier access to elements with respect to dynamic data structure. Unlike static data structures, dynamic data structures are flexible.