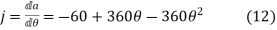Unit IV
Cam and Follower
Q1) Classify cams in detail.
Ans.
Cams are classified according to
2. Radial or disc cams
3. Spiral cams

4. Cylindrical cams

5. Conjugate cams:-

6. Globoid cams
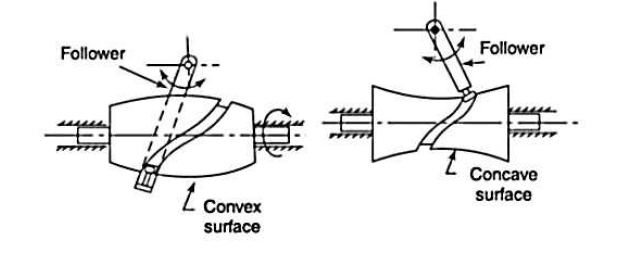
7. Spherical cams

b. According to follower movement
The motions of the followers are distinguished from each other by the dwells they have.
2. Dwell rise return dwell (D-R-R-D)
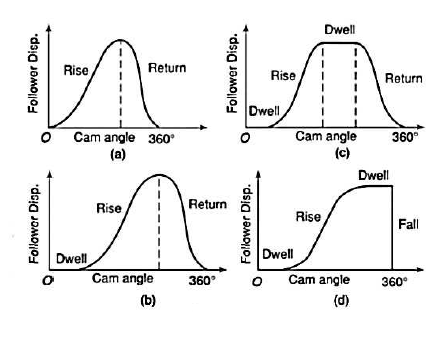
3. Dwell rise dwell return dwell (D-R-D-R-D)
Q2) Classify follower details.
Ans.
The followers may be classified as discussed below:
2. Roller follower:
3. Flat-faced or mushroom follower:-
4. Spherical faced follower:-

b. According to the motion of the follower the followers, according to its motion are of the following two types
2. Oscillating or rotating follower
c. According to the path of motion of the follower. The followers, according to its path of motion are of the following two types
2. Offset follower:-
Q3) Explain the procedure of drawing velocity & acceleration diagrams for uniform velocity motion.
Ans.
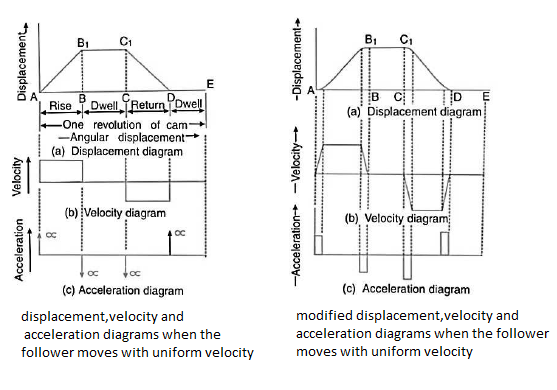
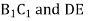
Q4) Explain the procedure of drawing velocity & acceleration diagrams for SHM motion.
Ans.
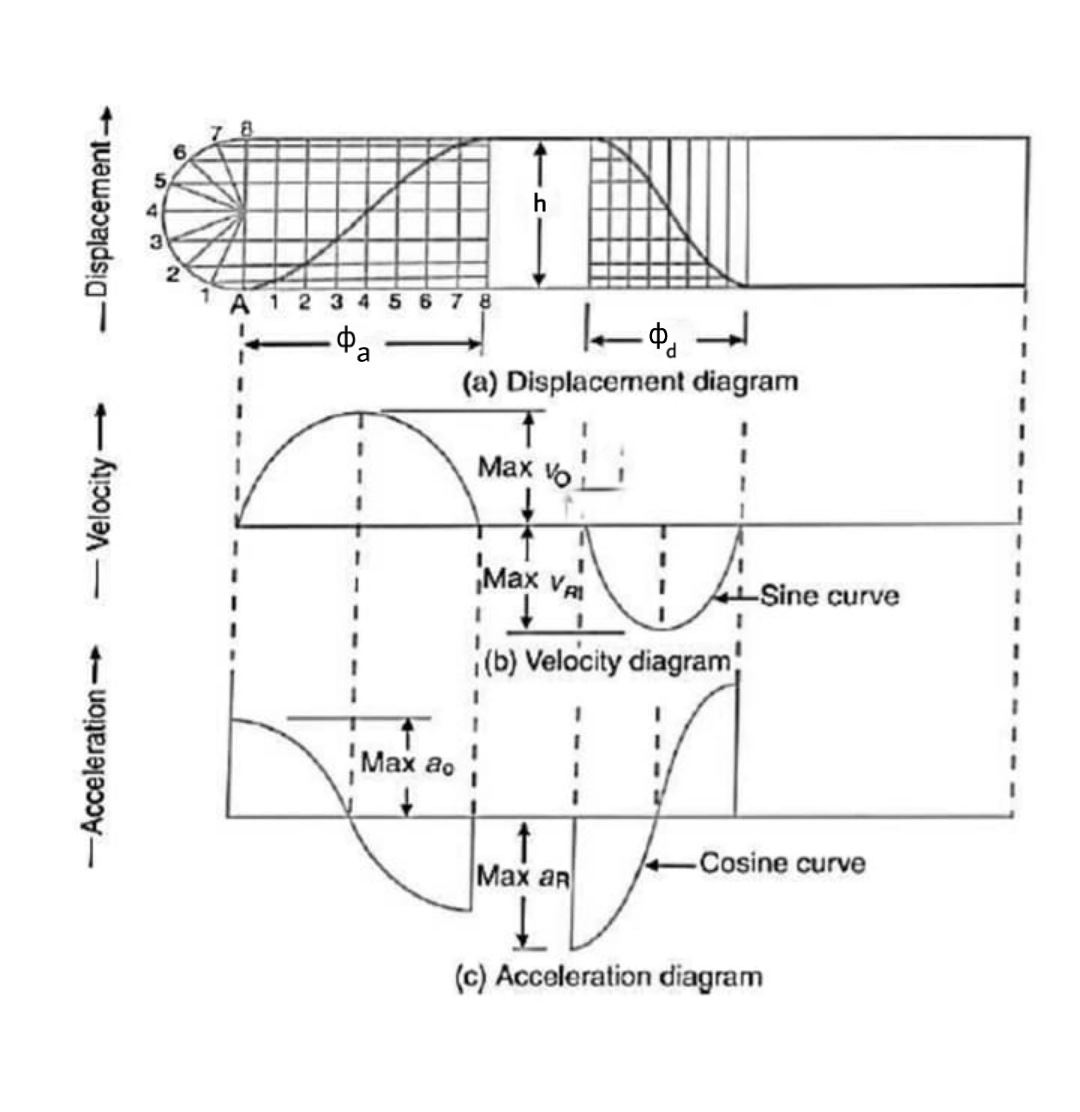
Let h =stroke of the follower,
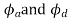 =angular displacement of the cam during out stroke and return stroke of the follower respectively, in radian, and
=angular displacement of the cam during out stroke and return stroke of the follower respectively, in radian, and
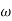 = Angular velocity of the cam in radian/s
= Angular velocity of the cam in radian/s
Maximum velocity of the follower on the outstroke
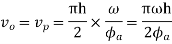
Maximum acceleration of the follower on the outstroke.

Similarly, the maximum velocity of the follower on the return stroke.
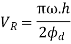
And the maximum acceleration of the follower on the return stroke.
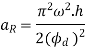
Q5) Explain the procedure of drawing velocity & acceleration diagrams for uniform acceleration uniform deacceleration motion.
Ans.
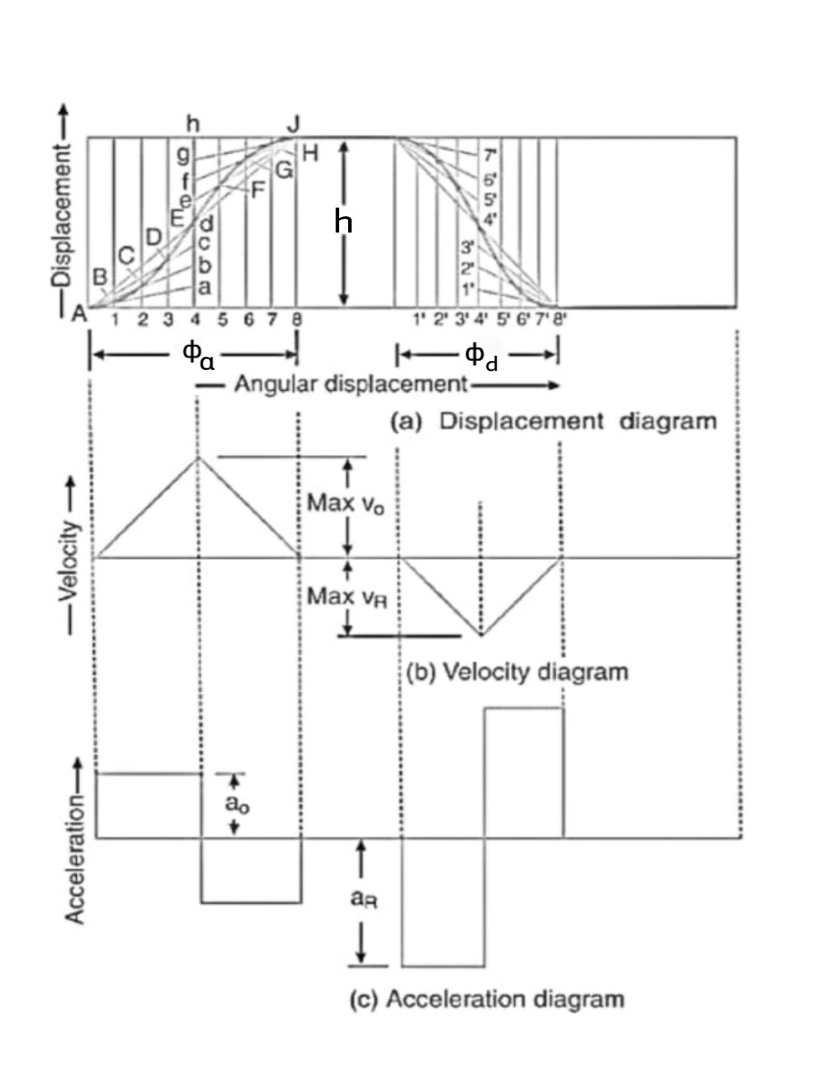
Let h=stroke of the follower.
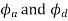 =angular displacement of the cam during out stroke and return stroke of the follower respectively, and
=angular displacement of the cam during out stroke and return stroke of the follower respectively, and
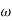 = Angular velocity of the cam.
= Angular velocity of the cam.
Maximum velocity of the follower during outstroke,

Similarly, the maximum velocity of the following during return stroke,
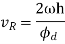


Maximum acceleration of the follower of during out stroke,
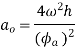
Similarly, maximum acceleration of the following during return stroke,
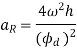
Q6) Explain the procedure of drawing velocity & acceleration diagrams for cycloidal motion.
Ans.
From a' draw a line parallel to AB intersecting the vertical lines through 1’ and 2’ at a and b respectively.
5. Similarly, from b’ draw a line parallel to AB intersecting the vertical lines through 4’ to 5’ at d & e respectively.
6. Joinpoint A a b c d e B by a smooth curve. This is the required cycloidal curve for the following during outstroke.
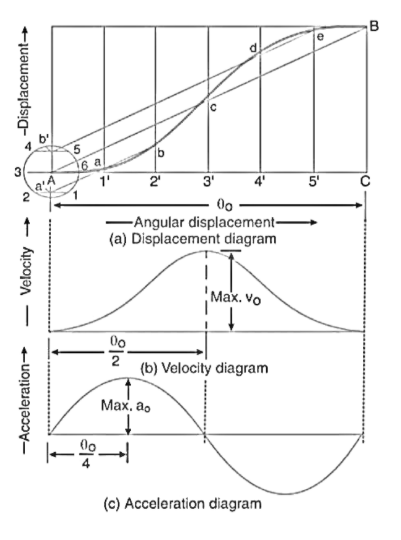
Let 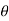 = angle through which the cam rotates in time t seconds, and
= angle through which the cam rotates in time t seconds, and
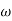 = Angular velocity of the cam.
= Angular velocity of the cam.
The velocity is maximum when
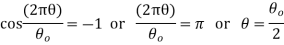
Maximum velocity of the following during outstroke,
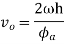
Similarly, the maximum velocity of the following during return stroke,
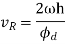
Maximum acceleration of the following due to out stroke,
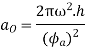
Similarly, maximum acceleration of the following during return stroke,
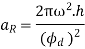
Q7) Explain the different processes of controlling the cam profile.
Ans.
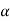
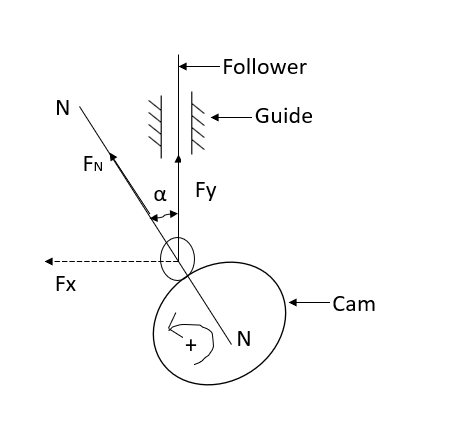



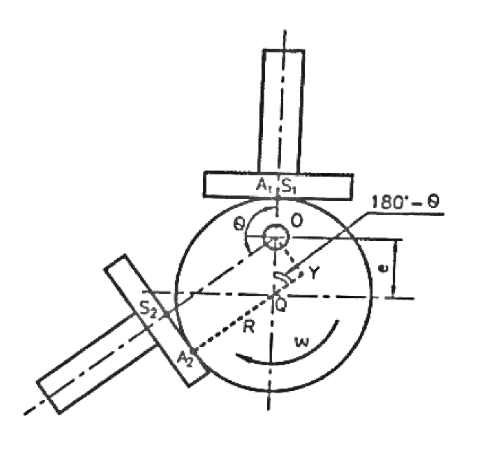
Q8) Explain undercutting with a neat sketch.
Ans.
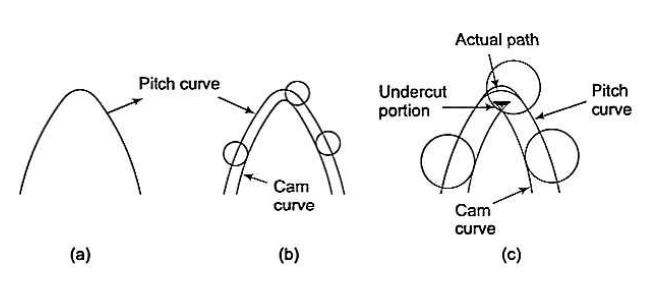
Q9) Explain the jump phenomenon with a neat sketch.
Ans.
Lift of follower = y = 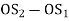
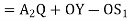

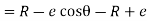

Differentiating equation with respect to time t we get
The velocity of follower = 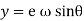
Differentiating equation with respect to time t, we get
Acceleration of follower=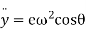
Where 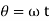 cam angle turned from the lowest position
cam angle turned from the lowest position

Let m=mass of follower
e=eccentricity
k = stiffness of spring
F = contact force between cam and follower
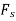 = total spring force
= total spring force
P = preload in spring
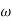 =Angular speed of cam
=Angular speed of cam
Then, from the free body diagram, we have
Inertia force =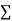 External forces
External forces
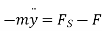
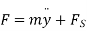

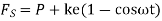
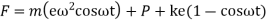
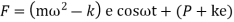

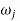
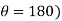

Where 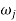 =jump speed
=jump speed
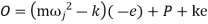
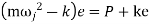

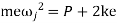
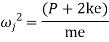

Therefore, to avoid jump
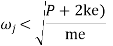
Or to avoid jump 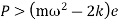
Q10) What do you mean by advanced cams? State its applications.
Ans.
Q11) Explain 2-3 polynomial cams.
Ans.
The 2-3 Polynomial D-R-D Cam
In this type of cam curves, four boundary conditions are used to hence displacement equation is given by,
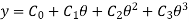 ……1
……1
Boundary condition is


Differentiating the above equation w.r.t  to get the velocity of the follower
to get the velocity of the follower

Initially put boundary conditions in equation (1),


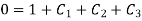
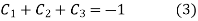
Now put the boundary conditions in equation (2)


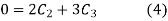
Put 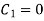 in equation (3)
in equation (3)
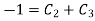 ……. 5
……. 5
Solving equation (4) and (5) we get
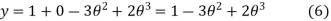
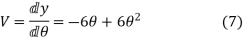
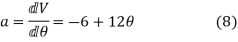

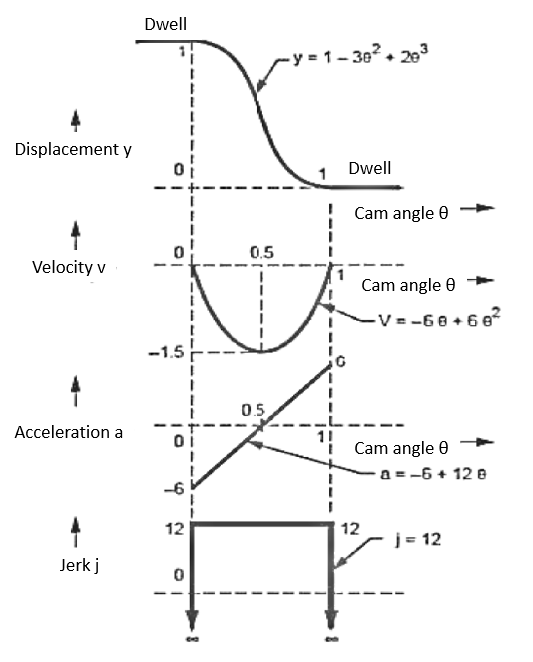
Q12) Explain 3-4-5 polynomial cams.
Ans.
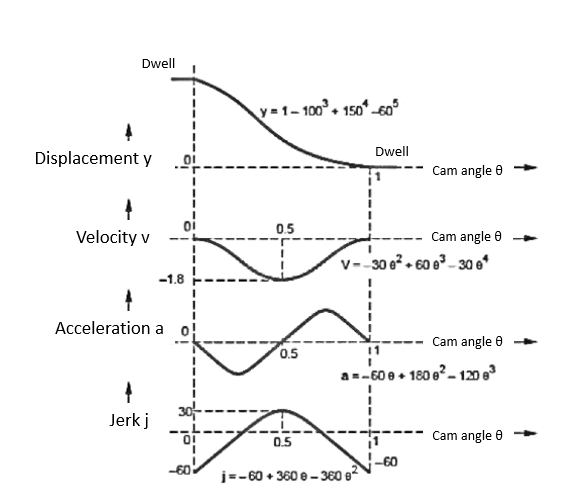
The 3-4-5 Polynomial D-R-D Cam
In this type of cam curves, six boundary conditions are used hence displacement equation is given by,
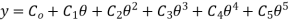 ……. 1
……. 1
Boundary conditions are
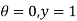
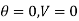
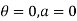
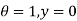
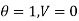
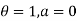
Differentiating the above equation w.r.t 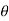 to get velocity follower,
to get velocity follower,

Again differentiating w.r.t. 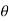 to get the acceleration of follower,
to get the acceleration of follower,
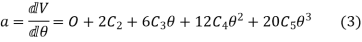
Initially put boundary conditions in equation (1)

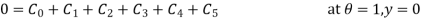
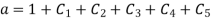
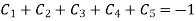 ……..(4)
……..(4)
Now put boundary condition in equation (2)

And 

Now put boundary conditions in equation (3)

And 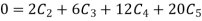
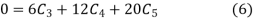
Put 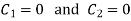 in equation (4) and (5)
in equation (4) and (5)
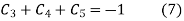
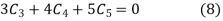
Solving equation (6),(7) and (8) we get
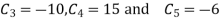
Substituting all these values in equation (1)
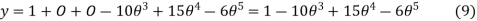
Velocity 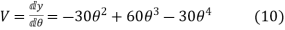
Acceleration 
Jerk