Unit II
Accounting for Consignment
Question Bank
Q.1.) RAWAL RATAN SINGH of Chittorgarh consigned 1000 units of 100 each to RANI PADMAVATI of SINGHAL. Expense made by RAWAL RATAN SINGH in such consignment are Rs. 20,000.
RANI PADMAVATI paid unloading charges Rs. 5,000 and Rs.2 P.U. selling expenses.
She sold all the goods at Rs.140 each and deducted 5% as commission and remitted draft for the balance. Prepare Ledger accounts in the books of Consignor.
A1) -
Ledger of Rawal Ratan Singh(Consignor)
Dr. CONSIGNMENT A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Goods sent on Consignment (1000 X 100) | 1,00,000 | By Padmavati (Sales-1000 X 140) | 1,40,000 |
T0 Cash (1000 X 20) | 20,000 |
|
|
To Padmavati Non selling exp (1,000 X 5) Selling exp (1,000 X 2) |
5,000 2,000 |
|
|
To Padmavati (Comm-1,40,000 X 5%) | 7,000 |
|
|
To P&L (Bal.Fig) | 6,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL | 1,40,000 | TOTAL | 1,40,000 |
Dr. PADMAVATI A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Consignment | 1,40,000 | By Consignment | 6,600 |
|
| By Consignment | 5,600 |
|
| By Bank (Bal.Fig) | 1,27,800 |
|
|
|
|
TOTAL | 1,40,000 | TOTAL | 1,40,000 |
Dr. Goods Sent On Consignment A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
|
| By Consignment | 1,00,000 |
To Trading (transfer) | 1,00,000 |
|
|
TOTAL | 1,00,000 | TOTAL | 1,00,000 |
Q.2.) On 15 Jan, 2013 J&K Co. of Mumbai sent to Muku & Co. of Kolkata 400 bicycle at an invoice price of Rs.100 per bicycle to be sold on commission. Freight and insurance were Rs.600.
Accounts sale was received from consignee as follow: -
15 March - 100 per bicycle were sold @ Rs.145 on which 5%. Commission and Rs.375 for expenses were deducted.
10 April - 150 per bicycle were sold @ Rs.140 on which 5%. Commission and Rs.290 for expenses were deducted.
From the above information prepare Consignment A/c in the books of J&K Co. and close it on 30 April, 2013 keeping in mind that no salves were made afterwards. Also show accounts in the books of Muku & Co.
A2) : -
Ledger of J&K CO. (Consignor)
Dr. CONSIGNMENT A/c Cr.
DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT | DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT |
2013 |
|
| 2013 |
|
|
Jan 15 | To GSOC | 40,000 | Mar. 15 | By Muku (sales) | 14,500 |
Jan 15 | To Cash/Bank (J&K exp.) | 600 | Apr. 10 | By Muku (sales) | 21,000 |
Mar. 15 | To Muku (exp.) | 375 | Apr. 30 | By Stock on Consignment | 15,225 |
Mar. 15 | To Muku (commission) | 725 |
|
|
|
Apr. 10 | To Muku (exp.) | 290 |
|
|
|
Apr. 10 | To Muku (commission) | 1,050 |
|
|
|
Apr. 30 | To P&L (Bal. Fig.) | 7,685 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TOTAL | 50,725 |
| TOTAL | 50,725 |
Dr. MUKU’s A/c (Consignee) Cr.
DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT | DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT |
2013 |
|
| 2013 |
|
|
Mar. 15 | To Consignment (Sales) | 14,500 | Mar. 15 | By Consignment (expense) | 375 |
Apr. 10 | To Consignment (Sales) | 21,000 | Mar. 15 | By Consignment (Commission) | 725 |
|
|
| Apr. 10 | By Consignment (expense) | 290 |
|
|
| Apr. 10 | By Consignment (Commission) | 1,050 |
|
|
| Apr. 30 | By Balance c/d | 33,060 |
| TOTAL | 35,500 |
| TOTAL | 35,500 |
Dr. Goods sent on Consignment A/c Cr.
DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT | DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT |
2013 |
|
|
| 2013 |
|
Apr. 30 | To Trading A/c (transfer) | 40,000 | Jan. 15 | By Consignment | 40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TOTAL | 40,000 |
| TOTAL | 40,000 |
LEDGER OF MUKU & CO. (Consignee)
Dr. J&K Co. A/c Cr.
DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT | DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT |
2013 |
|
| 2013 |
|
|
Mar. 15 | To Cash/Bank (expense) | 375 | Mar. 15 | By Cash/Bank (Sales) | 14,500 |
Mar.15 | To Commission | 725 | Apr. 10 | By Cash/Bank (Sales) | 21,000 |
Apr. 10 | To Cash /Bank (expense) | 290 |
|
|
|
Apr. 10 | To Commission | 1,050 |
|
|
|
Apr. 30 | To Balance c/d | 33,060 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TOTAL | 34,500 |
| TOTAL | 34,500 |
Dr. COMMISSION A /c Cr.
DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT | DATE | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT |
2013 |
|
| 2013 |
|
|
Apr. 30 | To P&L (Bal.Tfd.) | 1,775 | Mar.15 | By J&K (14,500 X 5%) | 725 |
|
|
| Apr. 10 | By J&K (21,000 X 5%) | 1,050 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TOTAL | 34,500 |
| TOTAL | 34,500 |
Working note: -
Closing Stock
Cost of Goods Sent.
Quantity sent 400
Cost of Goods (400 X 100) 40,000
Add: - J&K Co. Expense 600
b) Total Cost 40,600
c) Quantity Sold 250
d) Quantity in stock 150
e) Closing Stock - Cost
= Total Cost X Quantity in Stock / Quantity Sent
= 40,600 X 150/400
= 15,225
Note: - It is assumed that the consignee's expenses are incurred after the goods have reached their godown and hence not included in valuation of stock.
Q.3). On 1st November,2015, A of Calcutta sends goods costing Rs.1,00,000 to B of Delhi on Consignment basis. A paid Rs. 5,000 as freight and Rs. 2,000 as insurance.
On 31st December,2015, an Account Sales was received from B disclosing that the entire quantity of goods were sold for Rs.1,50,000 out of which Rs. 30,000 was sold on credit A customer who purchased goods for Rs. 5,000 failed to pay and the debt proved bad. All other debts were collected by B in full. As per the agreement, B is allowed a commission @ 10% on sales. B sends the amount due to A by cheque.
Prepare necessary Ledger accounts in the books of A & B.
A3) : -
LEDGER OF A
Dr. CONSIGNMENT A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Goods sent on Consignment | 1,00,000 | By B’s (Cash sales) | 1,20,000 |
To Cash/Bank Freight. 5,000 Insurance. 2000 | 7,000 | By B’s (Cr. Sales) | 30,000 |
To B's (commission) (10% of 1,50,000) | 15,000 |
|
|
To B's A/c (Bad debt) | 5,000 |
|
|
To P&L A/c (bal.fig.) | 23,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TOTAL | 1,50,000 | TOTAL | 1,50,000 |
Dr. B's A/c. Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Consignment (Cash sales) | 1,20,000 | By Consignment (commission) | 15,000 |
To Consignment (Cr. Sales) | 30,000 | By Consignment (bad debts) | 5,000 |
|
| By Bank A/c (Remittance) | 1,30,000 |
|
|
|
|
TOTAL | 1,50,000 | TOTAL | 1,50,000 |
Dr. Goods sent on Consignment A/c. Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Trading A/c (transfer) | 1,00,000 | By Consignment A/c | 1,00,000 |
TOTAL | 1,00,000 | TOTAL | 1,00,000 |
LEDGER OF B
Dr. A's A/c. Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Commission | 15,000 | By Cash/ Bank (Sales) | 1,20,000 |
To Consignment Debtors (Bad debts- no del credere comm) | 5,000 | By Consignment Debtors (Cr. Sales) | 30,000 |
To Cash/Bank (Remittance) | 1,30,000 |
|
|
TOTAL | 1,50,000 | TOTAL | 1,50,000 |
Dr. CONSIGNMENT DEBTORS A/c Cr.
PARTICULAR | AMOUNT | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT |
To A's | 30,000 | By Cash/Bank (collection) | 25,000 |
|
| By A's (Bad debts no del cr. commission) | 5,000 |
TOTAL | 30,000 | TOTAL | 30,000 |
Q.4) Refer to question 3. Prepare the necessary ledger account, if in the above question the consignee is given a del credere commission of 5% on sales (In addition to ordinary commission)—other things remaining the same.
A4) -
LEDGER OF A
Dr. CONSIGNMENT A/c. Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To GSOC | 1,00,000 | By B’s (Cash sales) | 1,20,000 |
To Cash/Bank Freight. 5,000 Insurance 2000 | 7,000 | By B's (Cr. Sales) | 30,000 |
To B's (commission) (10% of 1,50,000) | 15,000 |
|
|
To B's (Del-Credere Commission) | 7,500 |
|
|
To P&L (bal.fig.) | 23,000 |
|
|
TOTAL | 1,50,000 | TOTAL | 1,50,000 |
Dr. B's A/c. Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Consignment (Cash sales) | 1,20,000 | By Consignment (commission) | 15,000 |
To Consignment (Cr. Sales) | 30,000 | By Consignment (Del-cr. commission) | 7,500 |
|
| By Cash/Bank(Remittance) | 1,27,500 |
TOTAL | 1,50,000 | TOTAL | 1,50,000 |
Dr. Goods sent on Consignment A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Trading A/c (transfer) | 1,00,000 | By Consignment A/c | 1,00,000 |
TOTAL | 1,00,000 | TOTAL | 1,00,000 |
LEDGER OF B
Dr. A's A/c. Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To commission | 15,000 | By Cash/ Bank (Sales) | 1,20,000 |
To Del credere commission | 7,500 | By Consignment Debtors (Cr. Sales) | 30,000 |
To Cash/Bank (Remittance) | 1,27,500 |
|
|
TOTAL | 1,50,000 | TOTAL | 1,50,000 |
Dr. CONSIGNMENT DEBTORS A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To A's | 30,000 | By Cash/Bank (collection) | 25,000 |
|
| By A's (Bad debts Adjusted) | 5,000 |
TOTAL | 30,000 | TOTAL | 30,000 |
Dr. Del Credere Commission A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Consignment Debtors (Bad Debts) | 5,000 | By A's | 7,500 |
To P&L (Bal. Fig) | 2,500 |
|
|
TOTAL | 7,500 | TOTAL | 7,500 |
Dr. COMMISSION A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To P&L (Bal. Fig) | 15,000 | By A's | 15,000 |
TOTAL | 15,000 | TOTAL | 15,000 |
Dr. PROFIT & LOSS ACCOUNT Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Profit c/d to B/S | 17,500 | By Commission | 15,000 |
|
| By Del Credere Commission (Net trfd.) | 2,500 |
TOTAL | 17,500 | TOTAL | 17,500 |
Q.5) Amit of Mumbai consigned 100 sewing machines to Sanjay of Surat to be sold on his risk. The cost of one machine was Rs.150, but the invoice price was Rs.200. Amit paid freight Rs. 600 and insurance in transit Rs.200
Sanjay sent a draft to Amit for Rs. 10,000 as advance and later sent an account sales showing that 80 machine were sold at Rs.220 each. Expenses incurred by Sanjay were carriage inward Rs. 25, Octroi Rs.75, godown rent Rs.500 and advertisement Rs.300. Sanjay is entitled to a commission of 5% on sales.
Journalize the above transaction in the books of Amit and Sanjay.
A5) -
LEDGER OF AMIT
Dr. CONSIGNMENT A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To GSOC | 20,000 | By Sanjay (Sales) | 17,600 |
To Cash/Bank (Amit expenses) | 800 | By Stock on Consignment | 4,180 |
To Sanjay (Expenses) | 900 | By GSOC (Load) | 5,000 |
To Sanjay (Commission) | 880 |
|
|
To Stock Reserve c/d | 1,000 |
|
|
To P&L(bal.fig.) | 3,200 |
|
|
TOTAL | 26,780 | TOTAL | 26,780 |
Dr. SANJAY A/c. Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Consignment (Cash Sales) | 17,600 | By Cash/ Bank (Advance) | 10,000 |
|
| By Consignment (Expenses) | 900 |
|
| By Consignment (Commission) | 880 |
|
| By Balance c/d | 5,820 |
TOTAL | 17,600 | TOTAL | 17,600 |
Dr. Goods sent on Consignment A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Consignment | 5,000 | By Consignment A/c | 20,000 |
To Trading A/c (transfer) | 15,000 |
|
|
TOTAL | 20,000 | TOTAL | 20,000 |
LEDGER OF SANJAY
Dr. AMIT A/c Cr.
PARTICULAR | AMOUNT | PARTICULAR | AMOUNT |
To Cash/ Bank (Advance) | 10,000 | By Cash/ Bank | 17,600 |
To Cash/ Bank (Expenses) | 900 |
|
|
To Commission | 880 |
|
|
To Balance c/d | 5,820 |
|
|
TOTAL | 17,600 | TOTAL | 17,600 |
Q.6) On 1st July,2016, Rustom House of Ahmedabad consigned 100 keyboards to TCS of Mumbai. The cost of each keyboard was Rs.450 but the pro forma invoice price was Rs.600. Rustom House paid Rs.3000 for freight and insurance. On 7th July,2016, TCS accepted a 3 months’ bill drawn upon them by Rustom House for Rs. 30,000. TCS paid Rs. 1,200 as rent and Rs.750 for advertisement and up to 31st December,2016(On which Rustom House closes their books) they sold 80 keyboards @ 615 each. TCS were entitled to a commission of 5% on sales.
Show the ledger accounts recording the above transaction in the books of Rustom House and TCS
A6) -
LEDGER OF Rustom House
Dr. CONSIGNMENT A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To GSOC | 60,000 | By TCS (Sales) | 49,200 |
To Cash/Bank (Rustom House expenses) | 3,000 | By Stock on Consignment | 12,600 |
To TCS (Expenses) | 1,950 | By GSOC (Load) | 15,000 |
To TCS (Commission) (49,200 X 5%) | 2,460 |
|
|
To Stock Reserve (Load) | 3,000 |
|
|
To P&L(bal.fig.) | 6,390 |
|
|
TOTAL | 17,600 | TOTAL | 17,600 |
Dr. TCS A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Consignment (Cash Sales) | 49,200 | By Bills Receivable (Advance) | 30,000 |
|
| By Consignment (Expenses) | 1,950 |
|
| By Consignment (Commission) | 2,460 |
|
| By Balance c/d | 14,790 |
TOTAL | 49,200 | TOTAL | 49,200 |
Dr. Goods sent on Consignment A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Trading A/c (transfer) | 45,000 | By Consignment A/c | 60,000 |
To Consignment | 15,000 |
|
|
TOTAL | 60,000 | TOTAL | 60,000 |
LEDGER OF TCS
Dr. Rustom House A/c Cr.
PARTICULARS | AMOUNT | PARTICULARS | AMOUNT |
To Bills Payable (Advance) | 30,000 | By Cash/ Bank(Sales) | 49,200 |
To Cash/ Bank (Expenses) | 1,950 |
|
|
To Commission | 2,460 |
|
|
To Balance c/d | 14,790 |
|
|
TOTAL | 49,200 | TOTAL | 49,200 |
Q.7) D. Dogra of Delhi sent to his agent, M. Monga of Madras, 500 articles costing Rs.15/- per article at an invoice price of Rs.20 per article. The following payments were made by D. Dogra in this connection: freight and carriage Rs. 450, miscellaneous exp. Rs. 50. M. Monga sent a bank draft for Rs. 3,000 as an advance against the Consignment M. Monga sold 300 articles at a flat rate of Rs.28 per article and sent an Account Sales showing deduction for storage charges Rs.550 insurance Rs.550 and his Commission of 3% plus 2% Del Credere on gross sale proceeds, and remitted the amount due on consignment. M. Monga also informed D. Dogra that 50 articles were damaged in transit and thus they were valued at Rs.550. Journalise the above transactions in the books of the consignor and consignee.
A7: -
Books of Dogra (Consignor)
Journal
|
|
|
| Dr. | Cr. |
|
| Rs. | Rs. | ||
(1) | Consignment to madras A/c Dr | 7,500 |
| ||
| To Goods sent on Consignment A/c |
| 7,500 | ||
(500 articles sent to M. Monga, Agent, Cost being Rs.15 per article). | |||||
(2) | Consignment to Madras A/c Dr | 500 |
| ||
| To Bank Account |
| 500 | ||
(Expenses incurred on the Consignment) | |||||
| Freight & Carriage | Rs. | 450 |
|
|
| Miscellaneous Exp. | Rs. | 50 |
|
|
|
|
| 500 |
|
|
(3) | Bank Account Dr | 3,000 |
| ||
| To M. Monga |
| 3,000 | ||
(Advance received from the Agent in the form of Bank Draft.) | |||||
(4) | M. Monga Dr | 8,400 |
| ||
| To Consignment to Madras A/c |
| 8,400 | ||
(Sales affected by M. Monga as per Account Sales.) | |||||
(5) | Consignment to Madras A/c Dr | 570 |
| ||
| To M. Monga |
| 570 | ||
(Expenses incurred by M. Monga Rs.150 and Commission due to him, Rs.550 (5% of Rs. 8,400). | |||||
(6) | Bank Account Dr | 4,830 |
| ||
| To M. Monga |
| 4,830 | ||
(Amount due from the consignee received.) | |||||
(7) | P & Loss A/c Dr | 350 |
| ||
| To Consignment to Madras A/c |
| 350 | ||
(Abnormal Loss on 50 damaged Articles) | |||||
(8) | Stock on Consignment A/c Dr | 2,850 |
| ||
| To Consignment to Madras A/c |
| 2,850 | ||
| (Value of stock unsold at Madras) |
| Rs. |
|
|
| 150, goods articles, @ Rs.20 |
| 2,250 |
|
|
| Add: Expenses Rs.150 |
| 150 |
|
|
| 50 damaged articles |
| 450 |
|
|
|
|
| 2,850 |
|
|
(9) | Consignment to Madras A/c Dr | 3,030 |
| ||
| To Profit & Loss Account |
| 3,030 | ||
(Profit on consignment transferred to Profit & Loss Account) | |||||
(10) | Goods sent on Consignment A/c | 7,500 |
| ||
| To Trading A/c |
| 7,500 | ||
(Goods sent on consignment A/c closed by transfer to trading Account) | |||||
Books of M. Monga (Consignee)
Journal
|
|
|
| Dr. | Cr. |
|
| Rs. | Rs. | ||
(1) | D.Dogra A/c Dr | 3,000 |
| ||
| To Bank A/c |
| 3,000 | ||
(Advance sent to the Consignor against consignment) | |||||
(2) | D. Dogra A/c Dr | 150 |
| ||
| To Bank A/c |
| 150 | ||
(Expenses incurred on the Consignment on behalf of D. Dogra | |||||
| Storage |
| 50 |
|
|
| Insurance |
| 100 |
|
|
|
|
| 150 |
|
|
(3) | Bank A/c Dr | 8,400 |
| ||
| To D. Dogra A/c |
| 8,400 | ||
(Sale of 300 articles @ Rs.28 each out of the Consignment.) | |||||
(4) | D. Dogra A/c Dr | 420 |
| ||
| To Commission A/c |
| 420 | ||
(5% Commission on Sales made on half of D. Dogra; 3% Commission + 2% Del Credere) | |||||
(5) | D. Dogra A/c Dr | 4,830 |
| ||
| To Bank A/c |
| 4,830 | ||
(Amount due to D. Dogra remitted). | |||||
Q.8) Philips Radio of Calcutta despatched 1,000 transistors at Rs.700 each to Mohan Bros. of Delhi, the consignors paid freight Rs.7,500, cartage Rs.500 and insurance Rs.2,500 Mohan Bros. received only 900 sets and incurred he following expenses.
Rs.
Octroi and other Expenses 1,00,000
Cartage 5,000
Sales expenses 6,000
The consignee sold 600 sets only. You are required to calculate the value of closing stock.
A8) -
Calculation of value of unsold stock
Particulars | Units |
Sets Received | 900 |
Sets Sold | 300 |
Unsold Stock | 600 |
Particulars | Rs. |
Cost of Unsold Stock (300 x 700) | 2,10,000 |
Add: Proportionate expenses of Consignor (7500 + 500 + 2500) x 300/1000 | 3,150 |
Add: Proportionate expenses of Consignee (Octroi & Cartage) (1,00,000 + 5000) x 300/900 | 35,000 |
| 2,48,150 |
Q.9) Deepak sold goods on behalf of Geep Sales Corporation on consignment basis. On 1 January 2002 he had with him a stock of Rs.20,000 on consignment. During the year he received goods worth Rs.2,00,000.
Deepak had instructions to sell goods at cost plus 25% and was entitled to a commission of 4% on sales in addition to 1% del credere commission.
During the year ended 31 December 2002 cash sales were Rs.1,20,000; credit sales Rs.1,05,000; Deepak’s expenses relating to consignment Rs.3,000 being salaries and insurance bad debts amounted to Rs.3,000.
Prepare necessary accounts in the books of Geep Sales Corporation.
A9) -
|
|
|
|
In the books of Geep Sales Corporation | |||
Consignment Account | |||
Dr. |
|
| Cr. |
| Rs. |
| Rs. |
To Consignment Stock b/d | 20,000 | By Deepak |
|
To Goods sent on Consignment Account | 2,00,000 | Cash Sales 1,20,000 |
|
To Deepak (Commission) | 9,000 | Credit Sales 1,05,000 | 2,25,000 |
To Deepak (Commission) | 2,250 | By Consignment Stock c/d | 40,000 |
To Deepak (expenses) | 3,000 |
|
|
To Profit & Loss Account |
|
|
|
(Profit) | 30,750 |
|
|
| 2,65,000 |
| 2,65,000 |
Deepak’s Account | |||
Dr. |
|
| Cr. |
| Rs. |
| Rs. |
To Consignment account (Sales) | 2,25,000 | By Consignment account |
|
|
| (Commission) | 9,000 |
|
| By Consignment Account |
|
|
| (Commission) | 2,250 |
|
| By Consignment Account |
|
|
| (Exp.) | 3,000 |
|
| By Balance c/d | 2,10,750 |
| 2,25,000 |
| 2,25,000 |
Working Notes:
(1) Calculation of Consignment Stock Sale Price = 100 + 25 = 125
Cost of Sales = Sales × 100/125
= 2,25,000 × 100/125
= Rs.1,80,000
Cost of the goods available for sale = Rs. 20,000 + Rs. 2,00,000 = Rs.2,20,000. Hence stock at the end = Rs. 2,20,000 - Rs. 1,80,000 = Rs. 40,000
(2) Since Deepak is paid del-credere commission, bad debts of Rs. 3,000 would be borne by him.
Q.10) S of Bombay consigned 10,000 kg. of oil to D of Calcutta. The cost of oil was Rs.2 per kg. S paid Rs. 5,000 as freight and insurance. During transit 250 kg were accidentally destroyed for which the insurers paid directly to the consignors Rs.450 if full settlement of the claim.
D reported that 7,500 kg were sold @ Rs.3 per kg. The expenses being on godown rent Rs. 200 on advertisement Rs. 1,000 and on salesman salary Rs. 2,000 D. is entitled to a commission of 3% plus 1.5% del credere. D reported a loss of 100 kg. due to leakage. D. settled the accounts by bank draft. Prepare the accounts is the books of S.
A10) -
Consignment to Calcutta A/c | |||||
Dr. |
|
|
|
| Cr. |
|
| Rs. |
|
| Rs. |
To Goods on Consignment A/c |
| 20,000 | By Bank (Ins. Co.) |
| 450 |
To Bank—Freight & Insurance |
| 5,000 | By P & L A/c (abnormal loss |
| 175 |
To D—Expenses |
| 3,200 | By D— (Sale proceeds) |
| 22,500 |
To D—Commission |
|
|
|
|
|
Ordinary 3% | 675 |
| By Consignment Stock A/c |
| 5,431 |
Del Credere 1.5% | 338 | 1,013 | By P & L A/c—Loss |
| 657 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 29,213 |
|
| 29,213 |
Goods Sent on Consignment A/c | |||||
Dr. |
|
|
|
| Cr. |
|
| Rs. |
|
| Rs. |
To Trading A/c |
| 20,000 | By Consignment to Calcutta A/c |
| 20,000 |
Consignment Stock A/c | |||||
Dr. |
|
|
|
| Cr. |
|
| Rs. |
|
| Rs. |
To Consignment Calcutta A/c |
| 5,431 | By Balance c/d |
| 5,431 |
D’s A/c | |||||
Dr. |
|
|
|
| Cr. |
|
| Rs. |
|
| Rs. |
To Consignment to Calcutta A/c |
|
| By Consignment to Calcutta A/c |
|
|
—(sale proceeds) |
| 22,500 | (Exp.) |
| 3,200 |
|
|
| By Consignment to Calcutta A/c |
|
|
|
|
| (commission) |
| 1,013 |
|
|
| By Bank |
| 18,287 |
|
| 22,500 |
|
| 22,500 |
Working Notes: |
|
|
|
|
|
(A) Cost of Goods destroyed |
|
| Rs. |
|
|
Cost of 10,000 kg.@Rs.2 |
|
| 20,000 |
|
|
Freight |
|
| 5,000 |
|
|
Total cost of 10,000 kg. |
|
| 25,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(B) Value of Stock still unsold |
|
|
|
|
|
Quantity received by D (Excluding accidental loss) | 9,750 |
|
| ||
Less: Normal Leakage |
|
| (100) |
|
|
|
|
| 9,650 |
|
|
Cost of 9,650 kgs (25,000-625) | Rs. 24,375 |
|
| ||
Cost of 2,150 kgs (24,375 / 9650 x 2150) |
|
| Rs. 5,431 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q11) What is Joint Venture?
A11) Joint Venture is a temporary form of business, where two or more persons join together to meet the short term objectives. It is quiet similar to Partnership firm, but established without name or registration separately under any law.
Q12) Who are Co-Ventures?
A12) The two or more people who start Joint Venture to achieve the short term objectives and ready to share the risk and return in the venture, are called Co-Ventures. They are similar to Partners in the Partnership firm.
Q13) State any four features of Joint Venture.
A13) The following are the important features of Joint Venture.
Q14) State any two differences between Joint Venture and Partnership.
A14) Joint Venture is a temporary partnership; partnership is a long term Joint Venture. The following are the differences between Joint Venture and Partnership.
BASIS | JOINT VENTURE | PARTNERSHIP FIRM |
1. Name of the Venture | Joint Venture does not have any name of running business. | Partnership has its own name of running business. |
2. Nature of members | Members in Joint Venture are Co-Ventures | Members in Partnership firm are partners |
3. Nature of objectives | Temporary / short term objectives are set in joint venture | Long term objectives are set in partnership firm. |
4. Registration of firm | No registration of business under any law | Registration is optional, but available. |
5. Books of accounts | No separate set of books are maintained in the books of joint venture. | Separate set of books are maintained in the books of partnership firm. |
6.Freedom for additional business | Co-ventures have freedom to do similar business and complete. | Partners do not have freedom to do similar business and complete. |
7.DisA | Joint venture is dissolved as soon | Partnership is dissolved only at |
| as its work has been completed. | the mutual opinion of partners. |
8. Maintenance of separate set of books | Not necessary | Mandatory |
9. Status of Minor | A minor cannot become a co- venturer. | A minor can become a partner to the benefits of the firms. |
10. Governing Act | There is no such specific act. | The partnership is governed by the Indian Partnership Act, 1932. |
Q15) State any two differences between Joint Venture and Consignment.
A15) the following are the important differences between Joint Venture and Consignment.
BASIS | JOINT VENTURE | CONSIGNMENT |
1. Nature of parties | The parties of Joint Venture are Co-Venturers. | The parties of Consignment are Consignor and Consignee. |
2. Nature of relationship between parties | Relationship of Parties in Joint Venture are called partners | Relationships of Parties in consignment are Principal and Agent. |
3.Powers to Parties | Co-venturers have full powers to purchase and sale of assets, collection of dues. | Consignee has to act like an agent to consignor and has limited power. |
4. Law applicability | Partnership act is applicable to joint venture | Law of agency is applicable. |
5. sharing of profits or loss | Co-ventures have right to share profit or loss of venture. | Consignor and consignee do not share the profit or loss of consignment. |
6. scope of business | There is a wide scope for joint venture business. It includes different ventures. | The scope of consignment is narrow. It is concerned with the sale of movable goods. |
7. Number of persons | More than two persons are possible in joint venture. | One consignor, but more than two consignees in consignment. |
Q16) State the methods of accounting for Joint Venture.
A16) The accounting treatment for Joint Venture has been studied under two board classifications they are.
Q17) Why do you prepare Joint Venture Account?
A17) It is a normal ledger account, incorporates transactions made exclusively in Joint venture to find out its profit of loss. It is maintained from the starting date of Joint venture to the date of disA.
Q18) What is joint bank account?
A18) It is similar to normal bank account. It records all expense in the credit side and all incomes in the debit side. The contribution of cash made by co-venture’s, income through sale of goods etc., are debited and expenses of joint venture, purchase of goods are credited.
Q19) What is memorandum joint venture account?
A19) It is not an account prepared under double entry principles of accounts. All the expenses paid by each co-venture are debited and income (sales) made by each co-venture are credited in the respective co-ventures name. it is prepared to find out the profit or loss of joint venture.
Q20) State the feature of joint ventures.
A20)
Q 21) Kumar, Shy am and Ratan were partners of companies that each shared profit in a 5: 3: 2 ratios. We have decided to dissolve the company from April 1, 2013. On the day, the company's balance sheet is as follows on As of April 1, 2013.
Liabilities | Amount | Assets | Amount |
Creditors | 1,20,000 | Plant | 80,000 |
Capital A / cs Kumar 68,000 Siamese 50,000 Rattan 27,000 |
1,45,000
________ 2,65,000
| Stock Motor van furniture Debtor Cash
| 30,000 25,000 45,000 71,000 14,000 _______ 2,65,000 |
The following results were obtained due to the disA
Prepare realization accounts, partner capital accounts, and company bank accounts.
A21)
|
| Realisation Account |
| Cr | |
Particulars |
| Amount | Particulars |
| Amount |
To miscellaneous goods assets A / c Plant Furniture Motor van Inventory Debtor
To Cash A / c (Creditor WN2) To Cash A/c Expenses
|
80,000 45,000 25,000 30,000 71,000 _______
|
2,51,000
1,00,000 5,000
_______ 3,56,000
| By Miscellaneous goods liabilities A / c(creditors) By Kumar ’s Capital A / c (taken over by the plant) By Shyam ’s Capital A / c (taken over by motor van) By Cash A/c Plants Furniture Debtor (71,000 – 1,000)
By realized loss transferred to (WN1) to cash A / c (cost) Kumar's capital A / c Siamese capital A / c Rattan Capital A / c
|
50,000 40,000 70,000
500
300 200 | 1,20,000
45,000
30,000
1.60,000 ________
1,000 _______ 3,56,000
|
Note: If there is no information about the realization of an asset, it is assumed that nothing will be realized from that asset (such as a stock in this case).
Dr | Partners’ Capital Account | Cr | ||||||
Particulars | Kumar Rs | Shyam Rs | Ratan Rs | Particulars | Kumar Rs | Shyam Rs | Ratan Rs | |
To realization A / c (inherited asset | 45,000 | 30,000 | ----- | By balance b / d | 68,000 | 50,000 | 27,000 | |
To Realization A / c (Loss of Realization | 500 | 300 | 200 |
|
|
|
| |
To Cash A / c (final payment) | 22,500 | 19,700 | 26,800 |
|
|
|
| |
| 68,000 | 50,000 | 27,000 |
| 68,000 | 50,000 | 27,000 | |
Dr |
| Cash Account |
| Cr | |
Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount | ||
To balance b / d | 14,000 | By Realized A / c (creditors | 1,00,000 | ||
To Realization A / c (realization of plants, furniture, debtors) |
1,60,000 | By Realization A / c (cost)
| 5,000 | ||
|
| Kumar's capital A / c (final payment) Shyam ’s Capital A / c (final payment) Ratan ’s Capital A / c (final payment)
|
22,500
19,700
26,800
| ||
| 1,74,000
|
| 1,74,000 | ||
Working Note:
1. Realized loss = 1,000
Realized loss transferred to Kumar's capital account = 1,000 x 5/10 = 500
Realized loss transferred to Shyam's capital account = 1,000 x 3/10 = 300
Realized loss transferred to Rattan's capital account = 1,000 × 2 = 200
2. Creditor = 1,20,000
20,000 of them were untraceable
Therefore, the creditor was paid in full payment of 1,20,000 – 20,000 = 1,00,000.
Q 22) The Ravi and Mohan companies were dissolved on January 3, 2013. According to the agreement, Rabbi agreed to carry out the disA work with the agreed reward of 2,000 rupees and to bear all the realization costs. The disA cost was rupees. The same as 1,500 was paid by the company. Pass the journals required to pay the disA fee.
A22)
to cash A / c 1,500
(The cost of realization will be paid.)
ii. Realization A / c …… .. Dr. 600
To Mohan's capital A / c 600
(The cost of realization will be borne by the partner.)
iii. Realization account …… .. Dr 2,000
To the capital of Mohan, A / c 2,000
(The cost of realization will be paid to Mohan.)
no entry
Q23) How are undistributed profits such as general reserves and income statement credit balances treated when the company is dissolved?
A23) The court may order the dissolved of a partnership company in the event of bankruptcy of all partners or all but one partner.
Q 24) What is a partnership breakup?
A24) According to Section 39 of the Indian Partnership Act of 1932, the dissolution A of a partnership between all partners of a company is called the dissolution A of the company. The dissolution A of the company is a complete collapse of the partnership and the partners will not continue the company.
Dissolution A of a partnership means the restructuring of the company due to the retirement of a partner, and the remaining partners will provide the survival of the company in accordance with an explicit or implied agreement to that effect. When the company dissolves, the company is closed, so the company's assets are realized and the debt is exempted.
On the other hand, when the partnership is dissolved, the share of the seconded partner will be confirmed and the company will not be closed. Modes of DisA of a Company: Sections 40-44 of the Indian Partnership Act of 1932 deal with various methods by which a company may dissolve.
Q25) Identify situations in which the court may order the disA of the partnership company.
Pass the journal if:
A25)
iv. Realization A / c …… .. Dr 1,500
to cash A / c 1,500
(The cost of realization will be paid.)
v. Realization A / c …… .. Dr. 600
To Mohan's capital A / c 600
(The cost of realization will be borne by the partner.)
vi. Realization account …… .. Dr 2,000
To the capital of Mohan, A / c 2,000
(The cost of realization will be paid to Mohan.)
vii. no entry
Q 26) A and B share profits and losses in a 5: 2 ratios. They decided to dissolve the company. Assets and external debt have been transferred to Realization A/C. Pass in the journal entries that affect:
A26)
To bank A / c 12,000
(Repaying bank loan) …… 12,000
2. Realization A / c Dr. 400
To A / c, the capital of A 400
(Commission to A credited to A's capital account)
3. Capital of A A / c Dr. 20,000
B ’s Capital A / c Dr. 8,000
To postponed advertising expenses A / c 28,000
(Deleted advertising costs, or profit-sharing ratio, cancelled by debiting the partner's capital account at a ratio of 5: 2). 28,000
4. B's Capital A / c Dr. 1,200
To Realization A / c 1,200
(The shares have been taken over by B for 1,200 rupees at the agreed value)
5. Bank A / c Dr. 7,000
To Realization A / c 7,000
(Unrecorded computer sells for 7,000 rupees)
6. Realization A / c Dr. 2,000
To bank A / c 2,000
(It must be an unpaid invoice paid for repair)
Q 27) A, B, and C operate in partnerships that share profits and losses in proportions of 1/2, 3/8, and 1/8, respectively. On March 31, 2012, they agreed to sell their business to a limited liability company.
Their position on the day was:
| ₹ |
| ₹ |
A’s capital | 40,000 | Machinery | 48,000 |
B’s capital | 30,000 | Furniture | 42,000 |
C’s capital | 26,000 | Stock | 23,000 |
Loan on mortgage | 16,000 | Book debts | 15,000 |
Sundry creditors | 18,000 | Cash | 2,000 |
|
|
|
|
| 1,30,000 |
| 1,30,000 |
The company took the following assets at the valuation shown below-
| ₹ |
Machinery | 61,000 |
Furniture | 31,800 |
Stock | 22,000 |
Book debts | 14,000 |
Goodwill | 10,000 |
The company also agreed to pay the creditors which was agreed at 17,700. The company paid ₹ 67,000 in fully paid shares of ₹ 10 each and the balance in cash. The expenses amounted to ₹ 1,500.
Prepare ledger accounts in the books of the firm.
A27)
Dr. Realization account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To sundry assets- |
| March 31 | By loan on mortgage |
|
| Machinery 48,000 |
| March 31 | By sundry creditors |
|
| Furniture 42,000 |
| March 31 | By ltd’s company a/c |
|
| Stock 23,000 |
|
| Machinery 61,000 |
|
| Book debts 15,000 | 1,28,000 |
| Furniture 31,800 |
|
March 31 | To cash - expenses | 1,500 |
| Stock 22,000 |
|
March 31 | To cash – loan paid | 16,000 |
| Book debts 14,000 |
|
March 31 | To profits transferred to: |
|
| Goodwill 10,000 |
|
| A’s capital 4,800 |
|
| 1,38,800 |
|
| B’s capital 3,600 |
|
| Less – creditors 17,700 |
|
| C’s capital 1,200 | 9,600 |
|
| 1,21,100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1,55,100 |
|
| 1,55,100 |
Dr. Limited company’s account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To realisation a/c |
| March 31 | By shares in ltd. | 67,000 |
| -consideration | 1,21,100 | March 31 | By cash | 54,100 |
|
| 1,21,100 |
|
| 1,21,100 |
Dr. Cash account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To balance b/d | 2,000 | March 31 | By realisation a/c |
|
March 31 | To ltd. company | 54,100 |
| Expenses | 1,500 |
|
|
|
| Loan | 16,000 |
|
|
| March 31 | By capital a/c |
|
|
|
|
| A 16,380 |
|
|
|
|
| B 12,280 |
|
|
|
|
| C 9,940 | 38,600 |
|
| 56,100 |
|
| 56,100 |
Dr. Share in Ltd. Company a/c Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To ltd. company | 67,000 | March 31 | By A’s capital a/c | 28,420 |
|
|
| March 31 | By B’s capital a/c | 21,320 |
|
|
| March 31 | By C’s capital a/c | 17,360 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 67,000 |
|
| 67,000 |
Dr. Capital account Cr.
Particulars | A | B | C | Particulars | A | B | C |
| ₹ | ₹ | ₹ |
| ₹ | ₹ | ₹ |
To shares in ltd. company | 28,420 | 21,320 | 17,360 | By balance b/d | 40,000 | 30,000 | 26,000 |
To cash settlement, balancing figure | 16,380 | 12,280 | 9,940 | By realisation a/c - profits | 4,800 | 3,600 | 1,200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 44,800 | 33,600 | 27,200 |
| 44,800 | 33,600 | 27,200 |
Note – total number of shares received from the limited company is 6,700. These have been divided among A, B and C in the ratio 448,336 and 272 or 28, 21 and 17 respectively. Namely, in the ratio of the amount finally due to them. Hence
A gets  or 2,842 shares of ₹ 28,420 ;
or 2,842 shares of ₹ 28,420 ;
B gets  or 2,132 shares of ₹ 21,320 ; and
or 2,132 shares of ₹ 21,320 ; and
C gets 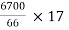 or 1,736 shares of ₹ 17,360 ;
or 1,736 shares of ₹ 17,360 ;
Q28) Mr. B and Mr. E are partners who share profits and losses in a 3: 2 ratio, respectively. On September 30, 2010, they recognized Mr. C as a partner and the new profit-sharing ratio is 2: 2: 1. C brings in equipment Rs 3,000 and cash Rs 10,000, and goodwill is (i) B and E Rs 20,000 and (ii) C Rs 10,000, but neither number is on the books.
On March 31, 2011, the partnership was dissolved, B retired, and the other two partners were EC (Pvt.) Ltd with equal capital. Formed a company called, taking over all the remaining assets and liabilities, goodwill agreed at Rs 40,000, the company's book. B agrees to take over the scooter for Rs 3,700. A machine with a book value of 4,000 rupees was sold for 3,000 rupees, exceeding the requirement.
It was agreed that the profits for the last two years were 17,200 rupees and 19,000 rupees, respectively, and the net profit for the half year ending September 30, 2010 would be equal to the average for the last two years and the current year.
When C was entered, no entry was made except for the cash received. EC (Pvt.,) Company Ltd., B has agreed to lend the company a loan of 50,000 rupees secured by 10% corporate bonds.
The trial balance as of March 31 is as follows. 2011:
| Debit (₹) | Credit (₹) |
Capital accounts |
|
|
B |
| 35,000 |
E |
| 20,000 |
C |
| 10,000 |
Drawing accounts |
|
|
B | 6,000 |
|
E | 5,000 |
|
C | 2,800 |
|
Debtors and creditors | 31,000 | 12,000 |
Machines | 23,000 |
|
Fixtures | 7,000 |
|
Scooter | 2,700 |
|
Stock as on 31st march 2011 | 13,000 |
|
Bank | 16,300 |
|
Profit and loss account for the year |
| 29,800 |
| 1,06,800 | 1,06,800 |
Prepare :
(i) Goodwill Adjustment Account
(ii) Capital accounts of the partners
(iii) Profit and Loss Appropriation Account
(iv) Balance Sheet of EC (Pvt.) Ltd. as on 318 March, 2011.
A28)
Dr. Goodwill adjustment account Cr.
2011 |
| ₹ | 2011 |
| ₹ |
March 31 | To partner’s capital account (to raise goodwill of all partners as on 30th September 2010) |
| March 31 | By partner’s capital account (to write off total goodwill as on 30th September 2010) |
|
| B (3/5 of ₹ 20,000) | 12,000 |
| B (2/5 of ₹ 30,000) | 12,000 |
| E (2/5 of ₹ 20,000) | 8,000 |
| E (2/5 of ₹ 30,000) | 12,000 |
| C | 10,000 |
| C (2/5 of ₹ 30,000) | 6,000 |
March 31 | To partner’s capital account (firm’s goodwill as on 31st March 2011): |
| March 31 | By goodwill account (account closed by transfer to goodwill account as the amount appear in the books of the company) | 40,000 |
| B (2/5 of ₹ 40,000) | 16,000 |
|
|
|
| E (2/5 of ₹ 40,000) | 16,000 |
|
|
|
| C (2/5 of ₹ 40,000) | 8,000 |
|
|
|
|
| 70,000 |
|
| 70,000 |
Dr. Capital account Cr.
2011 March 31 | B | E | C | 2011 March 31 | B | E | C |
| ₹ | ₹ | ₹ |
| ₹ | ₹ | ₹ |
To Drawings | 6,000 | 5,000 | 2,800 | By balance b/d | 35,000 | 20,000 | 10,000 |
To Goodwill Adjustment Account—written off | 12,000 | 12,000 | 6,000 | To Goodwill Adjustment Account— raised | 12,000 | 8,000 | 10,000 |
To scooter | 3,700 | 400 | 200 | To Goodwill Adjustment Account—raised | 16,000 | 16,000 | 8,000 |
To machines – loss on sale | 400 |
|
| By fixtures – not recorded earlier |
|
| 3,000 |
To loan from account* | 50,000 |
|
| By profit and loss - Appropriation account - Profit up to 30th September, 2008 |
| 13,200 | 8,800 |
To bank – settlement | 7,620 |
|
| By profit and loss Appropriation account - Profit of the new firm | 3,120 | 3,120 | 1,560 |
To bank – to make capital equal |
| 7,580 |
| By scooter – profit on takeover | 400 | 400 | 200 |
To share capital account - transfer |
| 31,340 | 31,340 | By bank – to make capitals equal |
|
| 7,580 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 79,720 | 56,320 | 40,340 |
| 79,720 | 56,320 | 40,340 |
Profit and loss appropriation account for the year ended on 31 march 2011
| ₹ |
| ₹ |
To partner’s capital accounts (distribution of profit upto 30th september 2010) |
| By profit and loss account – net profit for the year b/d | 29,800 |
B (3/5 of ₹ 22,000) | 13,200 |
|
|
E (2/5 of ₹ 22,000) | 8,800 |
|
|
To partner’s capital account (distribution of profits pertaining to new firm): |
|
|
|
B (2/5 of ₹ 7,800) | 3,120 |
|
|
E (2/5 of ₹ 7,800) | 3,120 |
|
|
C (1/5 of ₹ 7,800) | 1,560 |
|
|
| 29,800 |
| 29,800 |
Dr. Balance sheet of EC (pvt.) ltd. Cr.
As on 31st March, 2011
Liabilities | ₹ | Assets | ₹ |
Share capital: |
| Fixed assets |
|
Authorised | ? | Goodwill | 40,000 |
Issued and subscribed | 62,680 | Machines | 19,000 |
(all the shares have been allotted as fully paid up personant to a contract without payments being received in cash) |
| Fixtures | 10,000 |
Secured loans: |
| Current assets , loans and advances |
|
Loan from B | 50,000 | (A) Current assets |
|
10% debentures 50,000 |
| Stocks | 13,000 |
Less: debentures suspense account (50,000) | NIL | Debtors | 31,000 |
|
| Cash at bank | 11,680 |
|
| (B) Loans and advances | NIL |
Current liabilities and provisions: |
|
|
|
A) Current liabilities |
|
|
|
Creditors | 12,000 |
|
|
B) Provisions | NIL |
|
|
| 1,24,680 |
| 1,24,680 |
Working Notes :
(i) Break-up of total net profit for the year : ₹
Profits for the preceding two years = ₹ (17,200 + 19,000) 36,200
Add ; Current year’s profit 29,800
Total profit for the three years 66,000
Average = 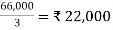
Profit upto 30th September, 2010 = ₹ 22,000
Profit for the remaining six months i.e., profit pertaining to the new firm
= ₹ 29,800 - ₹ 22,000 = ₹ 7,800.
(ii) Scooter account
| ₹ |
| ₹ |
To balance b/d | 2,700 | By B’s capital account – scooter taken over by B | 3,700 |
To partner’s capital account (transfer of profit on take-over) |
|
|
|
B (2/5 of ₹ 1,000) | 400 |
|
|
E (2/5 of ₹ 1,000) | 400 |
|
|
C (1/5 of ₹ 1,000) | 200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3,700 |
| 3,700 |
(iii) Machines account
| ₹ |
| ₹ |
To balance b/d | 23,000 | By bank (sale, book value ₹ 4,000) | 3,000 |
|
| By partner’s capital account (transfer of loss on sale) |
|
|
| B (2/5 of ₹ 1,000) | 400 |
|
| E (2/5 of ₹ 1,000) | 400 |
|
| C (1/5 of ₹ 1,000) | 200 |
|
| By balance c/d | 19,000 |
| 23,000 |
| 23,000 |
Alternatively, a realization account may be opened to transfer the profits from the scooter takeover and the losses from the sale of the machine. There is no transfer to the capital account because the realized account does not show profit or loss.
(iv) Adjustments to be made in the capitals of E and C : ₹
E's capital before adjustment 38,920
C's capital before adjustment 23,760
Total 62,680
E and C are to have equal capital.
Thus, each must have a capital of ₹ 31,340
C will being in ₹ (31,340-23,760) or ₹ 7,580 to make his capital equal to ₹ 31,340.
E will withdraw ₹ (38,920-31,340) or ₹ 7,580 to leave a balance of ₹ 31,340 in his capital account.
(v) Cash Book (Bank Columns)
| ₹ |
| ₹ |
To balance b/d | 16,300 | By B’s capital - settlement | 7,620 |
To machines a/c – sale | 3,000 | By E’s capital – amount withdrawn | 7,580 |
To C’s capital a/c – amount brought in | 7,580 |
|
|
|
| By balance c/d | 11,680 |
| 26,880 |
| 26,880 |
Q 29) W, S and T have partnered to share profits and losses in a 3: 2: 1 ratio, respectively. They split the approved equity capital of Rs. 6,00.000 into 45,000 shares of Rs. 10 and Rs. 15,000, respectively, a privately held company T & Co. , Ltd. Decided to establish.
The company was incorporated and took over the partnership's business, goodwill, and certain assets on March 31, 2012. The company's balance sheet for this date is as follows:
| ₹ |
| ₹ |
Capital accounts |
| Fixed assets at cost less depreciation: |
|
W 1,50,000 |
| Machinery | 65,000 |
S 1,00,000 |
| Scooters | 18,000 |
T 60,000 | 3,10,000 | Furniture and fittings | 6,000 |
Current accounts |
| Current assets: |
|
W 29,250 |
| Stock in trade | 1,80,000 |
T 20,750 |
| Debtors | 52,000 |
50,000 |
| Bank | 86,000 |
Less: S overdrawn 21,000 | 29,000 |
|
|
W’s loan account | 40,000 |
|
|
Creditors | 28,000 |
|
|
| 4,07,000 |
| 4,07,000 |
T owned free land that he had granted to the partnership and agreed to sell to the company for Rs 1,00,000. The consideration was issued to him for 10,000 rupees, 10% of the cumulative preferred stock of 10 rupees each.
Retired W was presented with one of the scooters by his partner and was valued at 6,000 rupees in the book. The remaining scooters were taken over by the company for 10,000 rupees. W also received certain furniture for which he was charged Rs 1,500. All debtors were considered good and were taken over by W, who agreed to repay the creditors.
The company took over the remaining furniture and accessories at a price of Rs 3,000, the machinery at its book value, the shares at an agreed price of Rs 1,66,000, and the bank's balance. The value of the partnership goodwill was agreed at Rs 40,000 for the purpose of the acquisition.
The company has agreed to repay W's loan for 3,000 rupees, 10% cumulative preferred stock, 10 rupees each and 10,000 rupees in cash.
The balance of consideration is to be issued by the company by issuing 30,000 shares of 10 rupees to the partner in proportion to the final balance of the total capital and checking account, and the balance is in cash. Will be paid. .. Calculate the consideration and show how it is discharged. Prepare the accounts needed to close the company's books.
A29)
Dr. Realisation account Cr.
2012 |
| ₹ | 2012 |
| ₹ |
March 31 | To sundry assets: |
| March 31 | By W’s capital a/c: |
|
| Machinery 65,000 |
|
| Furniture 1,500 |
|
| Scooters 18,000 |
|
| Debtors 52,000 | 53,500 |
| Furniture etc. 6,000 |
|
| By S’s capital a/c 4,000 |
|
| Stock in trade 1,80,000 |
|
| By T’s capital a/c 2,000 |
|
| Debtors 52,000 |
|
| (car presented to W by S and T) | 6,000 |
| Bank 86,000 | 4,07,000 |
| By T and Co. ltd – assets taken over | 3,70,000 |
| To profit transferred to: |
|
|
|
|
| W’s capital a/c (3/6) = 1,250 |
|
|
|
|
| S’s capital a/c (2/6) = 7,500 |
|
|
|
|
| T’s capital a/c (1/6) = 3,750 | 22,500 |
|
|
|
|
| 4,29,500 |
|
| 4,29,500 |
Dr. T and co. ltd. Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To realisation a/c | 3,70,000 | March 31 | By bank | 40,000 |
|
|
|
| By equity shares in T and co. ltd. | 3,00,000 |
|
|
|
| By 10% preference shares in T and co. ltd. | 30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 3,70,000 |
|
| 3,70,000 |
Dr. Cash account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To balance b/d | 86,000 | March 31 | By realisation a/c | 86,000 |
| To T and co. ltd | 40,000 |
| By W’s loan a/c | 10,000 |
|
|
|
| By W’s capital a/c | 15,000 |
|
|
|
| By S’s capital a/c | 7,500 |
|
|
|
| By T’s capital a/c | 7,500 |
|
| 40,000 |
|
| 40,000 |
Dr. Sundry creditors account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To W’s capital a/c – transfer | 28,000 | March 31 | By balance b/d | 28,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 28,000 |
|
| 28,000 |
Dr. Equity shares in T and co. ltd Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To T’s and co. ltd | 3,00,000 | March 31 | By W’s capital a/c | 1,50,000 |
|
|
|
| By S’s capital a/c | 75,000 |
|
|
|
| By T’s capital a/c | 75,000 |
|
| 3,00,000 |
|
| 3,00,000 |
Dr. 10% Cumulative preference shares in T and co. ltd. Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To T and co. ltd. | 30,000 | March 31 | By W’s loan | 30,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 30,000 |
|
| 30,000 |
Dr. W’s loan account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2012 |
|
| 2012 |
|
|
March 31 | To 10% cum. Pref. shares in T and co. ltd. | 30,000 | March 31 | By balance b/d | 40,000 |
| To bank | 10,000 |
|
|
|
|
| 40,000 |
|
| 40,000 |
Dr. Capital account Cr.
Particulars | W | S | T | Particulars | W | S | T |
| ₹ | ₹ | ₹ |
| ₹ | ₹ | ₹ |
To current a/c balance | 21,000 |
|
| By balance b/d | 1,50,000 | 1,00,000 | 60,000 |
To realisation a/c |
|
|
| By current a/c (balances) | 29,250 |
| 20,750 |
Furniture 1,500 Debtors 52,000 | 53,500 |
|
| By sundry creditors (taken over) | 28,000 |
|
|
To realisation a/c – scooter presented to W |
| 4,000 | 2,000 | By realisation a/c (profit) | 11,250 | 7,500 | 3,750 |
To balance b/d | 1,65,000 | 82,500 | 82,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2,18,500 | 1,07,500 | 84,500 |
| 2,18,500 | 1,07,500 | 84,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
To equity |
|
|
| By balance b/d | 1,65,000 | 82,500 | 82,500 |
Shares in T and co. ltd (in the ratio of final claims) | 1,50,000 | 75,000 | 75,000 |
|
|
|
|
To bank | 15,000 | 7,500 | 7,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1,65,000 | 82,500 | 82,500 |
| 1,65,000 | 82,500 | 82,500 |
Q30) The equal partner sheets A and M as of March 31, 2011 are as follows:
Liabilities | ₹ | Assets | ₹ |
Sundry creditors | 55,500 | Book debts | 60,000 |
Bank overdraft | 28,500 | Stock in trade | 42,000 |
Bills payable | 10,500 | Joint life policy – surrender value | 7,500 |
A’s capital | 33,000 | Office furniture | 1,500 |
M’s capital | 52,500 | Machinery and plant | 18,000 |
|
| Leasehold property | 22,500 |
|
| A’s drawing | 9,000 |
|
| M’s drawings | 3,000 |
|
| Profit and loss account | 16,500 |
|
|
|
|
| 1,80,000 |
| 1,80,000 |
The business continued until September 30, 2011, at which point a net profit of Rs 12,300 was obtained in half a year after the annual depreciation of 10% was amortized from the leasehold. On the other hand, general merchandise creditors were reduced by 12,000 rupees, bills payable by 2,925 rupees, and overdrafts by 3,000 rupees. Each partner's 6-month lottery reached 3,000 rupees. As of March 31, 2011, stock trading on September 30 was Rs 45,300, books and debt was Rs 46,200, and other assets that needed adjustments.
In December, the company took over the shares at a 5% discount and recorded debt at a 2.5% discount as of September 30th, based on G Ltd. I agree to sell my business to. The company pays 7,500 rupees. Profit for the period until December 31st, subject to a lottery of A for 2,000 rupees and M for 1,000 rupees for the three months until December 31st. The company does not take over joint life insurance. The company will take over all other assets and liabilities and pay 37,500 rupees for goodwill. The consideration is paid by paying 60,000 rupees in cash and the rest in preferred stock of 10 rupees each. Prepare an account to close the books.
A30)
Liabilities | ₹ | Assets | ₹ |
Sundry creditors | 43,500 | Book debts | 46,200 |
Bank overdraft | 25,500 | Stock in trade | 45,300 |
Bills payable | 7,575 | Joint life policy – surrender value | 7,500 |
A’s capital |
| Office furniture | 1,500 |
Balance on April 1, 2009 33,000 |
| Machinery and plant | 18,000 |
Less: drawings 12,000 |
| Leasehold property 22,500 |
|
= 21,000 |
| Less: 10% depreciation For 6 months 1,125 | 21,375 |
Less: loss up to 30th September (1/2) 2,100 | 18,900 |
|
|
M’s capital |
|
|
|
Balance on April 1, 2009 52,500 |
|
|
|
Less: drawings 6,000 |
|
|
|
= 46,500 |
|
|
|
Less: loss up to 30th September (1/2) 2,100 | 44,400 |
|
|
| 1,39,875 |
| 1,39,875 |
Assets taken over - | ₹ |
- Book debts - ₹46,200 less 2 ½ % | 45,045 |
- Stock - ₹ 45,300 less 5% | 43,035 |
- Office furniture | 1,500 |
- Machinery and plant | 18,000 |
- Leasehold property | 21,375 |
- Goodwill | 37,500 |
- Miscellaneous assets for profit up to 31st December Less: drawings (7,500 – 2,000 – 1,000) | 4,500 |
| 1,70,955 |
Less: liabilities taken over: |
|
- Sundry creditors | 43,500 |
- Bank overdraft | 25,500 |
- Bills payable | 5,575 |
| 76,575 |
Net assets to be paid for | 94,380 |
G Ltd. will pay ₹ 60,000 in cash and ₹ 34,380 in preference shares of ₹ 10 each, the number of shares being 3,438
Dr. Realisation account Cr.
2011 |
| ₹ | 2011 |
| ₹ |
Dec. 31 | To sundry assets: |
| Dec. 31 | By sundry creditors | 43,500 |
| Stock 65,000 |
|
| By bank overdraft | 25,500 |
| Machinery 18,000 |
|
| By bills payable | 7,575 |
| Furniture 6,000 |
|
| By G. ltd. – consideration | 94,380 |
| Book debts 1,80,000 |
|
| By bank (joint life policy realised) | 7,500 |
| Joint life policy 52,000 |
|
|
|
|
| Leasehold property 86,000 |
|
|
|
|
| Misc. Assets 4,500 | 1,44,375 |
|
|
|
| To profit transferred to: |
|
|
|
|
| A’s capital a/c 17,040 |
|
|
|
|
| M’s capital a/c 17,040 | 34,080 |
|
|
|
|
| 1,78,455 |
|
| 1,78,455 |
Dr. Cash account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2011 |
|
| 2011 |
|
|
Dec 31 | To realisation a/c - transfer | 3,70,000 | Sept 31 | By balance b/d | 25,500 |
| To realisation a/c - joint life policy realised | 7,500 | Dec 31 | By A’s capital | 24,970 |
| To G ltd. – cash received | 60,000 |
| By M’s capital | 42,530 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 93,000 |
|
| 93,000 |
Dr. Preference shares in G ltd. account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2011 |
|
| 2011 |
|
|
Dec 31 | To G ltd. | 34,380 | Dec 31 | By A’s capital | 12,720 |
|
|
|
| By M’s capital | 21,660 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 34,380 |
|
| 34,380 |
Dr. G ltd. account Cr.
|
| ₹ |
|
| ₹ |
2011 |
|
| 2011 |
|
|
Dec 31 | To realisation a/c – net assets taken over | 94,380 | Dec 31 | By bank | 60,000 |
|
|
|
| By preference shares in G ltd. | 34,380 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 94,380 |
|
| 94,380 |
Date | Particulars | A | M | Date | Particulars | A | M |
2011 |
| ₹ | ₹ | 2011 |
| ₹ | ₹ |
April 1 | To drawings | 9,000 | 3,000 | Apr 1 | By balance b/d | 33,000 | 52,500 |
April 1 | To P/L account | 8,250 | 8,250 | Sept 30 | By P/L account | 6,150 | 6,150 |
Sept 30 | To drawings | 3,000 | 3,000 | Dec 31 | By profit for 3 months up to Dec. 31 | 3,750 | 3,750 |
Dec 31 | To drawings | 2,000 | 1,000 | Dec 31 | By realisation a/c – profit | 17,040 | 17,040 |
Dec 31 | To balance b/d | 37,690 | 64,190 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 59,940 | 79,440 |
|
| 59,940 | 79,440 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dec 31 | To preference shares in G ltd | 12,720 | 21,660 | Dec 31 | By balance b/d | 37,690 | 64,190 |
Dec 31 | To bank | 24,970 | 42,530 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 37,690 | 64,190 |
|
| 37,690 | 64,190 |
Dr. Capital account Cr.
Notes: (1) The student should note the treatment of profit arising after September 30 and also of drawings. The entries to be made are:
Miscellaneous Assets* Dr. 7,500
(for profits)
To A's Capital Account 3,750
To B's Capital Account 3,750
(The assets arising out of profits after September, 30;
profits being credited to A and M.)
__________________________________________________________________________
A's Capital Account Dr. 2,000
M's Capital Account Dr. 1,000
To Miscellaneous Assets 3,000
(Drawings made by partners after September, 30, which
reduce the assets arising out of profits.)
__________________________________________________________________________
* The Miscellaneous Assets’ balance, ₹ 4,500, is then transferred to Realisation Account along with other assets.
(2) The preference shares, 3,438 in number, have been divided between 4 and M in the ratio of their final claims.
viz., A ₹ 37,690 and M ₹ 64,190. The calculations are—
A =  or 1,272 shares of & 10 each amounting to ₹ 12,720
or 1,272 shares of & 10 each amounting to ₹ 12,720
M =  or 2,166 shares of 2 10 each amounting to ₹ 21,660
or 2,166 shares of 2 10 each amounting to ₹ 21,660
The balances due to A and M have been paid in cash.