Unit 1
Management Accounting
Q1) Explain meaning of management accounting.
A1)
Meaning of Management Accounting:
The term management accounting consists of two phrases, "management" and "accounting". It is a study of the management aspects of accounting. This is a tool in the hands of management to make decisions. The focus of management accounting is to redesign accounting in a way that helps managers formulate policies and control their execution.
Management accounting has a recent origin. The term was first used in 1950 by a team of accountants who visited the United States under the auspices of the British-American Council on Productivity. The costing term did not mention the term "management accounting" before this research group visited. Fierce competition, large-scale production, dynamic development of technology, and the complexity of modern business have led to the development of management accounting-to solve many problems. Management accounting provides management with information to use as a basis for decision making.
J. Bati is used to describe management accounting as "accounting methods, systems, and techniques that, combined with special knowledge and capabilities, support management's mission to maximize profits or minimize losses. It is defined as "term".
Q2) Explain nature of management accounting.
A2)
Nature of Management Accounting
Management accounting is the latest division of accounting, but it may be considered partly science and partly art. It is the science of "quantification and summarization" of accounting data and the art of "interpretation".
Management accounting draws conclusions through the collection, processing, and objective analysis of data. Therefore, it relies on "progress and problem objectification and quantification". From this point of view, management accounting can be regarded as science.
However, management accounting also includes human judgment, impulses, whims, and prejudices, as evidenced by the inferences and conclusions drawn from the interpretation and analysis of data. The deduction must not be exactly scientific. The management accountant's personal judgment can have a significant impact on interpretation and deductions. From this point of view, management accounting can be regarded as an art.
As with all other social sciences, we can conclude that management accounting is partly science and partly art.
Characteristics of Management Accounting:
The purpose of management accounting is to record, analyze and present financial data to management. This helps you plan and execute your business systematically and effectively. The main features of management accounting are as follows.
(1) Provision of financial information: The main focus of management accounting is to provide management with financial information. Information is provided in a manner suitable for different levels of management for policy review and decision making.
(2) Analysis of cause and effect: Financial accounting is limited to displaying the income statement and balance sheet. Management accounting analyzes the causes and effects of the facts and numbers. If there is a loss, the cause of the loss is investigated. If there is a profit, the variables that affect the profit are also analyzed. Compare your profits with spending, sales, capital used, etc. and draw appropriate conclusions about the impact of these items on your profits.
(3) Use of special techniques and concepts: Controlling makes accounting data more useful and manageable using special techniques such as standard costing, budgeting, marginal costing, cash flows, cash flows, ratio analysis, and liability accounting. Each of these techniques or concepts is a tool that serves a specific purpose, such as analyzing and interpreting data or establishing control over operations.
(3) Use of special techniques and concepts: Management accounting uses special techniques such as standard cost accounting, budget management, marginal cost accounting, cash flow, cash flow, ratio analysis, and liability accounting to collect accounting data. It is more useful and useful for management. .. Each of these techniques or concepts is a tool that serves a specific purpose, such as analyzing and interpreting data or establishing control over operations.
(4) Decision-making: The main purpose of management accounting is to provide relevant information to management and make various important decisions. Historical information provides the basis for predicting future impacts, developing alternatives, and making decisions to select the most beneficial course of action.
(5) There is no set practice: Financial accounting has various established principles and rules in the creation of financial accounting. There are no such fixed rules in management accounting. The tools or techniques applied by management accounting are the same, but the application of these techniques varies from concern to concern and situation to situation.
The interpretation of the analyzed data depends on the person who uses it. The conclusions drawn from the application of the method depend on the intelligence and experience of the management account. The presentation of information depends on the requirements of your concern. All concern was applying the technology to meet that need.
(6) Achievement of purpose: Management accounting helps you achieve your company's goals. Based on historical information, adjust for future changes in predicates and set goals. The actual performance is recorded. A comparison is made between the actual result and the given result. If the performance deviates from the prescribed result, corrective action will be taken to achieve the predicted purpose. This is possible with the help of standard costing and budgetary management accounting techniques.
(7) Improvement of efficiency: The purpose of accounting is to provide information to improve efficiency. You can improve departmental or departmental efficiency by fixing goals or goals for a specific time period. Compare the actual performance with the target performance. The positive deviation is reviewed. Negative deviations are investigated to determine the cause. The methods and means of addressing the cause are analyzed and the goal is achieved. The process of modifying and achieving goals leads to a gradual improvement in overall efficiency.
(8) Forecast: Management accounting is involved in decision making for future implementations. This includes future forecasts and forecasts. This helps you plan and set goals.
(9) Providing information, not decisions: Management accounting provides financial information, not decisions. Therefore, management accounting is said to depend on management efficiency in utilizing information and making effective decisions.
Q3) Explain meaning and nature of management accounting.
A3)
Meaning of Management Accounting:
The term management accounting consists of two phrases, "management" and "accounting". It is a study of the management aspects of accounting. This is a tool in the hands of management to make decisions. The focus of management accounting is to redesign accounting in a way that helps managers formulate policies and control their execution.
Management accounting has a recent origin. The term was first used in 1950 by a team of accountants who visited the United States under the auspices of the British-American Council on Productivity. The costing term did not mention the term "management accounting" before this research group visited. Fierce competition, large-scale production, dynamic development of technology, and the complexity of modern business have led to the development of management accounting-to solve many problems. Management accounting provides management with information to use as a basis for decision making.
J. Bati is used to describe management accounting as "accounting methods, systems, and techniques that, combined with special knowledge and capabilities, support management's mission to maximize profits or minimize losses. It is defined as "term".
Nature of Management Accounting
Management accounting is the latest division of accounting, but it may be considered partly science and partly art. It is the science of "quantification and summarization" of accounting data and the art of "interpretation".
Management accounting draws conclusions through the collection, processing, and objective analysis of data. Therefore, it relies on "progress and problem objectification and quantification". From this point of view, management accounting can be regarded as science.
However, management accounting also includes human judgment, impulses, whims, and prejudices, as evidenced by the inferences and conclusions drawn from the interpretation and analysis of data. The deduction must not be exactly scientific. The management accountant's personal judgment can have a significant impact on interpretation and deductions. From this point of view, management accounting can be regarded as an art.
As with all other social sciences, we can conclude that management accounting is partly science and partly art.
Characteristics of Management Accounting:
The purpose of management accounting is to record, analyze and present financial data to management. This helps you plan and execute your business systematically and effectively. The main features of management accounting are as follows.
(1) Provision of financial information: The main focus of management accounting is to provide management with financial information. Information is provided in a manner suitable for different levels of management for policy review and decision making.
(2) Analysis of cause and effect: Financial accounting is limited to displaying the income statement and balance sheet. Management accounting analyzes the causes and effects of the facts and numbers. If there is a loss, the cause of the loss is investigated. If there is a profit, the variables that affect the profit are also analyzed. Compare your profits with spending, sales, capital used, etc. and draw appropriate conclusions about the impact of these items on your profits.
(3) Use of special techniques and concepts: Controlling makes accounting data more useful and manageable using special techniques such as standard costing, budgeting, marginal costing, cash flows, cash flows, ratio analysis, and liability accounting. Each of these techniques or concepts is a tool that serves a specific purpose, such as analyzing and interpreting data or establishing control over operations.
(3) Use of special techniques and concepts: Management accounting uses special techniques such as standard cost accounting, budget management, marginal cost accounting, cash flow, cash flow, ratio analysis, and liability accounting to collect accounting data. It is more useful and useful for management. .. Each of these techniques or concepts is a tool that serves a specific purpose, such as analyzing and interpreting data or establishing control over operations.
(4) Decision-making: The main purpose of management accounting is to provide relevant information to management and make various important decisions. Historical information provides the basis for predicting future impacts, developing alternatives, and making decisions to select the most beneficial course of action.
(5) There is no set practice: Financial accounting has various established principles and rules in the creation of financial accounting. There are no such fixed rules in management accounting. The tools or techniques applied by management accounting are the same, but the application of these techniques varies from concern to concern and situation to situation.
The interpretation of the analyzed data depends on the person who uses it. The conclusions drawn from the application of the method depend on the intelligence and experience of the management account. The presentation of information depends on the requirements of your concern. All concern was applying the technology to meet that need.
(6) Achievement of purpose: Management accounting helps you achieve your company's goals. Based on historical information, adjust for future changes in predicates and set goals. The actual performance is recorded. A comparison is made between the actual result and the given result. If the performance deviates from the prescribed result, corrective action will be taken to achieve the predicted purpose. This is possible with the help of standard costing and budgetary management accounting techniques.
(7) Improvement of efficiency: The purpose of accounting is to provide information to improve efficiency. You can improve departmental or departmental efficiency by fixing goals or goals for a specific time period. Compare the actual performance with the target performance. The positive deviation is reviewed. Negative deviations are investigated to determine the cause. The methods and means of addressing the cause are analyzed and the goal is achieved. The process of modifying and achieving goals leads to a gradual improvement in overall efficiency.
(8) Forecast: Management accounting is involved in decision making for future implementations. This includes future forecasts and forecasts. This helps you plan and set goals.
(9) Providing information, not decisions: Management accounting provides financial information, not decisions. Therefore, management accounting is said to depend on management efficiency in utilizing information and making effective decisions.
Q4) Explain difference between management and financial accounting.
A4)
What is financial accounting?
Financial accounting is the accounting department involved in summarizing, recording, and reporting financial transactions that arise from business concerns over a period of time. Financial accounting is used to create various financial statements that companies can use to show financial performance to different users of financial information such as creditors, investors, customers, and suppliers.
Management accounting
The purpose of management accounting is to assist the management in taking rational policy decisions and to evaluate the impact of its decisions and actions.
Points of difference | Financial accounting | Management accounting |
Aim | The main aim is to provide information to outside parties. Outside parties include creditors, investors, customers, etc. | Management of the company uses management accounting information to make informed business decisions |
Primary users | External (investors, governments, creditors, authorities) | Internal (managers of business, employees) |
Governing principles | Financial accounting statements are prepared based on ‘Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)’. | There is no standard basis for preparing management accounting statements. |
Time zone | The time horizon for financial accounting is ‘past’. | Current and future oriented |
Nature of information | Objective, auditable, reliable, consistent and precise | More subjective and judgmental, valid, relevant and accurate |
Scope | Highly aggregate information about the overall organization | Disaggregate information to support local decision |
Outputs | Financial accounting reports consist of profit and loss statements, balance sheet and cash flow statement. | Management accounting reports are the monthly, weekly or yearly analysis of products, geographies, functions, etc. |
Segment reporting | It is concerned with the whole business and it is an end in itself. | Segment reporting is the primary emphasis |
Perspective | It has a historical perspective | It has a futuristic perspective. |
Independent audit | Independent audit of financial accounting reports is mandatory in most countries. | There is no specific requirement for an independent audit. |
Behavioral implications | Concern about adequacy of disclosure | Concern about how reports will effect employees behaviour |
Q5) Explain difference between management, financial and cost accounting.
A5)
What is costing?
Costing, called the form of management accounting that companies use to classify, summarize, and analyze different costs, helps management make better decisions for cost control and cost savings. The main function of costing is said to be to adjust, record, and identify investment allocations that are appropriate for the investment in determining the cost of goods and services. It also helps present relevant data to administrators involved in searching for services, contracts, or shipping costs.
It also contains information related to production, distribution and sales costs.
What is financial accounting?
Financial accounting is the accounting department involved in summarizing, recording, and reporting financial transactions that arise from business concerns over a period of time. Financial accounting is used to create various financial statements that companies can use to show financial performance to different users of financial information such as creditors, investors, customers, and suppliers.
Management accounting
The purpose of management accounting is to assist the management in taking rational policy decisions and to evaluate the impact of its decisions and actions.
Points of difference | Financial accounting | Management accounting |
Aim | The main aim is to provide information to outside parties. Outside parties include creditors, investors, customers, etc. | Management of the company uses management accounting information to make informed business decisions |
Primary users | External (investors, governments, creditors, authorities) | Internal (managers of business, employees) |
Governing principles | Financial accounting statements are prepared based on ‘Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)’. | There is no standard basis for preparing management accounting statements. |
Time zone | The time horizon for financial accounting is ‘past’. | Current and future oriented |
Nature of information | Objective, auditable, reliable, consistent and precise | More subjective and judgmental, valid, relevant and accurate |
Scope | Highly aggregate information about the overall organization | Disaggregate information to support local decision |
Outputs | Financial accounting reports consist of profit and loss statements, balance sheet and cash flow statement. | Management accounting reports are the monthly, weekly or yearly analysis of products, geographies, functions, etc. |
Segment reporting | It is concerned with the whole business and it is an end in itself. | Segment reporting is the primary emphasis |
Perspective | It has a historical perspective | It has a futuristic perspective. |
Independent audit | Independent audit of financial accounting reports is mandatory in most countries. | There is no specific requirement for an independent audit. |
Behavioral implications | Concern about adequacy of disclosure | Concern about how reports will effect employees behaviour |
Cost Accounting | Financial Accounting |
Definition | |
Costing, called the form of management accounting that companies use to classify, summarize, and analyze different costs, helps management make better decisions for cost control and cost savings. | Financial accounting is the accounting department involved in summarizing, recording, and reporting financial transactions that arise from business concerns over a period of time. |
Type of Information documented | |
Document data related to the workforce and materials used in the manufacturing process | Document financial data |
Estimation of Stock | |
Stock value is estimated at cost | Stock value is estimated based on the net realizable value or the smaller value between costs |
Analysis of Profit | |
Profit is usually investigated for a particular job, batch, product, or procedure | Profit, income and expenses are investigated together for a particular period of time across trading concerns. |
Primary Objective | |
Cost management and reduction | To maintain a complete record of financial transactions |
Deals | |
This deals with estimates and this only deals with real values. Both actual data’s. | With financial transactions It's a number, not an estimate |
Scope | |
It is related to a particular one It includes all commercials product or service. | Organizational translation specific period . |
Parties Involved | |
This deals with the inside transactions within the department.
| Inter-party and external translation |
Financial Statement | |
Only one statement is created. P & L A / c and balance.That is, a statement of cost | Both sheets are available. |
Valuation of stocks | |
Stocks are valued at cost. | Market value or cost Whichever is lower is considered to be the value of stock. |
Nature | |
Not only that, it's related to history but Predetermined cost too. | Records only historical records. |
Classification | |
Clearly classify classification costs for fixed and variable costs | Not classified by this cost for fixed and variable costs. |
Legal Requirements | |
Requirements for complying with management law which has now become obligatory | Generally these accounts are required by the company, income tax law, etc.
|
Q6) Explain scope and duties of management accounting.
A6)
Scope of Management Accounting
The management accountant provides management with information related to business operations, both financial and non-financial. It is useful for short-term and long-term decisions. They require accounting knowledge and other studies such as management, industrial engineering, strategic management, and business economics in work and reporting. The scope of management accounting is to support the following:
- Effective performance measurement
- Cost management
- Budget plan
- Pricing, and
- Decision making by management.
The management accountant uses historical data and quotes to provide information. This helps you perform your day-to-day operations, plan your future operations, and develop your overall business strategy.
Duties of management accountant
The scope of duties of a management accountant depends on the needs of management. Here, we will explain five of them.
- Capital budget
- Product costing
- Margin analysis
- Constraint analysis
- Trend analysis
Capital budget
Management accounting uses some standard capital budget measures for decision making. The internal rate of return (IRR) and net present value (NPV) methods are two examples. These methods help you make long-term investment decisions such as buying new machines, replacing old machines, new factories, or acquiring companies. Usually, the management accountant reviews the proposal, decides if it is the best investment option, and finds the right way to fund the purchase. It also outlines revenue and timeframes so management can predict future economic returns.
To determine the source of investment funds, you need to create details about each source (debt, capital, or retained earnings). In addition, the management objectives of the capital structure are important considerations in deciding on appropriate financing.
Product costing
The management accountant determines the actual cost of the product or service. Costs fall into several groups, including variable costs, fixed costs, direct costs, and overhead costs. You then calculate these costs and assign them to your products using several methods, such as full costing or variable costing.
Product costing is essential for planning different business strategies. Management uses this information to make product pricing and promotional budget decisions.
Margin analysis
Margin analysis includes analysis of additional profits from increased production. In this case, the management accountant determines the best point between production, sales, revenue, and profit.
You may use break-even analysis to calculate the contribution margin of your sales structure. Its purpose is to determine the number of units whose revenue is equal to its cost. This information will help you determine the price of your product or service.
Constraint analysis
The management accountant analyzes the constraints that can occur in the operation of the company, from the production process to sales. Then identify the cause of the problem and calculate its impact on your company's revenue, profits, and cash flow. Since various fields are involved, technical knowledge is required.
Trend analysis
This includes reviewing operational cost trends and investigating anomalous variants or deviations. Accountants use the information from the previous period to calculate and forecast future financial and operational information, including:
- Selling price
- Sales volume
- Advertising budget
- Get Capital investment
- Cash flow
Q7) Explain duties of management accounting.
A7)
Duties of management accountant
The scope of duties of a management accountant depends on the needs of management. Here, we will explain five of them.
- Capital budget
- Product costing
- Margin analysis
- Constraint analysis
- Trend analysis
Capital budget
Management accounting uses some standard capital budget measures for decision making. The internal rate of return (IRR) and net present value (NPV) methods are two examples. These methods help you make long-term investment decisions such as buying new machines, replacing old machines, new factories, or acquiring companies. Usually, the management accountant reviews the proposal, decides if it is the best investment option, and finds the right way to fund the purchase. It also outlines revenue and timeframes so management can predict future economic returns.
To determine the source of investment funds, you need to create details about each source (debt, capital, or retained earnings). In addition, the management objectives of the capital structure are important considerations in deciding on appropriate financing.
Product costing
The management accountant determines the actual cost of the product or service. Costs fall into several groups, including variable costs, fixed costs, direct costs, and overhead costs. You then calculate these costs and assign them to your products using several methods, such as full costing or variable costing.
Product costing is essential for planning different business strategies. Management uses this information to make product pricing and promotional budget decisions.
Margin analysis
Margin analysis includes analysis of additional profits from increased production. In this case, the management accountant determines the best point between production, sales, revenue, and profit.
You may use break-even analysis to calculate the contribution margin of your sales structure. Its purpose is to determine the number of units whose revenue is equal to its cost. This information will help you determine the price of your product or service.
Constraint analysis
The management accountant analyzes the constraints that can occur in the operation of the company, from the production process to sales. Then identify the cause of the problem and calculate its impact on your company's revenue, profits, and cash flow. Since various fields are involved, technical knowledge is required.
Trend analysis
This includes reviewing operational cost trends and investigating anomalous variants or deviations. Accountants use the information from the previous period to calculate and forecast future financial and operational information, including:
- Selling price
- Sales volume
- Advertising budget
- Get Capital investment
- Cash flow
Q8) Explain tools and techniques of management accounting.
A8)
The tools and techniques used in Management Accounting are described below.
(1) Financial policy and accounting: All business concerns are planned for their sources of funding. The use of a particular source of funding depends on the service costs of that source of funding, the terms of repayment in the case of borrowing, and so on. The amount of stock capital raised and the legal definition of repayment will be taken into account. The capital structure, that is, the ratio of equity capital to borrowings, must be determined to have an optimal capital structure. Management accounting provides a capital budgeting method for financial planning.
(2) Analysis of financial statements: Analyzing financial statements is a means of classifying and presenting data in a way that is useful to management. The importance of the information provided is explained in non-technical languages in the form of ratio analysis, cash flow, and cash flow methods.
(3) Acquisition cost accounting: Expenses are recorded after they are incurred to compare with a given goal to assess performance.
(4) Budget management: Budgets are used as a tool for planning and management. Expenditures and income are predetermined. Performance is compared to the budget, revealing deviations and who is responsible for them. Corrective actions will be initiated to eliminate future negative deviations.
(5) Standard costing: In standard costing, systematic analysis predetermines costs. The actual cost is compared to the standard. Analyze the differences to identify the cause and take steps to eliminate the differences and increase efficiency. Standard costing is commonly used in conjunction with budgetary control to effectively manage operations.
(6) Marginal cost: At marginal cost, product costs are divided into fixed and variable parts. Variable costs are used for decision making, but fixed costs are treated as period costs charged in the income statement. Marginal costs help management make a variety of important decisions.
(7) Other tools for management accounting are as follows.
(A) Decision accounting: Here, alternatives are evaluated for choice in the decision-making situation.
(B) Revaluation accounting: This applies to the exchange of fixed assets whose prices rise over time. Here we are addressing the impact of inflation on fixed assets.
(C) Management accounting: Controlled accounting uses internal checks, internal audits and statutory audits.
(8) Management information system: An important function of management accounting is reporting. This feature has been improved in consideration with the development of electronic data processing systems. In modern enterprises, the process of making information available for management is integrated and computer-based, known as the "Management Information System" (MIS).
6. Installation of management accounting system: Installing the Controlling System involves the following steps:
(1) Organization manual: The first step is to prepare your organization's manual. This manual clearly demonstrates the obligations and responsibilities of managers at each level and the horizontal and vertical relationships between key personnel.
(2) Creating various forms and reports: The second step in the installation process is to design the execution of various reports. The purpose is to minimize and simplify their underscores to avoid "bureaucratization".
(3) Necessary staffing: You need to hire and train the staff needed to deploy the system.
(4) Account classification: Treasury and cost accounts should be categorized, limited, and integrated as much as possible to meet management accounting requirements.
(5) Establishment of cost center: Investment centers, profit centers, cost centers, and budget centers must be clearly configured to collect and analyze information in their respective contexts.
(6) Introduction of management accounting method: Various methods of management accounting are introduced based on the needs and feasibility of the company.
(7) Provision of usage of "operations research" (O.R) method: As businesses operate in a changing economic, political and social environment, they face new challenges every day.
7. Management accounting organization: The organization of the management accounting system depends on the scale of business, the nature of the business, the nature of the organization, and so on. A minor concern is that the Treasurer is directly under the owner. A major concern is that management accounting may be assigned to financial managers.
Concerns about establishing a department will have a different management organization. The role of management accountant is emphasized by Anderson, and Schmidt management accounting is of particular concern. When it comes to the issue of collaboration with everything else, no other functional element across the organization has the necessary relationships with so many different departments.
Management accounts relate to different levels of managers, supervisors, and operators in all sections of business operations.
An organizational chart for a large-scale concern is given below:
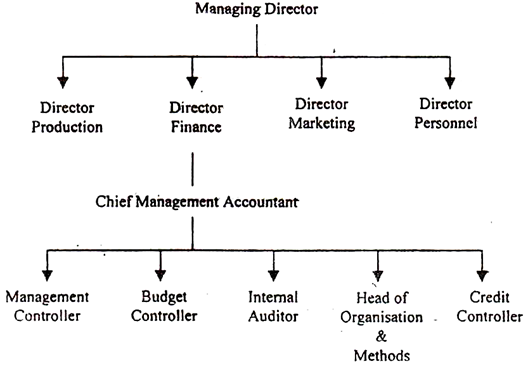
In the organizational chart, the director's finances are placed above the Chief Accountant. All functions such as budgeting, auditing, O & M, and credit management are under the control of the Chief Accountant.
Advantages/ Merits/ Uses of Management Accounting:
Management accounting has immeasurable value and usefulness for the management of any company, and has been considered essential, especially for large organizations with complex management tasks. The benefits or uses of management accounting can be listed below.
(1) Improvement of efficiency: Management accounting greatly contributes to improving the operational efficiency of a company. Budgets, standards, reports, etc. usually increase the level of performance.
(2) Effective planning: Through the "decision-making data" provided by management accounting, policy development and operational planning become more effective.
(3) Performance evaluation: Performance evaluation of employees, departments, etc. is facilitated by management accounting based on difference analysis and management ratio.
(4) Maximizing profits: Management accounting helps in profit planning to pursue profit-optimizing decisions.
(5) Reliability: Tools used in management accounting typically make the data provided for management accurate and reliable.
(6) Elimination of waste: Standard costs, budgets, cost control methods, etc. contribute to the elimination of waste and the production of defective products.
(7) Effective communication: Regular and systematic reporting ensures a continuous flow of operational information to different levels of administrators.
(8) Employee morale: Employee morale can be created and maintained through achievable standards, practical budgets, and incentive schemes.
9) Management and coordination: Managing costs and adjustments in efforts in different segments of your organization can be achieved through performance reports, variance analysis, follow-up actions, and more.
The greatest advantage of management accounting is its advisory role in helping managers makes the best possible decisions on a daily basis on everyday issues and important policy issues.
Q9) Explain the advantages of management accounting.
A9)
Advantages/ Merits/ Uses of Management Accounting:
Management accounting has immeasurable value and usefulness for the management of any company, and has been considered essential, especially for large organizations with complex management tasks. The benefits or uses of management accounting can be listed below.
(1) Improvement of efficiency: Management accounting greatly contributes to improving the operational efficiency of a company. Budgets, standards, reports, etc. usually increase the level of performance.
(2) Effective planning: Through the "decision-making data" provided by management accounting, policy development and operational planning become more effective.
(3) Performance evaluation: Performance evaluation of employees, departments, etc. is facilitated by management accounting based on difference analysis and management ratio.
(4) Maximizing profits: Management accounting helps in profit planning to pursue profit-optimizing decisions.
(5) Reliability: Tools used in management accounting typically make the data provided for management accurate and reliable.
(6) Elimination of waste: Standard costs, budgets, cost control methods, etc. contribute to the elimination of waste and the production of defective products.
(7) Effective communication: Regular and systematic reporting ensures a continuous flow of operational information to different levels of administrators.
(8) Employee morale: Employee morale can be created and maintained through achievable standards, practical budgets, and incentive schemes.
9) Management and coordination: Managing costs and adjustments in efforts in different segments of your organization can be achieved through performance reports, variance analysis, follow-up actions, and more.
The greatest advantage of management accounting is its advisory role in helping managers makes the best possible decisions on a daily basis on everyday issues and important policy issues.
Q10) Difference between cost accounting and financial accounting.
A10)
Cost Accounting | Financial Accounting |
Definition | |
Costing, called the form of management accounting that companies use to classify, summarize, and analyze different costs, helps management make better decisions for cost control and cost savings. | Financial accounting is the accounting department involved in summarizing, recording, and reporting financial transactions that arise from business concerns over a period of time. |
Type of Information documented | |
Document data related to the workforce and materials used in the manufacturing process | Document financial data |
Estimation of Stock | |
Stock value is estimated at cost | Stock value is estimated based on the net realizable value or the smaller value between costs |
Analysis of Profit | |
Profit is usually investigated for a particular job, batch, product, or procedure | Profit, income and expenses are investigated together for a particular period of time across trading concerns. |
Primary Objective | |
Cost management and reduction | To maintain a complete record of financial transactions |
Deals | |
This deals with estimates and this only deals with real values. Both actual data’s. | With financial transactions It's a number, not an estimate |
Scope | |
It is related to a particular one It includes all commercials product or service. | Organizational translation specific period . |
Parties Involved | |
This deals with the inside transactions within the department.
| Inter-party and external translation |
Financial Statement | |
Only one statement is created. P & L A / c and balance.That is, a statement of cost | Both sheets are available. |
Valuation of stocks | |
Stocks are valued at cost. | Market value or cost Whichever is lower is considered to be the value of stock. |
Nature | |
Not only that, it's related to history but Predetermined cost too. | Records only historical records. |
Classification | |
Clearly classify classification costs for fixed and variable costs | Not classified by this cost for fixed and variable costs. |
Legal Requirements | |
Requirements for complying with management law which has now become obligatory | Generally these accounts are required by the company, income tax law, etc.
|