Unit-III
Cost Accounting
Question and answers
Q1.Define Labour Cost.
Ans. Labor is an important element of production. It is a human resource and participates in the process of production. Wages paid for labor are an important cost item. Labor costs need to distinguish between direct and indirect labor. Direct labor costs can be directly identified and billed by product or job, but overhead costs are less identifiable and are included in overhead costs that may be assigned to different products or departments on appropriate criteria. Labor costing has three main purposes.
1. Determining labor costs in terms of product or service costs
2. Report labor costs for planning and management
3. Report labor costs for decision making.
Q2. What is Labor management?
Ans. Labor costs are an important part of total production costs. Therefore, labor costs and labor costs need to be managed effectively. Various departments contribute to the efficient use of the workforce and the proper management of costs. The HR department needs to provide an efficient workforce. The engineering department maintains control over the working conditions and production methods of each job and department or process by creating plans and specifications. The time management department keeps an accurate record of the time each employee spends. Payroll preparation from the clock card, job or time ticker, or timesheet is done by the payroll department. The costing department is responsible for accumulating and classifying all data for which labor costs are one of the most important items.
Personnel costs represent human contribution. Labor costs are inherently sensitive. The reason is that labor costs are entirely based on human behavior, labor behavior. To manage labor costs, it is necessary to manage labor behavior. Therefore, managers need to study human behavior, labor performance, time and movement studies, labor turnover, and labor approaches to manage labor costs.
The workforce cannot be saved for future reference. It is very similar to the perishable nature of the material. Some materials are of poor quality and may not be used for manufacturing purposes. Such materials are wasted. Similarly, once the workforce is lost, it cannot be recovered and cannot be used effectively in the next few days.
If the work is kept idle, management will have to pay compensation or wages for such idle time. Therefore, management suffered two losses. They are lost working hours and lost money. Therefore, management is very enthusiastic about managing labor costs.
Classification of labor costs
Labor costs can be categorized as follows.
1. Direct labor costs
Direct labor costs are part of salary or wages and can be identified and billed by a single unit price of production.
Characteristics of direct labor costs:
Direct labor costs have the following characteristics.
- It has a direct relationship to the product, process, or cost unit.
- It can be measured quantitatively.
- A sufficient amount of material.
2. Indirect labor costs
Even if it occurs directly, it cannot be identified in the production of goods or services. These costs are incurred at the production site. Some cost centers may serve production departments or production activities. These cost centers are responsible for purchasing, engineering, and time management.
3. Manageable labor costs
Labor costs can be managed by managers during production and even when there is no production. Standard hours and hourly rates are fixed and workers can be required to complete a job or order within such time. That way, labor costs can be reduced to some extent.
4. Uncontrollable labor costs
Labor costs that management cannot easily control. Jobs and orders can be completed by a group of workers. The efficiency of such labor groups is inherently different. Workers can maximize their efficiency according to the general environment of the product location. If so, costs cannot be controlled by management.
Q3. How do we calculate Labour Cost?
Ans. Techniques for managing labor costs can be effectively used by coordinating the activities of various labor-related departments.
(A) Human Resources Department
(B) Engineering and Operations Research Division
(C) Timekeeping department
(D) Payroll department and
(E) Cost accounting department.
(A) Human Resources Department:
The Board of Directors has policies regarding recruitment, training, placement, transfer and promotion of employees. The Human Resources Manager of the Human Resources Department must implement these policies. The main functions of this department are recruitment, training, and placement of workers in the right jobs.
The Human Resources department recruits workers when it receives employee placement requests from various departments
B) Engineering and Operations Research Division:
Preface:
This department is working to improve working conditions by carrying out the following activities.
(1) Conduct work studies such as method study, exercise study, and time study for each operation.
(2) Maintain the necessary safety standards.
(3) Perform job analysis and job evaluation.
(4) Prepare the specifications and time schedule for each job.
(5) Devise an appropriate wage system and
(6) Implementation of research and experimental work.
The engineering department is basically responsible for work content, standard time, work performance, and so on. These are achieved by performing detailed work studies, including method studies, motion studies, and time studies.
(C) Time management department:
This department is concerned with maintaining worker attendance and working hours. Attendance time is recorded for wage calculation, and job time or time reservations are spent on each department, job, operation, and process to calculate labor costs for each department, job, and each process and operation. It will be considered to calculate the time taken
(D) Payroll Preparation:
A department salary or wage table is created based on the time card. A full-fledged payroll shows total wages, various deductions, and net wages. Payroll is the basis for checking wages and posting entries to various management accounts. Payroll details depend on your organization's requirements.
(E) Cost accounting department:
The department is responsible for ensuring the correct production costs. Cost verification includes classification, collection, and calculation of output labor costs. In most organizations, cost department representatives
Posted to the manufacturing department to accumulate and categorize costs. The cost calculator oversees the work of the representative and uses the information contained in the timecard and payroll to find the labor costs of manufacturing by manufacturing department, operations, manufacturing instructions, and so on.
The costing department also analyses labor costs in the form of idle time and overtime. A labor cost report is also submitted to management to show the effectiveness of labor use.
Q4.What are the types of incentive wage systems?
Ans. There are the following types of incentive wage systems:
1. Halsey Premium Plan
2. Rowan Premium Plan
3. Taylor Differential Peace Rate System
4. Gantt Bonus Plan
5. Emerson Efficiency Plan
6. Bedo Point Premium
7. Merrick Differential Wage Multi-Piece Rate Plan
8. 100% bonus plan.
Q5. Write short note on Halsey Premium Plan.
Ans. Halsey Premium Plan was introduced in 1891 by American engineer F. A. Halsey. Recognize your personal efficiency and pay bonuses based on the lime saved. In this way, workers are paid at the rate of the hours they actually worked and are also paid a bonus if they can complete the work in less time than the time allotted to do the work.
Bonuses are paid at a fixed percentage of the time saved, usually 50% (although the percentage varies from 30% to 70% of the time saved). The remaining 50% of the time saved will be shared by the employer.
Therefore,
Total revenue = T.T. × H.R. + 50% (T.S. × H.R.)
Here, T.T. = Time required
H.R. = hourly wage
T.S. = Time saved
The main advantages of this method are:
(I) the method is simple to operate and easy to understand.
(II) Late workers are not punished because hourly wages are guaranteed.
(III) Provide incentives for more efficient workers.
(IV) Worker efficiency means reducing costs per unit.
(V) The benefits of time savings are shared equally between employers and employees.
The main drawbacks of this method are:
(I) many employee organizations do not like to share the benefits of time savings equally.
(II) Attracting bonuses reduces the quality of work.
(III) Poor quality means more waste, potential for corruption, defects and failures, and more oversight costs.
(IV) Not as attractive as peace rate payments.
(V) There are few incentives for workers compared to other incentive plans.
(VI) This can lead to higher bonuses if the time rate is not fixed properly.
Halsey-Weir Premium Scheme:
This scheme was introduced by Weir Ltd. In Glasgow around 1900. This scheme is similar to the Halsey scheme, except that employees get 33⅓% (often 30%) of the time saved as a bonus and the remaining 66⅔% is paid to the employer. ..
Therefore:
Total revenue = T.T. × H.R. + 33⅓% (T.S. × H.R.)
Here, T.T. = Time required
H.R. = hourly wage
T.S. = Time saved
Q6.How can we Compare Halsey and Rowan schemes?
Ans. Comparison of Halsey and Rowan schemes:
(1) With savings of up to 50%, premiums will be the same for the two schemes.
(2) In the Rowan scheme, the bonus rises faster than in the Halsey scheme until the job runs in half the standard time.
(3) However, if the work takes less than half the standard time, both the Halsey system premium and the total income will be higher than the Rowan system premium.
(4) On the other hand, if the work time exceeds half of the standard time, both the bonus and total income of the Rowan scheme will be larger than that of the Halsey scheme.
(5) The Halsey scheme provides more incentives to speed up production, but after certain stages there is an automatic check under the Rowan scheme.
(6) The Halsey scheme turns out to be costly if more than half the time is saved, while the Rowan scheme is costly if less than half the standard time is saved.
Q7. Explain Taylor's Differential Peace Rate System.
Ans. Differential Peace Rate system was first introduced by F.W. Taylor, the father of scientific management. This system does not provide a minimum guaranteed hourly wage. However, in this system, the two piece rates are fixed.
(A) Workers are paid a low peace rate for substandard production
(B) Higher fees are paid to workers who produce above the standard. Therefore, this system penalizes inefficient workers and rewards efficient workers.
Worker efficiency can be determined as one of the following percentages:
(I) from the time allowed for the job to the time actually taken, or
(II) From the actual output within the specified time to the standard output.
Q8. Explain overhead classification.
Ans. The process of grouping overheads according to common characteristics is known as overhead classification. It provides managers with information that allows them to effectively manage their business. Overhead can be categorized as follows:
a. Elements: indirect materials, labor costs;
b. Function: Expenses for production, management, sales and distribution.
c. Behavior: Fixed, variable, and semi-variable overhead.
1. Fixed overhead remains fixed and is not affected by changes in production levels. For example, rent, fees, salaries, statutory expenses, etc.
2. Variable overhead costs change in direct proportion to changes in production, such as indirect materials, fuel, electricity, stationery, and sales staff commissions.
3. Semi-variable overhead costs are partially fixed and partially variable costs. They remain fixed to production volume and change when production exceeds a certain volume. For example, telephone charges include machine depreciation, repair and maintenance, and supervision costs.
Collection of expenses and codification
Overhead is collected and systematized under the appropriate head. Similar overhead items should be grouped. Overhead grouping is done by a technique called "Codification". This is a way to identify and describe various expenses with numbers, letters, or a combination of both, making it easy to collect cost data. The coding of the entire item is done through a proper coding system. Expenses are collected through store requests, financial accounting, wage tables, registries, and report sources.
Q9. Define Overhead allocation.
Ans. Overhead allocation is the allocation of all items of costs to cost centers or costs to units. This refers to the billing of overhead costs to the cost center. This means that overhead was incurred due to the existence of that cost center. If a company offers multiple products, factory overhead is allocated to different production departments or cost centers. Appropriate overhead allocation is very important because incorrect allocations can distort income decisions, asset valuations, and performance valuations. The overhead allocation process is as follows:
I. Accumulate overhead costs based on department or product.
Ii. Identify cost targets for assigned costs
Iii. Choose how to associate such accumulated costs with cost goals.
Q10. Explain with the help of diagram the Wage analysis.
Ans. The wages charged for various jobs are shown on an analysis sheet called the Wage Analysis Sheet. This is suitable if your company is small and the number of jobs running is small. If you have a lot of work, as in a large company, the timesheet will pre-list the total labor costs and agree with a payroll overview.
The wage summary decisions are as follows:
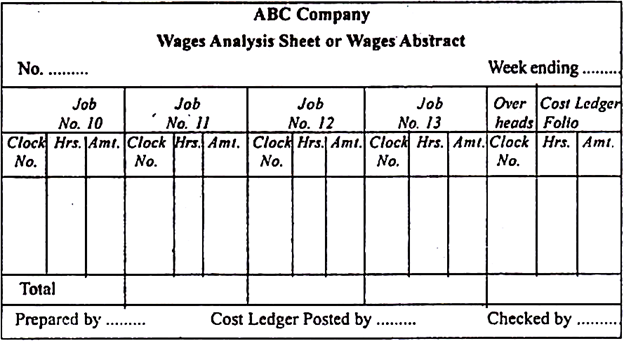
The analysis sheet shows the labor costs for various jobs and the overhead costs charged as overhead costs.