UNIT 1
Computer & Operating System
- What is computer explain in detail?
Being a modern-day kid you must have used, seen, or read about computers. This is because they are an integral part of our everyday existence. Be it school, banks, shops, railway stations, hospital or your own home, computers are present everywhere, making our work easier and faster for us. As they are such integral parts of our lives, we must know what they are and how they function. Let us start with defining the term computer formally.
The literal meaning of computer is a device that can calculate. However, modern computers can do a lot more than calculate. Computer is an electronic device that receives input, stores or processes the input as per user instructions and provides output in desired format.
Input-Process-Output Model
Computer input is called data and the output obtained after processing it, based on user’s instructions is called information. Raw facts and figures which can be processed using arithmetic and logical operations to obtain information are called data.

The processes that can be applied to data are of two types −
- Arithmetic operations − Examples include calculations like addition, subtraction, differentials, square root, etc.
- Logical operations − Examples include comparison operations like greater than, less than, equal to, opposite, etc.
The corresponding figure for an actual computer looks something like this −
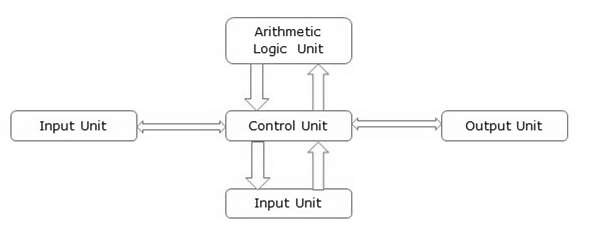
The basic parts of a computer are as follows −
- Input Unit − Devices like keyboard and mouse that are used to input data and instructions to the computer are called input unit.
- Output Unit − Devices like printer and visual display unit that are used to provide information to the user in desired format are called output unit.
- Control Unit − As the name suggests, this unit controls all the functions of the computer. All devices or parts of computer interact through the control unit.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit − This is the brain of the computer where all arithmetic operations and logical operations take place.
- Memory − All input data, instructions and data interim to the processes are stored in the memory. Memory is of two types – primary memory and secondary memory. Primary memory resides within the CPU whereas secondary memory is external to it.
Control unit, arithmetic logic unit and memory are together called the central processing unit or CPU. Computer devices like keyboard, mouse, printer, etc. that we can see and touch are the hardware components of a computer. The set of instructions or programs that make the computer function using these hardware parts are called software. We cannot see or touch software. Both hardware and software are necessary for working of a computer.
Advantages of Using Computer
Now that we know the characteristics of computers, we can see the advantages that computers offer−
- Computers can do the same task repetitively with same accuracy.
- Computers do not get tired or bored.
- Computers can take up routine tasks while releasing human resource for more intelligent functions.
Disadvantages of Using Computer
Despite so many advantages, computers have some disadvantages of their own −
- Computers have no intelligence; they follow the instructions blindly without considering the outcome.
- Regular electric supply is necessary to make computers work, which could prove difficult everywhere especially in developing nations.
Booting
Starting a computer or a computer-embedded device is called booting. Booting takes place in two steps −
- Switching on power supply
- Loading operating system into computer’s main memory
- Keeping all applications in a state of readiness in case needed by the user
The first program or set of instructions that run when the computer is switched on is called BIOS or Basic Input Output System. BIOS is a firmware, i.e. a piece of software permanently programmed into the hardware.
If a system is already running but needs to be restarted, it is called rebooting. Rebooting may be required if a software or hardware has been installed or system is unusually slow.
There are two types of booting −
- Cold Booting − When the system is started by switching on the power supply it is called cold booting. The next step in cold booting is loading of BIOS.
- Warm Booting − When the system is already running and needs to be restarted or rebooted, it is called warm booting. Warm booting is faster than cold booting because BIOS is not reloaded.
2. Write classification of computer
Computer scan is broadly classified by their speed and computing power.
Sr.No. | Type | Specifications |
1 | PC (Personal Computer) or Micro-Computers | It is a single user computer system having a moderately powerful microprocessor. It is termed as a computer that is equipped microprocessor as its CPU. |
2 | Workstation | It is also a single user computer system, similar to the personal computer, however, has a more powerful microprocessor. |
3 | Mini-Computer | It is a multi-user computer system, capable of supporting hundreds of users simultaneously. |
4 | Main Frame | It is a multi-user computer system, capable of supporting hundreds of users simultaneously. Software technology is different from minicomputer. |
5 | Super-Computer | It is an extremely fast computer, which can execute hundreds of millions of instructions per second. |
PC (Personal Computer)

A PC can be defined as a small, relatively inexpensive computer designed for an individual user. PCs are based on the microprocessor technology that enables manufacturers to put an entire CPU on one chip. Businesses use personal computers for word processing, accounting, desktop publishing, and for running spreadsheet and database management applications. At home, the most popular use for personal computers is playing games and surfing the Internet.
Although personal computers are designed as single-user systems, these systems are normally linked together to form a network. In terms of power, nowadays high-end models of the Macintosh and PC offer the same computing power and graphics capability as low-end workstations by Sun Microsystems, Hewlett-Packard, and Dell.
Workstation

The workstation is a computer used for engineering applications (CAD/CAM), desktop publishing, software development, and other such types of applications which require a moderate amount of computing power and relatively high-quality graphics capabilities.
Workstations generally come with a large, high-resolution graphics screen, a large amount of RAM, inbuilt network support, and a graphical user interface. Most workstations also have mass storage device such as a disk drive, but a special type of workstation, called diskless workstations, comes without a disk drive.
Common operating systems for workstations are UNIX and Windows NT. Like PC, workstations are also single-user computers like PC but are typically linked together to form a local area network, although they can also be used as stand-alone systems.
Minicomputer
It is a midsize multi-processing system capable of supporting up to 250 users simultaneously.

Mainframe
The mainframe is very large in size and is an expensive computer capable of supporting hundreds or even thousands of users simultaneously. Mainframe executes many programs concurrently and supports much simultaneous execution of programs.

Supercomputer
Supercomputers are one of the fastest computers currently available. Supercomputers are very expensive and are employed for specialized applications that require an immense amount of mathematical calculations (number-crunching).

For example, weather forecasting, scientific simulations, (animated)graphics, fluid dynamic calculations, nuclear energy research, electronic design, and analysis of geological data (e.g. In petrochemical prospecting).
3. Explain CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Central Processing Unit (CPU) consists of the following features −
- CPU is considered as the brain of the computer.
- CPU performs all types of data processing operations.
- It stores data, intermediate results, and instructions (program).
- It controls the operation of all parts of the computer.

CPU itself has following three components.
- Memory or Storage Unit
- Control Unit
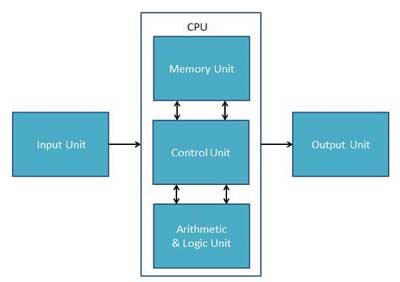 ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
Memory or Storage Unit
This unit can store instructions, data, and intermediate results. This unit supplies information to other units of the computer when needed. It is also known as internal storage unit or the main memory or the primary storage or Random Access Memory (RAM).
Its size affects speed, power, and capability. Primary memory and secondary memory are two types of memories in the computer. Functions of the memory unit are −
- It stores all the data and the instructions required for processing.
- It stores intermediate results of processing.
- It stores the final results of processing before these results are released to an output device.
- All inputs and outputs are transmitted through the main memory.
Control Unit
This unit controls the operations of all parts of the computer but does not carry out any actual data processing operations.
Functions of this unit are −
- It is responsible for controlling the transfer of data and instructions among other units of a computer.
- It manages and coordinates all the units of the computer.
- It obtains the instructions from the memory, interprets them, and directs the operation of the computer.
- It communicates with Input/output devices for transfer of data or results from storage.
- It does not process or store data.
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
This unit consists of two subsections namely,
- Arithmetic Section
- Logic Section
Arithmetic Section
Function of arithmetic section is to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. All complex operations are done by making repetitive use of the above operations.
Logic Section
Function of logic section is to perform logic operations such as comparing, selecting, matching, and merging of data.
4. Explain Computer Registers
Registers are a type of computer memory used to quickly accept, store, and transfer data and instructions that are being used immediately by the CPU. The registers used by the CPU are often termed as Processor registers.
A processor register may hold an instruction, a storage address, or any data (such as bit sequence or individual characters).
The computer needs processor registers for manipulating data and a register for holding a memory address. The register holding the memory location is used to calculate the address of the next instruction after the execution of the current instruction is completed.
Following is the list of some of the most common registers used in a basic computer:
Register | Symbol | Number of bits | Function |
Data register | DR | 16 | Holds memory operand |
Address register | AR | 12 | Holds address for the memory |
Accumulator | AC | 16 | Processor register |
Instruction register | IR | 16 | Holds instruction code |
Program counter | PC | 12 | Holds address of the instruction |
Temporary register | TR | 16 | Holds temporary data |
Input register | INPR | 8 | Carries input character |
Output register | OUTR | 8 | Carries output character |
The following image shows the register and memory configuration for a basic computer.
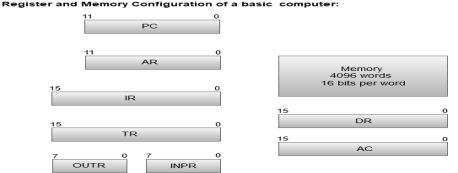
- The Memory unit has a capacity of 4096 words, and each word contains 16 bits.
- The Data Register (DR) contains 16 bits which hold the operand read from the memory location.
- The Memory Address Register (MAR) contains 12 bits which hold the address for the memory location.
- The Program Counter (PC) also contains 12 bits which hold the address of the next instruction to be read from memory after the current instruction is executed.
- The Accumulator (AC) register is a general purpose processing register.
- The instruction read from memory is placed in the Instruction register (IR).
- The Temporary Register (TR) is used for holding the temporary data during the processing.
- The Input Registers (IR) holds the input characters given by the user.
- The Output Registers (OR) holds the output after processing the input data.
5. Explain Bus architecture
- Bus is a communication channel.
- Characteristic of bus is shared transmission media.
- Limitation of a bus is only one transmission at a time.
- A bus which is used to provide the communication between the major components of a computer is called as System bus.
Computer:
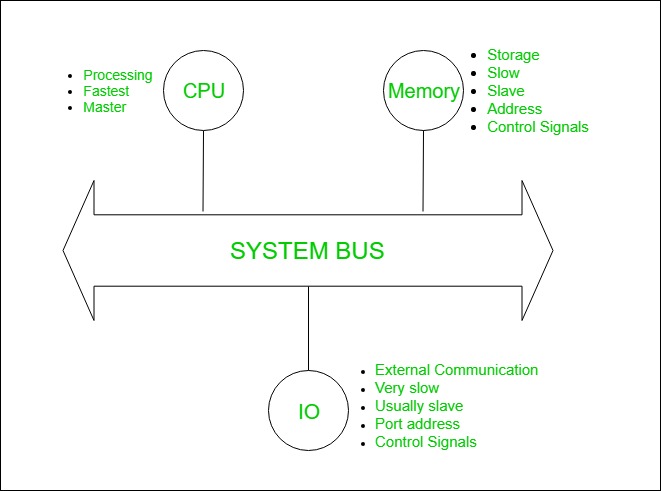
System bus contains 3 categories of lines used to provide the communication between the CPU, memory and IO named as:
1. Address lines (AL)
2. Data lines (DL)
3. Control lines (CL)
1. Address Lines:
- Used to carry the address to memory ad IO.
- Unidirectional.
- Based on width of a address bus we can determine the capacity of a main memory
Example:
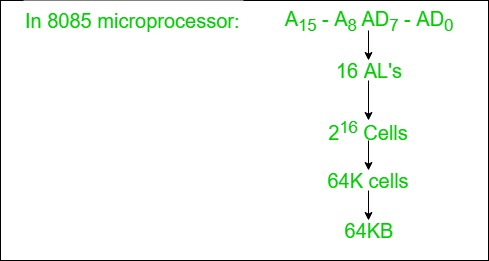
2. Data Lines:
- Used to carry the binary data between the CPU, memory and IO.
- Bidirectional.
- Based on the width of a data bus we can determine the word length of a CPU.
- Based on the word length we can determine the performance of a CPU.
Example:
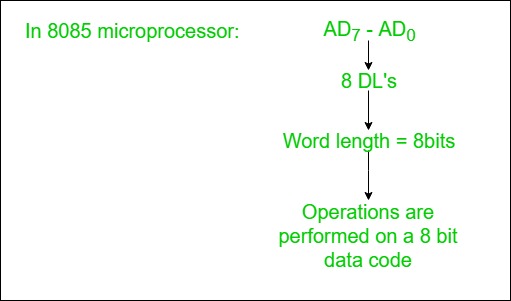
3. Control Lines:
- Used to carry the control signals and timing signals
- Control signals indicate type of operation.
- Timing Signals used to synchronize the memory and IO operations with a CPU clock.
6. Explain Instruction set
The instruction set, also called ISA (instruction set architecture), is part of a computer that pertains to programming, which is more or less machine language. The instruction set provides commands to the processor, to tell it what it needs to do. The instruction set consists of addressing modes, instructions, native data types, registers, memory architecture, interrupt, and exception handling, and external I/O.
An example of an instruction set is the x86 instruction set, which is common to find on computers today. Different computer processors can use almost the same instruction set while still having very different internal design. Both the Intel Pentium and AMD Athlon processors use nearly the same x86 instruction set. An instruction set can be built into the hardware of the processor, or it can be emulated in software, using an interpreter. The hardware design is more efficient and faster for running programs than the emulated software version.
Examples of instruction set
- ADD - Add two numbers together.
- COMPARE - Compare numbers.
- IN - Input information from a device, e.g., keyboard.
- JUMP - Jump to designated RAM address.
- JUMP IF - Conditional statement that jumps to a designated RAM address.
- LOAD - Load information from RAM to the CPU.
- OUT - Output information to device, e.g., monitor.
- STORE - Store information to RAM.
7. Explain memory
A memory is used to store data and instructions. Computer memory is the storage space in the computer, where data is to be processed and instructions required for processing are stored. The memory is divided into large number of small parts called cells. Each location or cell has a unique address, which varies from zero to memory size minus one.
For example, if the computer has 64k words, then this memory unit has 64 * 1024 = 65536 memory locations. The address of these locations varies from 0 to 65535.
Memory is primarily of three types −
- Cache Memory
- Primary Memory/Main Memory
- Secondary Memory
Cache Memory
Cache memory is a high -speed semiconductor memory which can speed up the CPU. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory. It is used to hold those parts of data and program which are most frequently used by the CPU. The parts of data and programs are transferred from the disk to cache memory by the operating system, from where the CPU can access them.
Advantages
The advantages of cache memory are as follows −
- Cache memory is faster than main memory.
- It consumes less access time as compared to main memory.
- It stores the program that can be executed within a short period of time.
- It stores data for temporary use.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of cache memory are as follows −
- Cache memory has limited capacity.
- It is too expensive.
Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory holds only those data and instructions on which the computer is currently working. It has a limited capacity and data is lost when power is switched off. It is generally made up of semiconductor device. These memories are not as fast as registers. The data and instruction required to be processed resides in the main memory. It is divided into two subcategories RAM and ROM.
Characteristics of Main Memory
- These are semiconductor memories.
- It is known as the main memory.
- Usually volatile memory.
- Data is lost in case power is switched off.
- It is the working memory of the computer.
- Faster than secondary memories.
- A computer cannot run without the primary memory.
Secondary Memory
This type of memory is also known as external memory or non-volatile. It is slower than the main memory. These are used for storing data/information permanently. CPU directly does not access these memories, instead they are accessed via input-output routines. The contents of secondary memories are first transferred to the main memory, and then the CPU can access it. For example, disk, CD-ROM, DVD, etc.
Characteristics of Secondary Memory
- These are magnetic and optical memories.
- It is known as the backup memory.
- It is a non-volatile memory.
- Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
- It is used for storage of data in a computer.
- Computer may run without the secondary memory.
- Slower than primary memories.
8. Explain processor
A processor (CPU) is the logic circuitry that responds to and processes the basic instructions that drive a computer. The CPU is the main integrated circuitry (IC) chip in a computer, as it is responsible for interpreting most of computers commands. CPUs will perform most basic arithmetic, logic, and I/O operations, as well as allocate commands for other chips and components running in a computer.
The basic elements of a processor include:
- The arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which carries out arithmetic and logic operations on the operands in instructions.
- The floating -point unit (FPU), also known as a math coprocessor or numeric coprocessor, a specialized co-processor that manipulates numbers more quickly than the basic microprocessor circuitry can.
- Registers, which hold instructions and other data. Registers supply operands to the ALU and store the results of operations.
- L1 and L2 cache memory. Their inclusion in the CPU saves time compared to having to get data from random access memory (RAM).
9. Explain CPU Operations
The four primary functions of a processor are fetch, decode, execute and write back.
Fetch- is the operation which receives instructions from program memory from a systems RAM.
Decode- is where the instruction is converted to understand which other parts of the CPU are needed to continue the operation. This is performed by the instruction decoder
Execute- is where the operation is performed. Each part of the CPU that is needed is activated to carry out the instructions.
Program stored and executed operating system:
Whenever you save your program(anything) into a file (any kind of file, say ‘add.c’), it automatically gets stored in the secondary storage that is the hard disk. The Operating System’s kernel (kernel’s File management system) does it for you.
When you run program, it is loaded into the main/primary memory of the computer called RAM (the entire program is transferred to the RAM, by a small program called the loader (which often comes with the compiler i.e. is a part of the compiler).
The program instructions are executed in the ALU (Arithmetic-Logic Unit) of the CPU (in its registers like the Accumulator). In order to execute the instructions , the CPU fetches the values of the variables (say, int a =10; int b =20;) in the program from the RAM, and stores the results also in the RAM (int sum =30;), which is then sent to the output buffer stream (stdout) , which prints the results (30) on the computer console/terminal, the Windows kernel (kernel’s I/O management system) does the printing .
10. Explain System and application software
What is System Software?
System Software is a set of programs that control and manage the operations of computer hardware. It also helps application programs to execute correctly.
System Software are designed to control the operation and extend the processing functionalities of a computer system. System software makes the operation of a computer more fast, effective, and secure. Example: Operating system, programming language, Communication software, etc.
What is an Application Software?
Application Software is a program that does real work for the user. It is mostly created to perform a specific task for a user.
Application Software acts as a mediator between the end-user and System Software. It is also known as an application package. This type of software is written using a high-level language like C, Java, VB. Net, etc. It is a user-specific and is designed to meet the requirements of the user.
You can also install multiple Application Software on a single System Software. You can store this kind of software on CDs, DVDs, flash derive, or keychain storage devices. Example: Word-processing, Spreadsheet, Database, etc.
KEY DIFFERENCES:
- System software are designed to manage the resources of the system, like memory and process management, security, etc. whereas Application software are designed to fulfil the requirements of the user for performing specific tasks.
- The System Software is a general-purpose software while the Application Software is specific purpose software.
- System Software is written in a low-level language like a machine or assembly language but Application software is a high-level language is used to write Application Software.
- System Software is capable of running independently while Application software can't run independently.
- The System Software starts running when the system is powered on and runs until the system is powered off while the Application Software starts when the user begins, and it ends when the user stops it.
- System software are independent of the application software while an Application software needs system software to run.