UNIT IV
Amalgamation of Firms
Question Bank
Q1). What is a "Merger" of a Partner Company? State its purpose.
A1). Amalgamation means a merger or merger. When two or more entities merge or combine into one entity, it is known as a "Merger." Similarly, when two or more union corporations merge, it is a "merger of union corporations".
Including the merger of her two or more single traders into the company
The scope of this chapter is broad enough to include situations where two or more individual traders merge to form a new partnership. This is generally known as a "merger to a partner company".
It also includes the merger of one or more single traders and one or more of his partnerships.
The scope of this chapter also includes situations where one or more sole ownerships he merges with one or more partnership companies to establish a new company.
Purpose of the Amalgamation of Companies:
The main purposes of the merger of the businesses are:

1. To avoid competition:
The main purpose of a merger is to avoid competition between companies. This provides the corporate a foothold over its competitors.
2. To Scale Back Costs:
The merged company can cash in of operating costs by lowering production costs. This is often possible for a "large economy".
3. The way to get financially:
The merged company will benefit financially within the sort of tax benefits, improved creditworthiness and lower borrowing rates.
4. To realize growth:
The merged company can pool resources to market internal growth and stop the emergence of latest competitors.
5. To diversify activities:
Diversifying your business across two or more industries can reduce your company's risk. In some cases, it can act to hedge weaker merger operations with stronger ones.
Q2). What are the Various forms of corporate "merger"?
A2). 
Q3). Explain the Accounting Procedure in own words.
A3). You need to study the accounting of "old companies" and "new companies".
Old Company: If there is a merger of companies, in the case of an old company, there are basically four things that happen.
The old company has dissolved: The old company has dissolved. They are involved. All results of the dissolution (see Chapter 3) follow. Assets and liabilities are either taken over by the new company or disposed of.
Financial Statements: As a result, the company's accounting books are closed as they were in the case of dissolution.
Asset and Liability Valuation: For this purpose, it is necessary to revaluate the existing assets and liabilities of the old company. Unrecorded assets and liabilities must also be considered for such valuations. This is done by mutual agreement.
Partner's final capital to check: At the time of the merger, the assets and liabilities of the old company will be taken over by the new company and an amount equal to this value (as mutually agreed) will be credited to the new company's capital account. When an old company partner becomes a new company partner. Therefore, needs to confirm the final capital of the partners of the old company, and the same becomes the starting capital of these partners of the new company.
New Office
Establishment of new company: Except in the case of absorption (Section 4.4), a new company will be established and take over the business of the old company.
Taking over the assets and liabilities of the old company: The basic purpose of the new company is to take over the running business using the assets and liabilities of the old company at an agreed price. The agreed value of an asset minus the agreed value of an inherited liability is called the "purchase consideration" or "price".
New Company Partner Capital: The "purchase consideration" above will not be paid in cash to the old partner as in the case of a normal dissolution. The “Purchase Consideration” will be credited to the capital account of the new company's old partner, as confirmed and explained in Section 5.1.4.
Devising a new share of profits: Partners united in a merger must agree to a new share of profits.
Partner Capital Restructuring: Often, the new company's partner's capital is restructured based on the new profit share. This may require the introduction of additional cash capital and, in some cases, the withdrawal of surplus capital. Excesses / shortages may even be transferred to your partner's checking / loan account.
Q4). What are the ways to close the books of an old company?
A4). In the case of a merger, "Old Enterprise: Dissolve. Therefore, conceptually, all the principles described in Chapter 3," Dissolution of Partnership Farms "apply to such farms. The old company passes the following entries:
The entries are:
Step 1: Open a Realization Account and a Partner's Capital Account.
Step 2: Same as step 1 of the reassessment method (see Section 6.1.1). Transfer the partner's capital to the partner's capital A / C credit side and transfer the past profits and reserves. The entries are:
Reserve P/L A/c Dr. To Partners Capital A/c (Various past profit transferred) | XX |
XX |
Step 3: Transfer all assets to the realization account. The entries are:
Realisation A/c Dr. To Concerned asset A/c (Various assets transferred) | XXX |
XXX |
What students should be aware of here is that the new company will take over due to the merger, so cash and bank balances (accounts) will be transferred.
However, you should not transfer your cash / bank account to a cash account if all your assets and liabilities are not taken over by the company.
Step 4: Transfer all debt to the realized account. The entries are:
Concerned liabilities A/c Dr. To Realisation A/c (Various liabilities transferred) | XXX |
XXX |
Step 5: Find out the consideration for the new company's takeover of assets and liabilities. A separate statement is usually created for the "Purchase Consideration". Then the following entry is passed:
Business purchase A/c Dr. To Realisation A/c (Value of purchase consideration on amalgamation now recorded) | XXX |
XXX |
Step 6: Assets that were not taken over by the new company and were sold to the outside world / taken over by a partner:
Cash/Bank/Partners capital A/c Dr. To Concerned asset A/c (Entry at agreed value) | XXX |
XXX |
Gain / Loss of such sale / acquisition transferred to Realization A / c:
Profit | Asset A/c Dr. To Realisation A/c | XXX |
XXX |
Loss | Realisation A/c Dr. To Asset A/c | XXX |
XXX |
Step 7: Partner disclaims / takes over responsibility instead of new company taking over responsibility
Concerned Liability A/c Dr. To Cash/Bank/Partners Capital A/c (Entry at agreed value) | XXX |
XXX |
Gains / losses from such emissions / take-backs transferred to Realization A / c:
Profit | Concerned Liability A/c Dr. To Realisation A/c (Surplus Transferred as Liability taken over at Lower Value) | XXX |
XXX |
Loss | Realisation A/c Dr. To Concerned liability A/c | XXX |
XXX |
Profit | Realisation A/c Dr. To Partners Capital A/c | XXX |
XXX |
Loss | Partners’ Capital A/c Dr. To Realisation A/c | XXX |
XXX |
Step 8: Realization A / c is closed by transferring profit or loss to the partner's capital account at a profit-sharing ratio.
Step 9: The final entry:
Partners’ capital A/c Dr. To Business Purchase A/c (Entry to Close the Books of the “Old Firm”) | XXX |
XXX |
Q5). Write short note on Accounting for Mergers.
A5) .ICAI has made this AS mandatory since January 4, 1995. The AS handles the accounting for mergers and the processing of the resulting goodwill or reserves. This is primarily intended for businesses, and only some of its requirements apply to partners' accounts, etc.
It states that there are two main ways to account for a merger.
The use of the "equity pooling method" is not discussed here as it is limited to mergers of companies.
The purchase method of accounting for mergers applies the same principles to the purchase of this regular asset. The problem in is solved using this method.
In this way, the assets and liabilities of the transferring company are either taken over by the new company at their existing value or the consideration is allocated to the individual assets and liabilities based on their fair value at that time, according to the contract. The date of the merger. The reserve will not be taken over by the new company, but will be distributed among the partners of the merged company.
AS 14 sets out the accounting procedures that should be followed in the books of the purchasing / transferring company, but does not specify the specific method that should be followed when closing the books of the merged company.
In the above accounting, students are aware of the following:
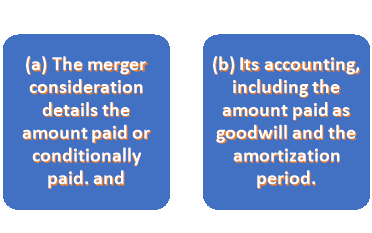
(i) If the consideration paid exceeds the net assets (assets-liabilities) acquired, the resulting amount is "GOOD WILL".
(ii) Alternatively, if the consideration paid is less than the net assets acquired, it is a "capital reserve".
Such goodwill resulting from the merger should be systematically amortized by the new company over its useful life. Generally, the amortization period should not exceed 5 years.
Para 45 of AS 14 sets disclosure requirements in the first financial statements of the new company after the merger.
Q6). Define Amalgamation.
A6). You have studied the units related to the final accounting of a partnership company in the XIIth standard. These final accounts are similar to the final accounts of individual traders, but with certain changes in the profit / loss distribution of partners in the profit-sharing ratio. However, there are various transactions that affect the accounting of a general partnership, such as partnership, retirement, death of the partnership, partnership, dissolution, and conversion of the partnership.
In this unit we will understand the need to learning Accounting for Mergers of Partnership Companies.
Meaning of Amalgamation of Partnership Companies:
A merger means merging or merging two or more business units that operate the same type of business to form a new business unit.
A merger of union corporations means that two or more union corporations merge to form a new union corporation. The merger of two or more existing partnership companies doing the same type of business, terminating another entity and forming a new company is called a partnership company merger.
Mergers can be formed in one of the following ways:

Q7). Write short note on Books of the New Firm.
A7). The entries in the books of the new firm can be divided into following stages:
1. Recording of the assets and liabilities taken over:
Debit: all assets’ accounts (which are taken over)
Credit: all liabilities accounts (which are taken over)
Credit: Partner’s capital accounts (as per the final balances in the capital accounts in the old firm)
With this entry the final capitals of the partners in the old firm become their initial capitals in the new firm.
2. Restructuring of partners capitals:
The partners may decide a particular capital structure in the new firm, which has to be contributed by the partners in their new profit-sharing ratio. Accordingly, the partners may bring further capital or withdraw excess capital. Alternatively, the excess or deficit may be transferred to current or loan accounts.
3. Removing effects of inter firm transactions of old firms:
(1) If debtors of one of the old firms, are creditors of the other firm the same party will be reflected as both debtor and creditor in the amalgamated firm,
Q8). What entries are being passed at time of cancellation of Debtors and Creditors Account.
A8). (1) If one of the debtors of the old company is the creditor of the other company, the same party will be reflected in both the debtor and the creditor of the merged company, and the common amount will be cancelled as follows.
Sunday Creditors A/c Dr. To Sundry Debtors A/c | XXX |
XXX |
(2) If the old company before the merger was a debtor / creditor of each other, the common amount will be cancelled in the company after the merger as follows.
Sundry Creditors A/c Dr. To Sundry Debtors A/c | XXX |
XXX |
(3) Similarly, if the old companies were accepting or withdrawing bills from each other, the same procedure would be performed.
Bills Payable A/c Dr. To Bills Receivable A/c | XXX |
XXX |
A similar method is used for cancellation of business-to-business loans.
(4) If one company purchased goods from the other company prior to the merger and all or part of the goods are still in stock or on the date of the merger, by the company that sold those goods. The amount of profit obtained is reduced from the combined inventory value as follows.
Goodwill A/c Dr. To Stock A/c | XXX |
XXX |
Q9). Distinguish between Amalgamation v/s Absorption.
A9). Where two or more existing business entities merge themselves to form a new business entity it is “amalgamation”. Therefore, the old entities are taken over by the newly formed business entity, e.g., where two firms viz. M/s AB & Co. And M/s. CD & Co. Merge to form a new firm M/s. ABCD & Co.
In absorption, one or more existing business entities are taken over by another existing business entity. No new business entity is formed for the purpose. E.g., where a firm AB & Co. ‘absorbs’ another firm CD & Co., it is known as absorption of CD & Co. By AB & Co.
Hence, whereas in amalgamation, all the old business entities are closed and a new business entity is formed, in absorption, one old entity will continue after taking over the other entity or entities.
Comparison Table Between Amalgamation and Absorption
Parameter of Comparison | Amalgamation | Absorption |
Meaning | Two or more different companies join to become one, the process is called Amalgamation. | When one company takes over the business of another company, the process is called Absorption. |
New entity | The new entity is formed. | No new entity is formed. |
Minimum number of companies involved | In the process of amalgamation, there are at least three companies involved (two liquidating and one newly formed). | While in Absorption there are at least two companies involved. |
Liquidating companies | At least two companies liquidate. | Only one company is liquidated (whose business is overtaken by the other). |
Domination | No company dominates any other company. | The bigger company dominates the weaker company. |
Q10). What are the different forms of ‘Amalgamation’ of firms?
A10). Amalgamation of firms may take any of the following forms:
Amalgamation of Two or more Sole-traders: Here, two or more sole-traders amalgamate themselves into a new partnership firm. E.g., Mr. A and Mr. B, two Chartered Accountants, practicing separately, merge their practice to form a new firm of Chartered Accountants viz. M/s AB.
Amalgamation of Sole-trader and Firm: Here, one or more existing sole-traders merge with one or more existing partnership firms, so that the existing entities lose their identity and a new partnership firm is formed to take over their businesses. E.g., Mr. X, a proprietor and M/s. YZ, a partnership firm, who are doing businesses separately, amalgamate to form a new firm, M/s. XYZ.
Amalgamation of Two or more Partnership Firms: Here, two or more existing partnership firms merge and form a new firm to take over the businesses of the existing firms. E.g., M/s. PQ and M/s. RS, two partnership firms doing competing businesses, amalgamate to form a new partnership firm viz. M/s PQRS. In all the above cases, A, B, X, YZ, PQ and RS lose their individual identity, close their businesses and new firms, M/s. AB, M/s. XYZ and M/s. PQRS respectively, come into existence to take over businesses.
Absorption: In this case, all the merging units do not lose their identity. One of them will continue to exist after taking over the other existing units. E.g., M/s. JK and M/s. MN are in competing business. M/s. JK absorbs or takes over M/s. MN so that M/s. MN is dissolved and M/s. JK continues to exist. It now has the assets and liabilities taken over from M/s. MN, in addition to its existing assets and liabilities.
Q.11) The following is the Balance Sheet of Kumar Ltd as on 30th September, 2009
Balance Sheet as on 30th September, 2009
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
Authorized Share Capital |
| Land & Buildings | 200000 |
10000 Equity Shares of Rs100 | 1000000 | Plant & Equipment’s | 300000 |
1000 6% Preference Shares of |
|
|
|
Rs 100 each | 100000 | Furnitures | 65000 |
Total | 1100000 | Patents | 45000 |
Issued capital |
| Sundry Debtors | 149450 |
6,000 Equity Shares | 600000 | Inventory | 68950 |
1000 6% Preference Shares of |
|
|
|
Rs 100 each | 100000 | Cash | 3700 |
10% Debentures | 100000 | Profit & loss A/C | 307900 |
Sundry Creditors | 100000 |
|
|
Bank Overdraft | 240000 |
|
|
| 1140000 |
| 1140000 |
A new Company Kishor Ltd was formed to take over this company. The Authorized capital of the new company was Rs 1500000 divided into 100000 Equity shares of Rs 10 each and 5000 7% Preference shares of Rs 100 each. The terms and conditions agreed for this were as follows:
- 10% debenture holders agreed to take new 9%Debentures of Rs.95000 in full satisfaction.
- 6% Preference shareholders were to receive 3 new 7% Preference shares of Rs.100 each for every 4 old preference shares.
- The equity shareholders to receive 30,000 Equity shares of Rs.10 each, credited as Rs.8 paid up
- Kishor Ltd. To issue 20,000 equity shares of Rs.10 each at par for cash
- Kishor Ltd to make a call of Rs.2 per share on shares issued to Kumar Ltd.
You are required to give necessary Ledger A/c s to close the books of Kumar ltd and Journal entries in the books of Kishor Ltd and Balance Sheet of Kishor Ltd.
A11).
Statement of Purchase consideration: (Net Payment method)
750 7% Preference shares of Rs.100 each 75000
30,000 Equity shares of Rs.10 each Rs. 8 paid up 240000
315000
Goodwill/Capital reserve (Net Assets taken over)
Land & Buildings | 200000 |
|
Plant & Equipments | 300000 |
|
Furnitures | 65000 |
|
Patents | 45000 |
|
Sundry Debtors | 149450 |
|
Inventory | 68950 |
|
Cash | 3700 | 832100 |
|
|
|
Less: Liabilities taken over at agreed values |
| |
10% Debentures | 100000 |
|
Sundry Creditors | 100000 |
|
Bank Overdraft | 240000 | 440000 |
Net Assets taken over |
| 392100 |
Purchase consideration |
| 315000 |
Capital Reserve |
| 77100 |
In the books of Kumar Ltd
Realization A/c
To Land & Buildings | 200000 | By 10% Debentures | 100000 |
To Plant & Equipments | 300000 | By Sundry Creditors | 100000 |
To Furnitures | 65000 | By Bank Overdraft | 240000 |
To Patents | 45000 | By Kishor | 315000 |
To Sundry Debtors | 149450 | By Pref Shareholders A/c | 25000 |
To Inventory | 68950 | By Equity Share holders A/c | 52100 |
To Cash | 3700 |
|
|
| 832100 |
| 832100 |
Equity Shareholders A/c
To Profit & Loss A/c | 307900 | By Equity Share Capital A/c | 600000 |
To Realization A/c | 52100 |
|
|
To Equity shares in Kishor Ltd |
240000 |
|
|
| 600000 |
| 600000 |
Kishor Ltd A/c
To Realisation A/c | 315000 | By Pref Shares in Kishor Ltd A/c By Equity Shares in Kishor Ltd A/c |
75000
240000 |
315000 | 315000 |
Preference Share Holders A/c
To Preference Shares in Kishor Ltd To Realisation A/c |
75000 25000 |
By Preference Share capital A/c |
100000 |
100000 | 100000 |
Equity Shares in Kishor Ltd
To Kishor Ltd | 240000 | By Equity Share Holders A/c | 240000 |
240000 | 240000 |
Preference Shares in Kishor Ltd
To Kishor Ltd | 75000 | By Preference Share Holders | 75000 |
75000 | 75000 |
Journal Entries in the Books of Kishor Ltd.
1 | Business Purchase A/c Dr To Liquidator of Kumar Ltd (Being Business Purchased) | 315000 |
315000 |
2 | Land and Buildings Dr Plant and Equipments Dr Furnitures Dr Patents Dr Sundry Debtors Dr Inventry A/c Dr Cash Dr To Business Purchase A/c To Sundry Creditors To Debentures To Bank Overdraft To Capital Reserve (Being Sundry Assets and Liabilities taken over recorded) | 200000 300000 65000 45000 149450 68950 3700 |
315000 100000 100000 240000 77100 |
3 | Liquidator of Kumar Ltd Dr To Equity Share Capital A/c To 7%Preference Share Capital A/c (Being Purchase Consideration Discharged.) | 315000 |
240000 75000 |
4 | Bank A/c Dr To Equity Share Capital A/c (Being 20000 Equity shares of Rs 10 each issued for cash.) | 200000 |
200000 |
5 | Equity Share Call A/c Dr To Equity Share Capital A/c (Being call made at Rs 2 per share on 30000 equity shares) | 60000 |
60000 |
6 | Bank A/c Dr To Equity Share Call A/c (Being Call amount received.) | 60000 |
60000 |
Balance Sheet of Kishor Ltd.
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
Authorised Share Capital |
| Land & Buildings | 200000 |
100000 Equity Shares of Rs10 |
|
|
|
Each | 1000000 | Plant & Equipments | 300000 |
5000 7% Preference Shares of |
|
|
|
Rs 100 each | 500000 | Furnitures | 65000 |
Total | 1500000 | Patents | 45000 |
Issued capital |
| Sundry Debtors | 149450 |
50000 Equity Shares of Rs 10 |
|
|
|
Each | 500000 | Inventory | 68950 |
750 7% Preference Shares of |
|
|
|
Rs 100 each | 75000 | Cash | 3700 |
Capital Reserve | 77100 | Bank Balance | 20000 |
10% Debentures | 100000 |
|
|
Sundry Creditors | 100000 |
|
|
| 852100 |
| 852100 |
Q11). The following are the Balance Sheets of P Ltd and S Ltd as on 31st March, 2009 Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2009
Liabilities | P Ltd | S Ltd | Assets | P Ltd | S Ltd |
Equity Share Capital (Rs |
|
| Land and Building | 250,000 | 155000 |
10 each) | 500,000 | 300,000 |
|
|
|
14% Preference Share |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital (Rs 100 each) | 220,000 | 170,000 | Plant and Machinery | 325,000 | 170000 |
General Reserve | 50,000 | 25,000 | Furniture and Fittings | 57,500 | 35000 |
Export Profit Reserve | 30,000 | 30,000 | Investments | 125,000 | 95000 |
Profit and Loss A/c | 75,000 | 50,000 | Stock | 90,000 | 103000 |
13% Debentures | 50,000 | 35,000 | Debtors | 72,500 | 52000 |
Sundry Creditors | 65,000 | 50,000 | Cash and Bank | 70,000 | 50000 |
| 990,000 | 660,000 |
| 990,000 | 660000 |
P Ltd takes over S Ltd on 1st April, 2009. P Ltd discharges the Purchase Consideration as below:
Issued 35000 equity shares of Rs 10 each at par to the equity shareholders of S Ltd.
Issued 15% Preference Shares of Rs 100 each
To discharge the Preference share holders of S Ltd at 10% premium.
The Debentures of S Ltd will be converted into equivalent numbers of debentures of P Ltd.
You are required to give necessary ledger accounts to close the books of S Ltd and Journal entries in t the books of P Ltd and Balance sheet of P Ltd after absorption.
A12 ) Statement of Purchase consideration: (Net Payment method)
35000 equity shares of Rs 10 each 350000
1870 15%Preference Shares of Rs 100 each
(Old Preference Share Capital 170000
Add : 10%Premium 17000 187000
537000
In the books of S Ltd
Realization A/c
To Land and Buildings | 155000 | By 13% Debentures | 35000 |
To Plant and Equipments | 170000 | By Current Liabilities | 50000 |
To Furnitures | 35000 | By P Ltd | 537000 |
To Investment | 95000 | By Equity Share holders A/c | 55000 |
To Inventory | 103000 |
|
|
To Sundry Debtors | 52000 |
|
|
To Cash | 50000 |
|
|
To Preference Share |
|
|
|
Holders | 17000 |
|
|
| 677000 |
| 677000 |
Equity Shareholders A/c
To Realisation A/c To Equity Shares In P Ltd | 55000 350000 |
By Equity Share Capital A/c By General Reserve A/c By Profit & Loss A/c By Export Profit Reserve |
300000 25000 50000 300000 |
405000 | 405000 |
P Ltd A/c
To Realisation A/c | 537000 | By Equity Shares in P Ltd By Preference Shares in P Ltd | 350000 187000
|
537000 | 537000 |
Preference Share Holders A/c
To Preference Shares in P Ltd | 187000 |
By Preference Share capital A/c By Realisation A/c |
170000 17000 |
187000 | 187000 |
Equity Shares in P Ltd
To P Ltd A/c | 350000 | By Equity Share Holders A/c | 350000 |
350000 | 350000 |
Preference Shares in P Ltd
To P Ltd A/c | 187000 | By Preference Share Holders A/c | 187000 |
187000 | 187000 |
Journal Entries in the books of P Ltd
Sr.No | Particulars | Dr. Rs. | Cr. Rs. |
i. | Business Purchase A/c Dr. | 5,37,000 |
|
| To Liquidator of Q Ltd. |
| 5,37,000 |
| (Being Business of Q Ltd. Purchased) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ii. | Building A/c Dr. | 155000 |
|
| Machinery A/c. Dr. | 170000 |
|
| Furniture and Fittings Dr | 35000 |
|
| Investment Dr | 95000 |
|
| Stock Dr. | 103000 |
|
| Debtors Dr. | 52000 |
|
| Cash and Bank A/c. Dr. | 50000 |
|
| To 13 % Debentures |
| 35000 |
| To Current Liabilities |
| 50000 |
| To Business Purchase |
| 537000 |
| To Capital Reserve |
| 38000 |
| (Being sundry assets & liabilities taken over of Q Ltd. Recorded) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iv. | Liquidator of P Ltd. A/c Dr. | 1875000 |
|
| To Equity share capital A/c |
| 1250000 |
| To Securities Premium A/c |
| 625000 |
| (Being Purchase consideration discharge) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
v. | Liquidator of Q Ltd. A/c. Dr. | 537000 |
|
| To Equity Share Capital A/c. |
| 350000 |
| To 15% Preference Share Capital A/c. |
| 187000 |
| (Being purchase consideration discharged) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vi. | Amalgamation Adjustment A/c. Dr. | 30000 |
|
| To Export profit reserve |
| 30000 |
| (Being statutory reserve maintained) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vii. | 13% Debentures in Q Ltd. A/c. Dr | 35000 |
|
| To 13% Debentures |
| 35000 |
Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2009
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
Equity Share Capital (Rs |
| Land and Building |
|
10 each) | 850,000 |
| 405,000 |
14% Preference Share |
|
|
|
Capital (Rs 100 each) | 220,000 | Plant and Machinery | 495,000 |
15% Preference Share |
|
|
|
Capital (Rs 100 each) | 187,000 | Furniture and Fittings | 92,500 |
General Reserve | 50,000 | Investments | 220,000 |
Export Profit Reserve | 60,000 | Stock | 193,000 |
Capital Reserve | 38,000 | Debtors | 124,500 |
Profit and Loss A/c | 75,000 | Cash and Bank | 120,000 |
13% Debentures | 85,000 | Amalgamation Adjustment A/c | 30000 |
Current Liabilities | 115,000 |
|
|
| 1,680,000 |
| 1,680,000 |
Q12). The following is the Balance Sheet of Shy Ltd as on 30th September, 2009
Balance Sheet as on 30th September, 2009
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
Issued capital |
| Land & Buildings | 85000 |
18000 Equity Shares of Rs10 |
| Plant & Equipments | 45000 |
General Reserve | 24000 | Furnitures | 15000 |
Profit & loss | 10400 | Trademarks | 7000 |
12% Debentures | 80000 | Investments | 23000 |
Sundry Creditors | 63720 | Sundry Debtors | 60000 |
|
| Stock | 112000 |
|
| Bank | 11120 |
| 358120 |
| 358120 |
Shy Ltd was absorbed by Chai Ltd., on the following terms and conditions:
- All liabilities and all assets are to be taken over except Investments which were sold by Shy Ltd. At 90% of book value.
- Debentures of Shy Ltd, to be discharged at a discount of 10% by the issue of 14% debentures of Rs 100 each in Chai Ltd.
- Trademarks were found useless.
- Issue of one equity share of Rs 10 each in Chai Ltd., issued at Rs 12 and a cash payment of Rs 3 for every s hare in Shy Ltd.
- Cost of absorption paid : Rs 1160
- Shy Ltd. Sold half the shares received from Chai Ltd. At Rs 15 per share.
You are required to give necessary Ledger A/c s to close the books of Shy Ltd. And Journal entries in the books of Chai Ltd.
A13).
Statement of Purchase consideration: (Net Payment method)
18000 Equity shares of Rs.10 each at Rs.12 per share 216000
Cash at Rs. 3 per share on 18000 Equity shares 54000
Purchase Consideration 270000
Goodwill/Capital reserve (Net Assets taken over)
Land & Buildings | 85000 |
|
Plant & Equipments | 45000 |
|
Furnitures | 15000 |
|
Sundry Debtors | 60000 |
|
Stock | 112000 |
|
Bank | 11120 |
|
|
| 328120 |
Less : |
|
|
Liabilities taken over |
|
|
Debentures | 80000 |
|
Creditors | 63720 | 143720 |
Net assets taken over |
| 184400 |
Less : |
|
|
Purchase consideration |
| 270000 |
Goodwill |
| 85600 |
In the books of Shy Ltd
Realization A/c
To Land & Buildings | 85000 | By 10% Debentures | 80000 |
To Plant & Equipments | 45000 | By Sundry Creditors | 63720 |
To Furnitures | 15000 | By Chai Ltd. | 270000 |
To Trademarks | 7000 | By Bank (Investment sold) | 20700 |
To Sundry Debtors | 60000 | By Bank (shares sold) | 27000 |
To Bank | 11120 |
|
|
To Investments | 23000 |
|
|
To Stock | 112000 |
|
|
To Equity Share holders A/c | 103300 |
|
|
| 461420 |
| 461420 |
Equity Shareholders A/c
To Bank A/c To Equity Shares in Chai Ltd | 209700 108000 | By Equity Share Capital A/c By Profit & Loss A/c By General Reserve A/c By Realisation A/c | 180000 10400 24000 103300 |
317700 | 317700 |
Chai Ltd A/c
To Realisation A/c | 270000 | By Equity Shares in Chai Ltd By Bank | 216000 54000 |
270000 | 270000 |
Bank A/c
To Equity shares in Chai Ltd To Realisation A/c To Chai Ltd. | 135000 20700 54000 |
By Equity Shareholders A/c |
209700 |
209700 | 209700 |
Equity Shares in Chai Ltd
To Chai Ltd. To Realisation A/c | 216000 27000 | By Bank By Equity Share Holders A/c | 135000 108000 |
| 243000 |
| 243000 |
Journal Entries in the Books of Chai Ltd.
1 | Business Purchase A/c To Liquidator of Shy Ltd (Being Business Purchased) | Dr | 270000 |
270000 | |
2 | Land and Buildings Dr Plant and Equipments Dr Furniture Dr Sundry Debtors Dr Stock Dr Bank Dr Goodwill (Bal Fig) Dr To Business Purchase A/c To Sundry Creditors To Debentures (Being Sundry Assets and Liabilities taken over recorded) | 85000 45000 15000 60000 112000 11120 85600 |
270000 63720 80000
| ||
3 | Liquidator of Shy Ltd To Equity Share Capital A/c To Securities Premium A/c To Bank (Being Purchase Consideration Discharged.) |
| Dr | 270000 |
180000 36000 54000 |
4 | Goodwill A/c To Bank (Being amalgamation expenses paid) | Dr. |
| 1160 |
1160 |
5 | Debentures in Shy A/c Dr. To Debentures in Chai Ltd A/c (Being new debentures issued in satisfaction of old Debentures) | 72000 |
72000 | ||
Q13) A Ltd and B Ltd agreed to amalgamate and form a new company C Ltd. Which will take over all the assets and liabilities of the two companies.
The assets and liabilities of A Ltd are to be taken over at a book value for shares in C Ltd. At the rate of 5 shares in C Ltd. At 10% premium (i.e. Rs 11 per share) for every four shares in A Ltd.
In the case of B Ltd:
The debentures of B Ltd. Would be paid off by the issue of an equal no. Of debentures in C Ltd.
The 11.5% Preference Shareholders of B Ltd. Would be allotted four 12% Preferences of Rs 100 each in C Ltd. For every five Preference shares in B Ltd.
Sufficient shares of C Ltd would be allotted to the equity share holders to cover the balance on their account after adjusting asset values by reducing Plant and Machinery by 10% and providing 5% on sundry debtors.
The summarized Balance Sheets of the two companies just prior to amalgamation were as follows:
Liabilities | A Ltd. | B Ltd | Assets | A Ltd. | B Ltd |
Issued capital |
|
| Plant & Equipments | 800000 | 800000 |
Equity Capital of Rs10 each | 400000 | 500000 | Stock | 65000 | 60000 |
11.5 Preference Shares of Rs 100 each. |
|
300000 | Profit and Loss A/c |
| 140000 |
12% Debentures |
| 200000 | Sundry Debtors | 95000 | 50000 |
Profit & loss A/C | 500000 |
| Bank | 65000 | 40000 |
Sundry Creditors Contingency Reserve | 75000 50000 | 90000 |
|
|
|
| 1025000 | 1090000 |
| 1025000 | 1090000 |
Show the Journal entries in the books of both the companies.
A14).
Statement of Purchase consideration for A Ltd.(Net Payment Method)
5 Equity Shares of Rs 10 each at 10% premium for
Every four shares in A Ltd. 550000
(40000 shares/4 x 5= 50000 shares x Rs.11)
Statement of Purchase Consideration for B Ltd(Net Assets Method) &
Net Assets taken over of A Ltd.
Assets Taken Over: | A Ltd | B Ltd |
Plant & Equipments | 800000 | 720000 |
Stock | 65000 | 60000 |
Sundry Debtors | 95000 | 47500 |
Bank | 65000 | 40000 |
| 1025000 | 867500 |
Less: Liabilities taken over |
|
|
Debentures |
| 200000 |
Sundry creditors | 75000 | 90000 |
Net Assets | 950000 | 577500 |
Less: P.C | 550000 |
|
Capital Reserve | 400000 |
|
P.C (Net Assets Method) |
| 577500 |
In the books of A Ltd and B Ltd
Realization A/c
Particulars | A Ltd | B Ltd | Particulars | A Ltd | B Ltd |
To Plant & Equipments A/c |
800000 |
800000 | By Debentures A/c |
| 200000 |
To Stock A/c | 65000 | 60000 | By Creditors A/c | 75000 | 90000 |
To Sundry Debtors A/c | 95000 | 50000 | By C Ltd A/c | 550000 | 577500 |
To Bank A/c | 65000 | 40000 | By Preference Shareholders A/c |
|
60000 |
|
|
| By Equity Share holders A/c | 400000 | 22500 |
| 1025000 | 950000 |
| 1025000 | 950000 |
C Ltd A/c
Particulars | A Ltd | B Ltd | Particulars | A Ltd | B Ltd |
To Realisation A/c | 550000 | 577500 | By Equity Shares in C Ltd By Preference Shares in C Ltd | 550000 | 337500
240000 |
550000 | 577500 | 550000 | 577500 |
Equity Shareholders A/c
Particulars | A Ltd | B Ltd | Particulars | A Ltd | B Ltd |
To Profit & Loss A/c To Equity shares in C Ltd To Realisation A/c |
550000 400000 | 140000 337500 22500 | By Equity Share Capital A/c By Profit & Loss A/c By General Reserve A/c | 400000 500000
50000 | 500000
|
950000 | 500000 | 950000 | 500000 |
Preference Share Holders A/c
To Preference Shares in C Ltd To Realisation A/c |
| 240000 60000 |
By Preference Share capital A/c |
|
300000 |
300000 | 300000 |
Equity Shares in C Ltd
To C Ltd A/c
|
| 337500 | By Equity Share Holders A/c | 550000 | 337500 |
| 550000 | 337500 |
| 550000 | 337500 |
Preference Shares in C Ltd
To C Ltd | B Ltd 240000 |
By Preference Share Holders A/c | B Ltd 240000 |
240000 | 240000 |
Journal Entries in the Books of C Ltd.
1 | Business Purchase A/c Dr To Liquidator of A Ltd A/c To Liquidator of B Ltd A/c (Being Business Purchased) | 1127500 |
550000 577500 | |
2 | Plant and Equipments A/c Dr Stock A/c Dr Debtors A/c Dr Bank A/c Dr To Business Purchase A/c To Sundry Creditors To Capital Reserve A/c (Being Sundry Assets and Liabilities taken over recorded) |
| 800000 65000 95000 65000 |
550000 75000 400000 |
3 | Plant and Equipments A/c Dr Stock A/c Dr Debtors A/c Dr Bank A/c Dr To Business Purchase A/c To Sundry Creditors To Debentures (Being Sundry Assets and Liabilities taken over recorded) |
| 720000 60000 47500 40000 |
577500 90000 200000 |
4 | Liquidator of A Ltd Dr To Equity Share Capital A/c To Security Premium A/c (Being Purchase Consideration Discharged.) | 550000 |
500000 50000 | |
5 | Liquidator of B Ltd Dr To Equity Share Capital A/c To Preference Share Capital A/c (Being Purchase Consideration Discharged.) | 577500 |
337500 240000 | |
6 | Old Debentures A/c To New Debenture A/c To Capital Reserve A/c (Being old Debentures settled at 10% discount.) | Dr | 200000 |
180000 20000 |
Balance Sheet of C Ltd.
Liabilities | Rs | Assets | Rs |
Issued capital |
| Plant & Equipments | 1520000 |
Equity Capital of Rs10 each | 837500 | Stock | 125000 |
11.5 Preference Shares of Rs |
|
|
|
100 each. | 240000 | Sundry Debtors | 142500 |
12% Debentures | 180000 | Bank | 105000 |
Sundry Creditors | 165000 |
|
|
Security Premium | 50000 |
|
|
Capital Reserve | 420000 |
|
|
| 1892500 |
| 1892500 |
Q14). Following were the balance sheets as on March 2014 of two firm’s M/s A & B and M/s C & D:
Balance Sheet
Liabilities | A & B | C & D | Assets | A & B | C & D | |
Sundry Creditors | 20,000 | 10,000 | Cash at bank |
| 15,000 | 8,000 |
Bills Payable | 5,000 | – | Investment at Cost |
| 10,000 | 8,000 |
Bank Overdraft | 2,000 | 10,000 | Debtors | 10,000 |
|
|
E’s Loan | 6,000 | – | Less: Provision | 1,000 |
|
|
Capitals |
|
|
|
| 9,000 | 8,000 |
A | 35,000 |
| Furniture |
| 12,000 | 6,000 |
B | 22,000 |
| Premises |
| 30,000 | – |
C |
| 36,000 | Land |
| – | 50,000 |
D |
| 20,000 | Machinery |
| 15,000 | – |
General Reserve | 8,000 | 3,000 | Goodwill |
| 9,000 | – |
Investment Fluctuation | 2,000 | 1,000 |
|
|
|
|
Fund |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1,00,000 | 80,000 |
| 1,00,000 | 80,000 | |
It was decided by both the firms to amalgamate their business on 1st April 2014 for this purpose it was decided that the new firm shall not take furniture of both the firms and shall take over investment at 10
% Less than the cost land at 80,000 premises at 45,000, machinery at 9,000 New firm agreed to take over only trade liabilities of both the firms and to pay 12,000 to each firm as goodwill Unrecorded typewriter with C & D valued at 800 was not taken over by the new firm.
A15). Journal in the Books of M/s. A & B
Date 31/3/14 | Particulars | L F | Debit | Credit | |
| Realisation A/c To Cash at Bank A/c To Investment A/c To Debtors To Furniture A/c To Premises A/c To Machinery A/c To Goodwill (Being Transfer of Assets to Realisation A/c) | Dr. |
| 1,01,000 |
|
| 15,000 | ||||
| 10,000 | ||||
| 10,000 | ||||
| 12,000 | ||||
| 30,000 | ||||
| 15,000 | ||||
| 9,000 | ||||
Creditors A/c Balance Payable A/c Bank OD A/c Provision for Doubtful Debt A/c A’S Loan A/c To Realisation (Being Transfer of Liabilities to Realisation A/c) | Dr. Dr. Dr. Dr. Dr. | 20,000 |
| ||
5,000 |
| ||||
2,000 |
| ||||
1,000 |
| ||||
6,000 |
| ||||
| 34,000 | ||||
Investment Fluctuation Fund A/c To Realisation A/c | Dr. | 1,000 |
| ||
| 1,000 | ||||
| (Being Reduction in the Value of Investment Accounted for) |
|
|
| |
General Reserve A/c Dr. To A’s Capital A/c To A’s Capital A/c (Being Reserve Distributed to old Partners in Profit Sharing Ratio) | 8,000 |
4,000 4,000 | |||
New Firm A/c To Realisation A/c (Being Purchase Consideration Recorded) | Dr. | 66,000 |
66,000 | ||
A’s Capital A/c B’s Capital A/c To Realisation A/c (Being Furniture taken over by Partners) | Dr. Dr. | 6,000 6,000 |
12,000 | ||
Investment Fluctuation Fund A/c Dr. To A’s Capital A/c To B’s Capital A/c (Being Surplus Balance Transferred to Partner’s Capital Accounts. | 1,000 |
500 500 | |||
Realisation A/c Dr. To A’s Capital A/c To B’s Capital A/c (Being Profit on Realisation Distributed to Partners in Profit) | 12,000 |
6,000 6,000 | |||
A’s Capital A/c B’s Capital A/c To New Firm A/c (Being balances in Partner’s Capital A/c Adjusted) | Dr. Dr. | 39,500 26,500 |
66,000 | ||
Ledger Accounts
Dr. Realisation A/c
|
|
|
| ||
To Sundry Assets: |
|
| By Sundry Liabilities |
|
|
Cash at Bank | 15,000 |
| Creditors | 20,000 |
|
Investment | 10,000 |
| Bills Payable | 5,000 |
|
Debtors | 10,000 |
| Bank Overdraft | 2,000 |
|
Furniture | 12,000 |
| RDD | 1,000 |
|
Premises | 30,000 |
| A’s Loan | 6,000 | 34,000 |
Machinery | 15,000 |
| By Investment Fluctuation |
| 1,000 |
|
|
| Fund A/c |
|
|
Goodwill | 9,000 | 1,01,000 | By Business Purchase A/c |
| 66,000 |
To Realisation Profit |
|
| By Partners Capital A/c |
| 12,000 |
A | 6,000 |
| (Furniture taken over) |
|
|
B | 6,000 | 12,000 |
|
|
|
|
| 1,13,000 |
|
| 1,13,000 |
Partner’s Capital A/c Cr.
Dr
| A | B |
| A | B |
To Furniture | 6,000 | 6,000 | By Balance b/d | 35,000 | 22,000 |
To Business Purchase A/c | 39,500 | 26,500 | By Realisation A/c By General Reserve By Inv.fluctuation Fund | 6,000 4,000 500 | 6,000 4,000 500 |
| 45,500 | 32,500 |
| 45,500 | 32,500 |
Dr. New Firm A/c (Business Purchase A/c) Cr.
|
| ||
To Realisation A/c | 66,000 | By Capital accounts: A B | 39,500 26,500 |
| 66,000 |
| 66,000 |
Working Note: Value of Business Purchase:
Particulars | A & B | C & D | ||
Assets taken over: Cash (*15,000 –2,000 – 6,000) Investment Debtors Land/Premises Machinery Goodwill Less: Liabilities Creditors RDD Bills payable |
*7,000 |
|
8,000 |
|
9,000 |
| 7,200 |
| |
10,000 |
| 8,000 |
| |
45,000 |
| 80,000 |
| |
9,000 |
| – |
| |
12,000 | 92,000 | 12,000 | 1,15,200 | |
20,000 |
| 10,000 |
| |
1,000 |
| – |
| |
5,000 | (26,000) |
| (10,000) | |
|
| 66,000 |
| 1,05,200 |
Journal Entries in the Books of M/s. C & D
Date | Particulars | LF | Debit | Credit | |
| Realisation A/c To Bank A/c To Investment A/c To Debtors A/c To Furniture A/c To Land A/c (Being Assets Transferred) | Dr. |
| 80,000 |
|
| 8,000 | ||||
| 8,000 | ||||
| 8,000 | ||||
| 6,000 | ||||
| 50,000 | ||||
| Creditors A/c To Realisation A/c (Being Liabilities transferred) | Dr. |
| 10,000 |
10,000 |
| Investment Fluctuation Fund A/c To Realisation A/c To C’s Capital A/c To D’s Capital A/c (Being reduction in value of investments transferred to Realisation A/c and balance distributed to Partners in profit sharing ratio) | Dr. |
| 1,000 |
|
| 800 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| 100 | ||||
| General Reserve A/c | Dr. |
| 3,000 |
|
| To C’s Capital A/c To D’s Capital A/c (Being general reserve distributed to partners in profit sharing ratio) |
|
| 1,500 1,500 | |
| Bank Overdraft A/c To C’s Capital A/c To D’s Capital A/c (Being Liabilities taken over by partners) | Dr. |
| 10,000 |
5,000 5,000 |
| New Firm A/c To Realisation A/c (Being Purchase Consideration Recorded) | Dr. |
| 1,05,200 |
1,05,200 |
| C’s Capital A/c D’s Capital A/c To Realisation A/c (Being Furniture taken over) | Dr. Dr. |
| 3,000 |
|
3,000 |
| ||||
| 6,000 | ||||
| C’s Capital A/c D’s Capital A/c To Realisation A/c (Being Type writer taken over) | Dr. Dr. |
| 400 |
|
400 |
| ||||
| 800 | ||||
| Realisation A/c To C’s Capital A/c To D’s Capital A/c (Being Profit on Realisation Transferred in Profit Sharing Ratio) | Dr. |
| 42,800 |
|
| 21,400 | ||||
| 21,400 | ||||
| C’s Capital A/c D’s Capital A/c To New Firm A/c (Being Balance in Partner’s Capital A/c Adjusted) | Dr. |
| 60,600 |
|
Ledger Accounts
Dr. Realisation A/c Cr.
|
|
| ||
To Sundry Assets: Cash at Bank Investment Debtors Furniture Land To Partner’s Capital: C D |
8,000 8,000 8,000 6,000 50,000 |
80,000
42,800 | By Sundry liabilities: Creditors By Investment fluctuation fund By Business purchase A/c By Partner’s capital A/c (furniture) By Partner’s capital A/c (typewriter) |
10,000 800 1,05,200 6,000 800 |
21,400 21,400 | ||||
|
| 1,22,800 |
| 1,22,800 |
Dr. Partner’s Capital A/c Cr.
| C | D |
| C | D |
To Realisation (Furniture) | 3,000 | 3,000 | By Balance b/d | 36,000 | 20,000 |
To Realisation (typewriter) | 400 | 400 | By Realisation | 21,400 | 21,400 |
To Balance c/d | 60,600 | 44,600 | By Bank o/d | 5,000 | 5,000 |
|
|
| By General Reserve | 1,500 | 1,500 |
|
|
| By Inv. Fluctuation Fund | 100 | 100 |
| 64,000 | 48,000 |
| 64,000 | 48,000 |
Dr. New Firm A/c (Business Purchase A/c) Cr.
|
| ||
To Realisation A/c | 1,05,200 | By Partners Capital A/c: C D | 60,600 44,600 |
| 1,05,200 |
| 1,05,200 |
Journal Entries in the Books of New Firm
Date 1/4/14 | Particulars | LF | Debit | Credit | |
(1) | Bank A/c Investments A/c Debtors A/c Premises A/c Machinery A/c Goodwill A/c To Sundry Creditors A/c To Bill payable A/c To Provision for Doubtful Debts A/c To A’s Capital A/c To B’s Capital A/c (Being Assets and Liabilities Taken over at Revised Values Credited to Capital of A & B) | Dr. Dr. Dr. Dr. Dr. Dr. |
| 7,000 |
|
| 9,000 |
| |||
| 10,000 |
| |||
| 45,000 |
| |||
| 9,000 |
| |||
| 12,000 |
| |||
|
| 20,000 | |||
|
| 5,000 | |||
|
| 1,000 | |||
|
| 39,500 | |||
|
| 26,500 | |||
(2) | Bank A/c Investments A/c Debtors A/c Land A/c Goodwill A/c To Sundry Creditors A/c To C’s Capital A/c To D’s Capital A/c (Being Assets and Liabilities of the Firm C and D taken over at Revised Value) | Dr. Dr. Dr. Dr. Dr. |
| 8,000 |
|
| 7,200 |
| |||
| 8,000 |
| |||
| 80,000 |
| |||
| 12,000 |
| |||
|
| 10,000 | |||
|
| 60,600 | |||
|
| 44,600 | |||
(3) | A Current A/c B’s Current A/c To A’s Capital A/c | Dr. Dr. |
| 500 |
|
| 13,500 |
| |||
|
| 500 | |||
| To B’s Capital A/c (Being shortfall in amount of fixed capital debited to current A/cs) |
|
| 13,500 | |
(4) | C’s Capital A/c D’s Capital A/c To C’s Current A/c To D’s Current A/c (Being Amount Excess over the Fixed Capital Transferred to Respective Current A/cs) | Dr. Dr. |
| 20,600 |
|
| 4,600 |
| |||
|
| 20,600 | |||
|
| 4,600 | |||
Balance Sheet of New Firm as on 1st April 2014
Liabilities | Assets |
| ||
Sundry Creditors | 30,000 | Bank Investment Debtors Less: Provision
Machinery Premises Land Goodwill Partner’s Current A/cs: A B |
| 15,000 |
Bills Payable | 5,000 |
| 16,200 | |
Partner’s Capital A/cs: |
| 18,000 |
| |
A | 40,000 | 1,000 | 17,000 | |
B | 40,000 |
|
| |
C | 40,000 |
| 9,000 | |
D | 40,000 |
| 45,000 | |
|
|
| 80,000 | |
Partner’s Current A/c |
|
| 24,000 | |
C | 20,600 | 500 |
| |
D | 4,600 | 13,500 | 14,000 | |
| 2,20,200 |
|
| 2,20,000 |
Notes: 1. Loss on investment is to be net out of investment fluctuation fund. The remaining fund is treated as accumulated profit.
2. Since there is no sufficient bank balance in the firm C and D. Liabilities not taken over have been transferred to capital accounts. Alternatively, it can be presumed that they have brought in the required money to pay off the liabilities. Of course, the net effect would be the same.
3. Trade liabilities include liabilities on account of goods. Bank overdraft is a liability but not trade liability. Similarly, salary outstanding, loans, etc., are all liabilities but not trade liabilities.
Working Note: For adjustment of capital:
| A | B | C | D |
Opening Balance | 39,500 | 26,500 | 60,600 | 44,600 |
Surplus/Deficit | +500 | +13,500 | –20,600 | –4,600 |
Required | 40,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 |
Q15). J and K were in partnership sharing profits and losses in the ration of 3:2. They were dealing in retail merchandising in the trade name of J & Co. Their balance sheet as on December 31, 2014 was as follows:
Liabilities | Assets | |||
Sundry Creditors |
| 15,000 | Cash at bank | 4,000 |
Capital A/cs: |
|
| Sundry debtors | 10,000 |
J | 75,000 |
| Stock-in-trade | 16,000 |
K | 60,000 | 1,35,000 | Furniture and fixtures | 15,000 |
|
| Delivery van Godown Land and building | 25,000 5,000 75,000 | |
| 1,50,000 |
| 1,50,000 | |
M and N were in partnership in the trade name of M & Co. Sharing profit and losses in the ratio of 2:3 doing the same business as J & Co. The balance sheet of M & Co. As on December 31, 2014 was as follows:
Liabilities |
| Assets | ||
Sundry Creditors |
| 6,000 | Sundry Debtors | 8,000 |
Bank Overdraft |
| 4,000 | Stock in Trade | 18,000 |
Capital A/cs: |
|
| Furniture and Fixtures | 10,000 |
M | 40,000 |
| Delivery van | 20,000 |
N | 60,000 | 1,00,000 | Land and Building | 54,000 |
|
| 1,10,000 |
| 1,10,000 |
It was mutually agreed by both the firms to amalgamate their businesses as on January 1, 2015 in trade name of F & Co. On the following terms and conditions:
| J & Co. | M & Co. |
Stock-in-trade | 18,000 | 14,000 |
Delivery Van | 20,000 | 18,000 |
Furniture and Fixture | 12,000 | – |
Land and Building | 90,000 | – |
Goodwill | 20,000 | 15,000 |
(1) F & Co. Should take over the assets of the two firms, as detailed below:
(2) It was mutually agreed that F & Co., was not to take over the furniture and fittings and land and building of M & Co. However, these assets were sold at 72,000 in cash on January 1, 2015.
(3) K took over the possession of the godown of his firm for a consideration of 4,000.
(4) It was decided to make provision for doubtful debts at 10% on the sundry debtors and also make a provision for discount at 5% on sundry creditors of both the firms.
(5) All the partners unanimously agreed to have a new profit-loss sharing ratio as follows: J – 2: K – 1: M – 1: and N – 2.
(6) The capital of F & Co. Was fixed at 2,40,000 and the partners were required to adjust their capitals in tune with their profit-loss sharing ratio, by making necessary adjustments in cash.
You are required to:
(i) Pass journal entries for opening new books.
(ii) Prepare Realisation accounts of the old partnership firms.
A16). Ledger Accounts in the Books of J & Co.
Dr. Realisation A/c Cr.
Particulars |
| Amount | Particulars | Amount |
To Sundry Assets |
|
| By Sundry Creditors | 15,000 |
Sundry Debtors | 10,000 | By K’s Capital A/c (Godown) | 4,000 | |
Stock | 16,000 | By F & C. A/c (Purchase | 1,58,750 | |
|
| Consideration) |
| |
Furniture and Fixtures | 15,000 |
|
| |
Delivery Van | 25,000 |
|
| |
Godown | 5,000 |
|
| |
Land and Building | 75,000 |
|
| |
Cash | 4,000 |
|
| |
To Profit Realisation Transferred to: |
|
|
| |
J’s Capital A/c | 16,650 |
|
|
|
K’s Capital A/c | 11,100 | 27,750 |
|
|
| 1,77,750 |
| 1,77,750 |
Dr Realisation A/c Cr.
Liabilities | Assets | ||
To Sundry Assets |
| By Sundry Creditors | 6,000 |
Stock | 18,000 | By Bank Overdraft | 4,000 |
Sundry Debtors | 8,000 | By F and Co. A/c (Purchase Consideration) | 1,16,500 |
Furniture and fixture | 10,000 |
|
|
Delivery Van Land and Building To Profit on Realisation Transferred to M’s Capital A/c 6,600 N’s Capital A/c 9,900 | 20,000 54,000
16,500 |
|
|
| 1,26,500 |
| 1,26,500 |
Q16). R and S are partners of Don & Co. Sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3:1 T and U are partners of John & Co. Sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2:1. On 31st July 2014, they decided to amalgamate and form a new firm M/s Don & John where in R, S, T and U were to be the partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4:2:3:2. Their balance sheets on that date were as under:
Liabilities | Don & Co. | John & Co. | Assets | Don & Co. | John & Co. |
Creditors | 16,000 |
| Cash | 10,000 | 5,000 |
Ram aur Shyam | 40,000 | – | Bank | 15,000 | 20,000 |
Don & Co. | – | 50,000 | Debtors: |
|
|
Others | 60,000 | 58,000 | John & Co. | 50,000 | – |
Reserves Capital | 25,000 | 50,000 | Ram aur Shyam | – | 30,000 |
R | 1,20,000 | – | Others | 80,000 | 1,00,000 |
S | 80,000 | – |
|
|
|
T | – | 1,00,000 | Stock | 60,000 | 70,000 |
U | – | 50,000 | Furniture & Office |
|
|
|
|
| Equipment | 10,000 | 3,000 |
|
|
| Vehicles | – | 80,000 |
|
|
| Plant & Machinery | 75,000 | – |
|
|
| Building | 25,000 |
|
| 3,25,000 | 3,08,000 |
| 3,25,000 | 3,08,000 |
The amalgamated firm took over the business on the following terms:
(a) Goodwill of Don & Co. Was worth 60,000; Goodwill of John & Co. Was 50,000. However goodwill account was not to be opened in the books of accounts. The adjustments for the change in the profit share are to be recorded through the capital accounts of the partners.
(b) Buildings, plant and machinery and vehicles are taken over at 50,000. 90,000 and 1,00,000 respectively.
(c) Provision for doubtful debts has to be carried forward at 4,000 in the case of Don & Co. And 5,000 in the case of John & Co.
You are asked to:
- Compute the adjustment for goodwill
2. Pass the entries in the books of Don and John assuming that excess capitals with reference to share in profits are to be transferred to loan accounts.
A17)
Computation of Adjustment for Goodwill
| Old Share in Goodwill | New Share in Goodwill | Change | ||
| |||||
R | 3/4 of 60,000 | 45,000 | 4/11 | 40,000 | (–)5,000 |
S | 1/4 of 60,000 | 15,000 | 2/11 | 20,000 | (+)5,000 |
T | 2/3 of 50,000 | 33,333 | 3/11 | 30,000 | (-)3,333 |
U | 1/3 of 50,000 | 16,667 | 2/11 | 20,000 | (+)3,333 |
|
| 1,10,000 |
| 1,10,000 |
|
Journal Entries M/s Don and John
Date 31/7/14 | LF | Debit | Credit | |
(1) | Cash A/c Dr. Bank A/c Dr. John & Co’s A/c Dr. Debtors A/c Dr. Stock A/c Dr. Furniture and office equipment A/c Dr. Plant and machinery A/c Dr. Building A/c Dr. To Provision for doubtful debts A/c To Ram aur Shyam A/c To Creditors A/c To B capital A/c To S capital A/c (Being the assets and liabilities of Don & Co. Taken over) |
| 10,000 |
|
| 15,000 |
| ||
| 50,000 |
| ||
| 80,000 |
| ||
| 60,000 |
| ||
| 10,000 |
| ||
| 90,000 |
| ||
| 50,000 |
| ||
|
| 4,000 | ||
|
| 40,000 | ||
|
| 60,000 | ||
|
| 1,65,750 | ||
|
| 95,250 | ||
|
|
| 3,65,000 | 3,65,000 |
Note: Working to arrive at capital balance:
Particulars | |||
Balance as per balance sheet | 1,20,000 | 80,000 | |
Reserves | 18,750 | 6,250 | |
Profit on revaluation: |
|
|
|
Buildings | 25,000 | ||
Plant | 15,000 | ||
Provision for doubtful debts | 40,000 4,000 |
|
|
Revaluation Profit (3:1) | 36,000 | 27,000 | 9,000 |
| 1,65,750 | 95,250 | |
Note: Working for capitals.
Particulars | ||
Balance as per Balance Sheet Reserves Profit on Revaluation Vehicles 20,000 Less: Provision for Doubtful Debts 5,000 Revaluation Profit (2:1) 15,000 | 1,00,000 33,333
10,000 | 50,000 16,667
5,000 |
| 1,43,333 | 71,667 |
We now record adjusting entries for goodwill and writing off the inter-firm debts.
Date |
| LF | Debit | Credit |
(3) | S’s capital A/c Dr. U’s capital A/c Dr. To R’s Capital A/c To T’s Capital A/c (Being the purchase of goodwill by the former partners from the latter Partners on amalgamation of the two firms) |
| 5,000 3,333 |
5,000 3,333 |
(4) | Don & Co.’s A/c Dr. To John & Co’s A/c (Being the closure of the above 2 accounts by transferring the balances on amalgamation of the 2 firms) |
| 50,000 |
50,000 |
Working for Balance Sheet
(1) The debit balance in Ram aur Shyam’s account (vide entry No. 2 will be adjusted against the credit balance in Ram aur Shyam’s account (vide entry no. 1). Ram aur Shyam will appear as net creditor for only 10,000 ( 40,000 – 30,000)
(2) Capital balances:
Share | R 4/11 | S 2/11 | T 3/11 | U 2/11 |
Entry no. 1 2 | 1,65,750 — | 95,250 — | — 1,43,333 | — 71,667 |
3
Capitals Required on the Basis of U’s Capital which is the Lowest | (+) 5,000 1,70,750 1,36,668 | (–) 5,000 90,250 68,334 | (+) 3,333 1,46,666 1,02,501 | (–)3,333 68,334 68,334 |
Transfer to Loan | 34,082 | 21,916 | 44,165 | Nil |
Date | Particulars | LF | Debit | Credit |
(5) | B’s Capital A/c Dr. S’s Capital A/c Dr. T’s Capital A/c Dr. To R’s Loan A/c To S’s Loan A/c To T’s Loan A/c (Being Excess Capital with Reference to Share in Profits Transferred to Loan Accounts) |
| 34,082 21,916 44,165 |
34,082 21,916 44,165 |
M/s Don and John Balance Sheet as on 1st August 2014
Liabilities | Assets | |||
Ram aur Shyam |
| 10,000 | Cash | 15,000 |
Other Creditors |
| 1,18,000 | Bank | 35,000 |
Loans |
|
| Debtors 1,80,000 |
|
B | 34,082 |
| Less: Provision for Doubtful Debts 9,000 | 1,71,000 |
S | 21,916 |
|
|
|
T | 44,165 | 1,00,163 | Stock | 1,30,000 |
Capitals: |
|
| Furniture and Office Equipment | 13,000 |
B | 1,36,668 |
| Vehicles | 1,00,000 |
S | 68,334 |
| Plant and Machinery | 90,000 |
T | 1,02,501 |
| Building | 50,000 |
T | 68,334 | 3,75,837 |
|
|
| 6,04,000 |
| 6,04,000 | |
Q17). A and Co. (consisting of A and B as partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2:1) and C & Co. (consisting of A and B as partners) decide to amalgamate their businesses with effect from December 31, 2014 on which date their respective Balance Sheets as under:
Liabilities |
| A & Co. | C & Co. | Assets | A & Co. | C & Co. |
Capitals |
|
|
| Goodwill | – | 12,000 |
A |
| 10,000 | 25,000 | Motor Vehicle | 10,000 | 8,000 |
B |
| 10,000 | – | Furniture | 2,000 | 5,000 |
C |
| – | 5,000 | Stock | 8,000 | 25,000 |
Investment Fluctuation |
|
|
| Debtors | 8,000 | 2,000 |
Reserves |
| – | 2,000 | Investments: |
|
|
Sundry Creditors |
| 8,000 | 15,000 | Shares in C Ltd. | – | – |
Bills Payable |
| 2,000 | 13,000 | Cash at Bank | 2,000 | 8,000 |
|
| 30,000 | 60,000 |
| 30,000 | 60,000 |
Note: (1) Included in the above Balance Sheet was an amount of 1,000 owing by A & Co. To C & Co.
On the above date the investment held by C & Co. In C Ltd. Were realized at 5,500. These had earlier been fully written off.
Goodwill of A & Co. Was to be valued at Nil.
Show journal entries in the books of the new amalgamated firm to record the opening entries and prepare the Balance Sheet of the new firm.
A18) Journal Entries in Books of the Amalgamated Firm
Date 31/12/14 | Particulars | LF | Debit | Credit |
| Motor Vehicles A/c Dr. Furniture A/c Dr. Stock A/c Dr. Debtors A/c Dr. Bank A/c Dr. To Bills Payable A/c To Sundry Creditors A/c (8,000–1,000) To Sundry Debtors A/c (inter firm debts) To A’s Capital A/c To B’s Capital A/c (Being the Assets and Liabilities of M/s × & Co. Taken over) |
| 10,000 |
|
2,000 |
| |||
8,000 |
| |||
8,000 |
| |||
2,000 |
| |||
| 2,000 | |||
| 7,000 | |||
| 1,000 | |||
| 10,000 | |||
| 10,000 | |||
|
Goodwill A/c Dr. Motor Vehicles A/c Dr. Furniture A/c Dr. Stock A/c Dr. Debtors A/c Dr. Debtors A/c (inter-firm debts) Dr. Bank A/c Dr. To Sundry Creditors A/c To Bills payable A/c To A’s capital A/c To C’s Capital (Being the assets and liabilities of M/s Z & Co. Taken over) | 30,000 | 30,000 | |
12,000 |
| |||
8,000 |
| |||
5,000 |
| |||
25,000 |
| |||
1,000 |
| |||
1,000 |
| |||
13,500 |
| |||
| 15,000 | |||
| 13,000 | |||
| *28,750 | |||
| *8,750 | |||
65,500 | 65,500 |
| X | Z |
Capitals as per Balance Sheet | 25,000 | 5,000 |
Investment Fluctuation Reserve | 1,000 | 1,000 |
Profit re: Z Ltd. Shares | 2,750 | 2,750 |
| 28,750 | 8,750 |
Balance Sheet of the Amalgamated Firm as on 31 st December 2014
Liabilities | Assets | |||
Capital Accounts: |
|
| Goodwill | 12,000 |
A | 38,750 |
| Furniture | 7,000 |
B | 10,000 |
| Motor Vehicles | 18,000 |
C | 8,750 | 57,500 | Stock | 33,000 |
Sundry Creditors |
| 22,000 | Debtors | 9,000 |
Bills Payable |
| 15,000 | Bank | 15,500 |
| 94,500 |
| 94,500 | |
Q18). 9: M/s. A & Co. Have A & B as partners decided to amalgamate with M/s. C & Co. Having C and D partners on the following terms and conditions:
(i) The new firm M/s. MO & Co. To consider Goodwill of both the firms at 12,000 each.
(ii) The new firm to take over investments at 10% depreciation; Debtors and Furniture at book value; Premises at 53,000; Land at 66,800; Machinery at 9,000 and such cash which remained after discharge of partners’ loans by the respective old firms before amalgamation.
(iii) The new firm also assumed other liabilities of old firms.
The following were the Balance Sheets of both the firms on the date amalgamation:
Liabilities | A & Co. | C & Co. | Particulars | A & Co. | C & Co. |
Creditors | 20,000 | 10,000 | Cash | 15,000 | 12,000 |
Bills Payable | 5,000 | – | Investments | 10,000 | 8,000 |
Loans: A | 8,000 | – | Debtors | 9,000 | 4,000 |
C | – | 10,000 | Furniture | 12,000 | 6,000 |
Reserves | 10,000 | 4,000 | Premises | 35,000 |
|
Capital A | 35,000 | – | Land | – | 50,000 |
B | 22,000 | – | Machinery | 14,000 |
|
C | – | 36,000 | Goodwill | 5,000 |
|
D | – | 20,000 |
|
|
|
| 1,00,000 | 80,000 |
| 1,00,000 | 80,000 |
Included in Debtors of A & Co. Was 3,000 receivable from X & Co. And included in creditors of C & Co. Was 5,000 payable to X & Co.
Prepare following ledger Accounts in each case:
- Realisation Account.
- Partners’ Capital Accounts.
- New Firm Account; and also prepare the Balance Sheet of the New Firm.
A19).
In the Books of A & Co.
Dr. Realisation A/c Cr.
Particulars | Particulars | ||
To Sundry Assets: Cash (15,000 – 8,000) 7,000 Investment 10,000 Debtors 9,000 Furniture 12,000 Premises 35,000 Machinery 14,000 Goodwill 5,000 To Profit on Realisation to: M 9,500 N 9,500 |
92,000 | By Sundry Liabilities: Creditors 20,000 Bills Payables 5,000
By MO & Co. A/c (Purchase Consideration) |
25,000
86,000 |
| 19,000 |
|
|
| 1,11,000 |
| 1,11,000 |
In the Books of C & Co.
Dr. Realisation A/c Cr.
Particulars | Particulars | ||
To Sundry Assets: |
| By Sundry Liabilities: Creditors
By MO & Co. A/c (Purchase Consideration) |
|
Cash (12000 – 10,000) 2,000 |
| 10,000 | |
Investment 8,000 |
|
| |
Debtors 4,000 |
| 88,000 | |
Furniture 6,000 |
|
| |
Land 50,000 | 70,000 |
| |
To Profit on Realisation to: |
|
| |
C 14,000 |
|
| |
D 14,000 | 28,000 |
| |
| 98,000 |
| 98,000 |
Partner’s Capital A/cs
Particulars | A | B | Particulars | A | B |
To MO & Co. A/c | 49,500 | 36,500 | By Balance b/d | 35,000 | 22,000 |
|
|
| By Reserves A/c | 5,000 | 5,000 |
|
|
| By Realisation A/c | 9,500 | 9,500 |
| 49,500 | 36,500 |
| 49,500 | 36,500 |
Dr. MO & Co. A/c Cr.
Particulars | Particulars | ||
To Realisation A/c | 86,000 | By M’s Capital A/c By N’s Capital A/c | 49,500 36,500 |
| 86,000 |
| 86,000 |
Partner’s Capital A/c
Dr Cr.
Particulars | C | D | Particulars | C | D |
To MO & Co. A/c | 52,000 | 36,000 | By Balance b/c | 36,000 | 20,000 |
|
|
| By Reserves A/c | 2,000 | 2,000 |
|
|
| By Realisation A/c | 14,000 | 14,000 |
| 52,000 | 36,000 |
| 52,000 | 36,000 |
Dr. MO & Co. A/c Cr.
Particulars | Particulars | ||
To Realisation A/c | 88,000 | By C’s Capital A/c By D’s Capital A/c | 52,000 36,000 |
| 88,000 |
| 88,000 |
MO & Co. Balance Sheet as at 31-12-2014
Liabilities | Assets | |||
Capital Accounts: |
|
| Fixed Assets: |
|
A | 49,500 | Goodwill | 24,000 | |
B | 36,500 | Land | 66,800 | |
C | 52,000 | Premises | 53,000 | |
D 36,000 | 1,74,000 | Plant and Machinery | 9,000 | |
|
| Furniture | 18,000 | |
Current Liabilities: |
| Investments | 16,200 | |
Sundry Creditors (30,000 – 3,000) | 27,000 | Current Assets: |
| |
Bills Payable | 5,000 | Debtors (13,000 – 3,000) | 10,000 | |
|
| Cash in Hand | 9,000 | |
| 2,06,000 |
| 2,06,000 | |
Note: Since X & Co. Becomes both debtor and creditors, its debits are set off against credit
Q19). Raj and Rohan are two sole traders. Their Balance Sheets as on 1st January, 2014 are given below:
Raj’s Balance Sheet as at 1st January, 2014
Liabilities | Assets | ||
Sundry Creditors Bank Overdraft Capital Account | 10,000 5,000 15,000 | Plant and Machinery Stock in Trade Sundry Debtors | 7,500 10,000 12,500 |
| 30,000 |
| 30,000 |
Rohan’s Balance Sheet as at 1st January, 2014
Liabilities | Assets | ||
Sundry Creditors | 8,500 | Plant and Machinery | 10,500 |
Capital Account | 20,000 | Stock in Trade | 5,000 |
|
| Sundry Debtors | 11,000 |
|
| Cash at Bank | 2,000 |
| 28,500 |
| 28,500 |
They agree to amalgamate their business as on 1st January, 2014. The following revaluations were to be made:
(1) Plant and Machinery were to be reduced by 10%
(2) Stock in Trade was to be reduced in case of Raj by 20% and in case of Rohan by 10%.
(3) A reserve of 2½% is to be raised against Sundry Debtors.
(4) Each partner is to be credited with Goodwill of 5,000.
(5) The bank overdraft of Raj is to be paid off by him.
Included in debtors of Raj is 2,000 due from Rohan and the same amount is included in creditors of Rohan.
You are required to give the journal entries for recording the above transactions in the books of Raj and Rohan. Give also the amalgamated balance sheet of the New Firm as on 1st January, 2014.
A20).
Journal Entries in the Books of Raj
Date 1/1/14 | Particulars | LF | Debit | Credit | |
(1) | Realisation A/c | Dr. |
| 30,000 |
|
| To Plant and Machinery A/c |
|
| 7,500 | |
| To Stock in Trade A/c To Stock in Debtors A/c (Being assets transferred to Realisation account) |
|
| 10,000 12,500 | |
(2) | Sundry Creditors A/c To Realisation A/c (Being liabilities transferred to realization account) | Dr. |
| 10,000 |
10,000 |
(3) | M/s Raj and Rohan A/c To Realisation A/c (Being purchase consideration due) | Dr. |
| 21,937 |
21,937 |
(4) | Realisation Raj To Raj Capital A/c (Being profit on realizations) | Dr. |
| 1,937 |
1,937 |
(5) | Bank Overdraft A/c To Raj Capital A/c (Being bank overdraft taken over by Raj personally) | Dr. |
| 5,000 |
5,000 |
(6) | Raj Capital A/c To M/s Raj and Rohan A/c (Being capital account settled) | Dr. |
| 21,937 |
21,937 |
Journal Entries in the Books of Rohan
Date | Particulars | LF | Debit | Credit | |
(1) | Realisation A/c To Plant and Machinery A/c To Stock in Trade A/c To Sundry Debtors A/c To Cash at Bank A/c (Being assets transferred to realizations account) | Dr. |
| 28,500 |
|
|
| 10,500 | |||
|
| 5,000 | |||
|
| 11,000 | |||
|
| 2,000 | |||
(2) | Sundry Creditors A/c To Realisation A/c (Being liabilities transferred to realizations account) | Dr. |
| 8,500 |
8,500 |
(3) | M/s Raj and Rohan A/c To Realisation A/c (Being purchase consideration due) | Dr. |
| 23,175 |
23,175 |
(4) | Realisation A/c To Rohan Capital A/c | Dr. |
| 3,175 |
|
| (Being profit on realizations) |
|
| 3,175 |
(5) | Rohan Capital A/c Dr. To M/s Raj and Rohan A/c (Being capital account settled) |
| 23,175 |
23,175 |
M/s. Raj and Rohan Balance Sheet as at 1-1-2014
Liabilities | Assets | ||||
Capital Accounts: |
|
| Fixed Assets: Goodwill Plant and Machinery Current Assets Stock Debtors Less: Provision For Bad Debts Cash at Bank |
21,500
(538) |
|
Raj | 19,987 |
| 10,000 | ||
Rohan | 25,175 |
| 16,200 | ||
|
| 45,162 |
| ||
Sundry Creditors |
| 16,500 | 12,500 | ||
|
|
|
20,962 | ||
|
|
| 2,000 | ||
| 61,662 |
| 61,662 | ||
Working Note
Particulars | Raj | Rohan |
Assets: |
|
|
Cash at Bank | – | 2,000 |
Plant and Machinery (90% of book value) | 6,750 | 9,450 |
Stock in Trade (Agreed value) | 8,000 | 4,500 |
Debtors (book value) | 10,500 | 11,000 |
Goodwill (agree value) | 5,000 | 5,000 |
| 30,250 | 31,950 |
Less: Liabilities: |
|
|
RDD (2½% of debtors) | 263 | 275 |
Creditors (book value) | 10,000 | 6,500 |
| 10,263 | 6,775 |
Purchase Consideration | 19,987 | 25,175 |
Internal Reconstruction
Q20). What is Reconstruction? State the purpose of it.
A1). Rebuilding is the process of restructuring a company in terms of law, operations, ownership and other structures by revaluing assets and revaluing liabilities. It refers to the transfer of the business of a company or multiple companies to a new company. Therefore, this means that the old company will be liquidated, and therefore shareholders agree to acquire shares of equal value in the new company. The financial statements do not reflect the true and fair position of the business, as if the company has suffered losses over the years, it will need to be rebuilt and the net worth will be higher than the actual net worth. Hmm.
In other words, "reconstruction" is the dissolution of an existing company and the transfer of its assets and liabilities to a new company established for the purpose of business succession or succession of the existing company. Shareholders of the existing company will become shareholders of the new company. The business content and shareholders of the new company are almost the same as those of the old company.
Purpose of Reconstruction
The main purposes of the reconstruction are:
Q21). What are the types of Reconstruction?
A2). Types of Reconstruction
The company can be rebuilt in one of two ways. These are:
External Restructuring: If a company suffers losses over the past few years and faces a financial crisis, it can sell its business to another newly established company. In fact, the new company was established to take over the assets and liabilities of the old company. This process is called external reconstruction. In other words, external reconstruction means selling the business of an existing company to another company established for that purpose. In the external reconstruction, one company will be liquidated and the other will be newly established. The liquidated company is called the "Vendor Company" and the new company is called the "Purchasing Company". The shareholders of the selling company are the shareholders of the purchasing company.
Internal Restructuring: Internal restructuring refers to the internal restructuring of a company's financial structure. It is also called a restructuring that allows an existing company to survive. In general, equity capital is reduced to amortize the company's past cumulative losses.
Q22). Write the significance of Internal Reconstruction.
A3). Internal reconstruction is done by the company in the following cases:

Conditions and regulations regarding Internal Reconstruction
1. Approval by Articles of Incorporation: The company must be approved by the Articles of Incorporation to appeal for capital reduction. The Articles of Incorporation contain all the details of the company's internal affairs and refer to provisions that include how to reduce capital.
2. Passing a special resolution: The company must pass a special resolution before appealing for a capital reduction. Special resolutions will only be passed if a majority of stakeholders agree to internal reconstruction. This special resolution must be signed by the arbitral tribunal and deposited with a registrar appointed under the Companies Act 2013.
3. Court Permission: The company must obtain the court or the court's legitimate permission before starting the capital reduction process. The court will only grant permission if the company is fair and is satisfied with the positive consent of all stakeholders.
4. Borrowing Payment: According to Article 66 of the Companies Act 2013, a company must repay all the amount deposited and its interest before reducing its capital.
5. Creditor Consent: The company that reduces the capital requires the written consent of the creditor. The court requires the company to secure the interests of the dissenting creditors. The company obtains the court's permission after the court determines that the reduction of capital does not harm the interests of the creditors.
6. Announcement: The company must announce according to the instructions of the tribe for a capital reduction. The company must also explain the justification.
Q23). Distinguish between Internal and External Reconstruction.
A4). The main difference between internal reconstruction and external reconstruction
Due to the difference between internal and external reconstructions, the subsequent points are relevant:
- Internal restructuring is often defined as a restructuring of a corporation without liquidating an existing company and establishing a replacement one. On the opposite hand, external restructuring may be a sort of corporate restructuring that liquidates an existing company and creates a replacement company so as to continue the business of the prevailing company.
- A new company won't substitute the interior reorganization. Conversely, a replacement company are going to be established for external reconstruction and therefore the business of the prevailing company is going to be appropriated.
- Internal restructuring reduces the company's capital, and external liabilities like bond holders and creditors waive their debt at a reduction. On the opposite hand, external reconstruction doesn't reduce the company's capital.
- Internal reconstruction requires court approval and court confirmation, as a discount in capital stock can affect shareholder rights. On the contrary, external reconstruction doesn't require such approval.
- If the corporate goes through an indoor rebuilding process, the record created after the method will include the term "And Reduced". In contrast, within the case of external reconstruction, no particular term is employed on the record.
- In internal reconstruction, no new company are going to be established, so there'll be no transfer of assets or liabilities.
Basis For Comparison | Internal Reconstruction | External Reconstruction |
Meaning | Internal reconstruction refers to the method of corporate restructuring wherein existing company is not liquidated to form a new one. | External reconstruction is one in which the company undergoing reconstruction is liquidated to take over the business of existing company. |
New company | No new company is formed. | New company is formed. |
Use of specific terms in Balance Sheet | Balance Sheet of the company contains "And Reduced". | No specific terms are used in the Balance sheet. |
Capital reduction | Capital is reduced and the external liability holders waive their claims. | No reduction in the capital |
Approval of court | Approval of court is must. | No approval of court is required. |
Transfer of Assets and Liabilities | No such transfer takes place. | Assets and liabilities of existing company are transferred to the new company. |
Q24). What are the various methods of Internal Reconstruction?
A5). There are various methods of internal reconstruction, shown :
1. Alteration of Share Capital
If approved by the Articles of Incorporation, the limited liability company may change (change) the capital clause of the Articles of Incorporation. There are various ways to change stock capital:
Increase in stock capital due to issuance of new shares
2. Reverse Stock Split
Consolidation refers to the conversion of shares with a smaller par value to shares with a larger par value.
Example: His 5000 shares of Rs. 10 pieces can be integrated into a stock of 500 rupees. 100 each.
3. Stock Split
Subdivision is the conversion of high par value stocks to low par value stocks.
Example: 5000 shares of Rs. Each 100 can be split into 50000 shares of Rs. 10 each.
4. Equity of Shares
The company can convert its shares into shares. Stocks can be fractions that are not possible in the case of stocks. Central government approval is required to convert shares into shares.
5. Transfer of Shares
Reconstruction plans may require shareholders to relinquish some of their ownership. Such a waiver may be issued prior to immediate cancellation or to satisfy some of the company's creditors.
6. Cancellation of Unissued Shares
If the company cancels unissued shares, it does not need to pass an accounting entry. The authorized share capital of the company will be the amount of unissued shares currently cancelled.
Q25). Write short note on Stock Split and Consolidation.
A6). If approved by the Articles of Incorporation, the company may, by passing a normal resolution, decide at the General Assembly to split or consolidate the shares into an amount less or higher than the amount stipulated in the Articles of Incorporation. The ratio of paid-in to unpaid shares will continue to be the same as for the original shares.
Notifications identifying changes must be submitted to the Registrar within 30 days of the changes.
For example, a company with capital of 10,000,000 split into 10,000 shares and paid 75 for every 100 shares decides to split 100 shares of 100 shares into 10 shares to recognize capital. Each. The resulting entry passed in such a case is —
| Dr. | Cr. | |
| |||
Equity Share Capital ( 100) A/c | Dr. | 7,50,000 |
7,50,000 |
To Equity Share Capital ( 10) A/c |
| ||
(Being the sub-division of 10,000 shares of 100 each with 75 paid up thereon into 1,00,000 shares of 10 each with 7.50 paid up thereon as per the resolution of shareholders passed in the General Meeting held on...) | |||
Similar entries are passed when consolidating a smaller amount of stock into a larger amount of stock.
Q26). How are Fully Paid-In Shares converted to Shares?
A7). According to Article 61 of the Companies Act 2013, a company may convert fully paid-in shares into shares and convert the shares back into shares. If approved by the Articles of Incorporation, the company may, by passing a normal resolution, convert the fully paid shares into shares and reconvert the shares into shares at a general meeting of shareholders. Stock is the integration of equity capital into one of his units that can be split into aliquot parts. A stock is a fully paid bundle of stock that, for convenience, can be split into any amount and transferred to any fraction and subdivision, regardless of the original par value of the stock. He cannot have one share of equity capital, but he can transfer any amount of shares. However, in reality, the company limits the transfer of shares to multiples, such as 100 times his. Companies can convert fully paid shares into shares. When the company converts its shares into shares, the bookkeeping items only record the transfer from the stock capital account to the stock account. Another share registration will be initiated where the details of the member's holdings are entered and the annual returns change accordingly.
Example
C Ltd. Split the authorized capital of 5,000,000 into 100 shares each on March 12, 20X1, of which 4,000 were issued and paid in full. In June 220X2, the Company converted the issued shares into shares. Decided to do. However, in June 20X3, we reconverted the shares to his 10 shares and paid in full.
Pass an entry to show how equity capital appears in the balance sheet notes, such as 31-12-20X1, 31-12-20X2, 31-12-20X3.
Journal Entries
20X2 |
| |||
June | Equity Share Capital A/c | Dr | 4,00,000 |
|
| To Equity Stock A/c |
|
| 4,00,000 |
| (Being conversion of 4,000 fully paid Equity Shares of 100 into 4,00,000 Equity Stock as per resolution in General meeting dated…) |
|
|
|
20X3 |
|
|
|
|
June | Equity Stock A/c | Dr | 4,00,000 |
|
| To Equity Share Capital A/c |
|
| 4,00,000 |
| (Being re-conversion of 4,00,000 Equity Stock into 40,000 shares of 10 fully paid Equity Shares as per Resolution in General Meeting dated...) |
|
|
|
Q27). What does changes in Shareholder Rights mean?
A8). Under Article 48 of the Companies Act 2013, if a company issues different types of shares and grants such shares different rights or privileges, the rights relating to dividends, voting rights, etc. may be changed in any way. I will. This is done by the written consent of his three or more owners of her quarter of the issued shares of that type, or by a special resolution adopted at another meeting of the owners of the issued shares of that type. I will. (a) If the company's memorandum or articles of incorporation include provisions for such variations. Or (b) if there is no such provision in the Memorandum of Understanding or the Articles of Incorporation, or if such changes are not prohibited by the terms and conditions of issuance of shares of that class, provided that changes made by a shareholder of one class are the rights of another shareholder. When Impacting Regarding the type of shareholders, the consent of three-quarters of the other types of shareholders shall also be obtained and the provisions of this section shall apply to such changes.
 For example, a company may (a) Change the dividend rate of preferred stock or (b) Convert cumulative preferred stock to non-cumulative preferred stock without changing the amount of equity capital by going through the following journal: can.
For example, a company may (a) Change the dividend rate of preferred stock or (b) Convert cumulative preferred stock to non-cumulative preferred stock without changing the amount of equity capital by going through the following journal: can.

Q28). Explain the process of Reduction of Stock Capital.
A9). Article 66 of the Companies Act 2013 provides procedures for reducing stock capital. Subject to court confirmation of the company's application, the company may, by special resolution, reduce its share capital in the following ways:

In general, the reduction of equity capital occurs when a company suffers continuous losses over a long period of time and is not truly reflected in its assets. In such cases, the capital reduction scheme must amortize the portion of the capital that has already been lost.
This reduction is a shareholder sacrifice, and the amount of the reduction or sacrifice is credited to a new account called a capital reduction account (or restructuring account). The accounting process is as follows.
(a) Shareholders' liability to extinguish or diminish their liability for the accrued amount of shares held by the shareholders
The shareholders are not required to pay the accrued amount of their shares in the future. For example, a company decides to reduce 10 per share from 10 to 7.5 by cancelling the unpaid amount of 2.5 per share. The entry in this case looks like this:
Share Capital (Partly Paid-Up) Account Dr. ( 7.5 X No. of Shares)
To Share Capital (Fully Paid-up) Account ( 7.5 X No. of Shares)
(b) If the paid-in excess capital is refunded: If the company is unable to secure profitability, it may decide to refund the paid-in capital as excess to shareholders. For example, if a company with 10 fully paid shares each decides to refund 2 shares per share to make 8 fully paid shares, the entry would be:
Share Capital Account ( 10) Dr. ( 10 X No. Of Shares)
To Share Capital Account ( 8) ( 8 X No. of Shares)
To Sundry Shareholders Account ( 2 X No. of Shares) Sundry Shareholders Account Dr. ( 2 X No. Of Shares)
To Bank Account ( 2 X No. of Shares)
(c) If lost or hidden paid-in capital is cancelled:
Share Capital Account Dr. ( 90 X No. of Shares)
To Capital Reduction Account
(90 X No. Of Shares)
Q29). Draw the Proforma of Capital Reduction Account
A10). Capital Reduction A/c
Particulars | Rs. | Particulars | Rs. |
To P & L A/c (Loss written off) To Goodwill A/c (Written off) To Preliminary expenses A/c (Written off) To Discount on Shares/Debentures (Written off) To Assets A/c (Decrease in value) To Bank A/c (payment of unrecorded liability) To Bank A/c (payment of Reconstruction Expenses) To Bank A/c (Refund of Directors Fees) To Capital Reserve (Balancing figure) | XX XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX XX XX | By Share Capital A/c (Amount of reduction) By Debentures A/c (Amount of Reduction) By Creditors A/c (Amount of Sacrifice) By Assets A/c (Increase in value) By Bank A/c (sate of unrecorded assets) | XX
XX
XX
XX
XX |
| XXX |
| XXX |
Q30). Following is the Balance sheet of M/s. Careful Ltd. As on 31st March, 2010.
Liabilities | Rs. | Assets | Rs. |
50,000 – 8% |
| Goodwill Freehold Property Leasehold Property Plant & Machinery Furniture Stock Debtors Preliminary Exp. Profit & Loss A/c | 1,00,000 1,50,000 2,40,000 3,00,000 1,00,000 50,000 1,00,000 9,000 2,07,000 |
Cumulative |
| ||
Preference Shares of |
| ||
Rs.10/- each. | 5,00,000 | ||
40,000 – Equity Shares of Rs.10/- each. | 4,00,000 | ||
|
| ||
Security Premium | 8,000 | ||
9% Debentures | 1,00,000 | ||
Accrued Debenture |
| ||
Interest | 6,000 | ||
Sundry Creditors | 1,00,000 | ||
Bank Overdraft | 1,42,000 | ||
| 12,56,000 |
| 12,56,000 |
Note –
- Preference dividend was in arrears for 3 years.
- There was a contingent liability of Rs.30,000/- for workmen compensation.
Following scheme of reconstruction was approved & implemented.
- The Preference shares were reduced to Rs.8/- per share fully paid & Equity Shares to Rs.3/- per share fully paid.
- One new Equity share of Rs.10/- each was issued of every Rs.50/- gross preference dividend in arrears.
- After reduction, both classes of shares were consolidated into Rs.10/- shares.
- The balance of Securities Premium was utilized.
- Plant & Machinery was written of down to Rs.2,50,000/-.
- Furniture was sold to Rs.75,000/-
- Preliminary expenses debit balance in Profit & Loss A/c, debt of Rs.25,000/- & obsolete stock Rs.18,000/- were to be written off.
- Contingent liability for which no provision has been made was settled at Rs.15,000/-. However, the amount of Rs.11,000/- was recovered from insurance company.
- Debenture holders agreed to Forgo principal amount by Rs.50,000/- & accrued debenture interest in full.
Pass journal entries. Prepare capital reduction account & Balance sheet after reconstruction.
A11).
Journal of Careful Ltd.
Date | Particulars | Debit (Rs.) | Credit (Rs.) |
1. | 8% Preference Share Cap. A/c.....Dr. (50,000X10) To 8% Preference Share Capital A/c (50,000X8) To Capital Reduction A/c (50,000X2) (Being reduction in 8% Preference Capital.) | 5,00,000 |
4,00,000
1,00,000 |
| 8% Preference Share Capital A/c….Dr. (40,000X8) To 8% Preference Share Capital A/c (32,000X10) (Being consolidation of 8% Preference Shares.) | 3,20,000 |
3,20,000 |
3. | Equity Share Capital A/c.........Dr. (40,000X10) To Equity Share Capital A/c (40,000X3) To Capital Reduction A/c (40,000X7) (Being reduction in Equity Share Capital) | 4,00,000 |
1,20,000 2,80,000 |
4. | Equity Share Capital A/c.........Dr. (40,000X3) To Equity Share Capital A/c (12,000X10) (Being consolidation of Equity Shares.) | 1,20,000 |
1,20,000 |
5. | Capital Reduction A/c............Dr. To Equity Share Capital A/c [(8%X5,00,000X 3)/50] (Being arrears of Preference dividend paid by issue of Equity shares.) | 24,000 |
24,000 |
6. | Security Premium A/c............Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being Security Premium used.) | 8,000 |
8,000 |
7. | Bank A/c.....................Dr. Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Furniture A/c (Being sale of Furniture at a loss of Rs.25,000/-) | 75,000 25,000 |
1,00,000 |
8. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Bank A/c (Being payment of contingent liability.) | 15,000 |
15,000 |
9. | Bank A/c.....................Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being recovery of claim from insurance company.) | 11,000 |
11,000 |
10. | 9% Debentures A/c.............Dr. Accrued Debenture interest A/c...Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being sacrifice made by debenture holders) | 50,000 6,000 |
56,000 |
11. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Plant & Machinery A/c (3,00,000 – 2,50,000) To Preliminary Expenses A/c To Profit & Loss A/c To Sundry Debtors A/c To Stock A/c To Capital Reserve A/c (Being losses & Assets written off.) | 3,91,000 |
50,000
9,000 2,07,000 25,000 18,000 82,000 |
Capital Reduction Account
Dr. Cr.
Particulars | Amt. | Particulars | Amt. |
To Equity Share Cap. A/c | 24,000 | By 8% Pref. Share Cap. A/c
By Equity Share Capital A/c By Security Premium By 9% Debentures
By Accrued interest on debentures By Bank (Insurance) |
1,00,000 |
(Preference Dividend) |
|
| |
To Furniture | 25,000 |
| |
To Plant & Machinery A/c | 50,000 | 2,50,000 | |
To Preliminary Expenses | 9,000 | 8,000 50,000 | |
To Profit & Loss A/c | 2,07,000 |
| |
To Sundry Debtors A/c | 25,000 |
| |
To Stock | 18,000 | 6,000 | |
To Bank | 15,000 | 11,000 | |
(Contingent liability) |
|
| |
To Capital Reserve | 82,000 |
| |
| 4,55,000 |
| 4,55,000 |
Balance Sheet of Careful Ltd (AND REDUCED)
| Notes | Current Year |
(in Rs.) | ||
EQUITY AND LIABILITIES |
|
|
Shareholders Fund |
|
|
Share Capital | 1 | 5,44,000 |
Reserves & Surplus | 2 | 82,000 |
Money Received against Warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share Application Money pending allotment |
|
|
|
|
|
Non-current Liabilities |
|
|
Long Term Borrowings | 3 | 50,000 |
Deferred Tax Liabilities (Net) |
|
|
Other Long Term Liabilities |
|
|
Long Term Provisions |
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities |
|
|
Short Term Borrowings | 4 | 71,000 |
Trade Payables |
| 1,00,000 |
Other Current Liabilities |
|
|
Short Term Provisions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
| 8,47,000 |
|
|
|
ASSETS |
|
|
Non-current Assets |
|
|
Fixed Assets | 5 |
|
Tangible Assets |
| 6,40,000 |
Intangible Assets |
| 1,00,000 |
Capital Work-in-Progress |
|
|
Intangible Assets under development |
|
|
Non-current Investments |
|
|
Deferred Tax Assets (Net) |
|
|
Long Term Loans & Advances |
|
|
Other Non-current Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
Current Assets |
|
|
Current Investments |
|
|
Inventories |
| 32,000 |
Trade Receivables |
| 75,000 |
Cash and Cash Equivalents |
|
|
Short Term Loans & Advances |
|
|
Other Current Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
| 8,47,000 |
|
|
|
Schedules forming a part of Balance Sheet
Particulars | Amount Rs | Amount Rs |
1. SHARE CAPITAL |
|
|
Authorised Share Capital : |
| - |
--- Equity Shares of Rs.-- each |
|
|
|
|
|
Issued Subscribed and Paid Up Capital : |
|
|
14,400 Equity Shares of Rs.10 each |
| 1,44,000 |
4,00,000, 8% Preference shares of Rs 10 each |
| 4,00,000 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 5,44,000 |
|
|
|
2. RESERVES & SURPLUS |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital Reserve |
| 82,000 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 82,000 |
|
|
|
3. LONG TERM BORROWINGS |
|
|
Secured |
|
|
9% Debentures(1,00,000-50,000) |
| 50,000 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 50,000 |
|
|
|
4. SHORT TERM BORROWINGS |
|
|
Unsecured |
|
|
Bank Overdraft |
| 71,000 |
Total |
| 71,000 |
|
|
|
5. FIXED ASSETS |
|
|
Tangible |
|
|
Freehold Property | 1,50,000 |
|
Leasehold Property | 2,40,000 |
|
Plant & Machinery | 2,50,000 | 6,40,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intangible Assets |
|
|
Goodwill |
| 1,00,000 |
|
|
|
Total Assets |
| 7,40,000 |
Q.12) Following is the Balance Sheet of Shobha Ltd. As on 31st March, 2008.
Liabilities | Amt. | Assets | Amt. |
Share Capital |
| Goodwill | 3,00,000 |
1,50,000 Equity Shares |
| Land & Building | 2,40,000 |
Of Rs.5/- each fully paid | 7,50,000 | Equipment | 2,10,000 |
|
| Sundry Debtors | 2,00,970 |
5,000 6% Preference Shares of Rs.100/- each fully paid |
5,00,000 | Stock Investment Cash at Bank | 3,32,440 44,000 21,000 |
8% Debentures | 3,00,000 | Profit & Loss A/c | 7,51,590 |
Bank Overdraft | 1,70,000 |
|
|
Sundry Creditors | 3,80,000 |
|
|
(including Rs.22,000 int. |
|
|
|
On Bank Overdraft) |
|
|
|
| 21,00,000 |
| 21,00,000 |
Note: Preference dividend is in arrears for Five years.
Following scheme of reconstruction was approved by the court.
1) Equity Shares be reduced to Rs.150/- each of then to be consolidated into shares of Rs.10/- each.
2) 6% Preference shares be reduced to Rs.50/- each & then to be subdivided into shares of Rs.10/- each.
3) Interest accrued but not due on 8% debentures. For half year ended 31st March 2008 has not been provided in the above Balance Sheet. The debenture holders have agreed to received 30% of this interest in cash immediately & provision for the balance be made in the books of account.
4) Rs.20,000/- be paid to Preference shareholders in lieu of arrears of Preference dividend.
5) The debenture holders have also agreed to accept equal number of 9% debentures of Rs.60/- each in exchange of 8% debentures of Rs.100/- each.
6) Bank has agreed to take over 50% stock in full satisfaction of its claim including interest. The remaining stock be revalued at Rs.80,000/-.
7) Investment be sold for Rs.39,000/-.
8) Tangible Fixed assets be appreciated by 15% & provision be made for doubtful debts of Rs.18,000/-.
Give journal entries for the above scheme of reconstruction. Prepare Capital Reduction Account in the books of Shobha Ltd. & Balance sheet of the company after reconstruction.
A12).
Journal of Shobha Ltd.
Sr No | Particulars | Debit (Rs.) | Credit (Rs.) |
1. | Equity Shares Capital A/c (5)......Dr. To Equity Share Capital A/c(1.50) To Capital Reduction A/c (3.50) (Being 1,50,000 Equity Shares of Rs.5/- each reduced to Rs.1.50 each.) | 7,50,000 |
2,25,000 5,25,000 |
2. | Equity Share Capital A/c (1.50)....Dr. To Equity Share Capital (10) (Being 1,50,000 Equity shares of Rs.1.50 consolidated into shares of Rs.10/- each.) | 2,25,000 |
2,25,000 |
3. | 6% Preference Share Capital A/c (100) ..Dr. To 6% Preference Share Capital A/c (50) To Capital Reduction A/c (Being 6% Preference shares of Rs.100/- each reduced to shares of Rs.50/- each.) | 5,00,000 |
2,50,000 2,50,000 |
4. | 6% Preference Share Capital A/c...Dr. To 6% Preference Shares Capital A/c (Being 6% Preference shares of Rs.50/- each subdivided into shares of Rs.10/- each.) | 2,50,000 |
2,50,000 |
5. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Bank A/c To Interest on Debentures A/c (Being payment of accrued interest on debentures to the extent of 30% & provided for the balance.) | 12,000 |
3,600 8,400 |
6. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Bank A/c (Being paid to preference share holders in lieu of arrears of dividend.) | 20,000 |
20,000 |
7. | 8% Preferences A/c (100)........Dr. To 9% Debentures A/c (60) To Capital Reduction A/c (Being exchanged 8% debentures by 9% debentures.) | 3,00,000 |
1,80,000 1,20,000 |
8. | Bank Overdraft A/c.............Dr. Sundry Creditors A/c............Dr. (Interest on Bank Overdraft) To Stock A/c To Capital Reduction A/c (Being taken over 50% of the Stock by the bank in satisfaction of bank overdraft.) | 1,70,000 22,000 |
1,66,220 25,780 |
9. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Stock A/c (Being reduction in Stock.) | 86,220 |
86,220 |
10. | Bank A/c.....................Dr. Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Investment A/c (Being sale of investment at a loss.) | 39,000 5,000 |
44,000 |
11. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Profit & Loss A/c To Provision for doubtful debts A/c To Capital Reserve A/c (Being written off profit & loss account debit balance, provided for reduction redemption reserve & transferred the remaining amount to Capital Reserve Account.) | 8,65,040 |
7,51,590 18,000 95,470 |
12. | Land & Building A/c............Dr. Equipment A/c................Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being appreciation in Land & Building & Equipment.) | 36,000 31,500 |
67,500 |
Capital Reduction Account
Dr. Cr.
Particulars | Amt. | Particulars | Amt. |
To Bank A/c | 3,600 | By Equity Share Capital A/c By 6% Preference Share Capital A/c By 8% Debentures A/c By Bank Overdraft & Creditors A/c By Land & Building A/c By Equipment’s A/c |
5,25,000
2,50,000 1,20,000
25,780 36,000 31,500 |
To Int. On debentures | 8,400 | ||
To Bank A/c | 20,000 | ||
To Stock A/c | 86,220 | ||
To Investment A/c | 5,000 | ||
To Profit & Loss A/c | 7,51,590 | ||
To Provision for doubtful |
| ||
Debts. | 18,000 | ||
To Capital Reserve | 95,470 | ||
| 9,88,280 |
| 9,88,280 |
Balance Sheet of Shobha Ltd (AND REDUCED)
| Notes | Current Year |
(in Rs.) | ||
EQUITY AND LIABILITIES |
|
|
Shareholders Fund |
|
|
Share Capital | 1 | 4,75,000 |
Reserves & Surplus | 2 | 95,470 |
Money Received against Warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share Application Money pending allotment |
|
|
|
|
|
Non-current Liabilities |
|
|
Long Term Borrowings | 3 | 1,80,000 |
Deferred Tax Liabilities (Net) |
|
|
Other Long Term Liabilities |
|
|
Long Term Provisions |
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities |
|
|
Short Term Borrowings |
|
|
Trade Payables |
| 3,58,000 |
Other Current Liabilities | 4 | 8,400 |
Short Term Provisions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
| 11,16,870 |
|
|
|
ASSETS |
|
|
Non-current Assets |
|
|
Fixed Assets | 5 |
|
Tangible Assets |
| 5,17,500 |
Intangible Assets |
| 3,00,000 |
Capital Work-in-Progress |
|
|
Intangible Assets under development |
|
|
Non-current Investments |
|
|
Deferred Tax Assets (Net) |
|
|
Long Term Loans & Advances |
|
|
Other Non-current Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
Current Assets |
|
|
Current Investments |
|
|
Inventories |
| 80,000 |
Trade Receivables | 6 | 1,82,970 |
Cash and Cash Equivalents |
| 36,400 |
Short Term Loans & Advances |
|
|
Other Current Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
| 11,16,870 |
|
|
|
Schedules forming a part of Balance Sheet
Particulars | Amount Rs | Amount Rs |
1. SHARE CAPITAL |
|
|
Authorised Share Capital : |
| - |
--- Equity Shares of Rs.-- each |
|
|
|
|
|
Issued Subscribed and Paid Up Capital : |
|
|
22,500 Equity Shares of Rs.10 each |
| 2,25,000 |
25,000, 6% Preference shares of Rs 10 each |
| 2,50,000 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 4,75,000 |
|
|
|
2. RESERVES & SURPLUS |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital Reserve |
| 95,470 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 95,470 |
|
|
|
3. LONG TERM BORROWINGS |
|
|
Secured |
|
|
30,000, 9% Debentures of Rs 60 each |
| 1,80,000 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 1,80,000 |
|
|
|
4. OTHER CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|
|
Interest payable on debentures |
| 8,400 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 8,400 |
|
|
|
5. FIXED ASSETS |
|
|
Tangible |
|
|
Land & Building | 2,76,000 |
|
Equipments | 2,41,500 | 5,17,500 |
|
|
|
Intangible Assets |
|
|
Goodwill |
| 3,00,000 |
Total Assets |
| 8,17,500 |
|
|
|
6. TRADE RECEIVABLES |
|
|
Sundry Debtors |
| 2,00,970 |
Less: Provision for Doubtful Debts |
| (18,000) |
|
| 1,82,970 |
Q.13) Following is the Balance sheet of Punjani Ltd. As on 31st March, 2010.
Liabilities | Amt. | Assets | Amt. |
16,000 12% Preference |
1,60,000
70,000
1,80,000
1,70,000
2,80,000
21,500
3,50,000 | Goodwill | 90,000 |
Shares of Rs.10/- each Fully paid up | Patents Land & Building | 50,000 1,50,000 | |
1,40,000 10% Preference shares of Rs.10/-, Rs.5/- per | Plant & Machinery Furniture Investment | 3,00,000 35,000 85,000 | |
Share paid up | Sundry Debtors | 3,00,000 | |
| Bills Receivables | 1,20,000 | |
18,000 Equity Share of | Bank | 30,000 | |
Rs.10/- each fully paid Up | Profit & Loss A/c | 71,500 | |
12% Debenture of |
|
| |
Rs.100/- each |
|
| |
11% Debentures of |
|
| |
Rs.100/- each |
|
| |
Interest due on |
|
| |
Debenture |
|
| |
Sundry Creditors |
|
| |
| 12,31,500 |
| 12,31,500 |
The following scheme of reconstruction was submitted & approved by the court.
1) 12% Preference Shares of the Rs.10/- each fully paid were reduced to 13% Preference Shares of Rs.10/- each, Rs.6/- per share paid up.
2) 10% Preference share of Rs.10/- each, Rs.5/- per share paid up were reduced to 13% Preference shares of Rs.10/- each, Rs.4/- per share paid up.
3) Equity Shares of Rs.10/- each fully paid were reduced to the denomination of Rs.7/- each fully paid.
4) 11% Debenture holders agreed to accept 44,800 Equity Shares of Rs.5/- each in full settlement of their claims.
5) Debentures holders agreed to Forgo the interest due on debentures.
6) Sundry Creditors agreed to Forgo 20% of their claims.
7) The company recovered as damages as sum of Rs.60,000/- which was not recorded in the books.
8) Cost of reconstruction was paid Rs.3,000/-.
9) Assets are to be revalued as under : Land & Buildings Rs.2,05,000/-, Plant & Machinery Rs.2,50,000/-, Furniture Rs.10,000/-, Investment Rs.1,05,000/-, Sundry Debtors Rs.2,77,000/-.
10) All intangible assets & accumulated losses are to be written off.
You are required to –
i) Pass journal entries in the books of Punjani Ltd.
Ii) Prepare Capital Reduction Account & Balance Sheet after reconstruction.
A13).
Journal of Punjani Ltd.
Date | Particulars | Debit (Rs.) | Credit (Rs.) |
1. | 12% Preference Share Capital A/c..Dr. To 13% Preference Share Capital A/c To Capital Reduction A/c (Being reduction in 12% Preference Capital.) | 1,60,000 |
96,000 64,000 |
2. | 10% Preference Share Capital A/c..Dr. To 13% Preference Share Capital A/c To Capital Reduction A/c (Being reduction in 13% Preference Capital.) | 70,000 |
56,000 14,000 |
3. | Equity Share Capital A/c.........Dr. To Equity Share Capital A/c To Capital Reduction A/c (Being reduction in Equity Share Capital.) | 1,80,000 |
1,26,000 54,000 |
4. | 11% Debenture A/c............Dr. To Equity Share Capital A/c To Capital Reduction A/c (Being reduction in debentures.) | 2,80,000 |
2,24,000 56,000 |
5. | Interest due on Debenture A/c.....Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being interest dues on debentures cancelled.) | 21,500 |
21,500 |
6. | Creditors A/c.................Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being Creditors dues reduced.) | 70,000 |
70,000 |
7. | Bank A/c.....................Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being damages recovered.) | 60,000 |
60,000 |
8. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Bank A/c (Being costs of reconstruction paid.) | 3,000 |
3,000 |
9. | Land & Building A/c............Dr. Investment A/c................Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being increase in valuations.) | 55,000 20,000 |
75,000 |
10. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Plant & Machinery A/c To Furniture A/c To Sundry Debtors A/c To Goodwill A/c To Patents A/c To Profit & Loss A/c To Capital Reserve A/c | 5,01,500 |
50,000 25,000 23,000 90,000 50,000 71,500 1,02,000 |
Capital Reduction Account
Dr. Cr.
Particulars | Amt. | Particulars | Amt. |
To Bank A/c | 3,000 | By 12% Preference Share Capital A/c By 10% Preference Share Capital A/c By Equity Share Capital A/c By 11% Debenture A/c By Interest due on Debentures By Sundry Creditors By Bank A/c By Land & Building A/c By Investment A/c |
|
To Plant & Machinery | 50,000 | 64,000 | |
To Furniture A/c | 25,000 |
| |
To Sundry Debtors A/c | 23,000 | 14,000 | |
To Goodwill A/c | 90,000 |
| |
To Patents A/c | 50,000 | 54,000 | |
To Profit & Loss A/c | 71,500 | 56,000 | |
To Capital Reserve A/c | 10,200 |
| |
|
| 21,500 | |
|
| 70,000 | |
|
| 60,000 | |
|
| 55,000 | |
|
| 20,000 | |
| 4,14,500 |
| 4,14,500 |
Balance Sheet of Punjani Ltd (AND REDUCED)
| Notes | Current Year |
(in Rs.) | ||
EQUITY AND LIABILITIES |
|
|
Shareholders Fund |
|
|
Share Capital | 1 | 5,02,000 |
Reserves & Surplus | 2 | 1,02,000 |
Money Received against Warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Share Application Money pending allotment |
|
|
|
|
|
Non-current Liabilities |
|
|
Long Term Borrowings | 3 | 1,70,000 |
Deferred Tax Liabilities (Net) |
|
|
Other Long Term Liabilities |
|
|
Long Term Provisions |
|
|
|
|
|
Current Liabilities |
|
|
Short Term Borrowings |
|
|
Trade Payables |
| 2,80,000 |
Other Current Liabilities |
|
|
Short Term Provisions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
| 10,54,000 |
|
|
|
ASSETS |
|
|
Non-current Assets |
|
|
Fixed Assets | 4 | 4,65,000 |
Tangible Assets |
|
|
Intangible Assets |
|
|
Capital Work-in-Progress |
|
|
Intangible Assets under development |
|
|
Non-current Investments |
| 1,05,000 |
Deferred Tax Assets (Net) |
|
|
Long Term Loans & Advances |
|
|
Other Non-current Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
Current Assets |
|
|
Current Investments |
|
|
Inventories |
|
|
Trade Receivables | 5 | 3,97,000 |
Cash and Cash Equivalents |
| 87,000 |
Short Term Loans & Advances |
|
|
Other Current Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
| 10,54,000 |
|
|
|
Schedules forming a part of Balance Sheet
Particulars | Amount Rs | Amount Rs |
1. SHARE CAPITAL |
|
|
Authorised Share Capital : |
| - |
--- Equity Shares of Rs.-- each |
|
|
|
|
|
Issued Subscribed and Paid Up Capital : |
|
|
18,000 Equity Shares of Rs.7 each |
| 1,26,000 |
44,800 Equity Shares of Rs.5 each |
| 2,24,000 |
16,000, 13% Preference shares of Rs 10 each, Rs 6 paid up |
| 96,000 |
14,000, 13% Preference shares of Rs 10 each, Rs 4 paid up |
| 56,000 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 5,02,000 |
|
|
|
2. RESERVES & SURPLUS |
|
|
|
|
|
Capital Reserve |
| 1,02,000 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 1,02,000 |
|
|
|
3. LONG TERM BORROWINGS |
|
|
Secured |
|
|
12% Debentures of Rs 100 each |
| 1,70,000 |
|
|
|
Total |
| 1,70,000 |
|
|
|
4. FIXED ASSETS |
|
|
Tangible |
|
|
Land & Building | 2,05,000 |
|
Plant & Machinery | 2,50,000 |
|
Furniture | 10,000 | 4,65,000 |
Intangible Assets |
|
|
|
| - |
Total Assets |
| 4,65,000 |
|
|
|
5. TRADE RECEIVABLES |
|
|
Sundry Debtors |
| 2,77,000 |
Bills Receivable |
| 1,20,000 |
|
| 3,97,000 |
Q.14)
Following is the Balance sheet of Roshni Ltd. As on 31st March, 2009.
Liabilities | Amt. | Assets | Amt. |
Share Capital |
| Fixed Assets |
|
7,000 10% Preference |
| Goodwill | 50,000 |
Share of Rs.10/- each. | 7,00,000 | Patents & Trade marks | 30,000 |
40,000 Equity Shares |
| Building | 3,20,000 |
Of Rs.10/- each. | 4,00,000 | Plant & Machinery | 2,80,000 |
|
| Furniture | 1,20,000 |
Reserve & Surplus |
|
|
|
Capital Reserve | 40,000 | Current Assets, Loans |
|
|
| & Advances |
|
Secured loans |
| Stock | 1,55,000 |
6% Debentures of |
| Sundry Debtors | 85,000 |
Rs.100/- each | 2,00,000 | Bank | 85,000 |
Debentures interest |
| Cash | 35,000 |
Due | 70,000 |
|
|
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
Current Liabilities & |
| Expenditure |
|
Provisions |
| Discount on |
|
Sundry Creditors | 1,40,000 | Debentures | 35,000 |
|
| Profit & Loss A/c | 3,55,000 |
| 15,50,000 |
| 15,50,000 |
Note : Preference dividend is in arrears for three years. The following scheme of reconstruction was prepared & duly approved by the court.
1) The Preference Shares shall be converted into equal number of 11% Preference shares of Rs.50/- each.
2) The Equity Share shall be reduced to Rs.2/- each. However, the Face Value will remain the same.
3) 6% Debentures shall be converted into equal number of 7% debentures of Rs.85/- each. The debenture holders also agreed to waived 60% of the accrued interest.
4) Arrears of Preference dividend is to be reduced to one years dividend which is paid in cash.
5) The sundry creditors agreed to waived 40% of their claims & to accept Equity Shares for Rs.40,000/- in part settlement renewed claims.
6) The assets are to be revalued as under :
Building Rs.4,00,000/-
Plant & Machinery Rs.2,20,000/-
Furniture Rs.70,000/-
Stock Rs.1,00,000/-
Debtors Rs.70,000/-
7) Intangible assets & fictitious assets are to be written off.
Pass journal entries.
Prepare Capital Reduction Account
A14)
Journal of Roshni Ltd
Date |
Particulars | Debit (Rs.) | Credit (Rs.) |
1. | 10% Preference Share Capital A/c..Dr. To 11% Preference Share Capital A/c To Capital Reduction A/c (Being 10% Preference shares converted into 11% Preference Shares.) | 7,00,000 |
3,50,000 3,50,000 |
2. | Equity Share Capital A/c Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being reduction in Equity Shares.) | 3,20,000 |
3,20,000 |
3. | 6% Debentures A/c Dr. To 7% Debentures A/c To Capital Reduction A/c (Being converted debentures into 7% debentures.) | 2,00,000 |
1,70,000 30,000 |
4. | Debentures Interest Due A/c Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being accrued interest on debentures waived.) | 45,000 |
45,000 |
5. | Preference Dividend A/c Dr. To Cash / Bank A/c (Being paid on year‟s dividend.) | 70,000 |
70,000 |
6. | Creditors A/c Dr. To Equity Share Capital A/c To Capital Reduction A/c (Being settled sundry creditors.) | 96,000 |
40,000 56,000 |
7. | Building A/c..................Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being appreciation in building.) | 80,000 |
80,000 |
8. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Discount on Debentures A/c To Profit & Loss A/c To Goodwill A/c To Patent & Trademark A/c To Preference Dividend A/c To Plant & Machinery A/c To Furniture A/c To Stock A/c To Debtors A/c To Capital Reserve A/c (Being assets/losses written off.) | 8,81,000 |
35,000 3,55,000 50,000 30,000 70,000 60,000 50,000 55,000 15,000 1,61,000 |
Capital Reduction Account
Dr. Cr.
Particulars | Amt. | Particulars | Amt. |
To Discount on |
| By 10% Preference Share Capital A/c By Equity Share Capital A/c By 6% Debentures A/c By Interest due on Debentures A/c By Creditors A/c By Building A/c |
3,50,000
3,20,000 30,000
45,000 56,000 80,000 |
Debentures A/c | 35,000 | ||
To Profit & Loss A/c | 3,55,000 | ||
To Goodwill A/c | 50,000 | ||
To Patent & Trademark |
| ||
A/c | 30,000 | ||
To Preference Dividend |
| ||
A/c | 70,000 | ||
To Plant & Machinery |
| ||
A/c | 60,000 | ||
To Furniture A/c | 50,000 | ||
To Stock A/c | 55,000 | ||
To Debtors A/c | 15,000 | ||
To Capital Reserve A/c | 1,61,000 | ||
| 8,81,000 |
| 8,81,000 |
Q31)
Following is the balance sheet of Bhushan Ltd. As on 31st March, 2010.
Liabilities | Amt. | Assets | Amt. |
Share Capital |
| Fixed Assets Premises Plant & Machinery Investment Current Assets, Loans & Advances Stock Debtors Deposits & Advance
IV Miscellaneous Expenditure Publicity Campaign Expenses Profit & Loss Account |
|
25,000 10% Preference |
| 3,25,000 | |
Shares of Rs.10/- each. | 2,50,000 | 5,00,000 | |
Equity Share of Rs.10/- |
|
| |
Each. | 4,50,000 | 1,50,000 | |
Secured loans |
|
| |
16% Debentures of |
|
| |
Rs.100/- each | 5,00,000 | 1,35,000 | |
Current Liabilities & Provisions |
| 1,00,000 50,000 | |
Sundry Creditors | 2,10,000 |
| |
Bank Overdraft | 1,30,000 |
| |
Other Liability | 1,10,000 |
| |
|
| 2,00,000 | |
|
| 1,90,000 | |
| 16,50,000 |
| 16,50,000 |
It is observed that the new product launched by the company has not succeeded even after three years of marketing. The management is of the opinion that the assets & liabilities are not valued correctly & also finds it difficult to raise finance.
To overcome the situation a scheme of reconstruction is prepared by the directors & approved by all authorities.
The salient features of the scheme are
1) Plant & Equipment having book value of Rs.10,000/- is obsolete. This is sold as scrap for Rs.36,000/-.
2) The auditors have pointed out that depreciation on plant is not provided to the extent Rs.30,000/-
3) Stock includes items valued Rs.50,000/- which is sold at a loss of 50%.
4) The present realizable value of investments is Rs.55,000/-.
5) Dividend on Preference Shares is in arrears for 3 years. This amount is not payable.
6) All losses & Fictitious assets are to be written off.
7) The expenses paid for forming & implementing scheme is Rs.10,000/-.
8) The paid up value of Equity Share is to be reduced to Rs.2/- per share & preference share to Rs.5/- per share. However, the face value remains unchanged.
9) The Creditors due are settled as.
• 30% immediate payment in Cash.
• 40% amount is cancelled.
• 30% paid by issue of 15% debentures.
10) Other Current liabilities includes Rs.45,000/- payable to directors towards remuneration. This liability is to be cancelled.
11) A call of Rs.3/- per share on Equity Share is made & received.
12) Bank Overdraft is paid off to the extent possible.
You are required to show :
i) Journal entries for above scheme of reconstruction.
Ii) Show Bank A/c & Capital Reduction A/c
A15).
Journal In the books of Bhushan Ltd.
Date | Particulars | Debit (Rs.) | Credit (Rs.) |
1. | Equity Share Capital A/c.........Dr. 10% Preference Share Capital A/c..Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being reduction of Equity & Preference Share Capital.) | 3,60,000 1,25,000 |
4,85,000 |
2. | Creditors A/c.................Dr. To Cash / Bank A/c (30%) To Capital Reduction A/c (40%) To 15% Debentures A/c (30%) (Being Creditors dues settled as per Scheme of reconstruction.) | 2,10,000 |
63,000 84,000 63,000 |
3. | Other Liabilities A/c............Dr. To Capital Reduction A/c (Being dues to directors cancelled.) | 45,000 |
45,000 |
4. | Cash / Bank A/c...............Dr. Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Plant & Equipment A/c (Being sale of plant having book value of Rs.1,00,000/- for Rs.36,000/-.) | 36,000 64,000 |
1,00,000 |
5. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Plant & Equipment A/c (Being depreciation provided.) | 30,000 |
30,000 |
6. | Cash / Bank A/c...............Dr. Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Plant & Machinery A/c (Being sale of stock having took value of Rs.50,000/- at a loss of 50%.) | 25,000 25,000 |
50,000 |
7. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Investment A/c (Being reduction in value by Rs.95,000/-.) | 95,000 |
95,000 |
8. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Profit & Loss A/c To Publicity Campaign Expenses A/c (Being brought forward losses & fictitious assets written off as per scheme of reconstruction.) | 3,90,000 |
1,90,000 2,00,000 |
9. | Capital Reduction A/c...........Dr. To Cash / Bank A/c (Being paid expenses on reconstruction.) | 10,000 |
10,000 |
10. | Cash / Bank A/c (45,000X3).......Dr. To Equity Share Capital A/c (Being receipt of all money on 45,000 shares @ Rs.3/- each.) | 1,35,000 |
1,35,000 |
11. | Bank Overdraft A/c.............Dr. To Cash / Bank A/c (Being balance in Cash / Bank used to pay off overdraft.) | 1,23,000 |
1,23,000 |
Bank Account
Dr. Cr.
Particulars | Amt. | Particulars | Amt. |
To Plant & Equipment A/c To Stock A/c To Equity Share Capital A/c |
36,000 25,000
1,35,000 | By Capital Reduction A/c By Sundry Creditors A/c By Bank Overdraft A/c | 10,000 63,000 1,23,000 |
| 1,96,000 |
| 1,96,000 |
Capital Reduction Account
Dr. Cr.
Particulars | Amt. | Particulars | Amt. |
To Plant (Loss on sale) | 64,000 | By Equity Share Capital A/c By Preference Share Capital A/c By Creditors By Other dues (Directors) |
|
To Plant (Depreciation) | 30,000 | 3,60,000 | |
To Stock | 25,000 |
| |
To Investment | 95,000 | 1,25,000 | |
To Profit & Loss A/c | 1,90,000 | 84,000 | |
To Publicity Expenses | 2,00,000 | 45,000 | |
To Cash (Exp.) | 10,000 |
| |
| 6,14,000 |
| 6,14,000 |
